Molecular Basis of Inheritance
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Two strains of bacterium
were used in Griffith's experiment to demonstrate transformation, highlighting how genetic material can be transferred between organisms.
Pathogenic (strain S) and non-pathogenic(harmless) (strain R) strains were used, where heat-killed pathogenic bacteria transformed the non-pathogenic bacteria into pathogenic forms.
Transformation
Bacteria cable of transferring genetic material
now defined as a change in genotype and phenotypes due to the uptake and expression of foreign DNA.
evidence that DNA can transform bacteria
F, Griffith mixed heat-killed remains of the pathogenic strain with living cells of the harmless strain, some living cells became pathogenic.
evidence that viral DNA can program cells
A. Hershey and M. Chase designed an experiment showing that only one od the components of T2 (DNA/ protein) enters E. coli cell during infection.
They concluded that the injected DNA of the phage provides the genetic information.
Chargaff rules (1950) - additional evidence that DNA is the genetic material
The base composition of DNA varies between species and the amount of adenine = thymine, while the amount of guanine = cytosine.
X-ray crystallography
Wilkins and Franklin used this technique to study molecular structure, helping to determine how DNA structure accounts for its role in heredity.
what did Franklin's x-ray crystallograph images of DNA show
DNA is a double helix
the helix is 2nm
.34nm of space between the nitrogen bases
One full turn every 10 bp = 3.4 nm
Linus Pauling
Father of structure and function
Determined that the essence of life is not from individual molecules but from the interactions between them
Studied how antibodies and enzymes work
Studied the molecular structure of sickle cell anemia
Discovered the Alpha Helix structure for proteins
base structure pairing (Watson and Crick)
Purine + Pyrimidine : A = T(U) , G = C
issue with pairing purine + purine and pyrimidine + pyrimkdine
Purine + Purine = too wide of a structure for the helix
Pyrimidine + Pyrimidine = too narrow for the helix
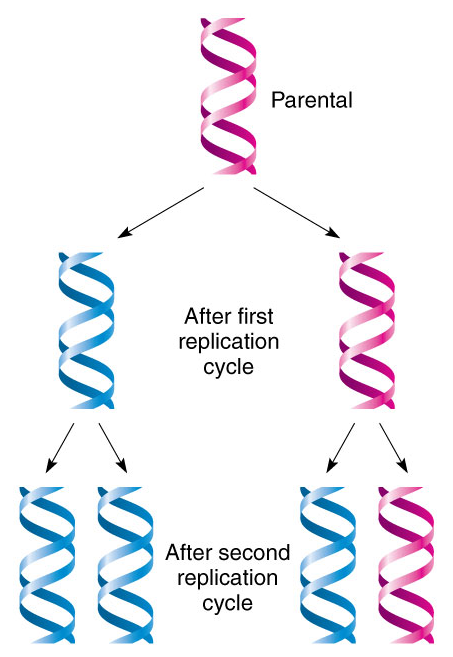
Watsons and cricks semiconservative model prediction
Predicts that when a double helix is replicated, each daughter molecule will have one old strand (conserved from the parent molecule) and one new strand
Conservative model of DNA replication
Original DNA is kept intact and creates a completely new copy
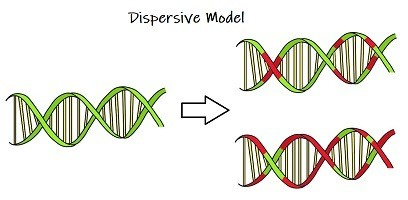
Dispersive model of DNA replication
During replication each strand is a mix of old and new strands
Origins of replication
the particular site where two DNA strands separate opening a replication “bubble”,
how eukaryotic replication different from bacteria replication
Many replication points, takes an hour to replicate entire genome
prokaryotic replication
1 point of origin
1-2 types of polymerases
No ends to synthesize
eukaryotic replication
C value paradox
Multiple points of origin
Telomere replication distinctive
4 types of polymerases
DNA Polymerase
enzyme used is replication,
catalyze the synthesis of new DNA at a replication fork
Most DNA polymerases require a primer & a DNA template strand
C value paradox
?
synthesizing new DNA strand
Primase can start an RNA chain from scratch & adds RNA nucleotides one at a time using the parental DNA as a template
3′ end serves as the starting point for the new DNA strand
(DNA polymerases require a primer to which they can add nucleotides, The initial nucleotide strand is a short RNA primer, This is synthesized by the enzyme primase)
Antiparallel Elongation
arrangement of two DNA stands in opposite directions, elongates only in the 5’ to 3’ direction
synthesis of lagging strand
synthesis leading strand
nucleotide excision repair of damaged DNA
evolutionary significance of altered DNA nucleotides
Helicases
enzymes that untwist the double helix at the replication forks
single - single binding proteins
binds to and stabilize single stranded DNA
Topoisomerase
relieves the strain of twisting of the double helix by breaking, swiveling, & rejoining DNA strands
Primase
Synthesize short RNA primer to it can be added to the DNAs original nucleotide
dehydration reaction
how monomers join the DNA strand, losing two phosphate groups as a molecule pyrophosphate
dATP
supplies adenine to DNA and differs from ATP as it has deoxyribose instead of ribose