Endocrine System: Glands, Hormones, and Regulatory Mechanisms
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What is the primary function of the endocrine system?
To release hormones into the bloodstream to maintain the body's balance.
What are the overall functions of the endocrine system?
Regulate metabolism, water and electrolyte balance, stress adaptation, growth and development, reproduction, and red blood cell production.
What is a hormone?
A chemical produced and secreted by endocrine glands that regulates the activity of specific cells or organs.
What are the basic functions of a hormone?
1.Promote and enable mental, physical and sexual development, 2.Promote and enable the adjustment of performance levels of organs and organ systems, 3.Keep some physiological parameters constant
What are the two categories of hormones based on solubility?
Hydrophilic (water-soluble) and lipophilic (fat-soluble).
What type of hormones are considered hydrophilic?
Peptide hormones (e.g., insulin, glucagon) and catecholamines (e.g., epinephrine, norepinephrine).
How do hydrophilic hormones work?
By binding with surface membrane receptors. They circulate dissolved in plasma
What type of hormones are considered lipophilic?
Steroid hormones and thyroid hormones.
How do lipophilic hormones work?
By binding with receptors within the cell.
How specific are hormones?
They have specificity to certain cells to only affect certain cells
What determines the specificity of a hormone?
Its chemical structure
What hormones are considered steroid hormones?
Glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, sex hormones, androgens, estrogen and progesterone
Glucocorticoids: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Adrenal cortex
Target tissue: All tissues of body
Major function: Increases blood glucose levels, protein breakdown
Mineralocorticoids: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Adrenal cortex
Target organ: Kidneys
Major function: Resorption of Na and excretion of K
Sex hormones: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Adrenal cortex
Target organ/tissue: Gonads, muscles and bones
Major function: Stimulation of reproductive organs
Androgens: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Testes
Target organ/tissue: Gonads, muscles and bones
Major function: Stimulation of male sexual characteristics
Estrogen and progesterone: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Ovaries
Target organ/tissue: Gonads, skin, muscles and bones
Major function: Stimulation of female sexual characteristics
What hormones are considered peptide hormones?
Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones, antidiuretic, oxytocin, androgens, calcitonin, parathyroid hormone and thymosins.
Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Hypothalamus
Target organ/tissue: Anterior pituitary gland
Major function: Regulation of anterior pituitary hormones
Antidiuretic: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Posterior pituitary
Target organ: Kidney
Major function: Stimulation of water resorption by the kidneys, raises blood pressure
Oxytocin: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Posterior pituitary
Target organ/tissue: Uterus and mammary glands
Major function: Stimulation of uterine cx, milk release
Calcitonin: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Thyroid gland
Target organ/tissue: Bones, kidneys, and intestines
Major function: Lowers Ca level in blood
Parathyroid hormone: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Parathyroid gland
Target organ/tissue: Bones, kidneys and intestines
Major function: Elevates Ca in blood
Thymosins: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Thymus
Target tissue: T-lymphocytes
Major function: Production and maturation of T-lymphocytes
TSH: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Anterior pituitary
Target tissue: Thyroid gland
Major function: Stimulation of thyroid gland
Gonadotropin: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Anterior pituitary
Target organ: Gonads
Major function: Egg, sperm, sex hormone production
Prolactin: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Anterior pituitary
Target organ/tissue: Mammary glands
Major function: Milk production during lactation
GH: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Anterior pituitary
Target organ/tissue: Bones and soft tissues
Major function: Cell division, bone growth
T4 and T3: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Thyroid gland
Target tissue: All tissues of the body
Major function: Regulation of metabolism, growth
Epi and norepi: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Adrenal medulla
Target organ/tissue: Cardiac and other muscles
Major function: Fight or flight response
Insulin: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Pancreas
Target organ/tissue: Liver, muscles and adipose tissue
Major function: Lowers blood glucose levels
Glucagon: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Pancreas
Target organ/tissue: Liver, muscles, and adipose tissues
Major function: Elevates blood glucose levels
Function of FSH
Promotes sperm production in men and stimulates the ovaries to enable ovulation in women
Melatonin: What gland releases it, what is its target organ/tissue, what is its function
Released by: Pineal gland
Target organ: Brain
Major function: Convey information of light and darkness to body
Function of LH
Regulates testosterone in men and estrogen in women
What is ADH also known as?
Vasopressin
What condition can be caused by too little ADH release?
Diabetes insipidus
What condition can be caused by too much ADH release?
Syndrome of inappropriate ADH
Describe the transport of hormones from hypothalamus to pituitary gland
Hypothalamic neurons → Primary capillary plexus → Portal veins → Secondary capillary plexus (anterior pituitary)
What hormones are secreted by the anterior pituitary gland?
FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH, Prolactin, and Growth Hormone.
What 2 hormones are secreted by the posterior pituitary gland?
ADH and oxytocin
What are the 2 lobes of the pituitary gland?
Adenohypophysis (anterior) and neurohypophysis (posterior)
Function of adenohypophysis (anterior) lobe
Glandular tissue producing hormones
Function of neurohypophysis (posterior)
Neural tissue storing hypothalamic hormones
What are hormones that produced by the anterior pituitary gland regulated by?
Hypothalamus
What is the role of the hypothalamus in the endocrine system?
To control hormone production in the pituitary gland through releasing hormones. It releases hormones that start and stop the release of pituitary hormones
How does thyrotropic-releasing hormone (TRH) act on the anterior pituitary?
Stimulates TSH secretion by thyrotrophs
How does Growth-hormone releasing hormone act on anterior pituitary?
Stimulates GH secretion by somatotrophs
How does somatostatin (SST) act on the anterior pituitary?
Inhibits GH secretion by somatotrophs
What is negative feedback in hormonal regulation?
A mechanism where the output of a system counteracts the input, preventing excessive hormone levels.
What is positive feedback in hormonal regulation?
A mechanism where hormone effects stimulate further secretion, such as oxytocin during labor.
Describe the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Stress activates the hypothalamus to release CRH, stimulating the pituitary to release ACTH, which prompts cortisol release from the adrenal cortex.
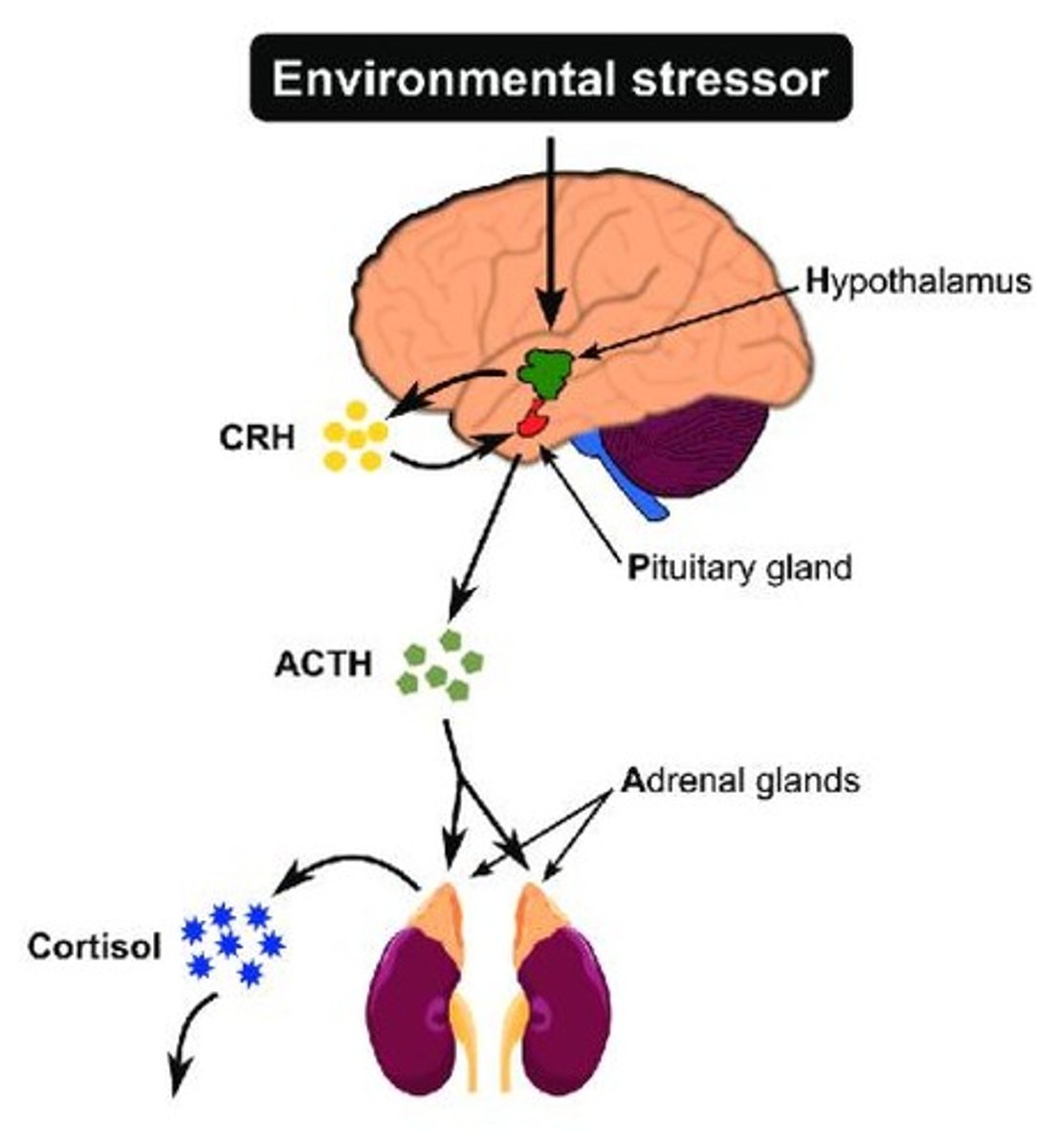
What does cortisol increase lead to?
Negative feedback loop in which CRH and ACTH are inhibited.
How does consistent glucose increase lead to DM2?
Glucose increase → Insulin increase (cells are resistant) → Glucose remains high → Pancreas overworks → B-cells fatigue → Insulin decreases → Glucose increases more
Describe the negative feedback loop of GH
Hypothalamus (GHRH increases, somatostatin decreases) → Anterior pituitary (increases GH) → Liver (increases IGF-1) → Growth of tissues → Negative feedback to hypothalamus/pituitary
What is the hormone of darkness?
Melatonin
How do hormones exert their effects on target cells?
By binding to specific receptors on the cell surface or within the cell, triggering a signal transduction pathway.
What is the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system?
A network of blood vessels that connects the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary, allowing rapid hormone transport.

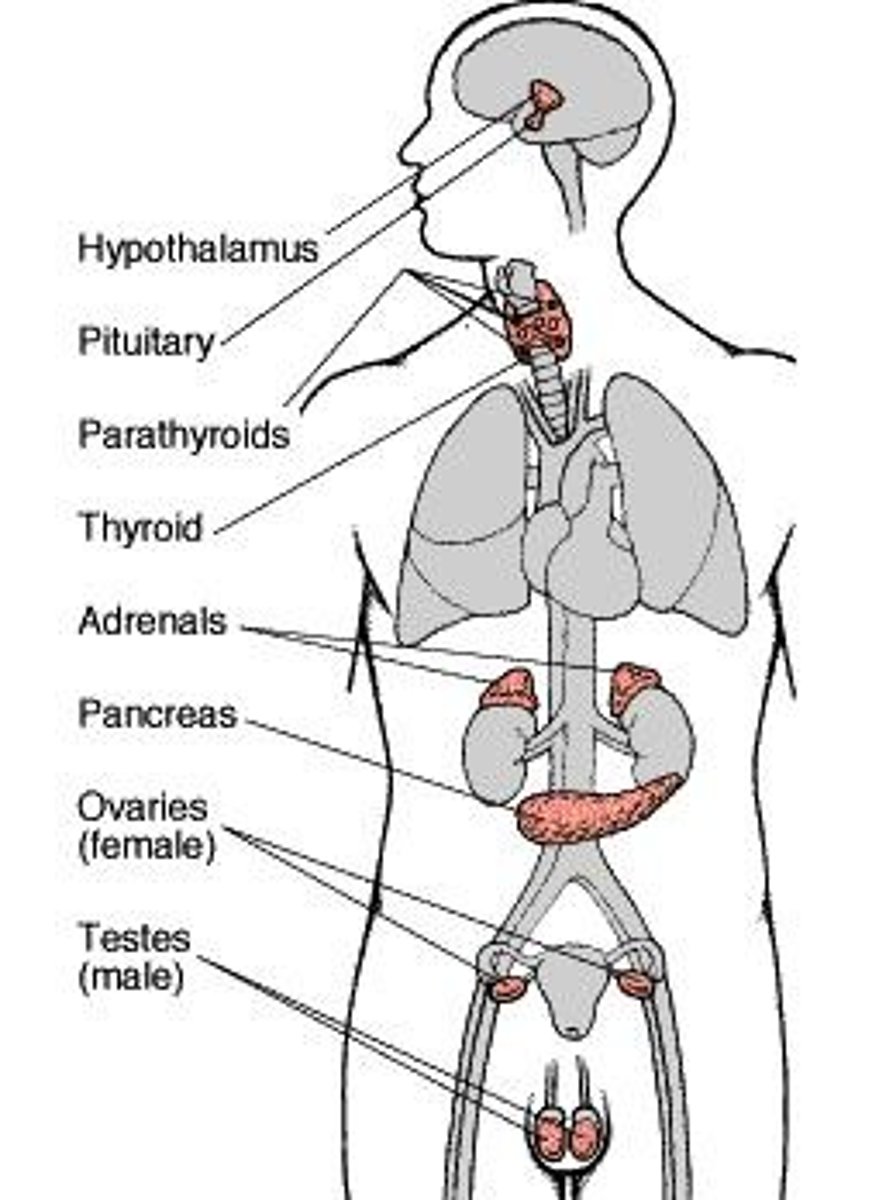
What are the major endocrine glands in the human body?
Pituitary gland, hypothalamus, thymus, pineal gland, testes/ovaries, thyroid, adrenal glands, parathyroid, pancreas.
What is the significance of the 'lock and key' system in hormone action?
It describes how hormones bind specifically to their target cell receptors to exert their effects.
What is the function of vasopressin in the kidneys?
To promote water reabsorption in the distal tubule and collecting duct.
How does the hypothalamus regulate the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)?
By releasing Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
How does insulin affect glucose in the liver?
Insulin converts glucose to glycogen.
What is the role of glucagon in the liver?
Glucagon converts glycogen back to glucose.
What are the three types of stimuli that trigger hormone secretion?
Neural stimuli, humoral stimuli, and hormonal stimuli.
How does the body respond to eating in terms of insulin?
Insulin is released to help cells absorb glucose, lowering blood sugar levels.
What is the role of growth hormone in growth regulation?
Growth hormone stimulates the liver to produce IGF-1, promoting tissue growth.
What is the function of the pineal gland?
It secretes melatonin, regulating circadian rhythms and promoting sleep.
How does light affect melatonin secretion?
Melatonin secretion decreases during daylight and increases in darkness.
What is the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)?
The body's master biological clock located in the hypothalamus, regulating circadian rhythms.
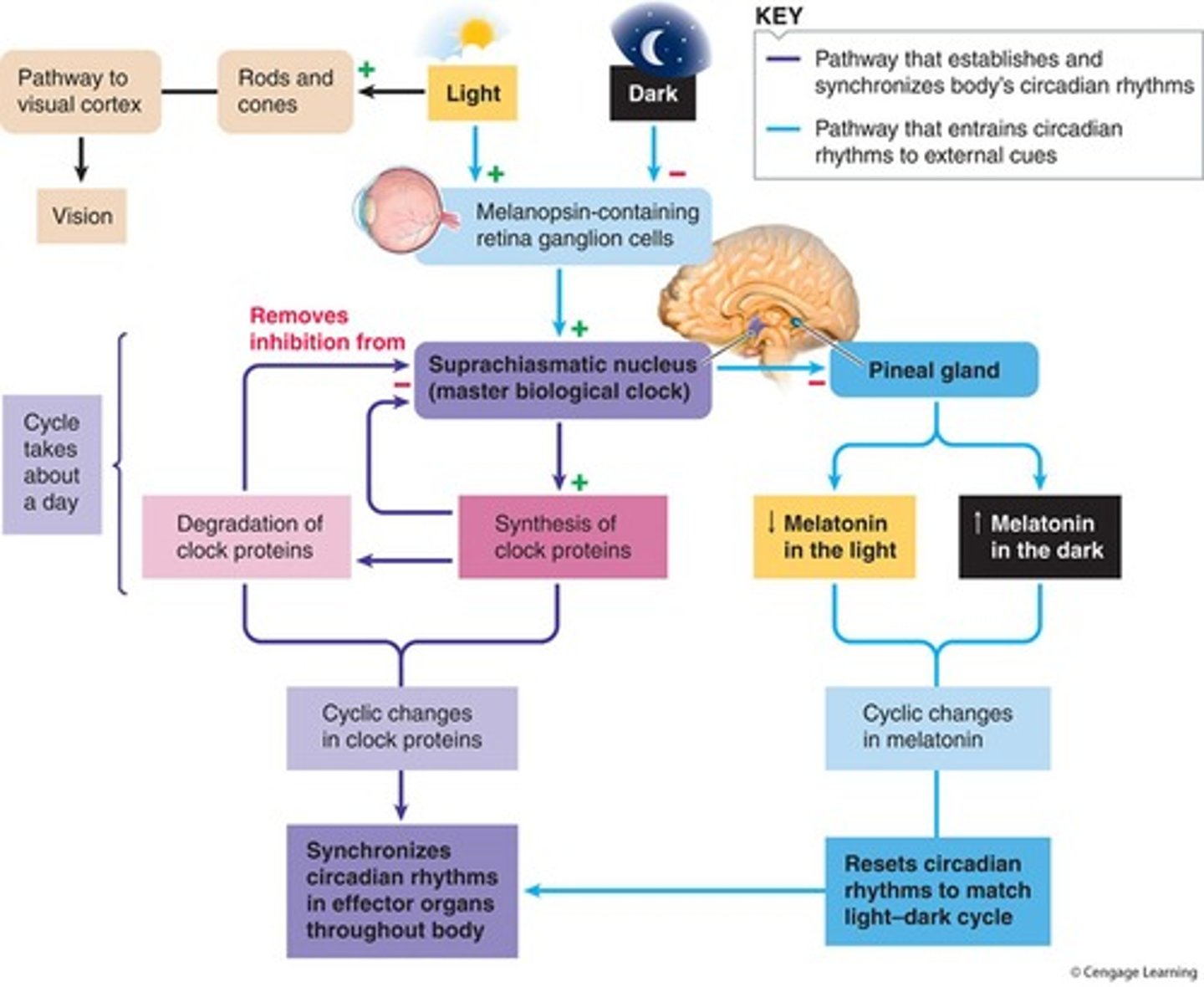
What is the relationship between melatonin and circadian rhythms?
Melatonin helps entrain circadian oscillators in peripheral tissues, influencing sleep and wake cycles.