SUPERFICIAL HEAD & NECK
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
(Neuro)cranium
encloses brain
skull cap = calvaria
cranial base or floor = basicranium
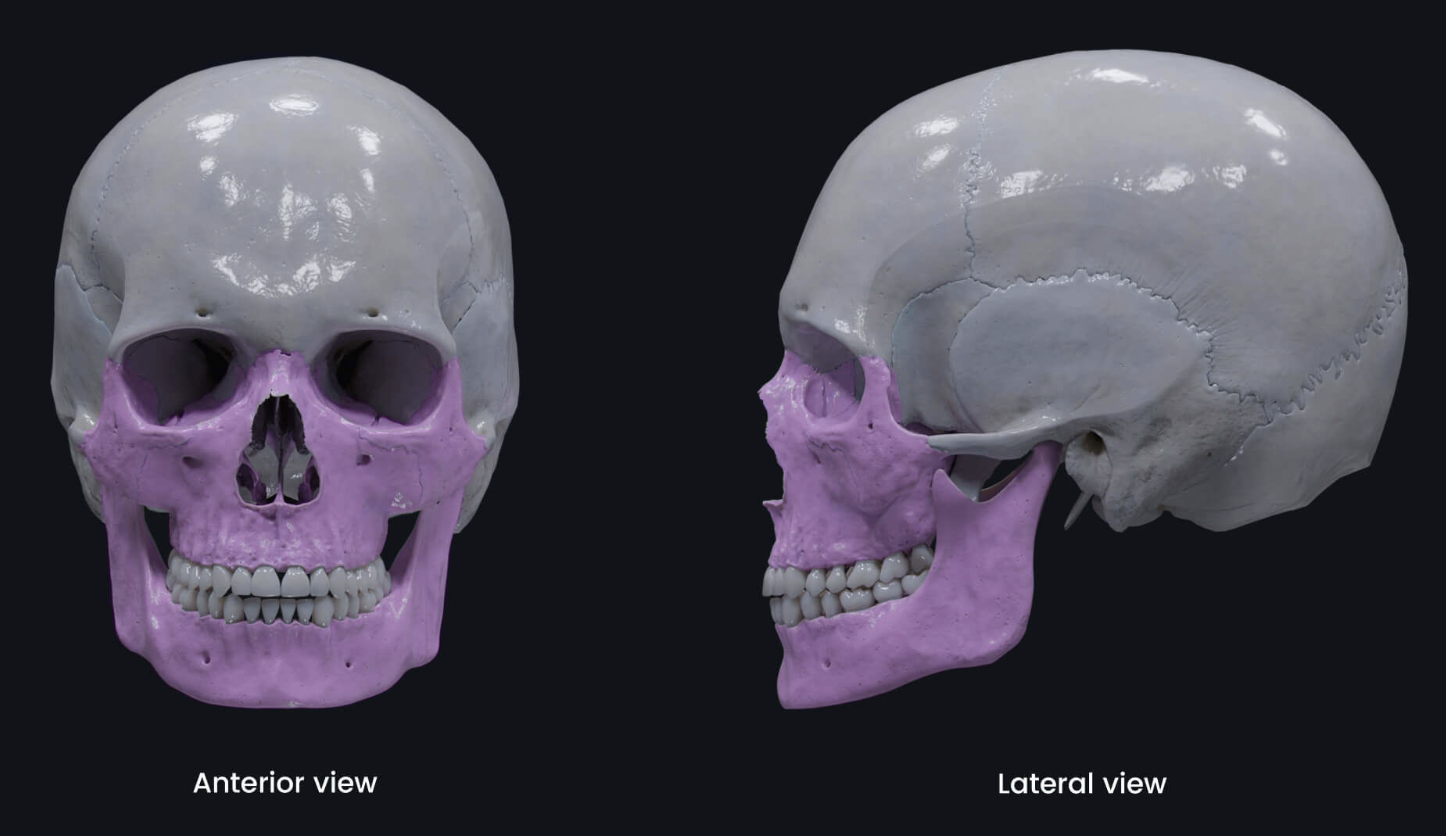
Viscerocranium
facial skeleton
lower part of orbit & down
Skull landmarks
glabella
nasion
superciliary arch
sutures
occiput
temporal fossa
pterion
temparomandibular joint (TMJ)
zygomatic arch
hard palate
Glabella
space between eyes
glabellar reflex
Nasion
suture between frontal & nasal bone
Superciliary arch
brow
more pronounced in males
Sutures
coronal
sagittal
lambdoid
squamous
Occiput
back of head
external occipital protuberance
Temporal fossa
includes temporalis M
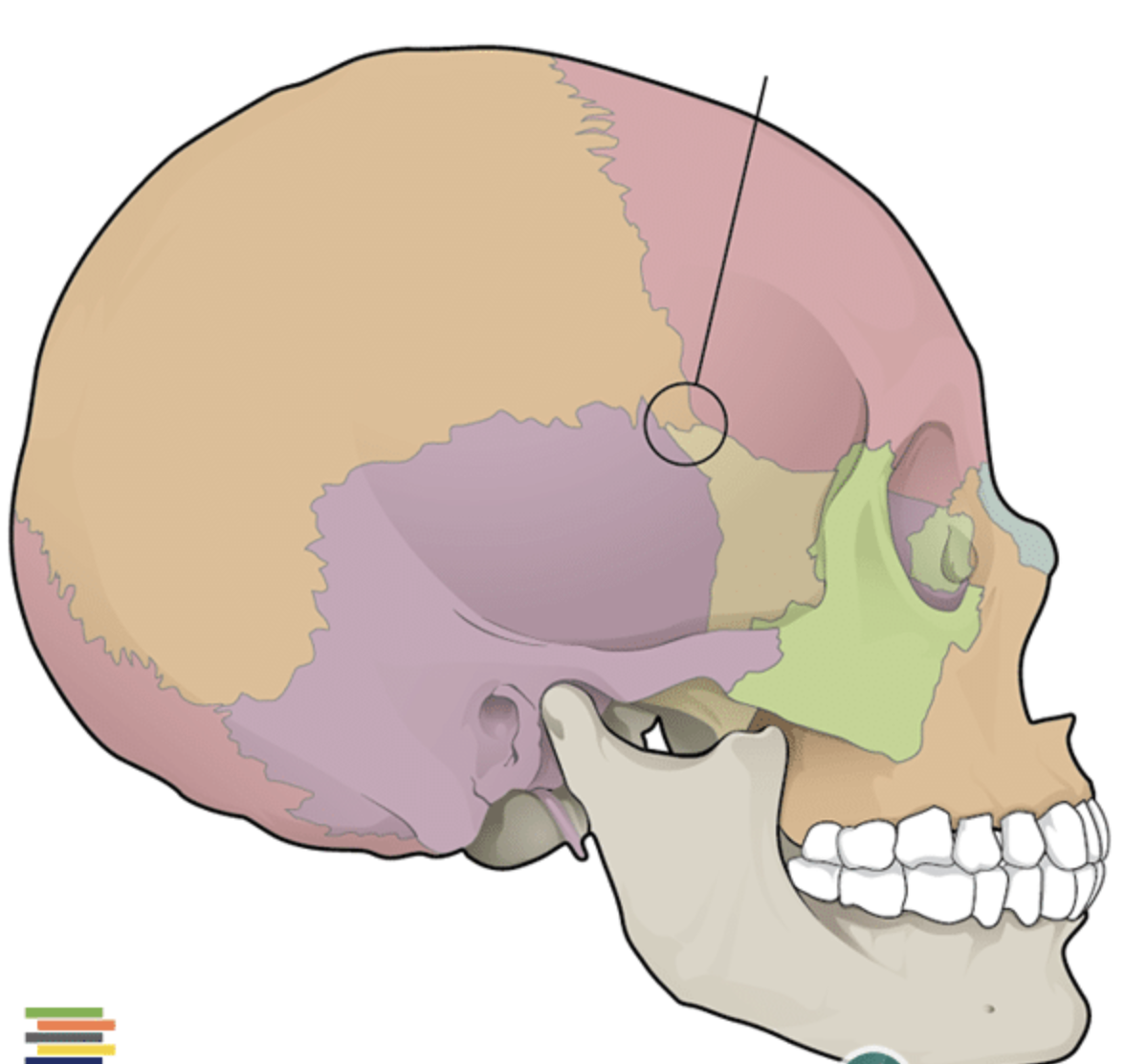
Pterion
clinically important part of jaw where 4 bones meet (parietal, sphenoid, temporal, frontal)
weak point of the skull
underneath is middle meningeal A
Temparomandibular joint (TMJ)
mandible (jaw) articulates with braincase
Hard palate
palatine process (of maxilla) + palatine
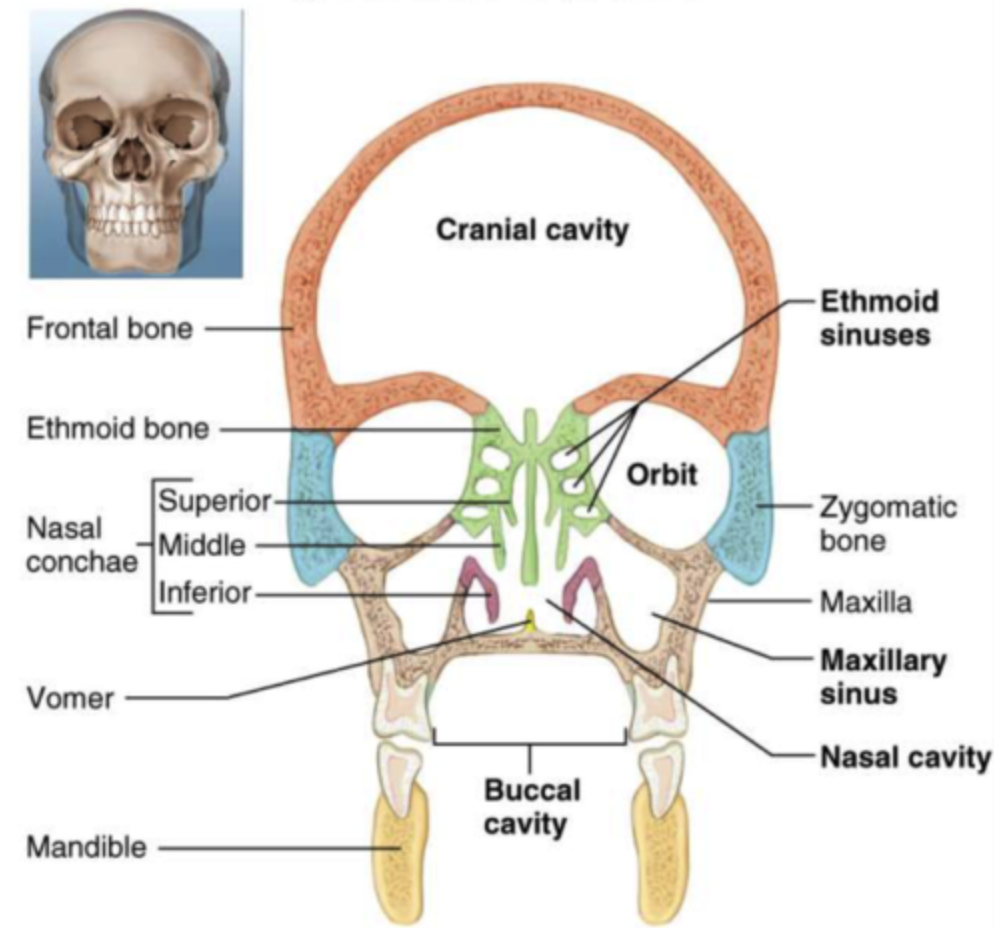
Skull cavities
cranial cavity
orbit
oral cavity
nasal cavity
paranasal sinuses: frontal, ethmoidal, maxillary, sphenoid
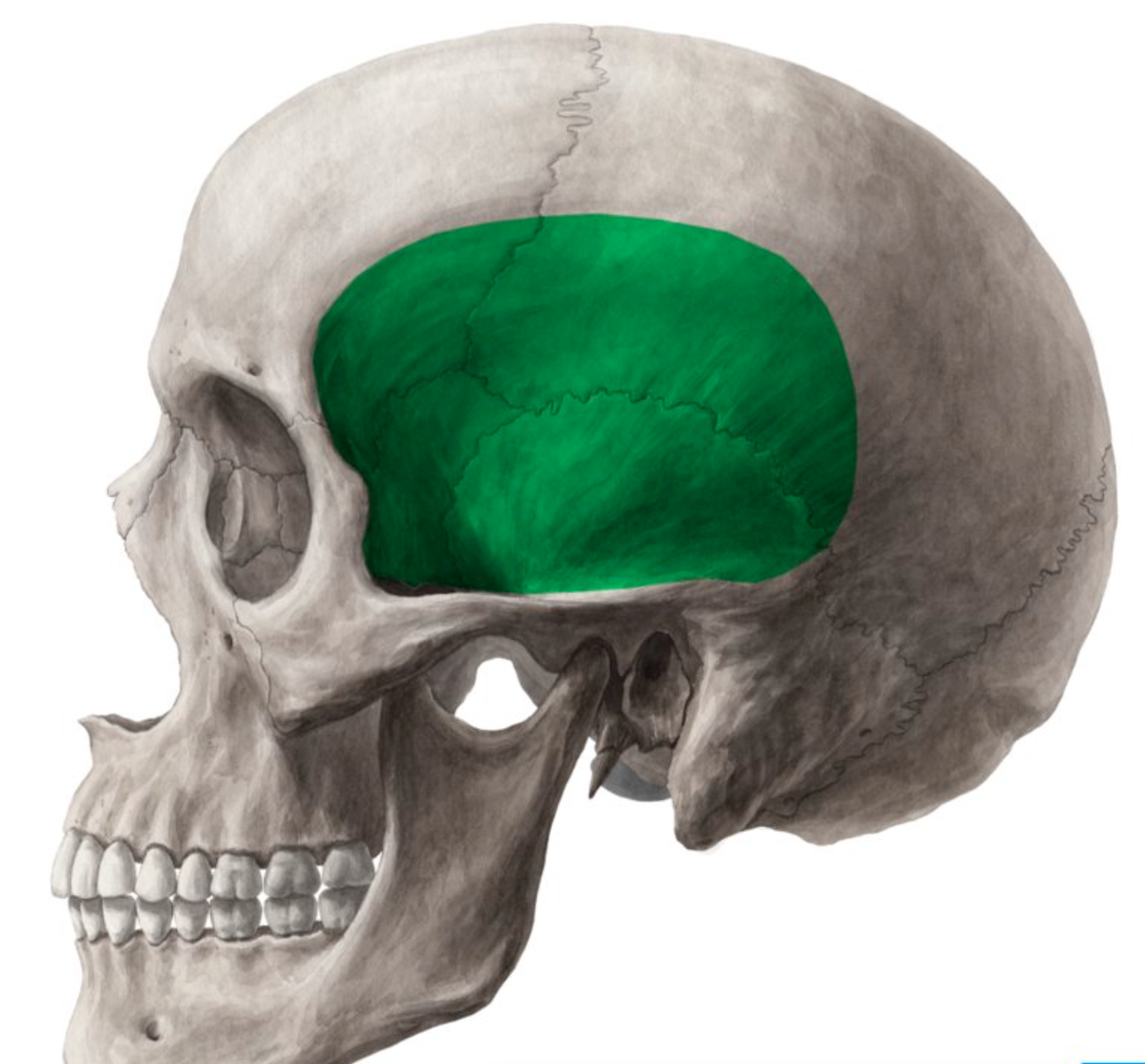
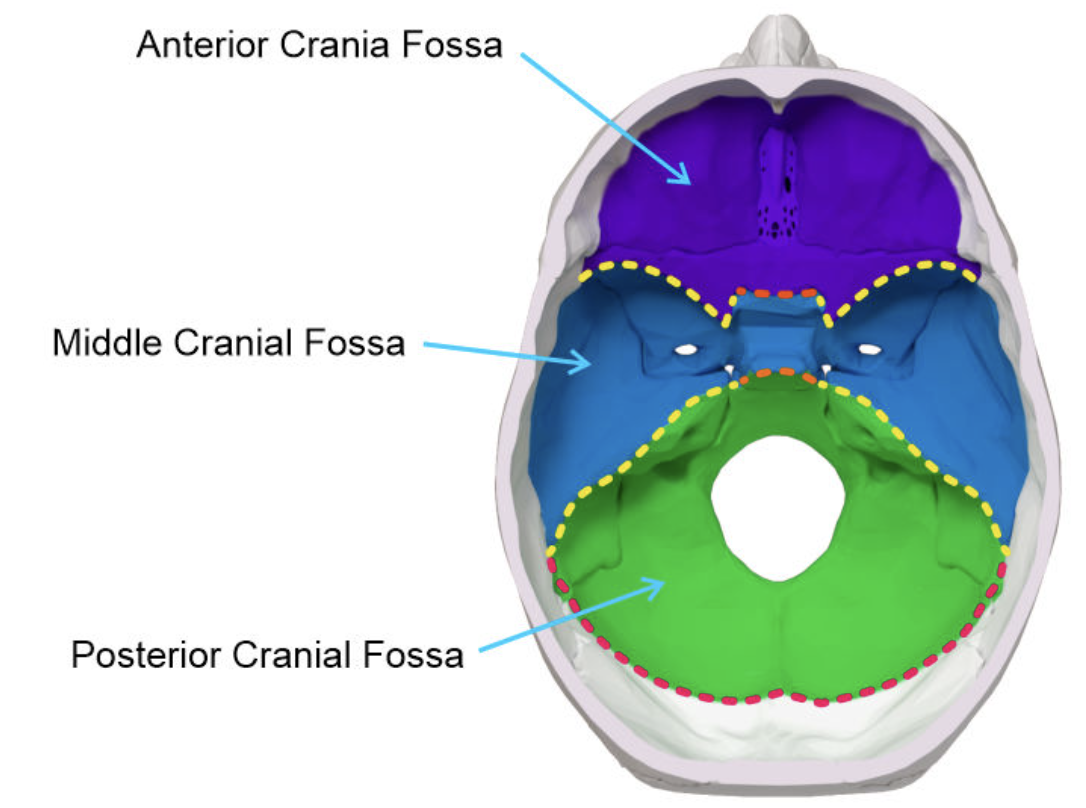
Cranial fossa
conform to the contours of the brain
anterior cranial fossa
middle cranial fossa
posterior cranial fossa
Scalp
five layers of tissues compose the scalp
Skin
CT - dense
Aponeurosis
Loose CT
Pericranium
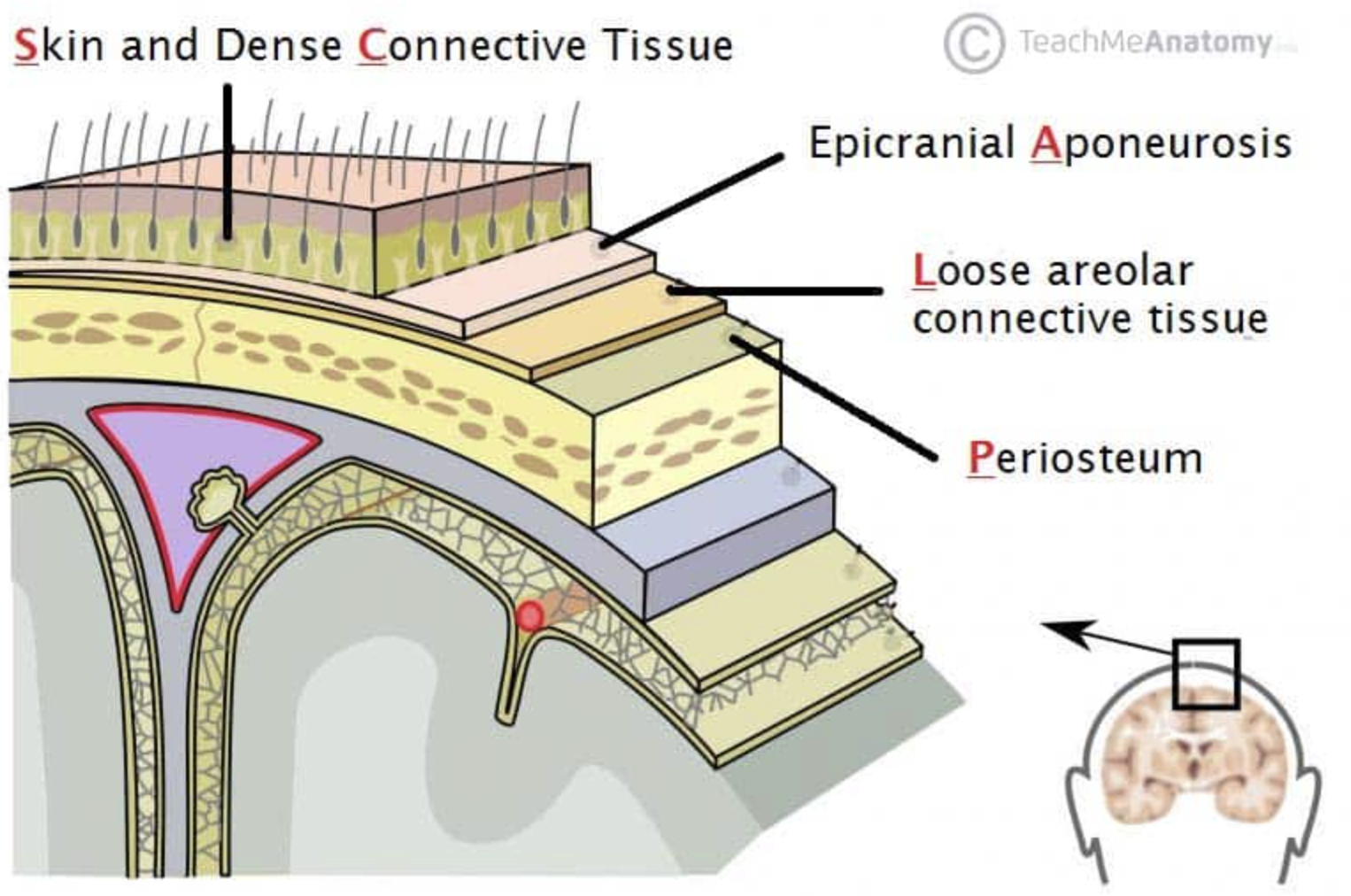
Scalp proper
scalp layers 1-3
Epicranial aponeurosis
= galea aponeurotica
tendinous sheet covering calvaria
Pericranium
dense CT
forms external periosteum of calvaria
Superficial face muscles
muscles of facial expression, sphincters/dilators of orifices
mainly attached to skin of face
supplied by facial N (CN VII)
temporalis, occipital, masseter = not MM of facial expression
Superficial muscles of lateral neck
platysma
sternocleidomastoid
trapezius
Platysma
tenses skin of neck
Sternocleidomastoid
divides neck into anterior & posterior triangles
bilateral fxn: flexes neck
unilateral fxn: lateral flexion, rotation of head to opposite side
Muscles of mastication
masseter
temporalis
lateral/medial pterygoid
innervation: mandibular N (trigeminal N)
Masseter
elevates/protracts mandible
Temporalis
elevates/retracts mandible
Lateral pterygoid
moves jaw side to side
Medial pterygoid
moves jaw side to side
protracts mandible
Superficial muscles of anterior neck
suprahyoid group
infrahyoid group
Suprahyoid M group
everything above hyoid group
elevates hyoid & larynx
geniohyoid (XII)
mylohoid (V)
stylohyoid (VII)
digastric anterior/posterior belly
cranial nerves V, VII, XII
Infrahyoid M group
everything below hyoid bone
depresses hyoid & larnyx
sternohyoid
sternothyroid
thyrohyoid (XII)
ansa cervicalis & cranial nerve XII
Salivary glands
parotid gland
sublingual gland
submandibular gland
Parotid gland
largest salivary gland
parotid duct
cranial N IX (glossopharyngeal N)
Parotid duct
pierces buccinator MM
empties into upper oral cavity
Sublingual gland
lies in floor of mouth between mandible & genioglossus M
sublingual ducts
cranial N VII (facial N)
Sublingual ducts
opens into floor of mouth
Submandibular gland
lies inferior to body of mandible
submandibular duct
cranial N VII (facial N)
Submandibular duct
empties near lingual frenulum
Teeth
32
tooth formula = (2,1,2,3/2,1,2,3 = incisor, canine, premolar, molar)
deciduous: (milk teeth) premolars, incisors, canines
permanents: molars
cusps: slicing, grabbing, chewing