Terminology, Osteology & Arthrology
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
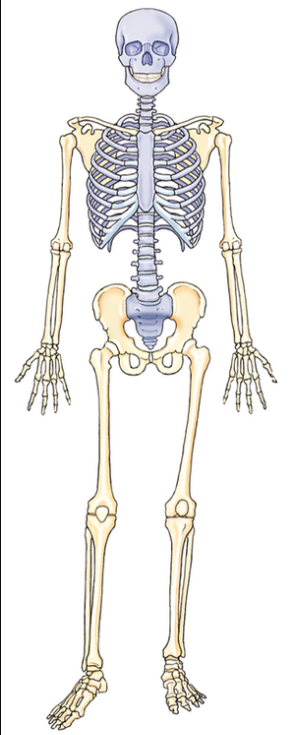
Which part of the skeleton is in blue?
Axial Skeleton
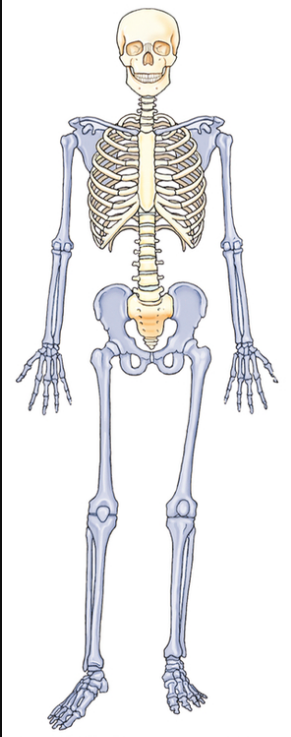
Which part of the skeleton is in blue?
Appendicular Skeleton
How many bones are in the human skeleton?
206
How many bones in axial skeleton?
80
How many bones in appendicular skeleton?
126
What is the axial skeleton comprised of?
Skull (facial bones & cranium), hyoid, auditory ossicles, vertebral column, thorax
What is the appendicular skeleton comprised of?
Extremities
List the levels of structural organization that make up the human body from smallest to largest.
Cells - Tissues - Organs - Organ Systems - Organism
How many organ systems are there?
10
List the organ systems.
Skeletal
Circulatory
Digestive
Respiratory
Urinary
Reproductive
Nervous
Muscular
Endocrine
Integumentary
List the 4 functions of the skeletal system.
Support/protect many soft tissues of the body.
Allow movement through interaction w/ muscles to form a system of levers.
Produce blood cells.
Store calcium.
Where are blood cells produced?
Skeletal system (bones)
List the 6 functions of the circulatory system.
Distribute oxygen and nutrients to the cells of the body.
Transport cell waste and carbon dioxide from the cells.
Transport water, electrolytes, hormones, and enzymes.
Protect against disease.
Prevent hemorrhage by forming blood clots.
Assist in regulating body temperature.
The circulatory system is composed of what two systems/organs?
Cardiovascular organs
Lymphatic system
Define osteology.
The study of bones.
Define arthrology.
The study of joints.
What is does the digestive system include (broad answer).
Alimentary canal and certain accessory organs.
What is the alimentary canal made of? (7 Structures)
Mouth
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Small intestine
Large intestine
Anus
List the accessory organs of the digestive system. (4 Structures)
Salivary glands
Liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas
List the two functions of the digestive system.
Prepare food for absorption by the cells.
Eliminate solid wastes from the body.
List the 3 functions of the respiratory system.
Supply oxygen to the blood and eventually the cells.
Eliminate carbon dioxide from the blood.
Assist in regulating the acid-base balance of the blood.
What is the respiratory system made of?
Two lungs and the passages that connect the lungs to the outside atmosphere.
What are the structures that make up the passageway from the exterior to the alveoli of the lungs?
Nose
mouth
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchial tree
List the 4 functions of the urinary system.
Regulate the chemical composition of blood.
Eliminate many waste products.
Regulate fluid and electrolyte balance and volume.
Maintain the acid-base balance of the body.
What are the four organs of the urinary system?
Kidneys
Ureters
Bladder
urethra
What is the function of the reproductive system?
Reproduce the organism.
What is the reproductive system made of?
Organs that produce, transport, and store germ cells.
What produce, store and transport germ cells in males?
Testes, vas deferense, prostate gland, and penis.
What produce, store and transport germ cells in females?
Ovaries, uterine (fallopian tubes), uterus, and vagina.
What is the function of the nervous system?
To coordinate voluntary and involuntary body activities and transmit electrical impulses to various parts of the body and brain.
What is the nervous system made of?
Brain
Spinal cord
Nerves
Ganglia
Special sense organs (eyes and ears)
What are the three functions of muscle tissue?
Allow movement such as locomotion of the body or movement.
Maintain posture.
Produce body heat.
What are the three types of muscles that comprise the muscular system?
Skeletal
Smooth
Cardiac
The endocrine system include what?
All ductless glands.
What are the 9 ductless glands of the endocrine system?
Testes
Ovaries
Pancreas
Adrenals
Thymus
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Pineal
Pituitary
What is the function of the endocrine system?
Regulate bodily activities through the various hormones carried by the cardiovascular system.
What is the integumentary system comprised of?
Skin and all structures derived from the skin.
What is the largest organ of the body?
Skin.
What are the derived structures of the skin?
Hair
Skin
Nails
Sweat & oil glands
What are the 5 functions of the integumentary system?
Regulate body temperature.
Protect the body (within limits) against microbial invasion and mechanical, chemical, and UV radiation damage.
Eliminate waste products through perspiration.
Receive Certain stimuli such as temperature, pressure, and pain.
Synthesize certain vitamins and biochemicals such as Vitamin D.
List the 4 classification of bones.
Long bones
Short bones
Flat bones
Irregular bones
What is the name of the special type of small, oval-shaped bones that are embedded in certain tendons?
Sesamoid bones
What are the two largest sesamoid bones?
The two patellae.
What are long bones comprised of?
Body
Two ends/extremities
What is the composition of long bones?
Compact bone/cortex
Body/shaft
Spongy/cancellous bone
Medullary cavity
Periosteum
Hyaline cartilage
What is compact bone?
Outer, dense shell of long bones.
Where is spongy/cancellous bone and what does it contain?
Inside of compact bone at both ends.
Contains red bone marrow (production of RBC).
Where are RBCs produced?
Inside of bone marrow in cancellous bone.
Where are the medullary cavities found?
The hollow portion of bone.
Where is fatty yellow marrow found?
Inside the medullary cavities of bone.
What are short bones mostly comprised of?
Cancellous tissue with a thin outer covering of compact bone.
Where are short bones found?
Carpals of the wrist & tarsals of the foot
What do flat bones consist of?
Two plates of compact bone with cancellous bone & bone marrow between them.
Provide examples of flat bones.
Skull cap, sternum, ribs, and scapulae.
Provide examples of irregular bones.
Vertebrae, facial bones, bones of the base of the cranium, and bones of the pelvis.
Define ossification.
The process by which bones form within the body.
In adults, what are some bones that RBCs are produced?
Ends of long bones, sternum, ribs, vertebrae, and pelvis.
What are the two types of bone formation?
Intramembranous
Endochondral
Define intramembranous ossification
When bone replaces membranes.
Define endochondral ossification.
When bone replaces cartilage.
True/False: Intramembranous ossification is a slow process that primarily occurs in long bones.
False: It is a rapidly occurring process that occurs in sutures of the skullcap.
True/False: Endochondral ossification is a slower process and occurs in most parts of the skeleton, especially long bones.
True.
Where is the primary center of ossification?
Midbody area.
Where is the primary center of ossification in growing bones, and what does it become?
Diaphysis that becomes the body in fully developed bones.
Where do secondary centers of ossification appear?
Near the ends of long bones.
What is each secondary center of ossification called?
Epiphysis
Where are epiphyseal plates found?
Between the metaphysis and epiphysis.
What is the age range of full (osteological) maturity?
20-25 years
What are the 3 functional classifications of joints?
Synarthrosis
Amphiarthrosis
Diarthrosis
Define synarthrosis
Immovable joints
Define amphiarthrosis
Limited movement
Define diarthrosis
Freely moveable joints
What is an example of a synarthrodial joint?
Sutures of the skull
What is an example of a amphiarthrodial joint?
Distal tib/fib joint.
What is an example of a diarthrodial joint?
Glenohumeral joint
What are the 3 structural classifications of joints?
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
Synovial
3 Types of fibrous joints.
Syndesmosis
Suture
Gomphosis
True/False: Syndesmotic joints are amphiarthrodial.
True
Example of syndesmotic joints.
Distal tib-fib, carpals and tarsals.
Which kind of functional joint is a suture?
Synarthrosis
Gomphosis joints are specific to what?
Gums
Cartilaginous joints lacks what?
A joint cavity
2 Types of cartilaginous joints.
Symphysis
Synchondrosis
Examples of symphysis joints.
Pubic symphysis, intervertebral disks
Synchondrosis joints are what kind of functional joints?
Synarthrosis.
Example of synchondrosis.
Epiphyseal plates
Synovial joints are characterized by what?
A fibrous joint capsule containing synovial fluid.
True/False: Synovial joints are amphiarthrodial.
False: Diarthrodial.
List the 7 movement types of synovial joints.
Plane (gliding)
Ginglymus (Hinge)
Pivot (trochoid)
Ellipsoid (condylar)
Saddle (sellar)
Ball & socket (spheroidal)
Bicondylar
Plane/gliding joints offer what type of movements?
Sliding or gliding between the articulating surfaces.
Examples of plane joints.
Intermetacarpal joints
Carpometacarpal joints
Intercarpal joints
Atlantoaxial joints
Ginglymus (hinge) joints offer what type of movements?
Flexion and extension only.
Examples of ginglymus/hinge joints.
Elbow
Interphalangeal joints of fingers & toes
Pivot (trochoid) joints provide what types of movement?
Rotational movement around a single axis.
Examples of pivot/trochoid joints.
Proximal/distal radioulnar joints
Between first and second cervical vertebrae
Ellipsoid (condylar) joints allow for what types of movement?
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and circumduction.
Examples of ellipsoid/condylar joints?
Metacarpophalangeal joints of fingers
Radiocarpal (wrist) joints
Metatarsophalangeal joints of toes
Saddle (sellar) joints offer what types of movement?
Flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, circumduction
What’s the difference between ellipsoidal and saddle joints?
Ellipsoid: Movement occurs primarily in one plane.
Saddle: Ends of the bones are shaped concave-convex and are positioned opposite each other.