Socialism for Today (Part 2: Negotiated Coordination, DPP and Transitions)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are the two main principles of negotiated coordination?
NC strives to maximize participation on the part of everybody affected by a given economic process
NC supports a division between market exchanges and market forces

Through what main principle should major economic decisions be taken in Negotiated Coordination? What is that principle?
The subsidiarity principle: the principle which makes sure that decisions should be primarily made by those who are the most affected by them, because they know their own needs best

What are some main benefits of subsidiarity?
Locally based economic activity
Shorter supply chains (goods are produced, processed and distributed closer to where they are used)
Reduced ecological damage

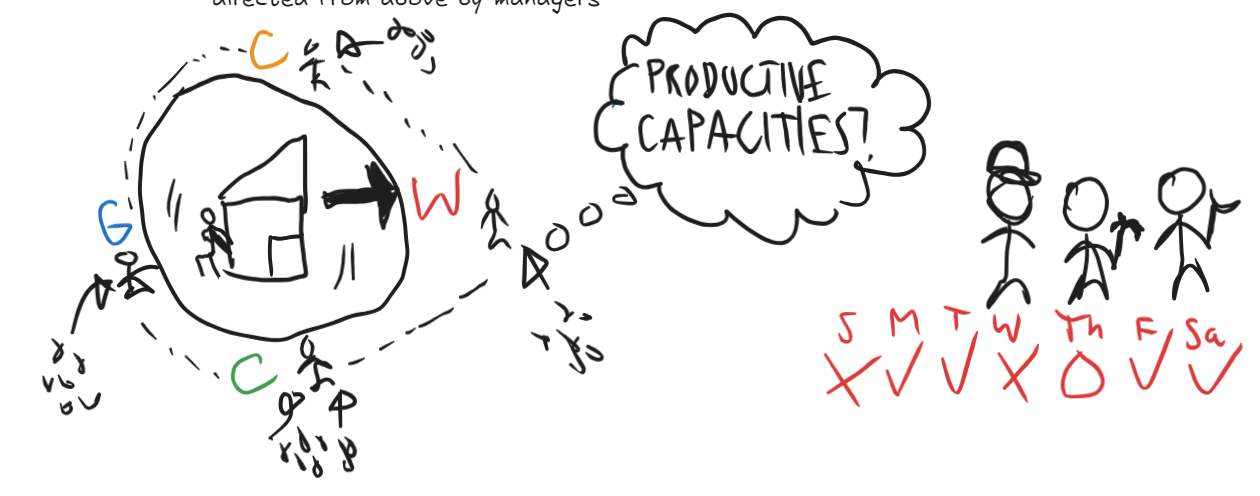
Explain the economic landscape of Negotiated Coordination in brief.
Enterprises (production units) are owned collectively, and representatives from four sectors sit on the decision-making body of each production unit:
General interest (national, regional and local Planning Commissions and Negotiated Coordination Bodies)
Consumers, users and suppliers (consumer associations, government & public services)
Workers and their unions (workers’ organizations)
The community (interest groups and activist groups)
Representatives negotiate how productive resources ought to be used through negotiation (considering each other's interests), deciding on the overall direction the enterprise is going.
Meanwhile, workers organize the day-to-day operation of the workplace through self-management.
Self-management: employees organize and control their own work processes rather than being directed from above by managers
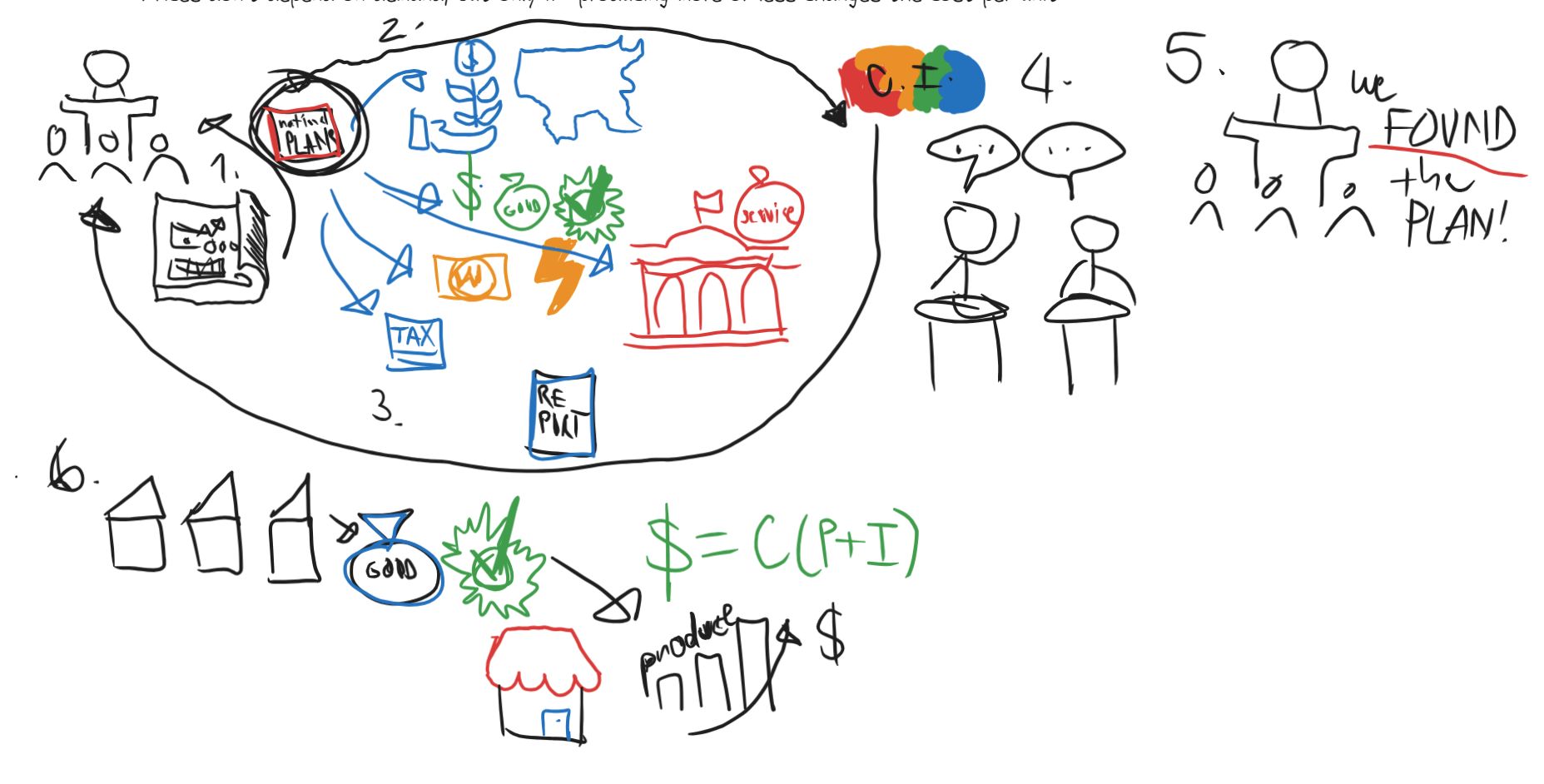
What is the planning/ production process like in Negotiated Coordination?
The law-making Representative Assembly receives a series of national plans designed by a Planning Commission (which consists of members of concerned governments, productions units, NCBs and interest/cause groups); these national plans establish:
National investment priorities
Money, goods and services offered for free to those who aren't working (the young, the sick, the elderly)
Primary input prices (wages, energy, national resources)
Taxation
Government public services offered directly to households
A Chamber of Interests (a group of people representing different sections, causes and interests of society) reviews these plans and presents a report to the Representative Assembly on what elements civil society agrees/disagrees with.
After public debate, the Representative Assembly selects one plan and adopts it.
Enterprises put their goods and services on the market at a price that equals the cost required to produce those goods.
That price equals the sum of the primary and intermediate inputs (supply, infrastructure, parts, repairs, etc.)
Prices don't depend on demand, but only if producing more or less changes the cost per unit
What is the difference between market exchange and market forces? Which one does Negotiated Coordination endorse?
NC permits market exchange, which gives consumers and producers a way to share important information about their needs through selling and buying at given prices
Day-to-day production can consequently adapt to market signals
But it does not permit market forces, or the investment decisions based on profit and capital accumulation
In NC, rather than the capitalist making investment decisions through the lens of profit maximization, it is ALL THE AFFECTED PARTIES that make investment decisions in advance.
How can DPP permit a role for small-scale enterprises?
Property of the worker: Single-person establishments could be considered the worker’s property.
Social property: small-scale enterprises with a larger number of workers would be a form of social property.
They would be owned by a local government unit but managed by one of the workers or worker collective, generating wage/salary income but not property income for a private owner.
What does DPP do rather than give workers the same rate of pay?
Living standard floors: There would be a floor set to provide a decent living standard relative to what the society can afford given the level of economic development.
Varying wages for types of work (relative unpleasantness of the job, supply of workers relative to the number required, skill & effort required)
What are some necessary additions to the DPP system (in terms of childcare, pensions, income, etc.)?
Free high-quality childcare available to parents working outside the home
Adequate pensions for retired people
Income for those unable to work due to disabilities
Free high-quality education at all levels, including continuing education
High-quality housing at low cost
Healthcare as a public service financed by the state w/o fees for service and directed towards maintaining good health for the population
What is the biggest role that public banks under democratic socialism can play?
To provide finance for those to work out an idea for something new to create that they have in mind
Once the new product or process has been worked out, its introduction would have to go through the DPP process of negotiation and compromise with all (potentially affected parties)
How did Soviet imperialism work and how was it different from capitalist imperialism?
Soviet rule over neighboring states WAS a form of imperialist domination.
However, it differed from conventional capitalist imperialism.
Because the USSR had vast supplies of raw materials, the Soviet economy didn’t really have a drive to export or invest abroad.
If anything, they exported raw materials at low prices in exchange for imports of manufactured goods from neighboring Communist Party ruled states.
What would freedom in general be like under DPP?
Democracy must go beyond simply electing state officials.
The public has to have access to information about state policies, trends, and how state officials are performing.
There must also be mass media that are free to criticize.
Individuals must be free to pursue their lifestyle in ways that don’t negatively affect others’ well-being
What is the main strategy that the author advocates for to transition from capitalism to socialism?
The “above and below” strategy
Combines pursuing an electoral road AND organizing in the workplace
The employment of multiple tactics and organizing methods (union organizing, community organizing, tenant organizing, anti-racism work, running for elected office, seeking office in trade unions, organizing protests)
Engaging in educational work
Participating in building local institutions that embody principles of a future socialist system (cooperatives, worker-run companies)