(erika)EM Exam 1: Key Terms on Wound Management & Emergencies
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
when assessing a patient with a laceration, what components of a history do we need to collect?
- time of injury
- location of injury
- MOI
- degree of contamination
- PMH, meds, allergies
- tetanus immunization status
- occupation and handedness
laceration with paresthesia is associated w/ what?
laceration with loss of function is associated w/ what?
nerve injury
tendon injury
what are factors that can affect wound healing?
- pt age
- location of injury
- MOI
- meds
- PMH
- presence of foreign body
- previous keloid or scar formation
what factors can help us predict the risk for infection assoc/w a laceration
- time since injury
- MOI (crush vs lac)
- location of injury
- degree of contamination
which location of the body is infection of a wound more likely to occur?
less likely to occur?
extremities and moist areas
face and scalp
what are the four key aspects of a physical exam when assessing a laceration on a patient?
- location and damage to underlying structures
- presence of devitalized tissue
- contamination and/or presence of FB
- complete neuro exam (gross motor, sensory, vascular)
T/F: imaging is often needed for most lacerations
false; imaging is not needed for most lacerations
1 multiple choice option
in what scenarios would it be appropriate to obtain imaging of a laceration?
- eval for FB
- eval for underlying fx
- bite wounds
which imaging modality can obtain most FBs
plain XR
this is an essential component to wound preparation and involves removing bacteria and other particles to reduce infection risk
wound irrigation
what can be given before wound irrigation to promote better tolerance from the patient?
wound anesthesia
T/F: wound soaking is not effective
true
1 multiple choice option
what solution(s) should be used to irrigate a wound?
tap water, sterile water, or normal saline solution
how much solution should be used to irrigate a wound?
50-100 mL per cm wound length
low pressure wound irrigation is used for what types of wounds?
high pressure irrigation?
simple, uncontaminated wounds (face, scalp)
contaminated wounds
what equipment is needed to perform irrigation of a wound?
- 18G angiocath or irrigation shield
- 20-50 mL syringe
- sterile saline or tap water
- gloves
- face shield
what exam needs to be performed prior to administration of anesthesia?
neurovascular exam
what trio of anesthetics are used topically for wound care?
LET - lidocaine, epi, tetracaine
which injected anesthetic is most commonly used?
which prolongs the duration of use by 25-50%?
which provides a longer duration of 1.5-3hrs?
lidocaine
lido + epi
bupivacaine
what is the major problem assoc/w all local anesthetics?
systemic absorption, can lead to CV and CNS toxicity
when injecting local anesthesia near a wound, what needs to be done prior to injection to avoid inadvertent injection into vasculature?
aspiration
this type of anesthetic is used around peripheral nerves; it does not distort the wound, it offers better pain control, but it does require more time
nerve blocks
what is the most common nerve block?
digital nerve block
what are signs of tissue necrosis?
- gray or black in color
- lack of bleeding when tissue incised
T/F: hair removal during wound debridement can help decrease the risk of infection
false; hair removal has no effect on infections, and shaving may increase infection risk
1 multiple choice option
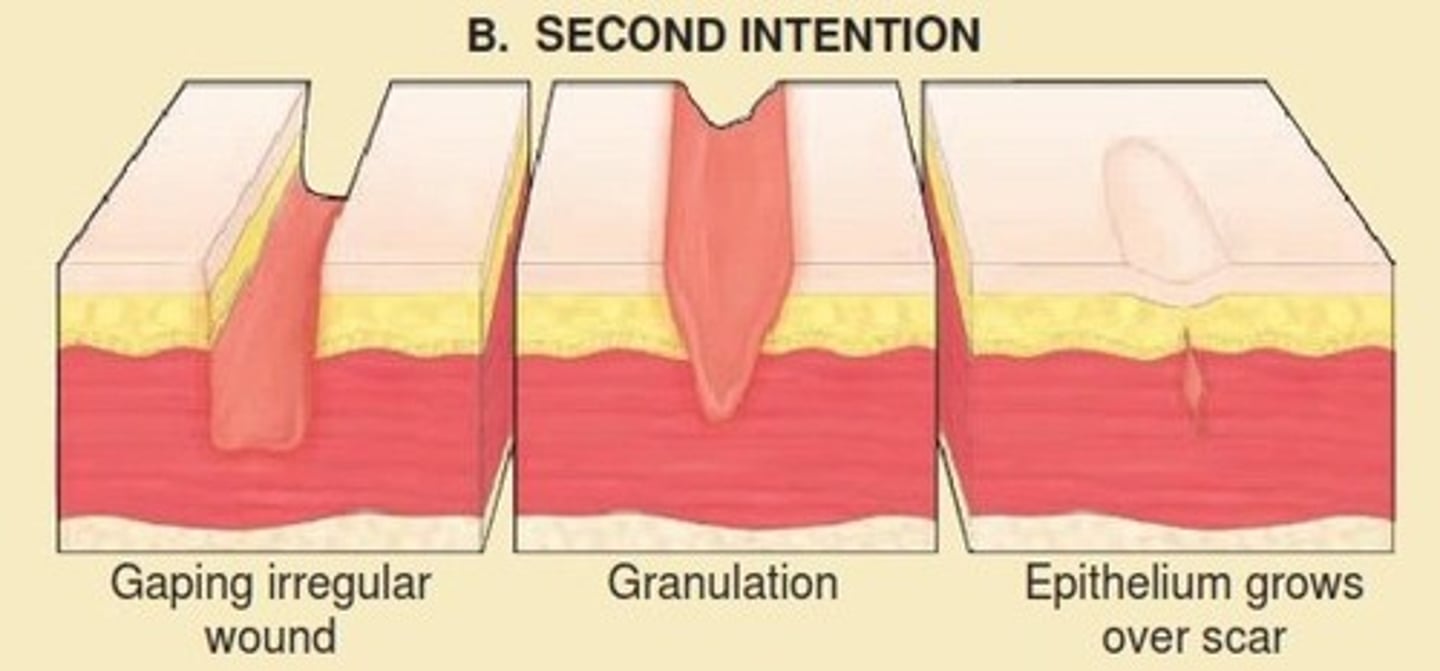
identify the wound closure approach:
- closed in acute phase on presentation
- optimal time not defined (<12 hrs old)
- low risk: infection, retained FB, NV compromise, damage to underlying structures
primary closure
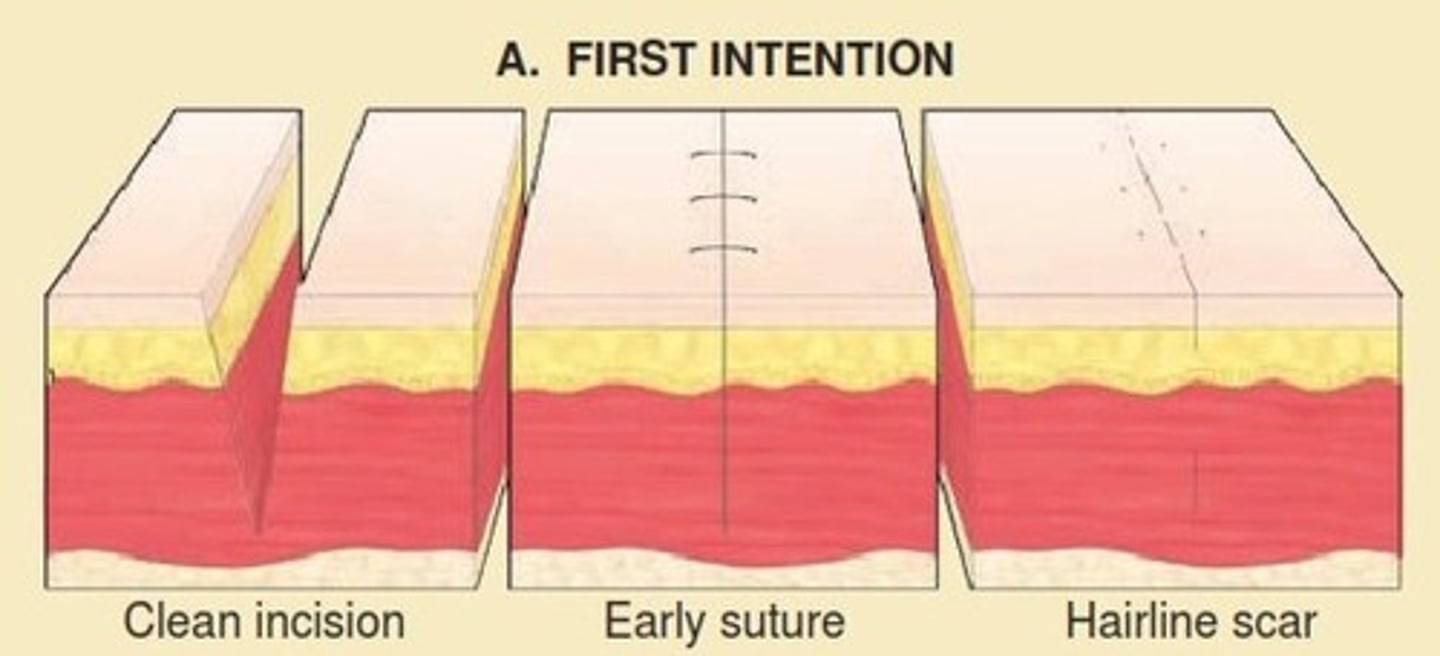
identify the wound closure approach:
- high risk of infection
- wound irrigated, cleaned, debrided, bandaged
- repair in 4-6 days
delayed primary closure
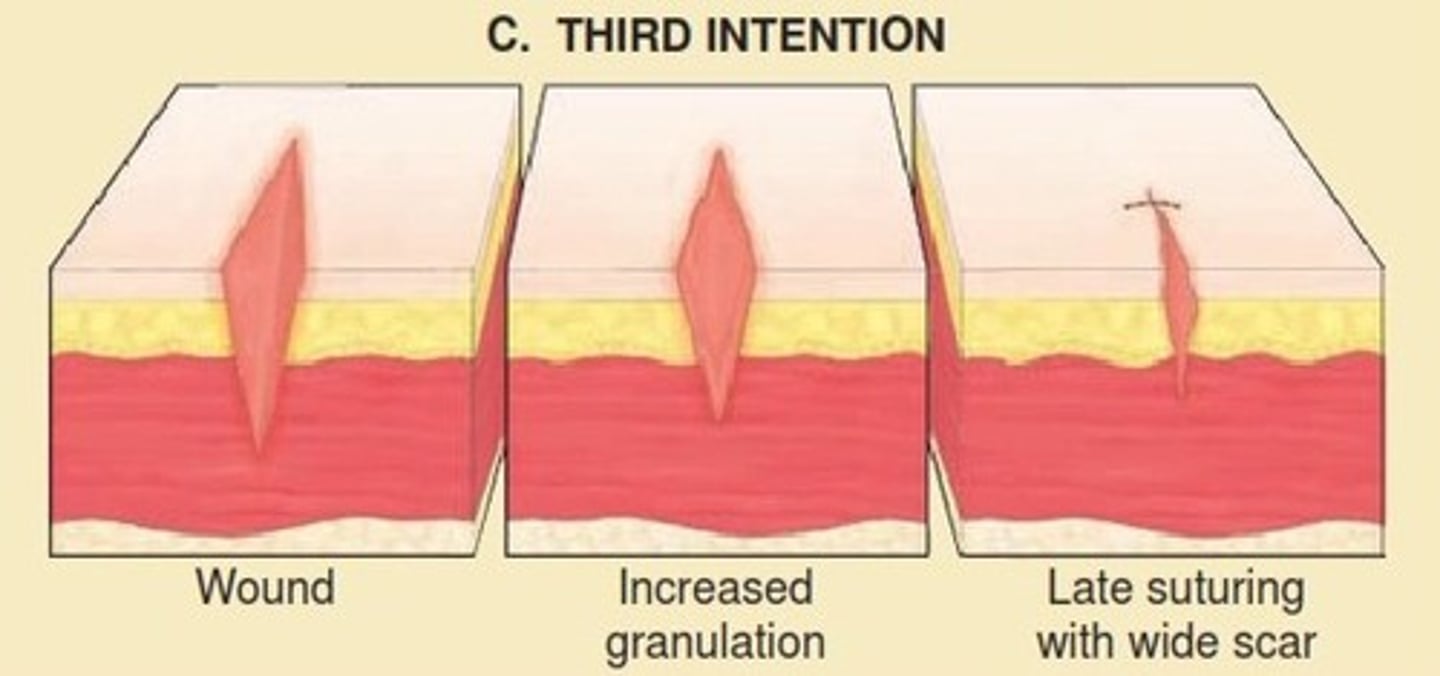
identify the wound closure approach:
- wounds presenting very late after injury
- heals spontaneously and slowly
- larger scar
secondary intention
what are the indications for using adhesive tape (steristrips) to close a wound? (3)
- linear and low tension
- superficial
- thin skin that may not hold sutures (skin tears)
what are the contraindications to using steristrips for wound closure? (3)
- high tension wounds (i.e. over joints, gaping wounds)
- wounds that require layered closure
- wounds in high-moisture areas
what can be applied to the skin to help improve adhesion of steristrips?
tincture of benzoin
what are the indications for using tissue adhesives ("glues") for wound closure? (3)
- linear and low tension
- superficial
- < 4cm length
what are the contraindications for using tissue adhesives for wound closure? (3)
- high tension wounds
- active infection
- use on mucosal surfaces, skin exposed to bodily fluids, or w/ dense hair
when using Dermabond or Liquiband for closing a wound, what can be added to the closure to provide extra strength?
steri-strips
what are the indications for using staples to close a wound?
contraindications?
scalp lacerations, linear trunk lacerations if cosmesis not priority
gaping wounds w/ layered closure; areas w/ high priority cosmesis
what is the technique for placing staples to close a wound?
- evert wound margins w/ forceps/fingers
- place 1st staple at center of wound using staple gun
- continue bisecting w/ staples until well-approximated
indications for using sutures to close a wound (3)
- clean wounds w/ low risk of infection
- areas of cosmetic concern
- wounds over tendons or nerves
contraindications for using sutures to close a wound (4)
- heavily contaminated wounds
- high risk of infection (i.e. puncture wounds)
- non-cosmetic animal bites
- high risk of tissue destruction (high pressure wounds)
suture type that is used for deep tissue structures or to avoid need for removal
absorbable (gut or vicryl)
suture type that requires removal
nonabsorbable (nylon or prolene)
what needs to be taken into consideration when deciding what type of sutures to use in wound closure?
- cosmetic considerations
- wound tension
which suture types are larger and stronger?
which types are smaller and minimize scarring?
small gauge sizes (3-0, 4-0)
large gauge sizes (5-0, 6-0)
what is the most common type of suture used?
simple interrupted sutures
T/F: most wounds need abx to prevent wound infection
false; most wounds don't need abx; good wound irrigation is sufficient
1 multiple choice option
what is MC bacteria assoc/w animal (dog/cat) bites?
assoc/w human bites?
Pasteurella multocida
Eikenella corrodens
what is the preferred abx for animal and human bites?
augmentin is dogmentin bby
preferred abx for intraoral gaping lacerations?
PCN or amoxicillin
preferred abx for excessive wound contamination (i.e. open/public waters, soil, feces)
abx is based on epidemiology of exposure and pt factors
is it tetanus prone?
wound <6 hrs
no
1 multiple choice option
is it tetanus prone?
wound w/ depth of 2 cm
yes
1 multiple choice option
is it tetanus prone?
wound caused by sharp surface such as knife of glass
no
1 multiple choice option
is it tetanus prone?
wound caused by missile, crush, burn, or frostbite
yes
1 multiple choice option
is it tetanus prone?
infection is present
yes
1 multiple choice option
is it tetanus prone?
wound does not show any signs of devitalized tissue
no
1 multiple choice option
is it tetanus prone?
wound is from a human bite
yes
1 multiple choice option
is it tetanus prone?
wound does not show signs of denervated or ischemic tissue
no
1 multiple choice option
when should a tetanus vaccine be administered following a wound?
what is the incubation period?
ASAP
2-21 days (usually w/in 8 days)
indications for tetanus prophylaxis following a laceration
- incomplete tetanus vax (<3 previous doses)
- 5+ yrs since last vax if tetanus prone
- 10+ yrs since last vax for any open wound
- recovery from tetanus (infection does not confer immunity)
T/F: tetanus vaccination is safe to give in pregnancy
true
1 multiple choice option
contraindication to administering tetanus prophylaxis following laceration
hx of neuro or severe systemic rxn after previous dose
when would TIG (tetanus immune globulin) be given to a patient presenting with a laceration?
if tetanus immunization series is incomplete or uncertain
when educating the patient on care of their laceration, under what circumstances should they return to the office (prior to their scheduled f/u)? (5)
- signs of infection (redness, pain, pus around injury, fever)
- bleeding that will not stop after 10 minutes of direct pressure
- new numbness/tingling around wound or beyond it
- pain at site that is not relieved by taking OTC pain meds
- stitches or staples that come out too soon
what is the protocol when examining an extensor tendon laceration?
- examine extremity/joint in position when injured
- assess tendon extensor function
- close skin, splint in position of function, refer to hand surgeon
what is the protocol for a flexor tendon laceration?
- assess function
- FDS tendon = PIP joint
- FDP tendon = DIP joint
- not repaired in ED
- repair in OR, refer to hand surgeon w/in 24 hrs
punch to the mouth w/ lacerations over MCP joint from teeth
is this sutured?
what abx is given?
clenched fist injury (fight bite)
no d/t infection risk
augmentin
what is the protocol for a fingertip injury where only the skin or pulp is affected?
if there is exposed bone?
conservative tx w/ dressing changes
abx, splint, refer to hand surg
with a subungual hematoma, what percentage of the nail has to be affected to trephinate?
>50%
when would we remove the nail if there was injury to the nail/nailbed?
if avulsion or nailfold disruption
what is the protocol for repairing a nailbed laceration?
repair w/ 6-0 absorbable suture, secure nail in position
when should a soft tissue FB be suspected? (5)
- broken, shattered, splintered objects
- thorns, spikes, branches
- FB sensation
- healed wounds w/ continued sharp pain
- poor wound healing, infection
which foreign bodies are likely to be left in place?
which are likely to be removed?
- small, inert, deeply embedded, asyx
- thorns, wood splinters, vegetative materials, contaminated objects; if neurovascular compromise/infection
where are puncture wounds common?
extremities - plantar foot
when would a puncture wound be considered high risk?
- forefoot
- through athletic shoes
- immunocompromised
what med is given for most puncture wounds if needed?
what med is given for PW through athletic shoes to cover Pseudomonas?
1st gen cephalosporin (cephalexin)
FQ
MC cause of cellulitis when MRSA is not suspected
group A beta-hemolytic strep
tx for cellulitis not caused by MRSA?
tx for cellulitis if MRSA is suspected?
cephalexin, dicloxacillin, clinda
TMP/SMX, clinda, doxy
breakdown of cutaneous barrier leading to localized collections of pus that occur w/in dermis and subcutaneous space
cutaneous abscess
what is the tx of a cutaneous abscess?
when would abx be required?
local incision using scalpel and drainage of purulence
fever, multiple, immunocompromised, large surrounding cellulitis
what are the indications for primary closure of mammalian bites?
- animal (dog if low risk)
- location (face or scalp, esp if gaping wound)
- wound (non-contaminated, simple for single layer closure, no devitalized tissue)
- host (not immunocompromised)
which types of mammalian bites are of high infection risk?
- cat or human bites
- hand or foot wounds
- puncture wounds
what is the initial assessment process for thermal burns?
- stabilize ABCs
- remove clothing and debris
- assess depth and extent of burns
what are the components of a directed history as it pertains to thermal burns?
- burning agent (hot liquids, steam, flame, flash)
- exposure duration (open or closed)
- possible injury (blast, contact w/ electricity, LOC, other trauma)
- if possible, AMPLE hx (allergies, meds, PMH, last meal, events)
what type of burn?
- epidermis only
- no blisters, red
- painful
superficial (first degree)

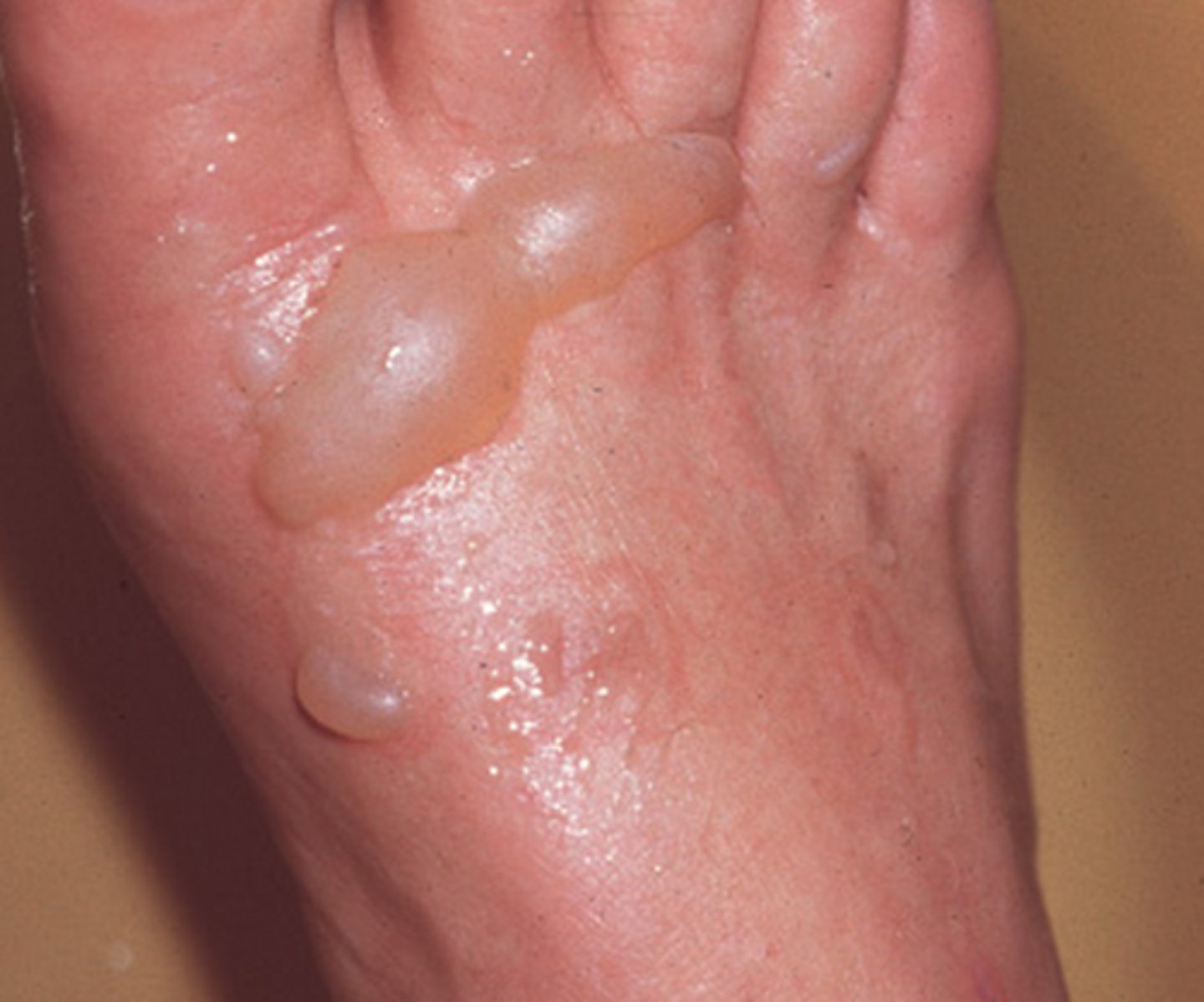
what type of burn?
- epidermis and superficial dermis
- blisters, moist, red, weeping
- painful to temp, air touch
superficial partial thickness (second degree superficial)
what type of burn?
- epidermis, deep dermis, sweat glands, hair follicles
- blisters, red to cheesy white, wet or waxy dry
- painful to pressure only
- usually requires surgery
deep partial thickness (second degree deep)
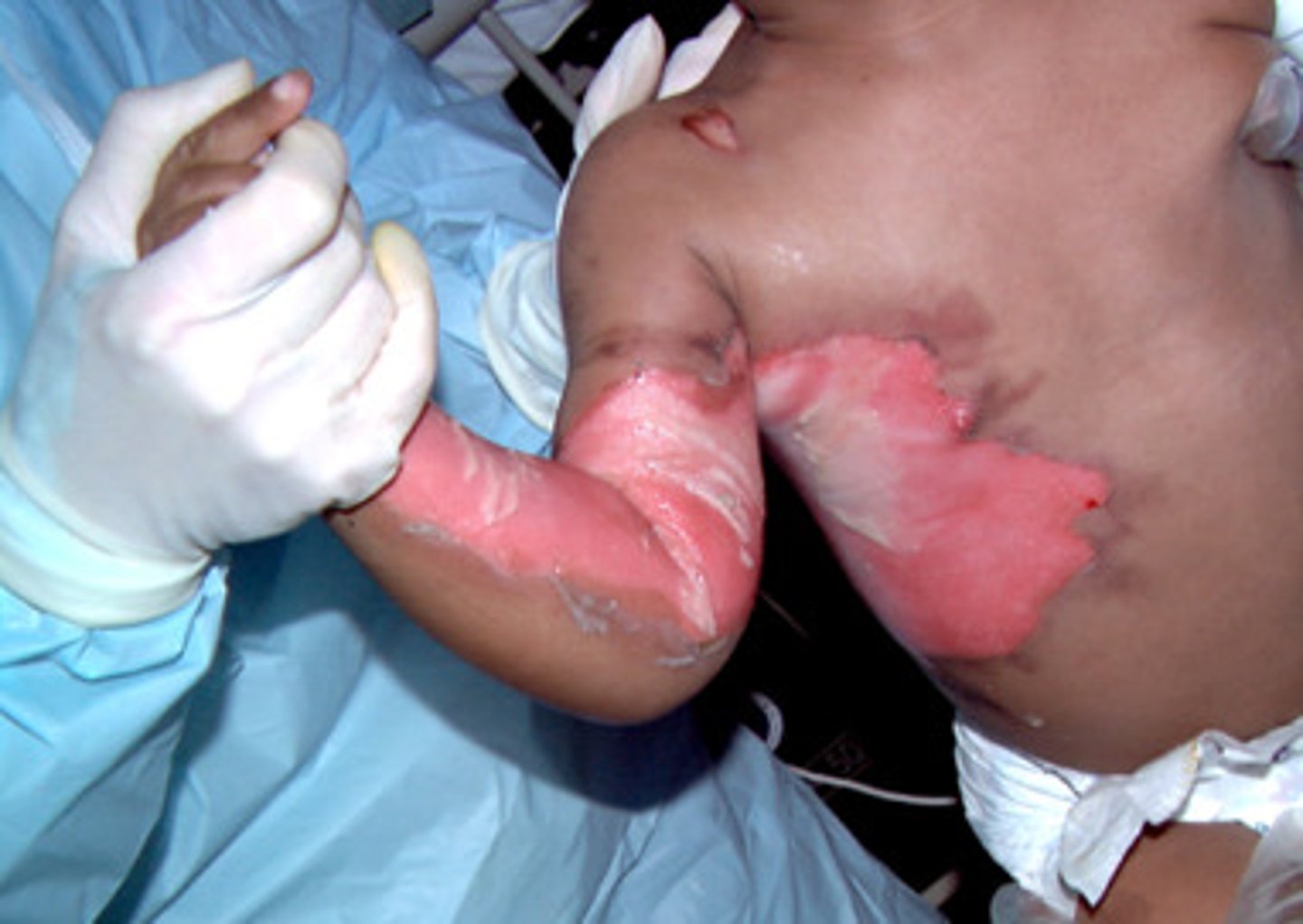
what type of burn?
- entire epidermis and dermis
- charred, waxy white, leathery
- no pain
- requires surgery
full thickness (third degree)
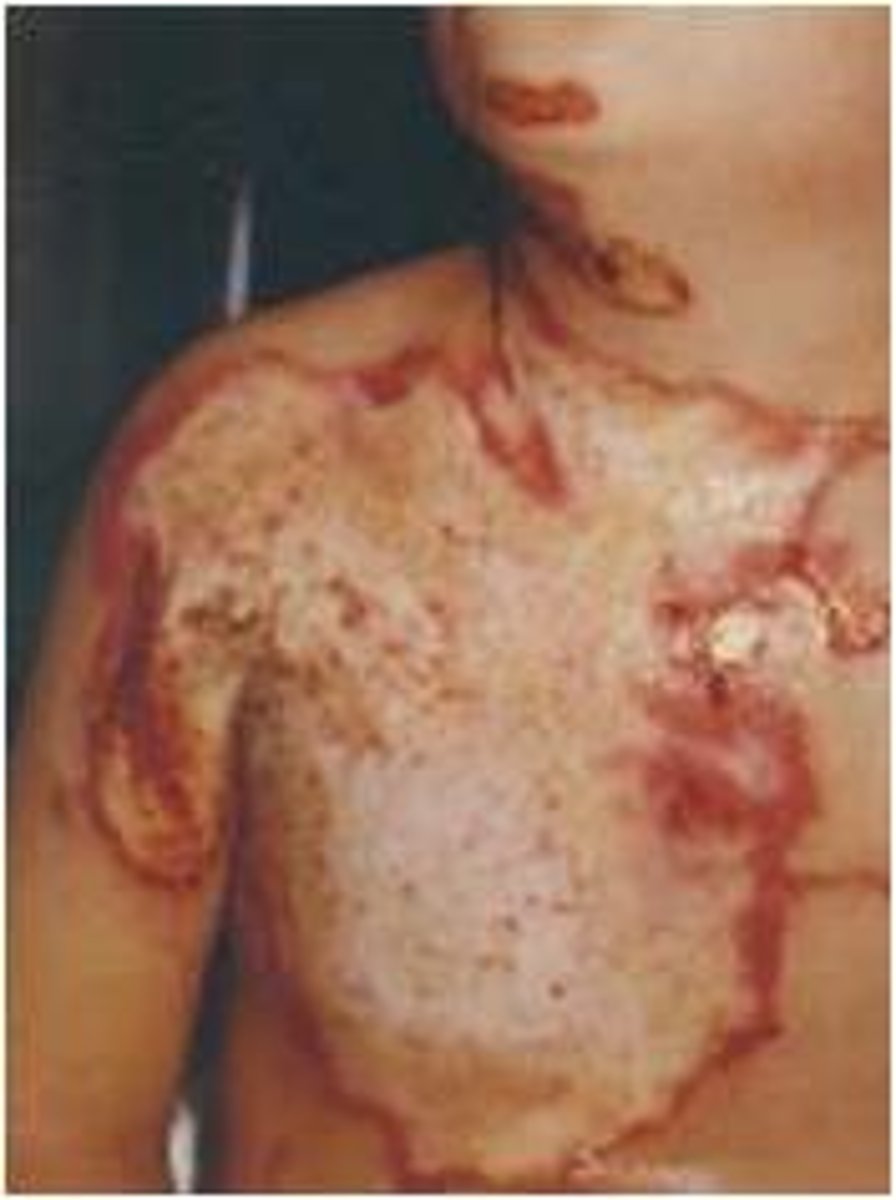
what type of burn?
- entire epidermis and dermis
- extends into fascia and/or muscle
- requires surgery
deeper injury (fourth degree)
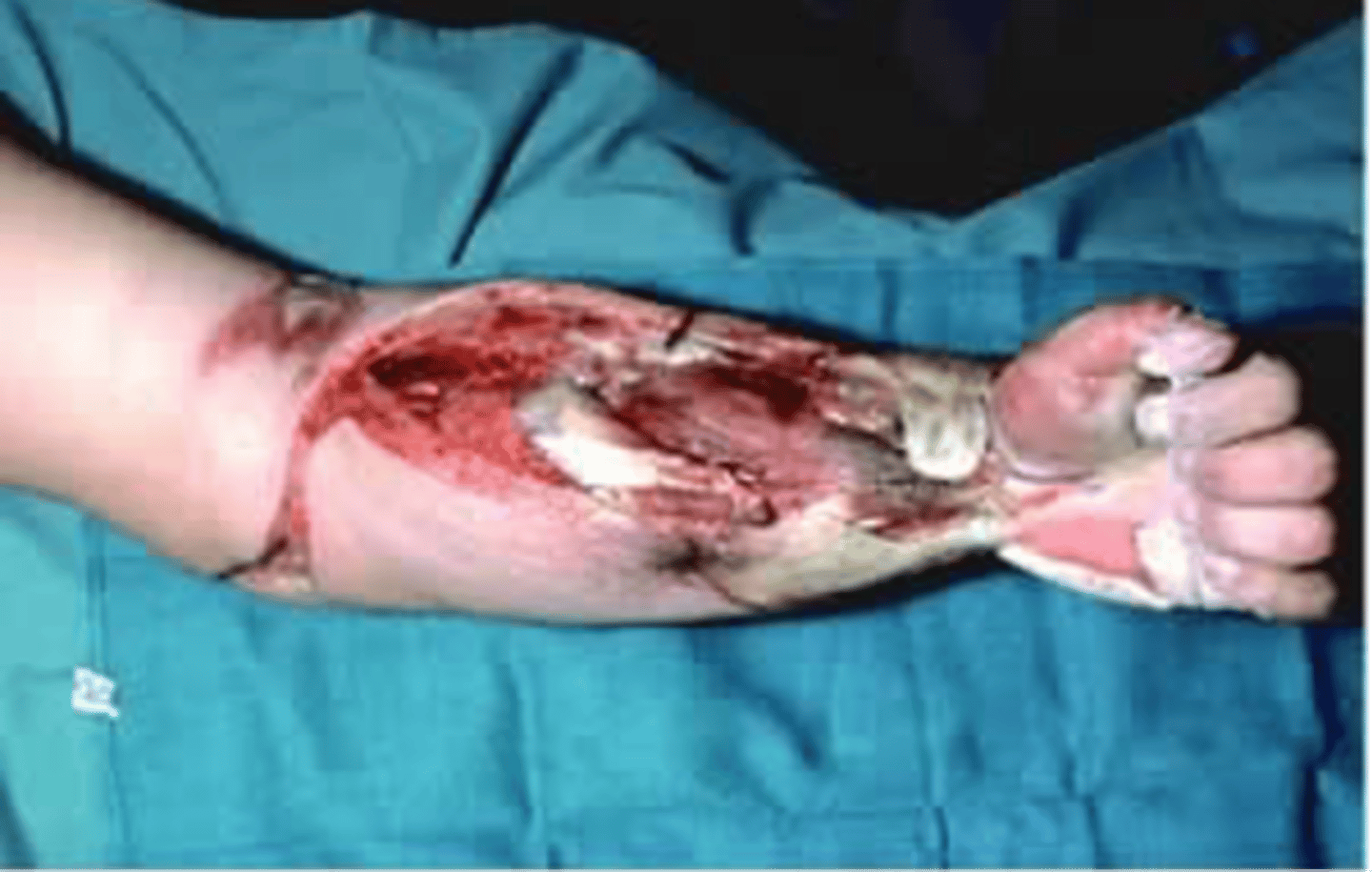
what is the most common method of categorizing adult thermal burns?
rule of nines
describe the rule of nines
head = 9%
each arm = 9%
torso front = 18%
torso back = 18%
each leg = 18%
for smaller burns, how can we calculate the percentage of BSA involved?
using patient's palm and fingers (1% BSA)
- palm alone = 0.5% BSA
- number of "hands" represents total BSA burned
what is the treatment protocol for minor burns?
- run cool water over burn until skin temp normalizes
- pain control w/ NSAIDs or opioids
- cleanse area w/ soap and water
- apply topical ointment and sterile dressing
- update tetanus if needed
what is the treatment protocol for mod/major burns?
- eval airway and monitor vitals
- labs = ABG, carboxyhemoglobin level, CXR
- est 2 large bore IV lines for fluid resuscitation
- eval and tx traumatic injuries
- address burn wound care
- IV opioid analgesia early, titrate to pain
- update tetanus PRN
- admit to hosp or burn center
in patients with major burns, what is the preferred fluid for fluid resuscitation?
what formula is used to determine the amount of fluids given over the first 24 hrs?
lactated ringers
Parkland formula (adults)
- 4mL x weight (kg) x %BSA burned over initial 24 hrs
- half over first 8 hrs from time of burn
- half in the subsequent 16 hours
for patients with mod/major burns, what is applied to the small burn areas?
what is applied to larger burns?
cool compresses
covered with sterile dry sheets
which burns are treated in the ED?
superficial or localized burns
which burns are transferred to a regional burn center?
- full thickness/third degree burns in any age group
- inhalation injury
- preexisting med disorders that may complicate management
- associated major trauma
- pts who will require special social, emotional, or long-term rehab intervention
most fire-related deaths are from what?
smoke inhalation
what are the physical signs of an inhalation injury?
- facial burns
- singed nasal hairs
- soot in upper airways
- hoarseness, stridor, resp distress
what should be suspected in all pts with smoke inhalation?
how can this be definitively diagnosed?
carbon monoxide exposure
ABG
which subgroup of hymenoptera stings only when provoked but host a subspecies that is more aggressive and will attack in swarms
honeybees and bumblebees