Lecture 1: Pregnancy hormones and twins equine
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Why would a lower MHz might be preferred over a higher MHz?
Provides a deeper scan
What type of US prob is preferred for rectal pregnancy scans?
5.0 MHz
What does the secondary CLs provide during pregnancies?
Extra P4 boost
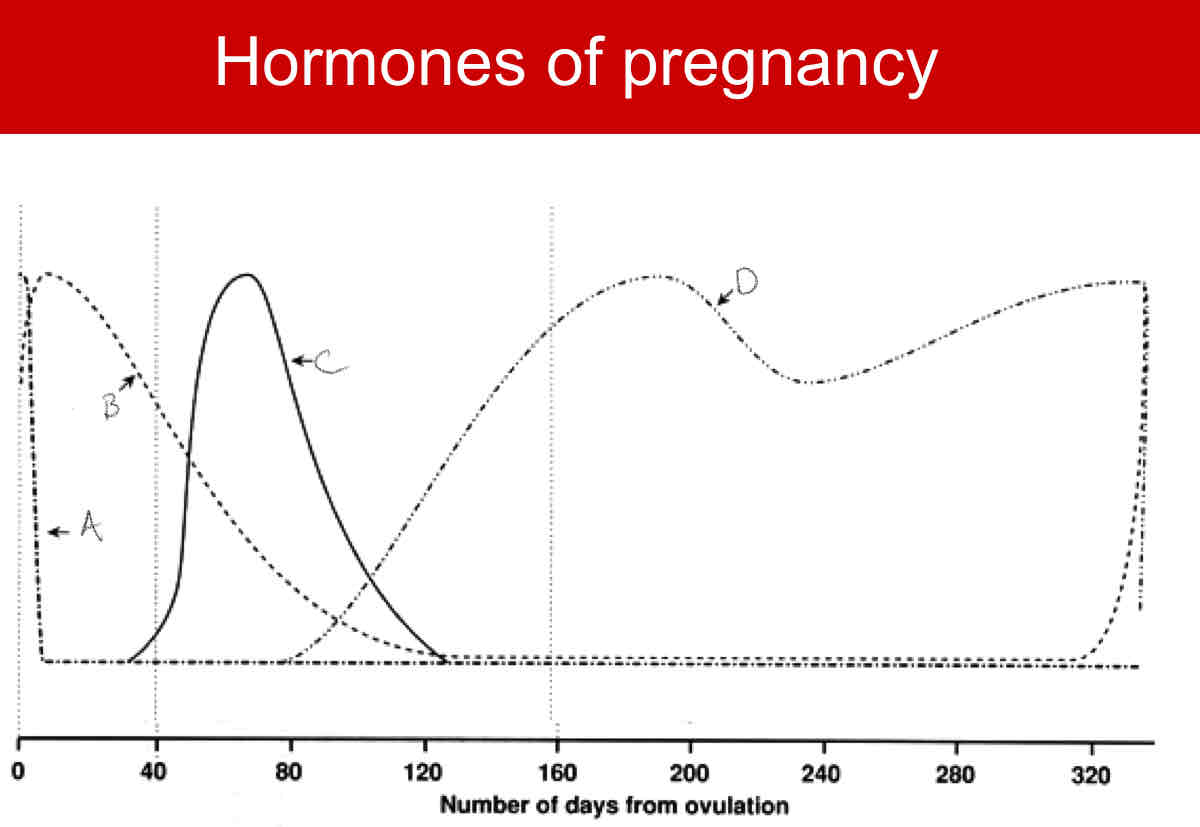
A?
LH
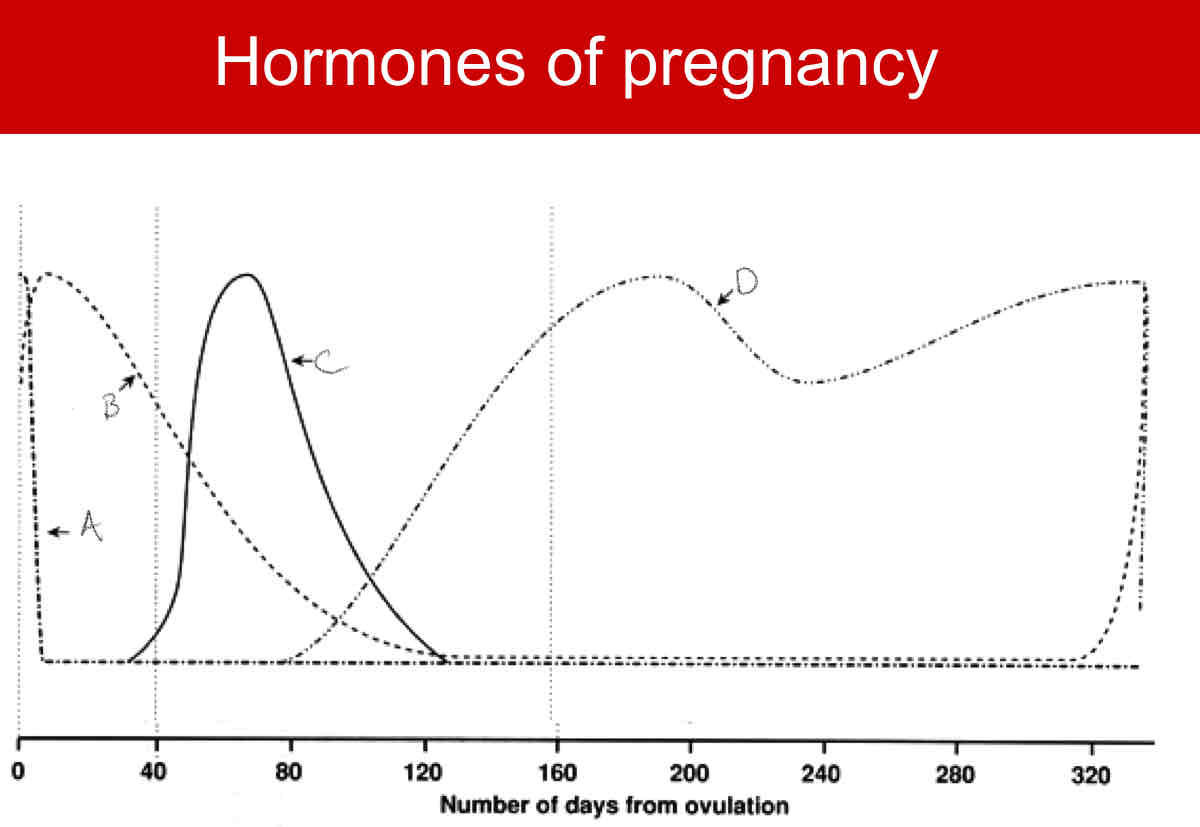
B?
FSH
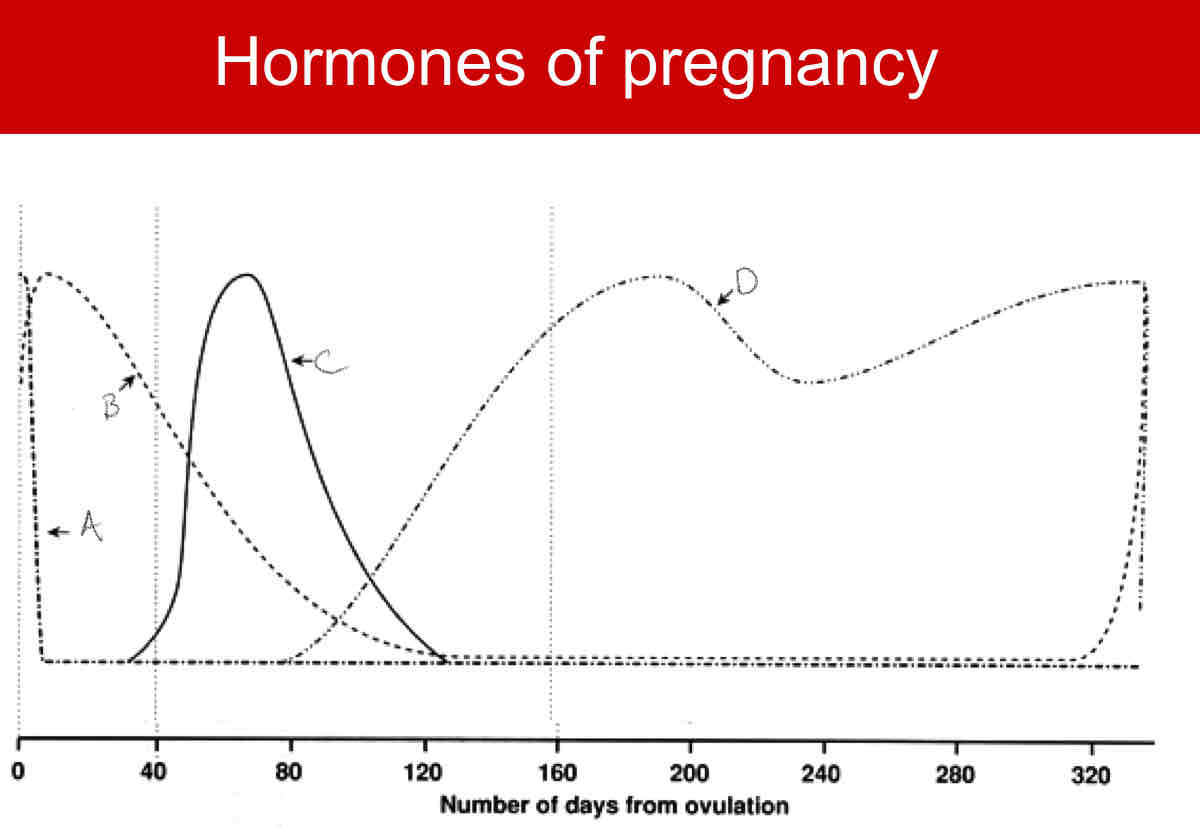
C?
CG
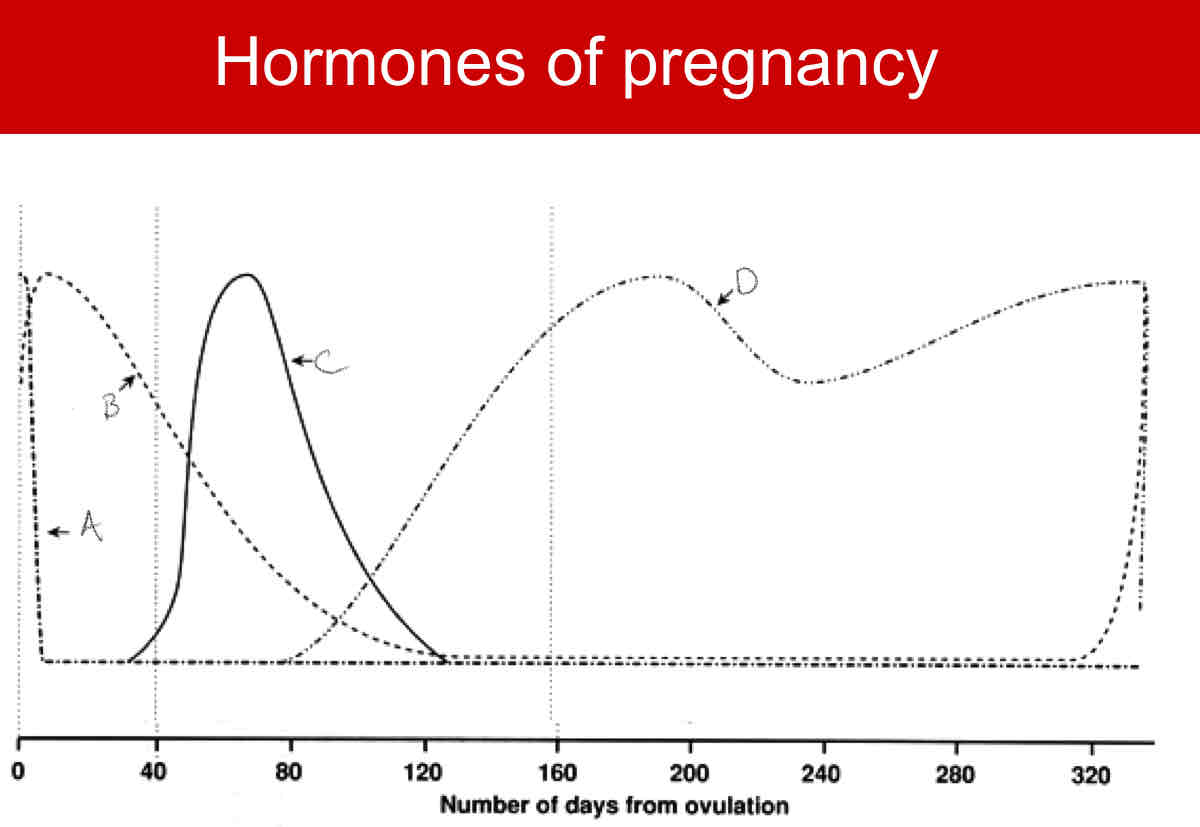
D?
Relaxin
Where is eCG or PMSG released from?
Endometrial cups
When does eCG or PMSG start to be produced?
~day 40-120
What is the function of eCG or PMSG?
acts like LH to help form secondary CLs
When are horses no longer CL dependent?
~day 100
When does estrone sulfates rise during pregnancy?
~day 80
P4 stays low from mid to late pregnancy, when does it rise again?
Before foaling
What is the size of the embryo at 25-30 days?
Golf ball, hen’s egg
How big is the embryo at 45-50 days?
Softball, grapefruit
How big is the embryo at 35-40 days?
Tennis or baseball
When preg checking what do you have to feel?
The ventral aspect of the uterine horn
How long is the fetus palpable for?
Up to day 150
When is the fetus over the pelvis and may be unreachable for rectal palpation?
5-7 months
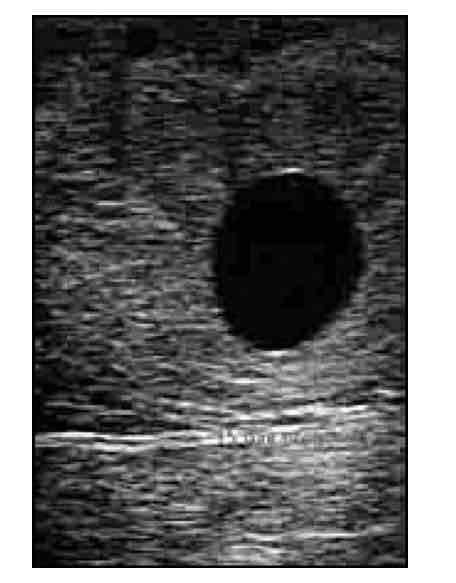
16 day US
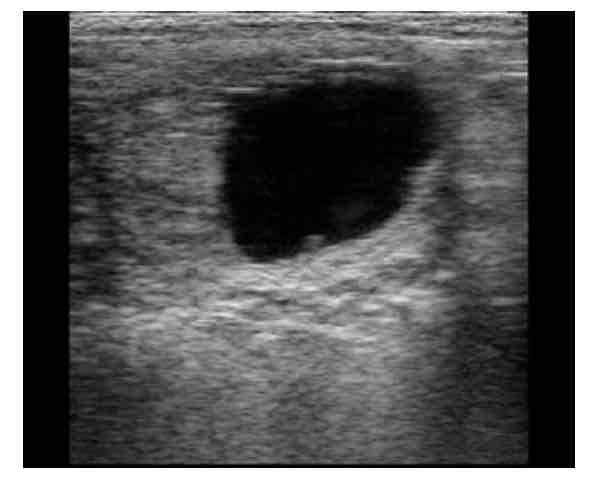
21 day embryo
What happens at day 5-6?
Embryo enters uterus
What happens at day 16?
Fixation or prostaglandin release
What happens about day 25?
Heartbeat detectable
What happens on day 35-40?
Implantation, endometrial cup formation and placental formation starts
What happens about days 90-100?
No longer CL dependent
What happens at day 100-120?
Endometrial cups regress
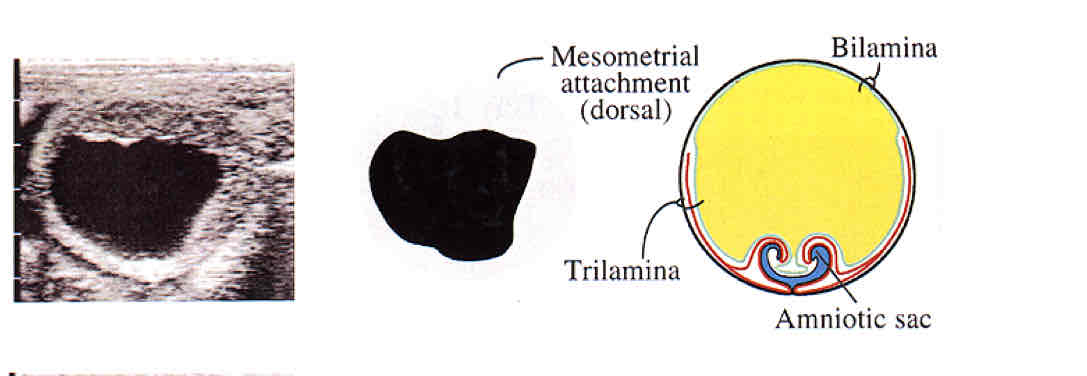
Day 18

Days 22

Day 24

Day 26
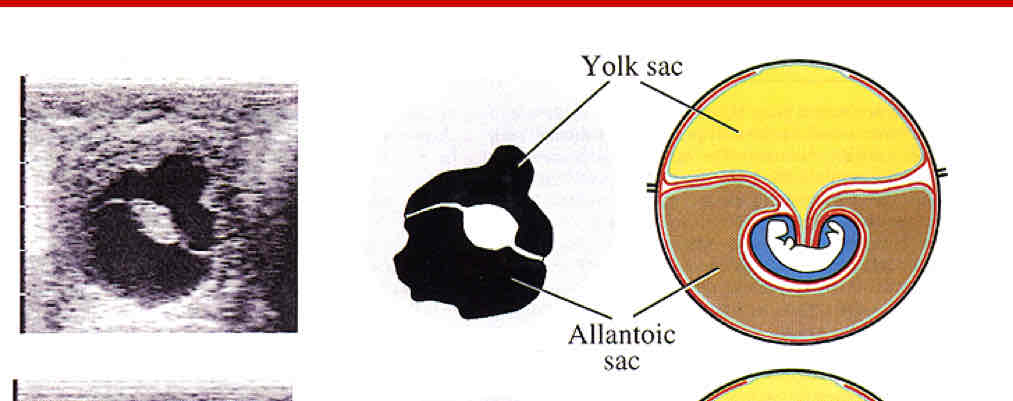
Day 29
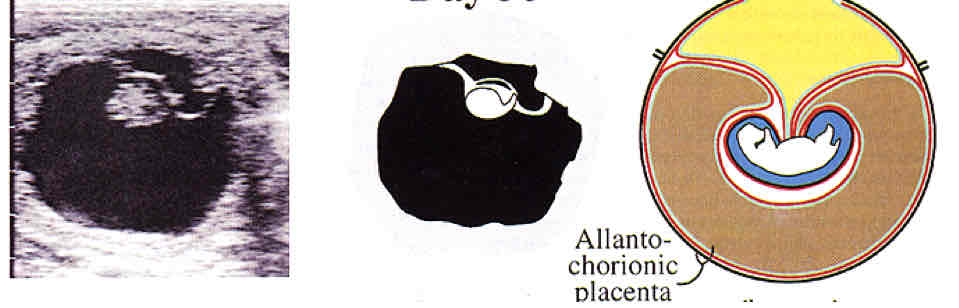
Day 36

Day 40

Day 45
What hormone test can you run on unhandled pregnancy horse?
Estrone sulfate (high=pregnant). More reliable than P4
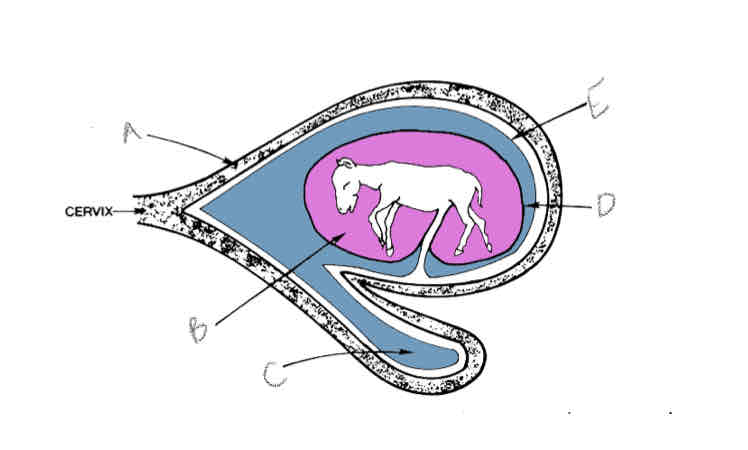
A?
Uterus
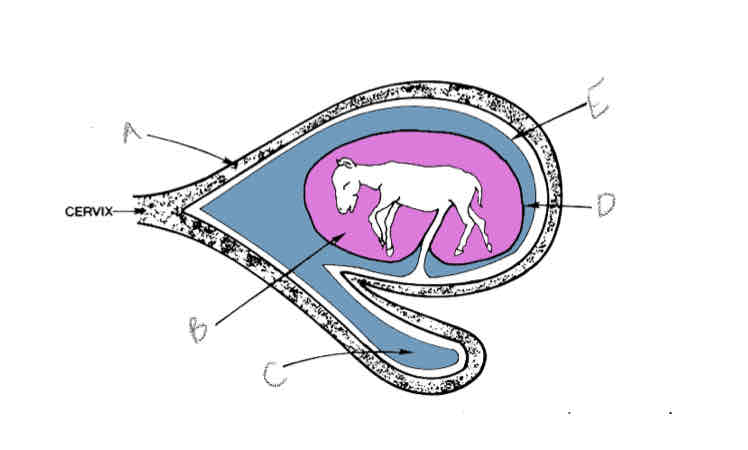
B?
Amniotic cavity
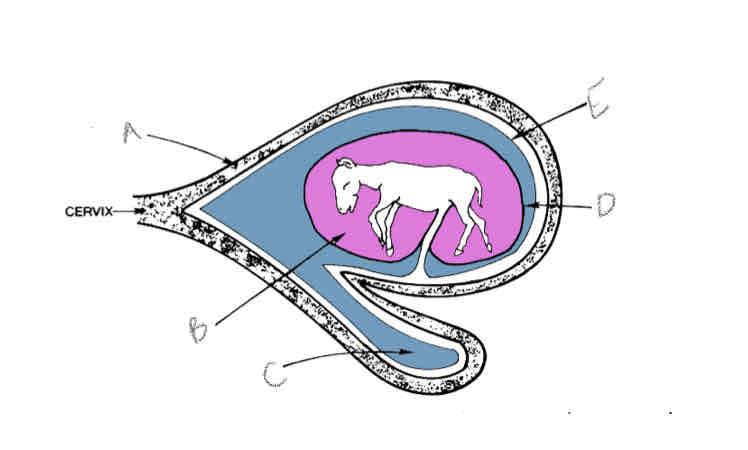
C?
Allantoic cavity
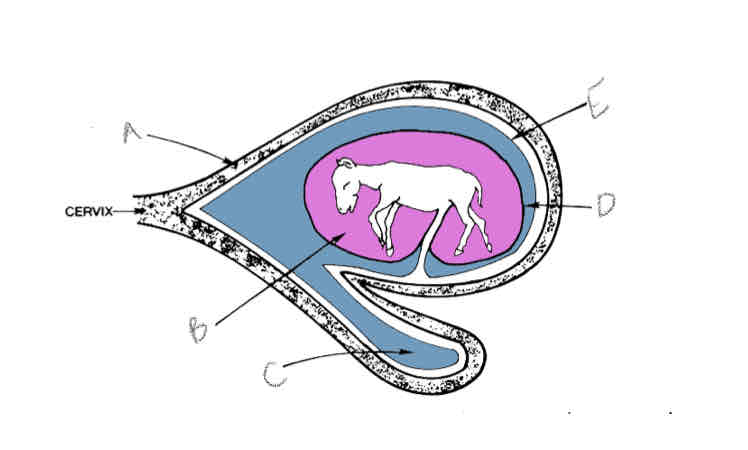
D?
Allantoamnion
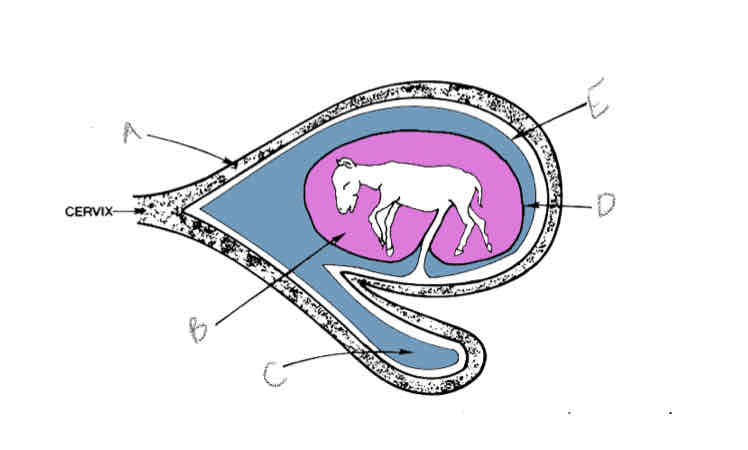
E?
Allantochorion
One egg, one ovulation twins. Identical genomes and result from splitting a fertilized ovum.
Monozygotic twins
Why are gestations longer if due in spring time?
She is most fertile in summer and there is a longer daylight length in summer
What causes the “pinching effect”?
During the hatching of the blastocyst the zona pellucida can cause splitting of egg
Two eggs, two ovulation twins
Dizygotic twins
Two eggs, one ovulation twins
Dizygotic twins, rare
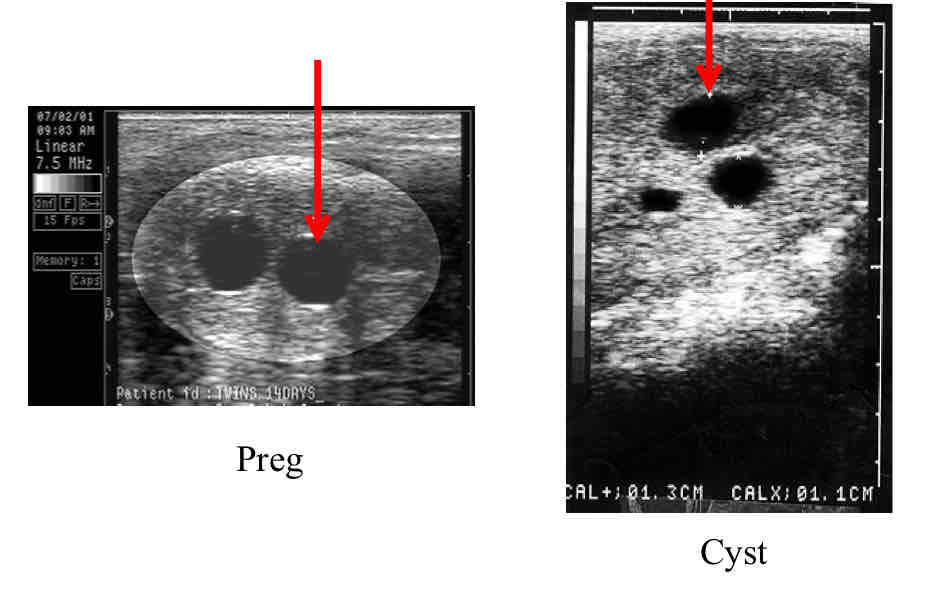
How can you tell the difference between a fetus and cyst?
Speculation reflection on embryo before day 20 of pregnancy.
What kind of twins are equine twins?
Dizygotic
Why are most equine twins dizygotic?
Results of asynchronous ovulations within 24 hours. The capsule of equine embryo is through to prevent pinching effect.
Why do ansynchrous ovulations occur more than 24 hours apart?
the hormonal signals that trigger ovulation can vary in timing, potentially due to fluctuations in follicle development, hormonal imbalances, or underlying medical conditions, causing one follicle to mature and release its egg significantly later than the other
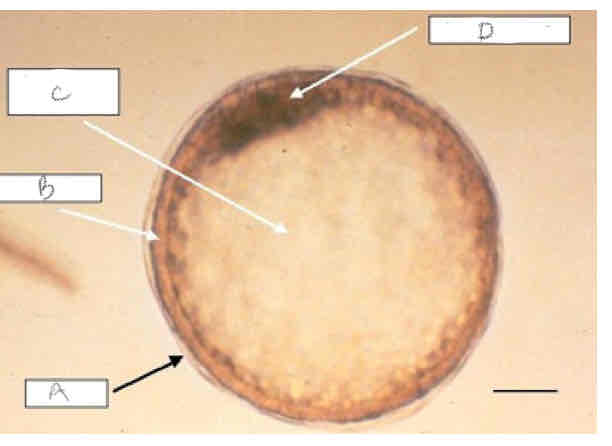
A?
Capsule
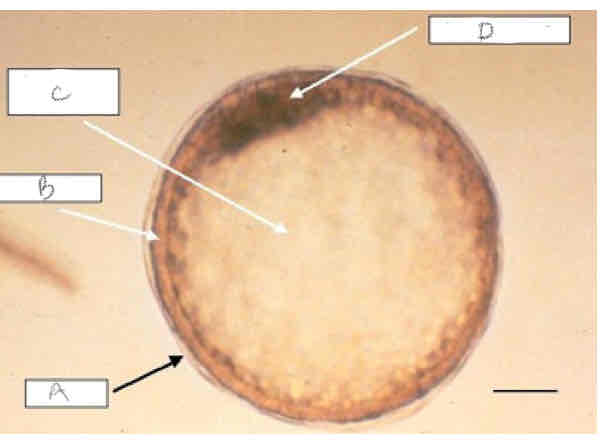
B?
Trophoblast?
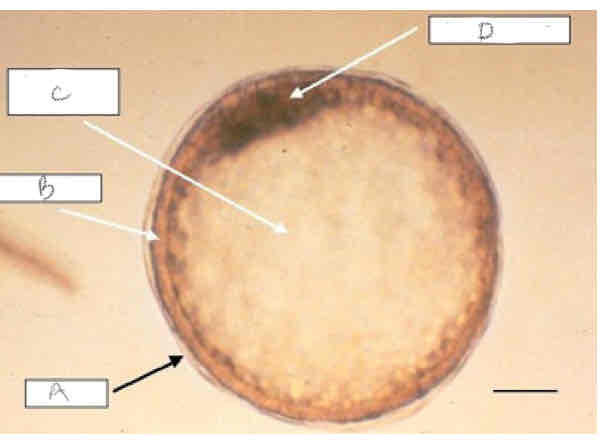
C?
Blastocoele
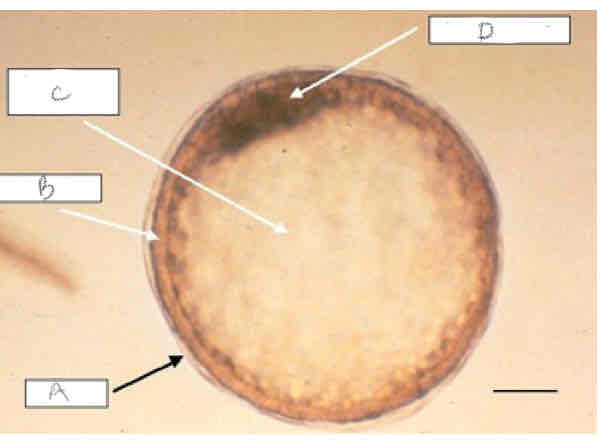
D?
Inner cell mass
When do twins have to be dealt with by?
In the first 40 days of pregnancy
What causes a higher incidence of twinning in the mare?
Ovulatory drugs
Mares who previously twinned
Thoroughbreds and draft mares
6-10 years of age
Bred within 80 days of foaling
When is the US view half allantoic sack and half yolk sac?
Day 30
What are the possible outcomes of twins?
Single foal birth (60%)
Loss of both pregnancies (31%)
Carry both to term (9%)
How often are both twins born alive?
1.26% of the time
Why are win pregnancies undesirable?
Placental insufficiency
Rare that both fetuses survive
Mares may require more assistance
Surviving foals are weaker
Higher incidence of retained placenta
What are you checking for day 14-16?
Bilateral or unilateral attachement
Why is it harder to freeze horse eggs?
Capsule makes it difficult for freezing all the way through egg
When can transabdominal ultrasound be performed?
After day 80
How effective are natural reduction mechanisms post-fixation?
Less efficient when ovulations are asynchronous
Coincident with cessation of embryonic mobility
Related to orientation of twin vesicles writhing uterine lumen
Associated with nutrient deprivation of one twin
Less efficient when twins are bilateral
Why do unilateral fixations have 85% natural reduction?
Early development of non-functional membrane of membrane contact
Reduced nutrient exchange from endometrium
Why do you have to wait till 14-16 days to check for twins?
Because the second embryo may be too small to see before day 14.
Why does bilateral fixation often have lower natural reduction?
Late development of non-functional membrane
Both embryos grow
Eventual weakening of one or both due to compromised contact
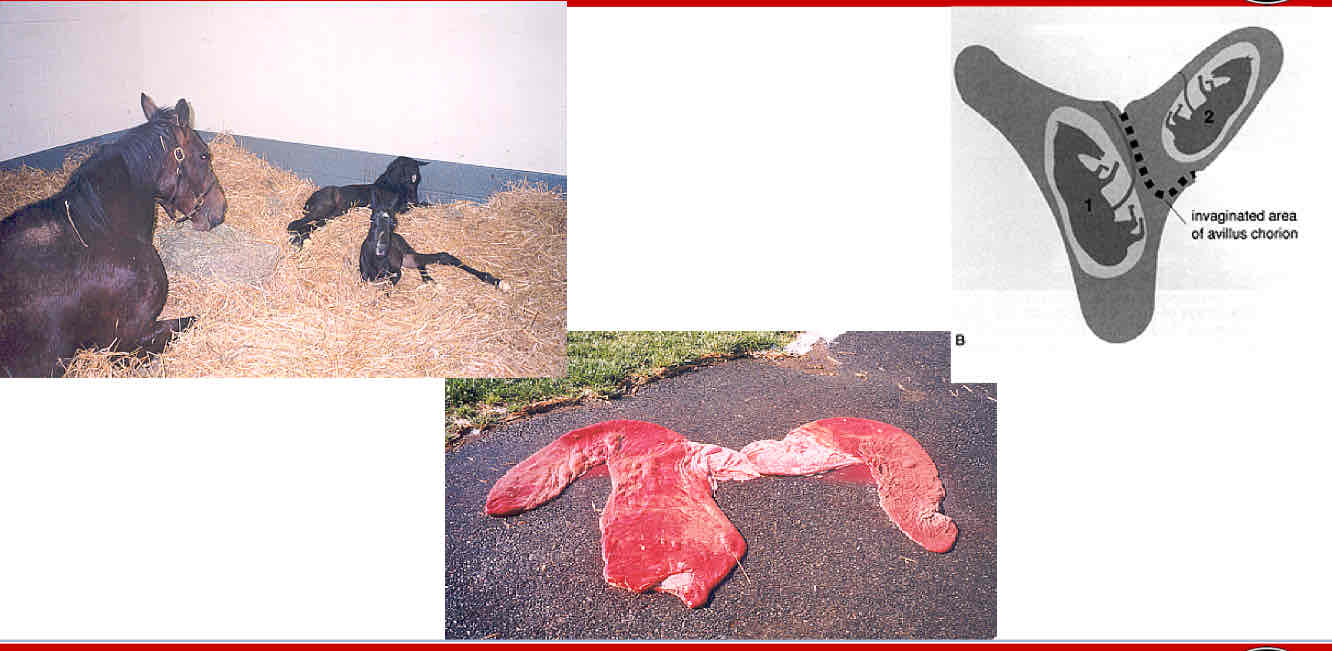

Type A placentation
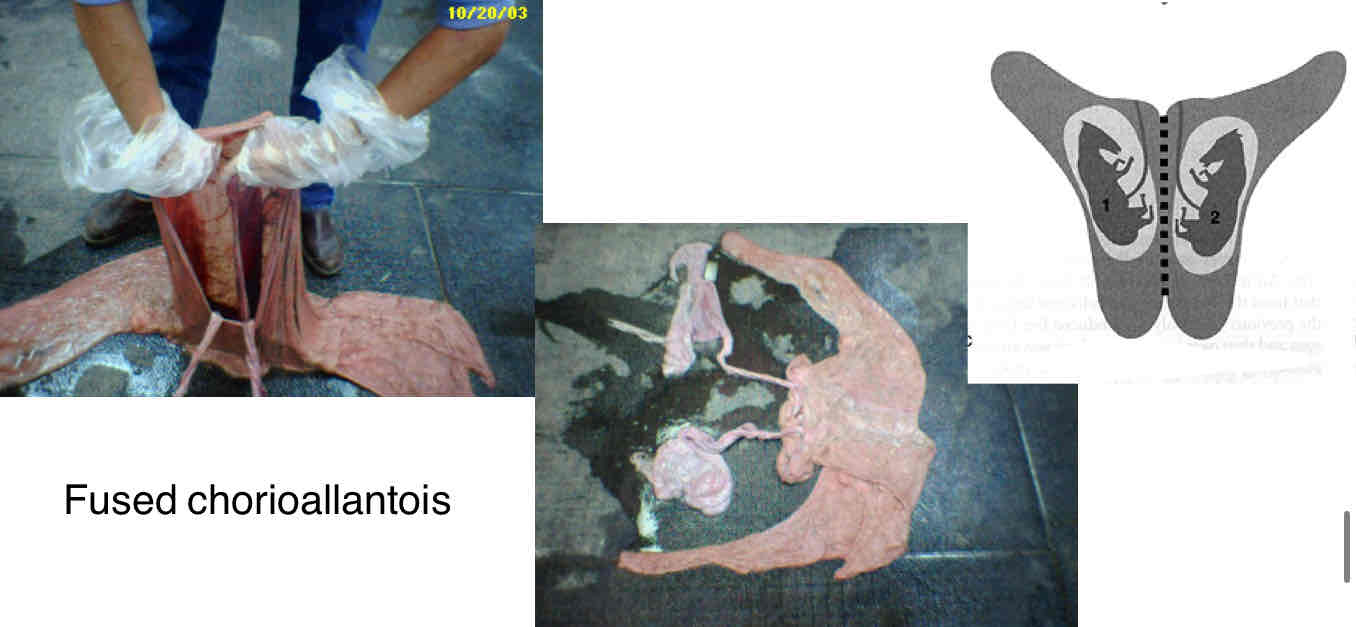

Type B placentation
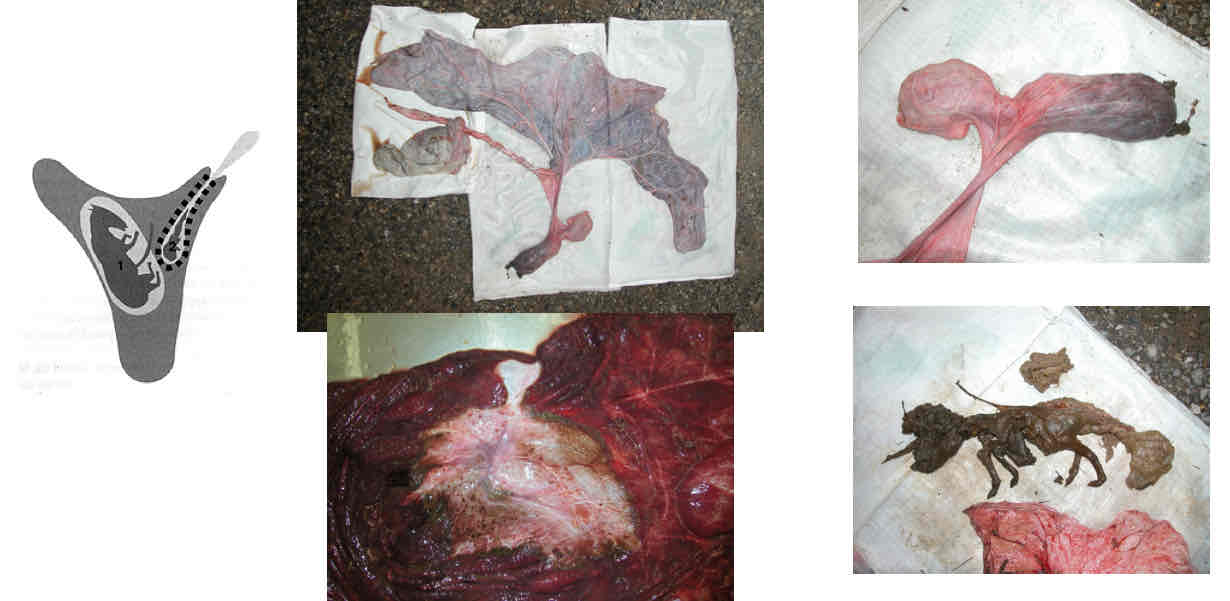
Type C placentation
Breeding strategies for management of twins
Breed all mares
Examine for twins regardless if double ovulation detected
If unilateral wait for natural reduction
If bilateral then manually reduce before d18
What is the most common method to reduce a twin?
Crushing a twin
Should you worry about multiple follicles on an ovary?
No! Go ahead and breed, can deal with twins later
When does crushing have decreased success?
After day 19
What can you give prior to crushing twins?
NSAIDs
pretreat with P4
When is aspiration performed?
After fixation (d20-40)
What is the success of aspiration?
~40%
What approach is needed for fetal cranio-cervical dislocation?
Flank laparotomy
When is fetal cranio-cervical dislocation performed?
d60-110.
What is thoracic compression?
Done between d55 to d65. Compress fetus against pelvis using US for extended period to compress heart. Should see heart slow dow.
When is a fetal cardiac puncture performed?
150 days
What pre-treatment is needed for fetal cardiac puncture?
P4
Flunixin meglumine
Clenbuterol
Antibiotics (TMS)
Intra-cardiac infusion of procaine penicillin.
Fetal cardiac puncture
What is the most common way to terminate pregnancy before day 35?
Prostaglandins
1. What is the primary function of equine chorionic gonadotropin (eCG) during pregnancy?
a. To stimulate milk production
b. To maintain the primary corpus luteum
c. To aid in the formation of secondary corpora lutea
d. To initiate parturition
c. To aid in the formation of secondary corpora lutea
2. At approximately what day of gestation do endometrial cups form in mares?
a. Day 20-25
b. Day 35-40
c. Day 60-65
d. Day 80-85
b. Day 35-40
3. When does a mare's pregnancy typically become corpus luteum independent?
a. Around day 50
b. Around day 100
c. Around day 150
d. Around day 200
b. Around day 100
4. Which hormone can be used as a diagnostic indicator of pregnancy after approximately day 80?
a. Progesterone
b. Testosterone
c. Estrone sulfate
d. Follicle-stimulating hormone
c. Estrone sulfate
5. What is the average gestation length for a mare?
a. 280 days
b. 310 days
c. 343 days
d. 365 days
c. 343 days
6. At what stage of gestation can the fetal heartbeat typically be detected via ultrasound?
a. Day 16
b. Day 25
c. Day 35
d. Day 45
b. Day 25
7. Which of the following is NOT a clinically important event in equine pregnancy?
a. Fixation at day 16
b. Embryo entering the uterus at day 5-6
c. Implantation at day 35-40
d. Fetal movement detection at day 10
d. Fetal movement detection at day 10
8. What percentage of equine twins are typically dizygotic?
a. Less than 50%
b. Approximately 75%
c. Greater than 95%
d. 100%
c. Greater than 95%
9. Which breed of horse has the highest incidence of twinning?
a. Arabian
b. Quarter Horse
c. Thoroughbred
d. Pony breeds
c. Thoroughbred
10. What is the most common outcome of twin pregnancies in mares?
a. Birth of two healthy foals
b. Birth of a single foal
c. Loss of both pregnancies
d. One live foal and one stillborn
b. Birth of a single foal
11. When is the optimal time to perform the first pregnancy exam for twins via ultrasonography?
a. Day 5-6 post-ovulation
b. Day 14-16 post-ovulation
c. Day 25-30 post-ovulation
d. Day 40-45 post-ovulation
b. Day 14-16 post-ovulation
12. Which type of twin fixation has the highest chance of natural reduction?
a. Bilateral fixation
b. Unilateral fixation
c. Monozygotic fixation
d. There is no difference in reduction rates
b. Unilateral fixation
13. What is the most common method used to reduce a twin pregnancy in mares?
a. Fetal aspiration
b. Crushing a twin
c. Fetal cranio-cervical dislocation
d. Thoracic compression
b. Crushing a twin
14. Up to what day of gestation is crushing a twin considered to have a high success rate?
a. Day 14
b. Day 19
c. Day 25
d. Day 30
b. Day 19
15. Which of the following is NOT a factor to consider when deciding how to manage twins in a mare?
a. Stage of gestation
b. Time of season
c. Mare's coat color
d. Subsequent fertility of mare
c. Mare's coat color
16. What is the approximate success rate of twin reduction by aspiration?
a. 20%
b. 40%
c. 60%
d. 80%
b. 40%