Introduction To Biological Science
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Causality
A principle of science that conveys the general proposition that every event has a cause.
Uniformity
A principle of science about the idea that Earth has always changed in uniform ways and that the present is the key to the past.
Inductive Reasoning
A scientific reasoning from Specific to general
Deductive Reasoning
A scientific reasoning from General to specific
anatomy
Specializations in Biology in concerned with the identification and description of the body structures of living things
Botany
Specializations in Biology, the scientific study of plants
Plant Physiology
Specializations in Biology, a branch of botany that specifically deals with the functional aspects necessary to sustain the plant growth.
Zoology
Specializations in Biology, the study of all animals of all shapes and sizes, from tiny insects to large mammals.
Microbiology
Specializations in Biology, the study of the biology of microscopic organisms - viruses, bacteria, algae, fungi, slime molds, and protozoa. The methods used to study and manipulate these minute and mostly unicellular organisms differ from those used in most other biological investigations.
mycology
Specializations in Biology, the study of fungi, a group that includes the mushrooms and yeasts. Many fungi are useful in medicine and industry.
Theoretical biology
Specializations in Biology, a field of study that seeks to explain biological phenomena using mathematical models and theoretical frameworks.
phycology
Specializations in Biology, the study of algae, a large heterogeneous group of chiefly aquatic plants ranging in size from microscopic forms to species as large as shrubs or trees. The discipline is of immediate interest to humans because of algae's importance in ecology.
parasitology
Specializations in Biology, the study of animal and plant parasitism as a biological phenomenon. Parasites occur in virtually all major animal groups and in many plant groups, with hosts as varied as the parasites themselves.
Virology
Specializations in Biology, the study of viruses and virus-like agents, including, but not limited to, their taxonomy, disease-producing properties, cultivation, and genetics. (blank) is often considered a part of microbiology or pathology.
physiology
Specializations in Biology, the branch of biology that deals with the normal functions of living organisms and their parts.
Molecular Biology
Specializations in Biology, is the field of biology that studies the composition, structure and interactions of cellular molecules – such as nucleic acids and proteins – that carry out the biological processes essential for the cell's functions and maintenance.
Biotechnology
Specializations in Biology, technology that utilizes biological systems, living organisms or parts of this to develop or create different products. Brewing and baking bread are examples of processes that fall within the concept of (blank) (use of yeast (= living organism) to produce the desired product).
Cell biology
Specializations in Biology, the study of cell structure and function, and it revolves around the concept that the cell is the fundamental unit of life. Focusing on the cell permits a detailed understanding of the tissues and organisms that cells compose.
Genetics
Specializations in Biology, the study of how genes and how traits are passed down from one generation to the next. Our genes carry information that affects our health, our appearance, and even our personality
Ecology
Specializations in Biology, the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment; it seeks to understand the vital connections between plants and animals and the world around them.
Immunology
Specializations in Biology, the study of the immune system and is a very important branch of the medical and biological sciences. The immune system protects us from infection through various lines of defence. If the immune system is not functioning as it should, it can result in disease, such as autoimmunity, allergy and cancer.
Marine biology
Specializations in Biology, the study of marine organisms, their behaviors and interactions with the environment. (blank) study biological oceanography and the associated fields of chemical, physical, and geological oceanography to understand marine organisms.
Photobiology
Specializations in Biology, the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation (e.g., the optical spectral range 400–700 nm) and biological molecules. It thus involves the study of photochemical reactions caused by light and the resulting biological responses.
Radiobiology
Specializations in Biology, a branch of science that deals with the action of ionizing radiation on biological tissues and living organisms, is a combination of two disciplines: radiation physics and biology. All living things are made up of protoplasm that consists of inorganic and organic compounds dissolved or suspended in water.
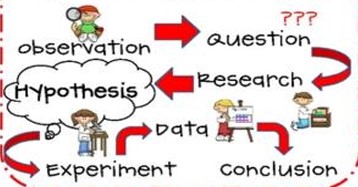
Scientific Method
Scientific Attitude
1. Problems have solutions
2. Respect for power of theoretical structure
3. Thirst for knowledge
4. Ability to separate fundamental concepts from irrelevant
5. Ability to suspend judgement
6. Appreciation of probability and statistics
7. Automatic preference for scientific explanation
8. Understanding the tolerance limits
9. Awareness of assumptions
10. Determinism
11. Empathy for human conditions
12. Empiricism
13. Loyalty to reality
14. Parsimony
15. Precision
16.Respect for quantification and appreciation of mathematics
17. Respect for scientific paradigms
18. Scientific manipulation
19. Skepticism
20. Willingness to change position
Limitations of Science
Science cannot: 1. Answer questions about value 2. Answer questions of morality 3. Deal with unique 4. Answer the questions about Supernatural
Life
The existence of an individual human being or animal
Characteristics of Living things
Cellular Organization • Metabolism • Movement or Motility • Irritability or Responsiveness • Reproduction • Growth and development • Living things evolve • Adaptiveness
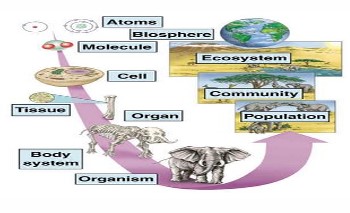
Cellular Organization
Divine Creation Theory
*based on the belief that the Bible is a credible source, which gives the story of Creation. In the span of six days (24 hour days), God created the heavens and the earth, the sun, moon, stars, and all of the creatures of the earth.
Abiogenesis Theory
the origin of life from nonliving matter. specifically : a theory in the evolution of early life on earth: organic molecules and subsequent simple life forms first originated from inorganic substances.
Biogenesis Theory
*the theory that living things can only come from other living things. It was developed in 1858 by Rudolf Virchow as a counter-hypothesis to spontaneous generation. Before Virchow, it was widely accepted that microorganisms simply appeared as a result of spontaneous generation.
Chevalier de Lamarck’s Concept
explains the descent with modifications, change in environment caused a change in the organism. 1. Theory of Needs 2. Theory of Use and Disuse 3. Theory of Inheritance of Acquired Traits; a theory of evolution based on the principle that physical changes in organisms during their lifetime—such as greater development of an organ or a part through increased use—could be transmitted to their offspring.
Charles Darwin’s Natural Selection Theory
Survival of the fittest 1. Overproduction 2. Struggles for Existence 3. Survival of the Fittest 4. Variations of Characters 5. Transmissions of Variations of Characters; Also known as “natural selection,” it is a simple statement of the fact that in dangerous circumstances, only those individuals most adapted to their environment survive—and the world, with its limited food supply, fearsome predators, and devastating diseases is always a dangerous place.
Mutation Theory
*According to Hugo de Vries' mutation theory, living organisms can develop changes to their genes that greatly alter the organism. These changes are passed down to the next generation, and lead to the development of new species. Once a new species has evolved, it becomes fixed and stops changing.