achem chapter 21 Atomic Spectroscopy slides
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:45 AM on 4/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
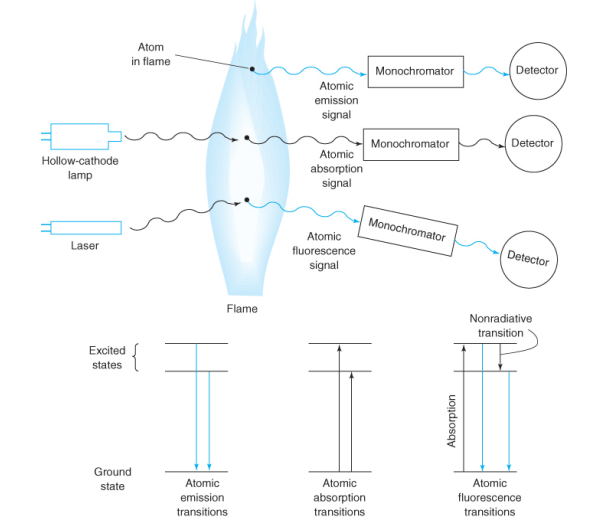
atomic spectroscopy
• Samples are vaporized and decompose into atoms and ions at high temperature.
• Some of the metal atoms may be raised to higher energy level and emit characteristic radiation. But large amount of metal atoms will remain in non emitting ground state and can absorb light.
• Concentrations are measured based on their absorbance or emission of light.
• in absorption the electron is excited and goes up a state (then relaxes back down). In florescence the excited electrode can jump up more than 1 state then relax back down 1, 2, etc. In emission you record it relaxing down.
• Some of the metal atoms may be raised to higher energy level and emit characteristic radiation. But large amount of metal atoms will remain in non emitting ground state and can absorb light.
• Concentrations are measured based on their absorbance or emission of light.
• in absorption the electron is excited and goes up a state (then relaxes back down). In florescence the excited electrode can jump up more than 1 state then relax back down 1, 2, etc. In emission you record it relaxing down.
2
New cards
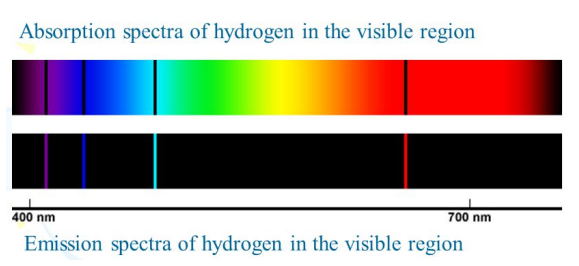
absorption spectra vs emission spectra
3
New cards
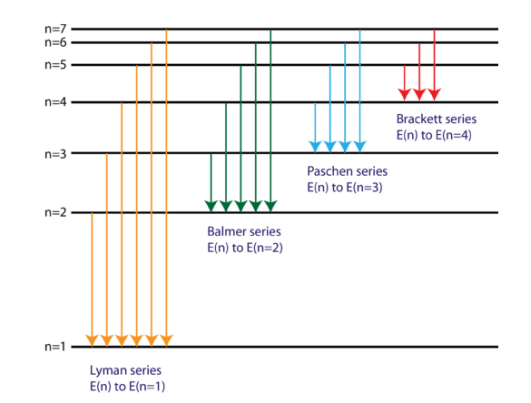
electron transitions
\
4
New cards
lyman series
UV emission. E(n) to E(n=1)
5
New cards
balmer series
Vis emission. E(n) to E(n=2)
6
New cards
Paschen series
IR emission. E(n) to E(n=3)
7
New cards
Brachett series
IR emission. E(n) to E(n=4)
8
New cards
Types of atomic spectroscopy based on atomization type
• Flame Atomic Absorbance Spectroscopy (FAAS)
• Graphite Furnace Absorbance Spectroscopy (GFAAS)
• Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES)
• Graphite Furnace Absorbance Spectroscopy (GFAAS)
• Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES)
9
New cards
Types of atomic spectroscopy
• Atomic absorption spectroscopy
• Atomic emission spectroscopy
• Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy
• Atomic emission spectroscopy
• Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy
10
New cards
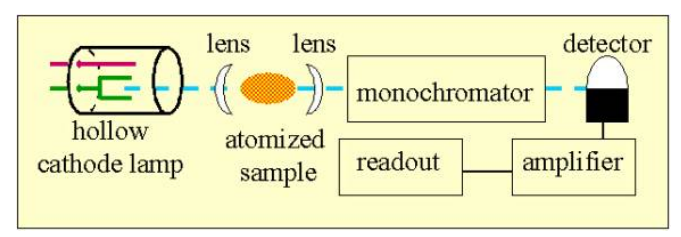
Basic schematic diagram atomic absorption spectroscopy
11
New cards
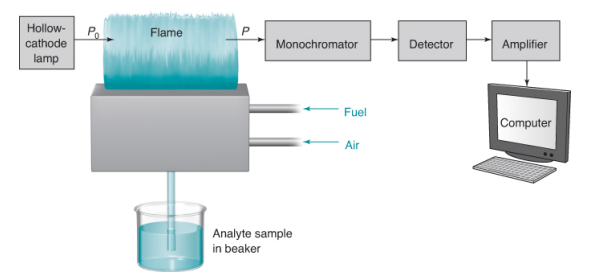
Flame Atomic Absorbance Spectroscopy (FAAS)
• A liquid sample is aspirated into the flame (2 000-3 000 K).
• Liquid evaporates and the remaining solid is atomized in the flame. Atoms absorbs light of specific λs
• Determination of one element at a time. (one lamp one element)
• A hollow-cathode lamp passes light through the sample in the flame and the intensity of the transmitted radiation is measured by a photon transducer.
• Spectra of molecules have bandwidths of \~10-100 nm, whereas spectra of atoms consist of sharp lines with widths of \~0.001 nm.
• Lines are so sharp that there is little overlap between spectra of different elements in the same sample.
• Some instruments can measure more than 70 elements simultaneously.
• Liquid evaporates and the remaining solid is atomized in the flame. Atoms absorbs light of specific λs
• Determination of one element at a time. (one lamp one element)
• A hollow-cathode lamp passes light through the sample in the flame and the intensity of the transmitted radiation is measured by a photon transducer.
• Spectra of molecules have bandwidths of \~10-100 nm, whereas spectra of atoms consist of sharp lines with widths of \~0.001 nm.
• Lines are so sharp that there is little overlap between spectra of different elements in the same sample.
• Some instruments can measure more than 70 elements simultaneously.
12
New cards
hollow-cathode lamp
passes light through the sample in the flame and the intensity of the transmitted radiation is measured by a photon transducer. for flame atomic absorbance spectroscopy (FAAS). will contain the atom being measured in the lamp to excite it and give light from the relaxed energy states
13
New cards
atomic emission spectroscopy
• radiation from hot atoms whose electrons have been promoted to an excited state in the flame or plasma is emitted.
• No lamp is needed, but atomization at higher temperatures (5000 – 8000 K).
• Heat from ICP or spark/arc.
• Determination several elements.
• No lamp is needed, but atomization at higher temperatures (5000 – 8000 K).
• Heat from ICP or spark/arc.
• Determination several elements.
14
New cards
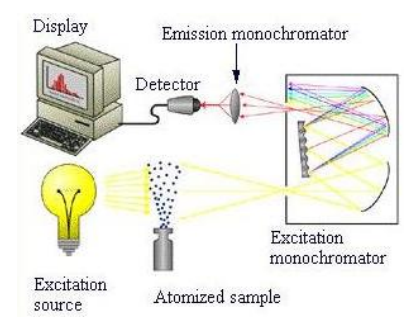
atomic fluorescence spectroscopy
atoms in the flame are irradiated by a laser to promote them to an excited state from which they can fluoresce to return to the ground state.
15
New cards
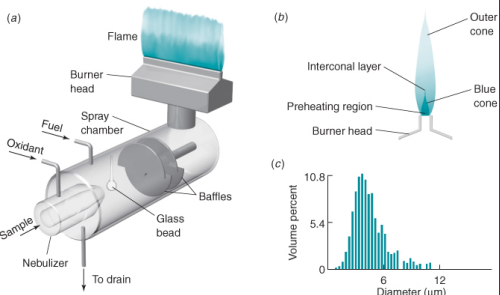
Flames
• use a premix burner, in which fuel, oxidant, and sample are mixed prior to introduction into the flame.
• Sample solution is drawn into the pneumatic nebulizer by rapid flow of oxidant (usually air) past the tip of the sample capillary.
• Liquid breaks into a fine mist as it leaves the capillary.
• The spray is directed against a glass bead, upon which the droplets break into smaller particles.
• The formation of small droplets is called nebulization.
• A fine suspension of liquid (or solid) particles in a gas is called an aerosol.
• The nebulizer creates an aerosol from the liquid sample.
• The mist, oxidant, and fuel flow past baffles that promote further mixing and block large droplets of liquid.
• Excess liquid collects at the bottom of the spray chamber and flows out to a drain.
• Aerosol reaching the flame contains only about 5% of the initial sample.
• Most common use air/acetylene giving temps of 2400 - 2700K
• Sample solution is drawn into the pneumatic nebulizer by rapid flow of oxidant (usually air) past the tip of the sample capillary.
• Liquid breaks into a fine mist as it leaves the capillary.
• The spray is directed against a glass bead, upon which the droplets break into smaller particles.
• The formation of small droplets is called nebulization.
• A fine suspension of liquid (or solid) particles in a gas is called an aerosol.
• The nebulizer creates an aerosol from the liquid sample.
• The mist, oxidant, and fuel flow past baffles that promote further mixing and block large droplets of liquid.
• Excess liquid collects at the bottom of the spray chamber and flows out to a drain.
• Aerosol reaching the flame contains only about 5% of the initial sample.
• Most common use air/acetylene giving temps of 2400 - 2700K
16
New cards
rich flame
(excess fuel) increases sensitivity because excess carbon can reduce the metal oxides and hydroxides.
17
New cards
lean flame
(excess oxidant) gives a hotter flame
18
New cards
Furnaces
• An electrically heated graphite furnace is more sensitive than a flame and requires less sample.
• 1-100 µL of sample is injected into the furnace through a hole at the center. The sample should go to the floor.
• Light from a hollow cathode lamp travels through the window at each end of the graphite tube.
• A temperature program is applied (drying, charring, atomization, cleaning)
• 1-100 µL of sample is injected into the furnace through a hole at the center. The sample should go to the floor.
• Light from a hollow cathode lamp travels through the window at each end of the graphite tube.
• A temperature program is applied (drying, charring, atomization, cleaning)
19
New cards
Furnaces have several advantages over flames, leading to an increase in sensitivity:
1. 1-2mL sample volume is the minimum required
for a flame compared to 1µL for a furnace.
2. Flames hold the sample in the optical path for
\~1s as it rises thru the flame; however, a
furnace confines the sample in the light path for
several s.
3. Multiple aliquots of sample can be injected onto
the furnace platform and evaporated, preconcentrating the sample in the furnace prior to
analysis.
4. Flames require nebulization, which can dilute
sample; there is no nebulization step using a
furnace.
\
Note:
• Graphite furnaces do have a limited lifetime.
• Memory effect – interference from previous runs.
20
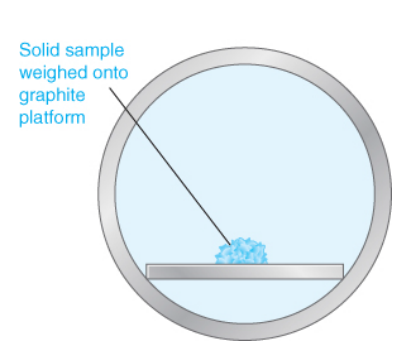
New cards
direct solid sampling
a solid is analyzed without sample preparation
21
New cards
matrix
Everything in the sample other than the analyte
22
New cards
matrix modifier
a substance added to the sample to reduce the loss of the analyte during the charring by making the matrix more volatile or the analyte less volatile.
23
New cards
Inductively coupled plasma
• Twice as hot as the flame
• Stable
• Inert Ar environment
• Simultaneous multielement analysis
• Costs more to purchase and operate than the flame
• Stable
• Inert Ar environment
• Simultaneous multielement analysis
• Costs more to purchase and operate than the flame
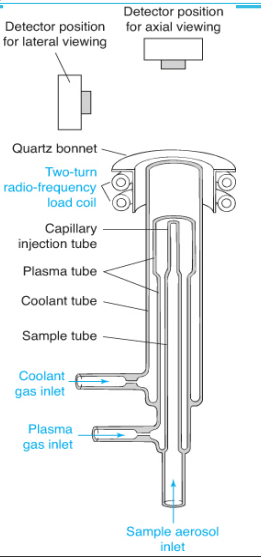
24
New cards
plasmas
• Two turns of a 27- or 41-MHz radio frequency induction coil wrapped around the upper opening of the quartz apparatus.
• High-purity argon is fed into the plasma gas inlet at 14-18 L per minute.
• A spark from a Tesla coil initiates ionization of Ar forming Ar+ and electrons, which are accelerated by the radio frequency field.
• Electrons collide with Ar atoms and transfer their energy to the entire gas, maintaining a temperature of 6 000 to 10 000 K.
• The quartz torch is protected from overheating by Ar coolant gas.
• High-purity argon is fed into the plasma gas inlet at 14-18 L per minute.
• A spark from a Tesla coil initiates ionization of Ar forming Ar+ and electrons, which are accelerated by the radio frequency field.
• Electrons collide with Ar atoms and transfer their energy to the entire gas, maintaining a temperature of 6 000 to 10 000 K.
• The quartz torch is protected from overheating by Ar coolant gas.
25
New cards
How Temperature Affects Atomic Spectroscopy
1. It determines the degree to which a sample breaks
down into atoms.
2. It determines the extent to which an atom is found
in its ground, excited, or ionized state (Boltzmann
distribution)
Both of these affect the strength of the observed
signal.
26
New cards
Boltzmann distribution
describes the relative populations of different states at thermal equilibrium
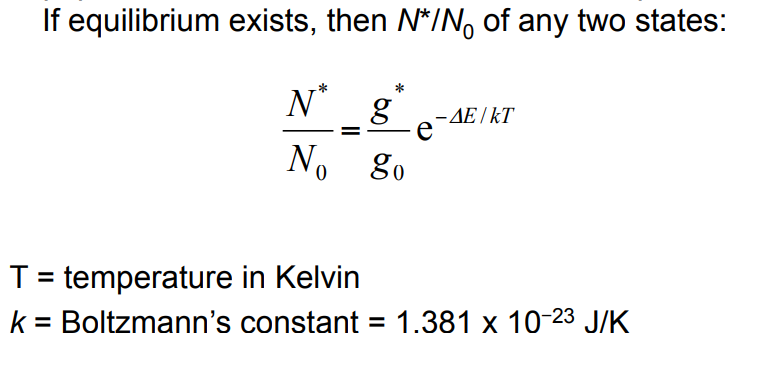
27
New cards
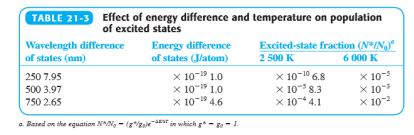
Temperatures and Energies of Excited States
• The lowest excited state of a Na atom lies 3.371 x 10^-19 J/atom above the ground state.
• The fraction of Na in the excited state in an acetylene-air flame at 2600 K is 1.67 x 10^-4. (That is, less than 0.02% of the atoms are in the excited state.)
• If the temperature is increased to 2610 K, the fraction of atoms in the excited state is 1.74 x 10^-4.
• By increasing the temperature by 10 K, the excited state population increases by 4%.
• At 2600 K, 99.98% of the atoms are in their ground state.
• Varying the temperature by 10 K hardly affects the ground-state population and would not noticeably affect the signal in atomic absorption.
• Atomic emission occurs from the excited state, therefore 4% increase in the excited state would increase the emission intensity by 4%.
• Atomic emission typically uses plasmas.
• The fraction of Na in the excited state in an acetylene-air flame at 2600 K is 1.67 x 10^-4. (That is, less than 0.02% of the atoms are in the excited state.)
• If the temperature is increased to 2610 K, the fraction of atoms in the excited state is 1.74 x 10^-4.
• By increasing the temperature by 10 K, the excited state population increases by 4%.
• At 2600 K, 99.98% of the atoms are in their ground state.
• Varying the temperature by 10 K hardly affects the ground-state population and would not noticeably affect the signal in atomic absorption.
• Atomic emission occurs from the excited state, therefore 4% increase in the excited state would increase the emission intensity by 4%.
• Atomic emission typically uses plasmas.
28
New cards
Monochromators
• generally cannot isolate lines narrower than 10^-3 to 10^-2 nm.
• To produce narrow lines of the correct frequency, we use hollow-cathode lamps containing vapor of the same element being analyzed.
• To produce narrow lines of the correct frequency, we use hollow-cathode lamps containing vapor of the same element being analyzed.
29
New cards
Beer’s law requires…
…that the linewidth of the radiation source should be substantially narrower than the linewidth of the absorbing sample.
30
New cards
Atomic absorption linewidths
have an intrinsic width of \~10^-4 nm due to Heisenberg uncertainty, Doppler broadening and Pressure broadening
31
New cards
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
states that the shorter the lifetime of the excited state, the more uncertain its energy
32
New cards
Doppler broadening
atomic motion occurs in every direction.
33
New cards
higher frequency
An atom moving toward the radiation source “sees” a ____ light than one moving away.
34
New cards
no shift
There is ____ for atoms moving perpendicular to the source. The result is a symmetric distribution of λs
35
New cards
Pressure broadening
caused by collisions of the emitting or absorbing species with other atoms or ions in a hot environment.
36
New cards
shorten
Collisions between atoms ____ the lifetime of the excited state.
37
New cards
collision frequency
proportional to the pressure. This is similar in magnitude to the effect of Doppler broadening and yields linewidths of 10^-3 to 10^-2 nm in atomic spectroscopy
38
New cards
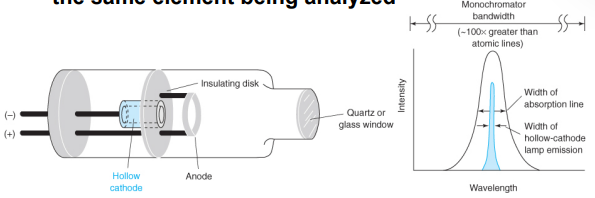
hollow cathode lamp structure
• These consist of a tungsten anode and a cylindrical cathode, and a glass tube filled with neon or argon at a pressure of 1-5 torr.
• The cathode is constructed of the metal whose spectrum is desired.
• A potential difference is applied across the electrodes, generating a current and ionizing the inert gas.
• The cathode is constructed of the metal whose spectrum is desired.
• A potential difference is applied across the electrodes, generating a current and ionizing the inert gas.
39
New cards
sputtering
Gaseous cations can acquire enough kinetic energy to dislodge some of the metal atoms from the cathode surface producing an electron cloud through this process.
A portion of the metal atoms are in their excited state and emit characteristic radiation as they return to their ground state. The metal atoms eventually diffuse back to the cathode, or deposit on the glass walls of the tube.
A portion of the metal atoms are in their excited state and emit characteristic radiation as they return to their ground state. The metal atoms eventually diffuse back to the cathode, or deposit on the glass walls of the tube.
40
New cards
Background correction
necessary in atomic spectroscopy to distinguish the analyte signal from absorption, emission, and optical scattering of the sample matrix, the flame, plasma, or graphite furnace. critical for graphite furnaces due to residual smoke from charring.
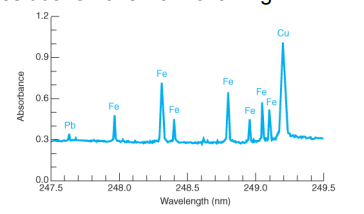
41
New cards
beam chopping
For atomic absorption, electrical modulation of the hollow-cathode lamp (pulsing it on and off) can distinguish the signal of the flame from the atomic line at the same wavelength. Referred to as this.
The figure shows light from the lamp being periodically blocked by a rotating chopper. Signal reaching the detector while the beam is blocked must be from the flame emission. Signal reaching the detector when the beam is not blocked is from the lamp and the flame. The difference between the two is the analytical signal.
does not correct for scattering
The figure shows light from the lamp being periodically blocked by a rotating chopper. Signal reaching the detector while the beam is blocked must be from the flame emission. Signal reaching the detector when the beam is not blocked is from the lamp and the flame. The difference between the two is the analytical signal.
does not correct for scattering
42
New cards
Deuterium lamp background correction
broad emission from a D2 lamp is passed through the flame in alternation with that from the hollow cathode. Light from the hollow cathode lamp is absorbed by the analyte as well as absorbed and scattered by the background.
Light from the D2 lamp is only absorbed and scattered by the background. The difference between the two is the absorbance of the analyte.
Light from the D2 lamp is only absorbed and scattered by the background. The difference between the two is the absorbance of the analyte.
43
New cards
Zeeman effect
For a graphite furnace, the background correction relies on the ____
44
New cards
magnetic field
A ____ applied parallel to the light path through the furnace splits the analyte signal into three components. Two are shifted and one is not. The unshifted one does not absorb the light because it does not have the correct polarization.
The strong ____ is pulsed on and off (same blank fill). Sample and background are observed when the ____ is off. The difference between them is the corrected signal
The strong ____ is pulsed on and off (same blank fill). Sample and background are observed when the ____ is off. The difference between them is the corrected signal
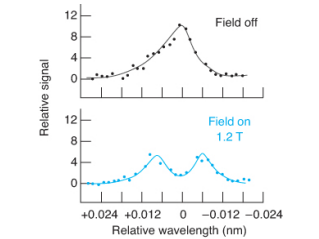
45
New cards
detection limit for furnaces
typically two orders of magnitude lower than that observed with a flame because the sample is confined in the small volume of the furnace for a relatively long time
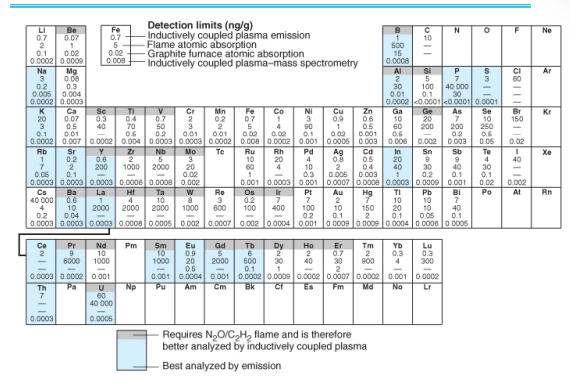
46
New cards
ICP is intermediate
with ultrasonic nebulization and axial plasma viewing, the sensitivity of the ICP is close to that of the graphite furnace.
47
New cards
X-ray fluorescence
the emission of X-rays following the absorption of X-rays by a material. Elements are identified by their peak energies and quantified by the number of photons in each peak.
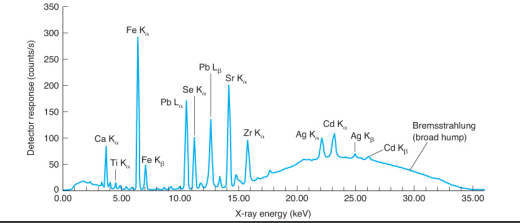
48
New cards
Handheld X-ray fluorescence analyzers
can detect levels as low as 1 ppm for As, Pb, and Hg.
should be mounted in a lead-lined test stand to prevent user exposure to X-rays.
In the field, you should remain behind the analyzer.
should be mounted in a lead-lined test stand to prevent user exposure to X-rays.
In the field, you should remain behind the analyzer.
