Lactation, Bonding, and Attachment
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
immunity, diarrhea, low, bonding, uterine, loss, cancer
Benefits of Breastfeeding
-Infant __________
Transfer of immunoglobulins, macrophages, and leukocytes
Prevention of illnesses including gastroenteritis, _______, respiratory disease, COVID-19, otitis media, and SIDS
Most impactful in ___ to middle resource countries
-Improves infant GI function
-Mother-infant _________ → skin-to-skin contact and early breastfeeding recommended
-Economic savings
-May decrease risk of type 1 diabetes, IBD, and wheezing
-Maternal benefits → accelerated ______ recovery and reduced risk of postpartum blood ____. Reduced risk of breast ________, ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes
extra, calories, prenatal, alcohol, engorged, two, caffeine, mercury
Maternal Nutrition During Lactation
-Nursing mothers should have a fluid intake of > 3 L/day
-25 grams of ______ protein
-330 extra _______/day in the first 6 months of nursing
-Continuation of a _________ vitamin and mineral supplement
-Alcohol and caffeine → a small percentage of ________ is transferred into breastmilk
“Pump and dump” not necessary unless the breasts become uncomfortable ___________
Wait at least ___ hours per serving of alcohol before breastfeeding
Most breastfeeding women can drink a moderate amount of _______ without significant effects on their infants
-Breastfeeding women should avoid fish with high concentrations of ________
growth, secretory, ducts, development
Breasts During Pregnancy and Lactation
-The mammary glands undergo _______ during pregnancy
Cell proliferation in __________ alveoli at the ends of intralobular ______
-Degree of glandular _____________ varies among lobules, even within a single lobule
estrogen, alveoli, inhibits, production, contracts, growth
Hormones Involved in Lactation
-_________ → milk duct growth
-Progesterone → _______ and lobe growth. _______ milk production during pregnancy. Drops at birth, starts milk production.
-Prolactin → alveoli growth. Maintains milk ___________ after pregnancy by continued stimulation of alveoli. Induces a-lactalbumin that increases galactosyl transferase affinity for glucose. Negative feedback on GnRH suppresses FSH and LH secretion and, thereby, menstruation and ovulation
-Oxytocin → _______ smooth muscle around milk duct alveoli to squeeze milk into ducts and out of areolae. Maintains milk production after pregnancy
-Human placental lactogen → augments ______ of breasts, nipples, and areolae
dilated, colostrum, proteins, prolactin, IgA, passive
Colostrum
-Late in pregnancy, the glandular alveoli and ducts are _______ by an accumulation of _________
Fluid rich in ________ and containing leukocytes
Produced under the influence of __________
-___ antibodies pass into colostrum
________ acquired immunity is conferred on the breastfed newborn
alveoli, prolactin, enlarge, bilaterally, milk
Lactation
-After childbirth…
_______ of mammary glands start active milk production
Stimulated primarily by ________ from the anterior pituitary
Epithelial cells of the alveoli _______
May take 2-3 days for the milk to “come in”
Breasts enlarge ___________
In non-breastfeeding women, _____ will accumulate in the glands until the body stops making it
suckling, oxytocin, production, contraction, ejection
Milk Ejection
-_________ stimulates the release of prolactin and _________
-Prolactin stimulates milk ___________ in readiness for the next feed
-Oxytocin causes ____________ of the myoepithelial cells lining the duct walls, causing _________ of the milk
first, hunger, weighed, caloric, lose
Normal Milk Intake
-During the _____ week of life, mothers with term infants should nurse when the infant exhibits ________ cues
Usually 8-12 times in 24 hours
By the 5th day of life, infants with adequate intake urinate at least 6-8 times daily and have 3 or more pale yellow and seedy stools daily
-Infants must be _________ naked at each office visit and at any time a parent is concerned about having enough milk
To determine if _______ intake is adequate
Term infants generally _____ weight in the first 3-5 days of life. Typically regain their birth weight b 1-2 weeks
removal, volume, demand, decrease, emptying, stress, illness, smoking
Milk Removal
-Milk _______ by the infant and/or the timing and frequency of milk expression si the major factor in determining milk ________
-More _______→ more volume
-Factors that may _________ milk production
Incomplete breast ___________
Infrequent milk expression
Maternal ______ and anxiety
Maternal fatigue
Maternal __________
Maternal insulin resistance
Use of combined hormonal oral contraceptives
Maternal __________
Separation from the infant
production, pain, bloody, jaundice, medications
Common Breastfeeding Problems
-Inadequate milk ____________
-Inadequate milk intake
-Nipple and breast ____
-Breast infections
-________ nipple discharge
-Milk oversupply
-Neonatal __________
-Maternal use of ______________
surgery, PCOS, swallowing, latch, technique, gain, stress
Inadequate Milk Intake: Potential Causes and Management
-Potential causes → breast ________, nipple conditions, medications, hormonal (____, hypertension, hypothyroidism), prematurity, ankyloglossia, sucking and __________ disorders, separation of mother and infant, and poor _____
-Management → optimize breastfeeding __________, monitor infant’s weight ____ closely and supplement if weight gain is inadequate, relaxation techniques for maternal ______, and frenulotomy if absolutely indicated
injury, latch, blocked, infections, positioning, moisture, mupirocin, compresses
Nipple and Breast Pain
-Potential Causes
Nipple _______ from breastfeeding or pumping, due to improper _____ or poorly fitted breast shield
Nipple vasoconstriction
Engorgement
Narrowed (_______) ducts
Nipple and breast __________
Excessive milk supply
Nipple dermatitis/psoriasis
-Management
Ensure proper __________ and latch of the infant
Avoid excess _________ on the nipples and irritating cleansers. The nipples should be allowed to air dry after breastfeeding.
Bacitracin or ________ ointment for cracked or abraded nipples
Cool or warm ____________
Acetaminophen or ibuprofen
lingual, pain
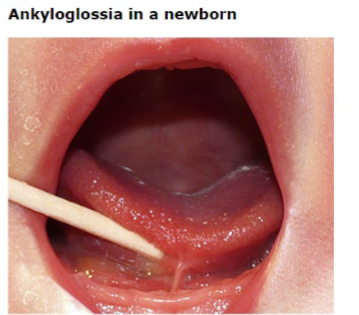
Ankyloglossia
-_______ frenulotomy has been shown to decrease nipple ____ and may facilitate breastfeeding
-Colloquially known as being tongue tied
itchy, burning, rash, psoriasis, steroids
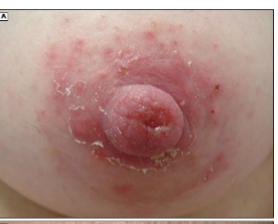
Areolar Dermatitis
-Typically presents as _____ and painful __________ of the areola and nipples with a red scaly ____
-More common in women with a history of eczema or __________
-Management → avoid potential irritants and allergens, medium potency topical ________ applied after feeding
vasospasm, vasoconstriction, Raynaud, pain, cold, trauma, warm, nicotine
Nipple Vasoconstriction
-Cutaneous __________ of the nipple due to arteriolar ______________
-Can occur in mothers who have ________, unusual cold sensitivity, or nipple trauma
-Presents with nipple _____, burning, and paresthesia with ____ exposure, nursing, or nipple _______
-Management → breastfeed in ____ conditions, heating source applied over the bra, avoid vasoconstricting substances such as ________ and caffeine, and nifedipine
edema, firmness, small, areola, warm, decrease, Ibuprofen, cabbage
Engorgement
-Interstitial ______ with accumulation of excess milk, presenting as breast fullness and ____________ accompanied by pain and tenderness
-Management
Manual expression of _____ amounts of milk before feeding to soften the _______ and facilitate latching
Warm compresses or a _____ showed to enhance let-down, which is the reflex where nerves in the breast send signals to release the milk in the ducts
Cold compresses between feedings to __________ swelling and discomfort
___________ or acetaminophen
Application of cool green _________ leaves
blocked, painful, white, feeding, massage, triamcinolone
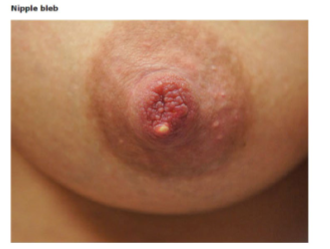
Ductal Narrowing
-Localized duct narrowing → commonly called __________ milk ducts
A tender and often __________ palpable lump due to obstruction of a mammary duct
Obstruction of the nipple pore ducts may also occur and present as a _____ bleb at the end of the nipple, “milk blister”
-Management → optimize ________ technique, cool compresses, manual _________, Ibuprofen and acetaminophen, and topical 0.1% ____________ cream for nipple blebs to reduce inflammation
cysts, inflammation, blocking, large, infected, thicker, ultrasound, aspiration
Galactocele
-Milk retention _______
-More common where there is a breast ___________ or edema, causing external pressure on milk ducts, thus __________ the ducts
-Sometimes very _____ masses
-Usually painless unless ___________
-Initially contain milky fluid but over time contents become _______, creamy, or oily
-Diagnosed on ___________
-Management → needle __________ or surgical excision only if the galactocele is bothersome to the mother. Breastfeeding can generally continue
inflammation, fever, pain, tender, dicloxacillin, bactrim, continue
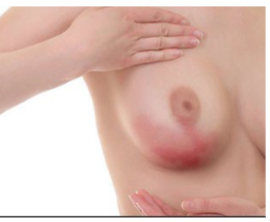
Lactational Mastitis
-Localized _____________ of the breast that is associated with _____, myalgia, breast ____, and redness
-Most common during the three months postpartum
-Presents as a firm, red, and ______ area of one breast and systemic illness including fever
-Treatment with ___________ or cephalexin
-If MRSA suspected, _________ or clindamycin
-Breastfeeding can _________ during infection, or may pump for comfort while supplementing if too painful
pus, mastitis, fluctuant, mass, aspiration, drainage
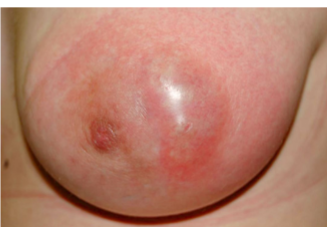
Breast Abscess
-Localized collection of ___ within the breast tissue that is often preceded by _______
-________, tender, and palpable ____
-Treat with needle _________ and surgical ________
-May continue breastfeeding
pain, infant, flaky, scraping, fluconazole, nystatin
Candida
-Diagnosis
Breast ____ out of proportion to physical findings
History of _____ oral candidiasis, diaper candida infection, or maternal candida vulvovaginitis
Physical finding of shiny or _____ skin of the affected nipple
If available, a positive skin __________ of nipple or areolar region demonstrating candida or positive breastmilk culture for Candida
-Management
Topical miconazole or clotrimazole
Oral ___________
Treat the infant for oral candidiasis, typically with _______
bloody, increased, alveoli, cracked, culture, stool, Apt
Bloody Nipple Discharge
-_______ nipple discharge during the first days of lactation → “rusty pipe syndrome”
-Thought to be due to _________ vascularization of the ________ and ducts with the onset of milk production
-Generally resolves within a few days
-Other causes include ________ nipples or subacute mastitis, should be evaluated with a thorough breast exam and breastmilk _______
-If the infant is spitting up blood-tinged milk or has blood in the _____, an ___ test is used to confirm whether the source of bleeding is from the mother or the infant
hyperlactation, supply, forceful, choke, drugs, dopamine, position, compresses
Milk Oversupply
-Also known as hypergalactia or ___________, which is when the ______ exceeds the demand
-In some cases, the rush of milk with the mother’s ejection reflex may be too ________ and the infant may have trouble feeding
Infants may _____, cough, become irritable with feeding, and may bite to clamp the nipple
-Evaluate for _____ that increase milk production
Psychiatric meds that may be ________ antagonists
Herbs like fenugreek
-Also evaluate the mother for hypo or hyperthyroidism
-Management → change nursing _______, manual reduction of flow, interrupt feeding as needed, pumping, cold ____________ for discomfort, low-dose oral contraceptives may be helpful, and milk collection shells to fit inside the bra to collect any leaked milk
persistence, weeks, declines, mild, calories, loss, breastfeeding
Neonatal Jaundice
-Breast milk jaundice → the __________ of benign neonatal hyperbilirubinemia beyond the first 2-3 ______ of age
Typically presents after the first 3-5 days of like, peaks within 2 weeks after birth, and progressively ________ to normal levels over 3-12 weeks
Generally ____ and does not require intervention, but it should be monitored to ensure that it remains in the unconjugated form and does not increase
-Inadequate milk intake
Breastfeeding difficulties → inadequate intake of fluids and _________ → hypovolemia and significant weight ____ → hyperbilirubinemia and, in some cases, hypernatremia
Establishment of successful __________ is challenging due to shortened postpartum length of stay for newborn infants and their mothers
compatible, safe, dopamine, statins, chemotherapy, codeine, aspirin
Maternal Use of Medications
-Most, but not all, therapeutic drugs are _________ with breastfeeding
-If the medication could otherwise be prescribed to the infant for a medical condition, it is generally considered ____ for the mother to take while breastfeeding
-Doses of medications transferred via breastmilk are generally much lower
-Medications that can decrease breastmilk volume → ________ agonists, decongestants, estrogens
-Drugs that are not compatible with breastfeeding → ______, amphetamines, ergotamines, and _________ agents
-Most analgesics are safe, but ______ and tramadol should be avoided. Use oxycodone and _______ with caution
HIV, suppression, HTLV, ilicit, ebola, HSV, tuberculosis, varicella
Contraindications to Breastfeeding
-Do not breastfeed or feed expressed milk
If the infant has classic galactosemia
If the mother has ___ and is not on ART or is on ART but does not have sustained viral ____________ with confirmed undetectable viral load
If the mother has human T-lymphotropic virus (____)
If the mother uses _____ drugs
If the mother has suspected or confirmed _____ virus disease
-Temporarily do not breastfeed or feed expressed milk
If the mother has untreated brucellosis
If the mother is taking certain medications
If the mother has an active ___ infection with lesions present on the breast
If the mother has monkeypox
-Temporarily do not breastfeed but may feed expressed breastmilk
If the mother has active ______________ (TB)
If the mother has active _______ that developed between 5 days prior to delivery and 2 days following delivery
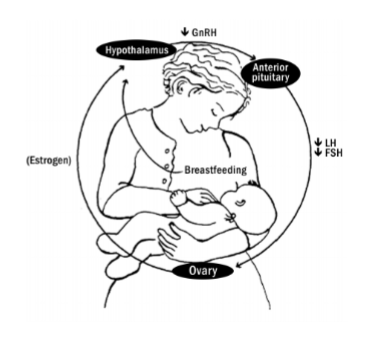
prolactin, GnRh, amenorrhea
Lactation Amenorrhea
-Regular suckling maintains ________ levels
-Prolactin inhibits ____ → thus no FSH/LH
-Results in anovulation and ____________
after, feelings, trust, gradually, mood, sleep
Bonding and Attachment
-Bonding occurs shortly _____ births and reflects the ________ of the parents toward the newborn
-Attachment involves reciprocal feelings between the parent and the infant
“Emotional exchange”
Infant cues the parent that she/he is unhappy and the parent responds, leading to _____ development
Develops _________ over the first year
Crucial for optimal development
-Bonding and attachment can be affected by postpartum mood disorders, maternal/paternal stress, and _____ deprivation