History of Life on Earth and Human Evolution
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Spontaneous generation
The idea that nonliving material could give rise to living organisms.
Biogenesis
The concept of 'life-from-life'.
Big Bang theory
States that a cosmic explosion occurred billions of years ago, resulting in the formation of clouds of hydrogen and helium atoms.

Reducing atmosphere hypothesis
Proposes that early Earth had an oxygen-poor atmosphere rich in inorganic molecules, leading to the formation of organic molecules.
Extraterrestrial hypothesis
Suggests that organic molecules/life came from other planets.
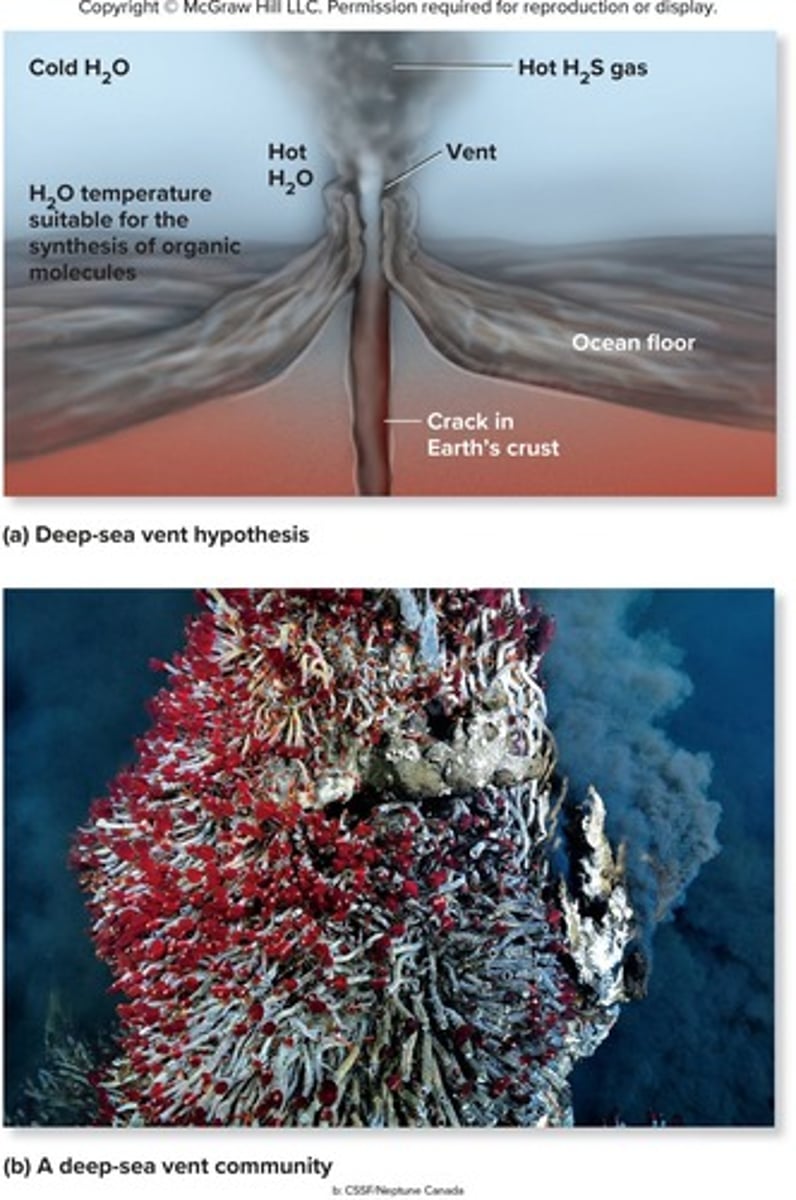
Deep-sea vent hypothesis
Proposes that key organic molecules originated from deep-sea vents.
Creationism
The belief that humans, life, the Earth, and/or the universe were created by a supreme being or deity's supernatural intervention.
Four overlapping stages hypothesis
A proposed process for the origin of cells, consisting of four stages: formation of nucleotides and amino acids, formation of RNA, DNA, and proteins, molecules being enclosed in membranes, and acquisition of cellular/living properties.
Stage 1 of cell formation
Involves the formation of nucleotides and amino acids prior to the existence of cells.
Stage 2 of cell formation
Involves the formation of RNA, DNA, and proteins.
Stage 3 of cell formation
Involves molecules being enclosed in membranes.
Stage 4 of cell formation
Involves the acquisition of cellular/living properties.
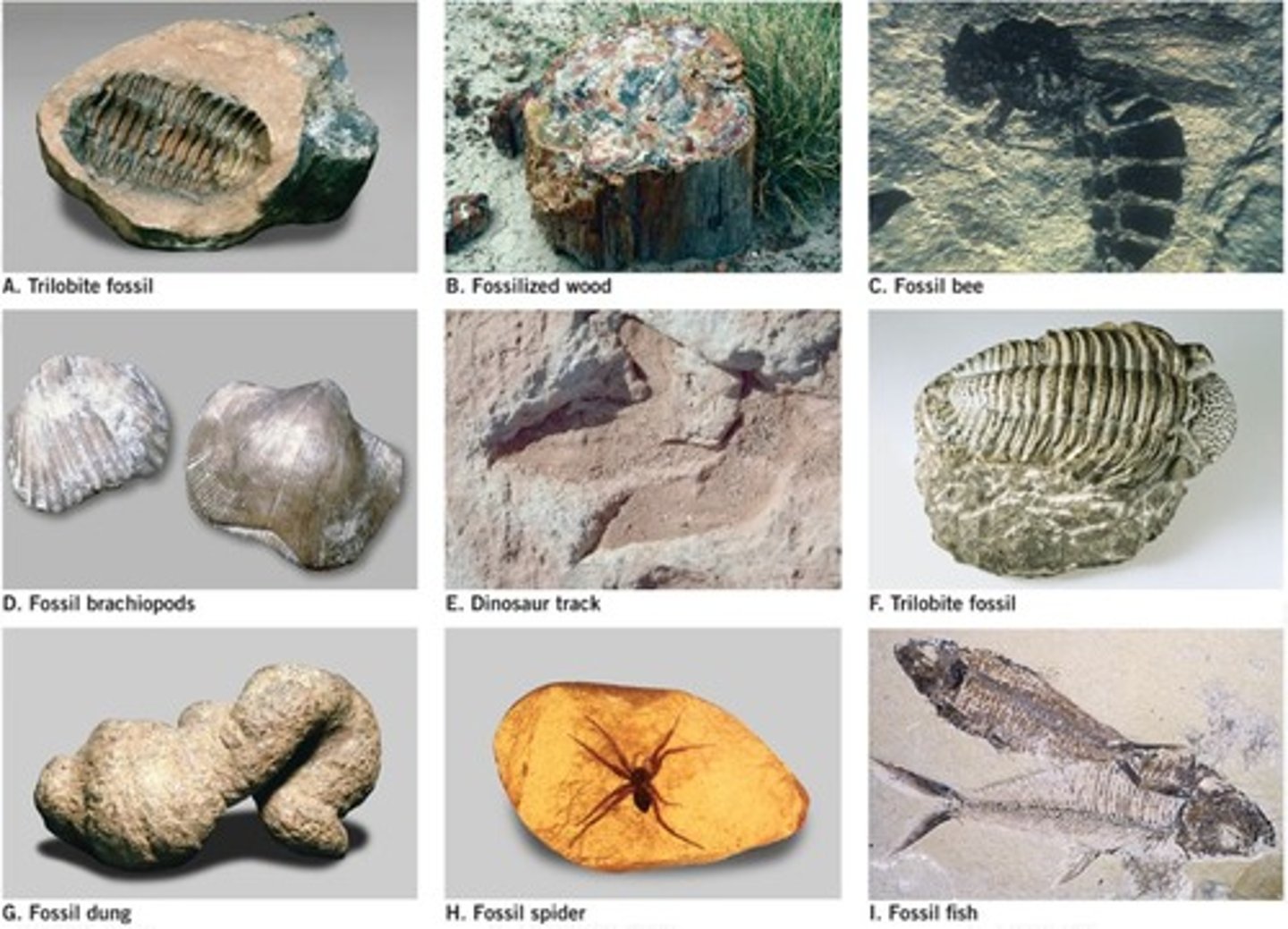
Fossils
Remains or impressions of ancient organisms preserved in geological formations.
Fossil record
Used to help place important events and species in the appropriate geologic era.
Geological timescale
A timeline that describes the timing and relationships of events in Earth's history.
Environmental changes
Types of changes that have affected the history of life on Earth.
Louis Pasteur
Scientist who disproved spontaneous generation in 1862 through pasteurization.
Aristotle
Philosopher who proposed the idea of spontaneous generation.
Cosmic explosion
The event that led to the formation of hydrogen and helium clouds in the Big Bang theory.
Gravitational forces
Forces that collapsed clouds of hydrogen and helium to create stars.
Macromolecules
Large molecules formed from smaller molecules (monomers) during the origin of life.
Water Vapor
Speculated to have supplied atoms of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
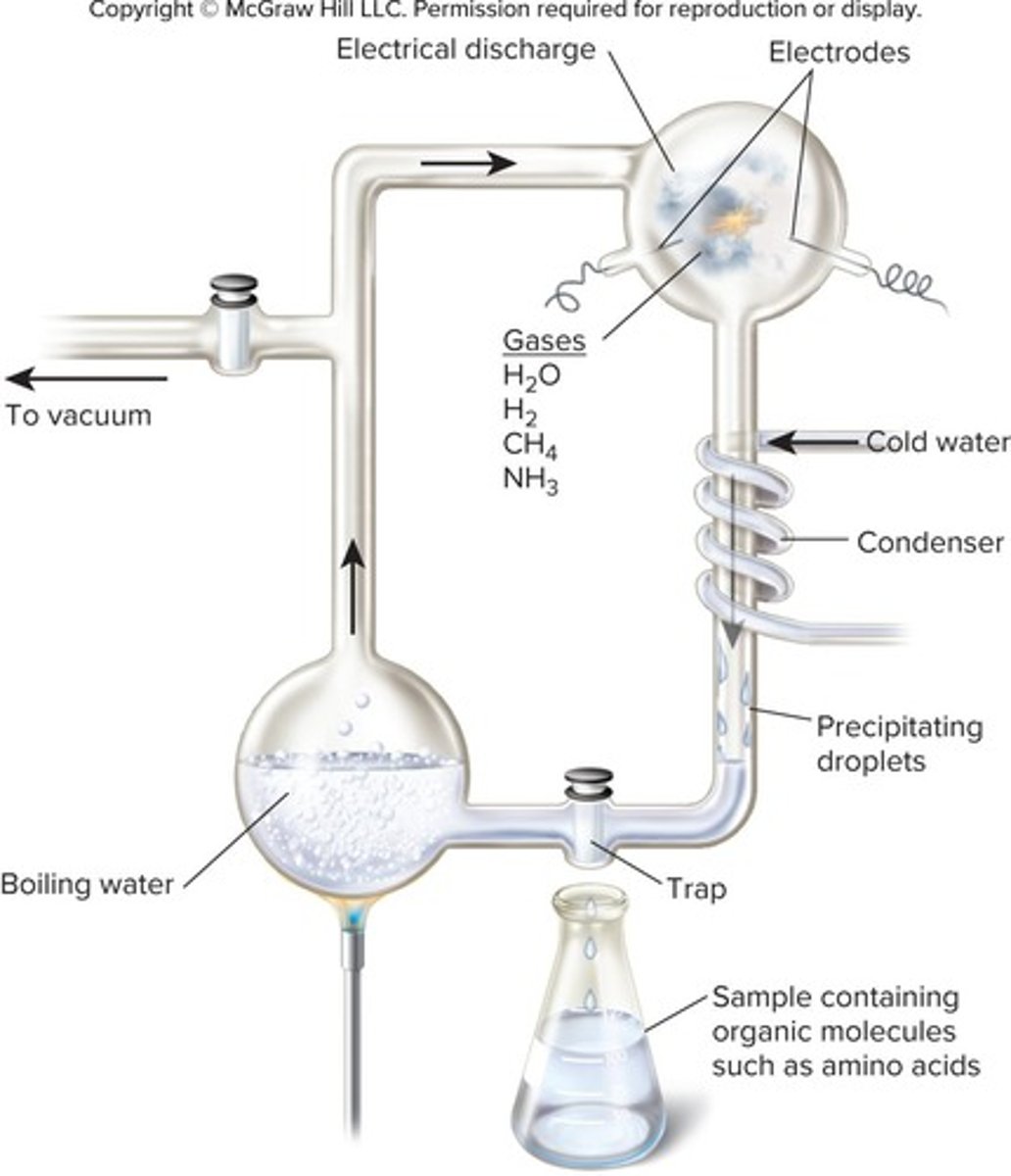
Energy Sources for Organic Synthesis
Lightning, heat from volcanoes, and ultraviolet radiation are thought to have provided the energy needed.
Laboratory Reproduction of Experiments
Experiments have been reproduced in the laboratory but cannot prove what actually happened.
Stage 2: Organic Polymers
Simple organic molecules, such as nucleotides and amino acids, became polymerized to form DNA/RNA and proteins.
Clay Minerals
Scientific evidence suggests that organic molecules could polymerize on the surface of clay.
Absence of Enzymes
Polymerization occurred without chemical assistance.
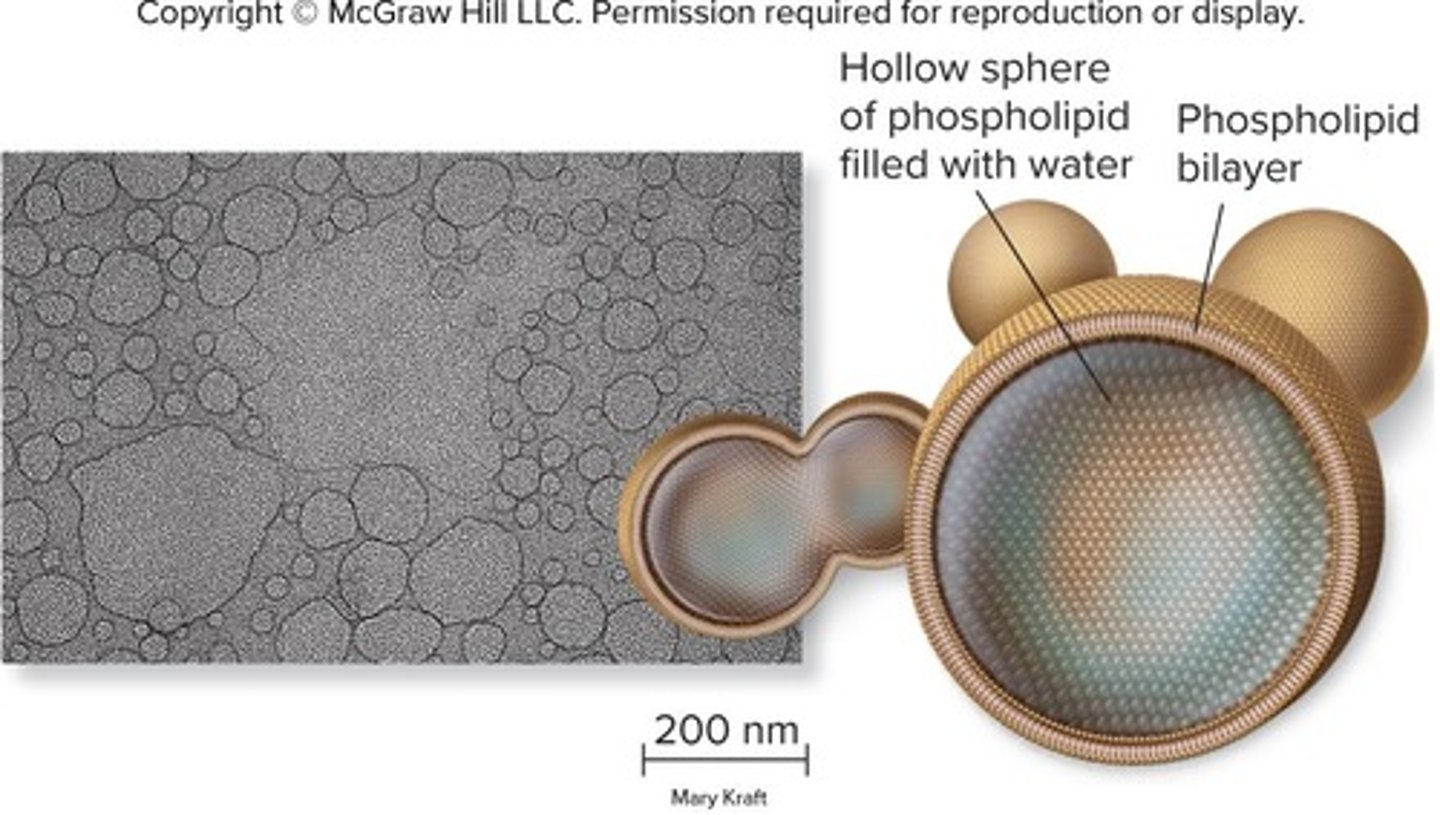
Stage 3: Protobionts
Polymers became enclosed in membranes, forming aggregates of molecules with an outer boundary.
Lipid Bilayer
An outer boundary of protobionts, allowing for the containment of information and catalytic functions.
Self-Replication
Protobionts developed the capability of self-replication.
Liposomes
Vesicles surrounded by a phospholipid layer that could form cell-like structures.
Stage 4: Cellular Properties
Polymers enclosed in membranes acquired characteristics of cells.
RNA as First Macromolecule
Hypothesized to be the first macromolecule found in protobionts.
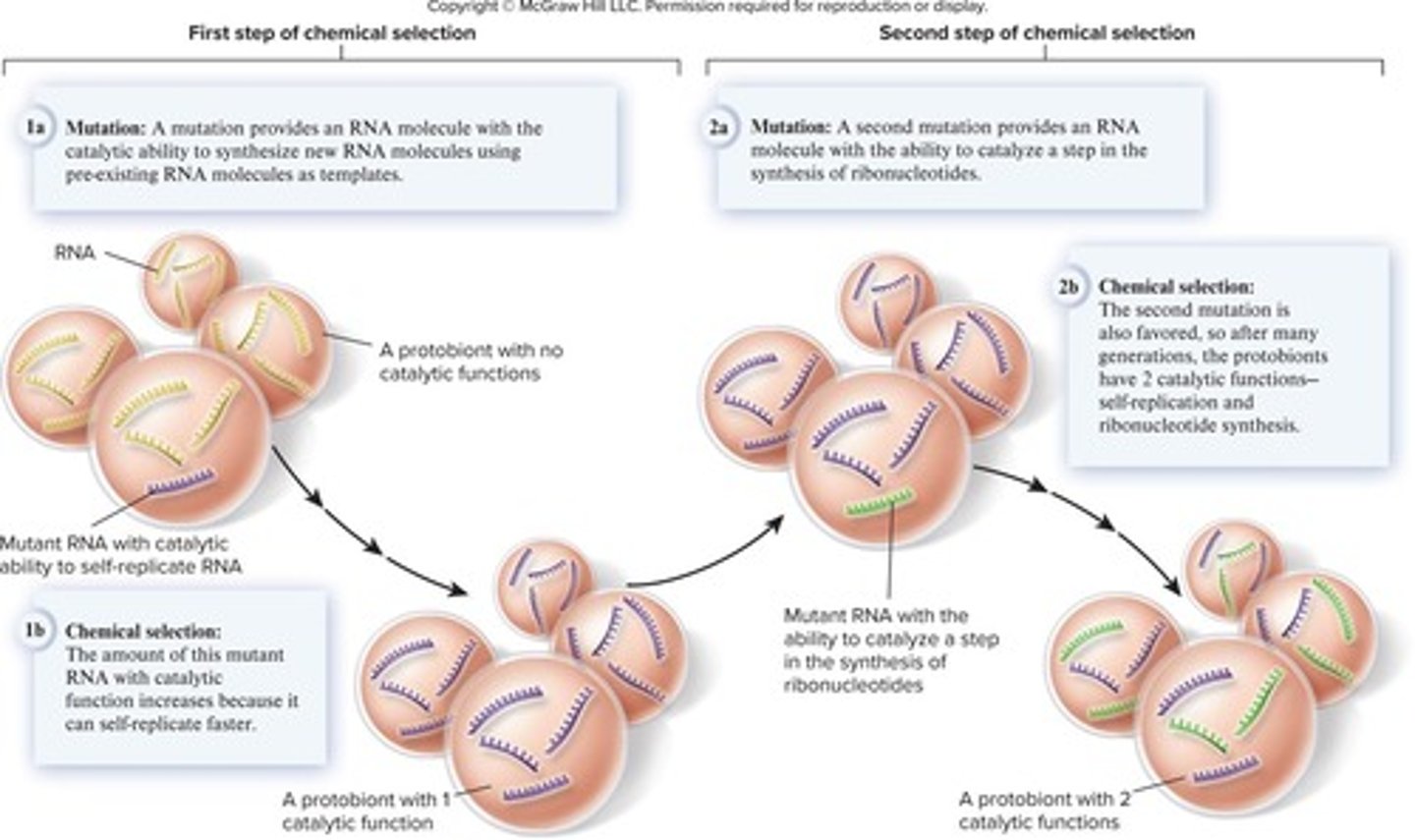
Chemical Evolution
Once protobionts had genetic material, they could mutate and evolve.
Fossils
Preserved remains of past life on Earth, including bones, shells, and impressions.
Sedimentary Rocks
Fossils are often found in these rocks, formed from particles of older rocks.
Fossil Formation
Most fossils form when organisms are buried quickly, preserving them as sediments pile up.

Paleontologists
Scientists who study fossils.
Relative Ages of Fossils
Determined by their locations within rock layers, with lower layers usually being older.
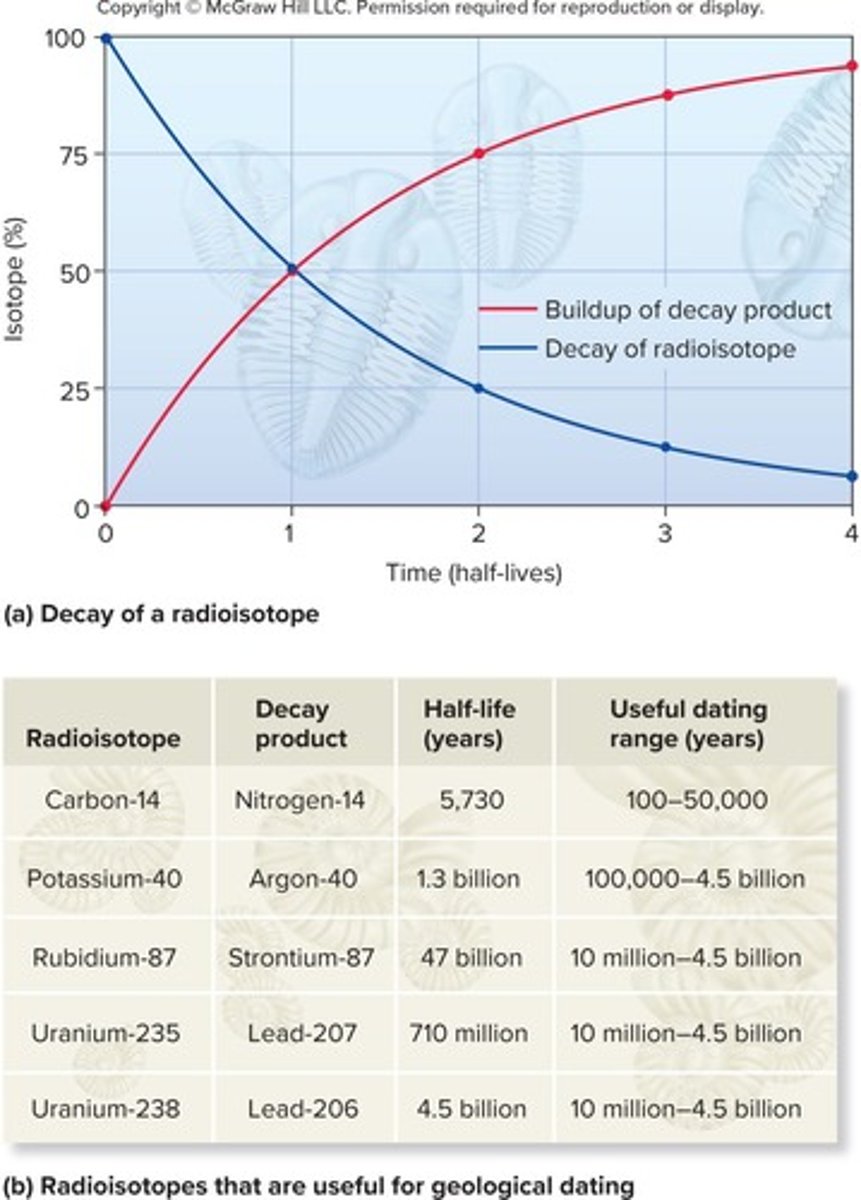
Radiometric Dating
A method used to estimate the age of fossils.
Geological timescale
A timeline of Earth's history.
Earth formation
Earth was formed about 4.55 billion years ago (bya).
Prokaryotes appearance
Prokaryotes appeared about 3.8-3.5 bya.
Oxygen-producing prokaryotes
Prokaryotes that produce oxygen appeared about 2.4 bya.
Single-celled eukaryotes
Single-celled eukaryotes evolved about 1.8 bya.
Multicellular eukaryotes
Multicellular eukaryotes appeared about 1.5 bya.
First animals
First animals appeared about 632 million years ago (mya).
Plants colonization
About 520 mya, plants started to colonize the land and first invertebrates appeared.
Terrestrial colonization
440 mya - large terrestrial colonization by plants and animals.
Seed plants and insects
400 mya - seed plants and insects first appear.
Reptiles appearance
300 mya - reptiles first appear.
Dinosaurs and mammals
225 mya - dinosaurs and mammals first appear.
Birds appearance
160 mya - birds first appear.
Flowering plants
135 mya - flowering plants first appear.
Apes appearance
7 mya - apes (chimpanzees, gorillas, orangutans, and gibbons) first appear.
Anatomically modern humans
300,000 ya - anatomically modern humans appear.
Environmental changes
Changes that have influenced the types of organisms that have existed during different periods of time.
Extinction
The complete loss of a species or groups of species.
Temperature fluctuations
Temperature changes over time, causing periods that are colder (Ice Ages) and warmer.
Atmospheric changes
Started out with little to no oxygen, then about 2.4 bya, O2 levels began to rise significantly.
Landmasses
Formation of landmasses surrounded by water resulted in two different environments, terrestrial and aquatic.
Floods and glaciations
Events that affect living organisms in the location of these occurrences.
Volcanic eruptions
Can affect living organisms in the vicinity and cause formation of new landmasses, such as islands.
Meteorite impacts
Can affect living organisms in the vicinity and surrounding landmasses and environment, potentially causing mass extinction.
Natural selection
A mechanism that results in evolutionary change, influenced by environmental factors.
Examples of human evolution
Lactose tolerance, blue eye color, and red hair color are examples of traits influenced by natural selection.