Bio Unit 6: Photosynthesis
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
10% Rule
Abiotic Factor
No living components that can influence food chains
Autotroph
Produce their own food through photosynthesis (producer)
Biotic Factor
Living components that can influence food chains
Calvin Cycle/dark reaction
Carbon Fixation
Chemical potential energy
Chloroplast
Double membrane bound organelle thats found in plant cells where photosynthesis occurs
=what role does chlorophyll play in photosynthesis?
Absorbs that sun light and converts it from light energy to chemical energy, and absorbs certain wavelengths of light
What are the main wavelengths chlorophyll a absorbs?
Purple, blue, red
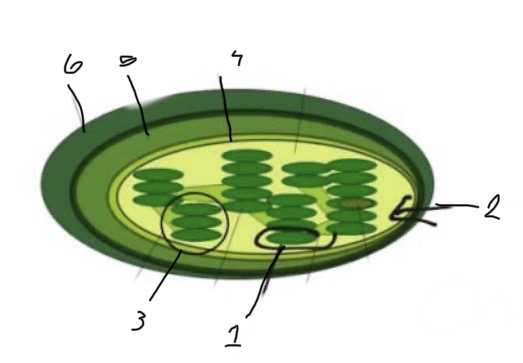
What is 3?
Granum
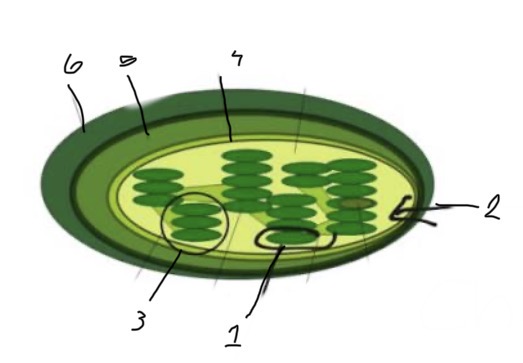
What is 1?
Thylakoid
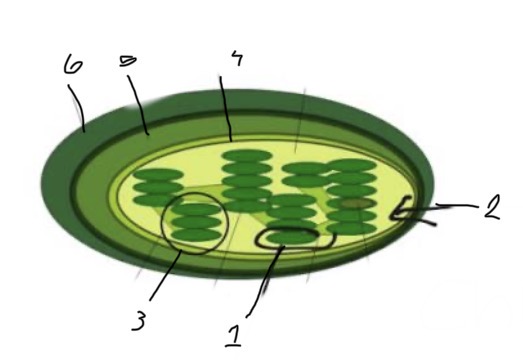
What is 2?
Stroma
Chlorophyll
Commensalism
Competition
Energy pyramid
Food chain/web
Model hat identifies the feeding relationships and the flow of energy in an ecosystem
Producer
Herbivore
Species that consume plants
Carnivore
Species that consume other animals
Omnivore
Species that consume both plants and animals
Consumer
Producer
G3P
Glucose
Granum
Single stack of thylakoid
Heterotroph
Consumers that eat animals, plants or decompose organic matter
Keystone species
Species that play an oversized role in their environment
Light reaction
Mutualism
NADP+
Coenzyme used in photosynthesis thats used as a universal electron carrier to help transport electrons
Parasitism
Photosynthesis
Process in which green plants use the energy of sunlight to convert CO2 and H2O to carbs and O2
Photosystem
Cluster of chlorophyll and other pigments that help capture sunlight
Pigment
Light absorbing molecules in plants
Predation
Radiant energy
RuBP
Rubisco
Stroma
Liquid region around thylakoid
Symbiosis
Tropic cascade
Tropic levels
An organisms rank, or place, in any given food chain
What do detritivores eat?
Dead organisms
What do decomposers eat?
Break down organic matter
Thylakoid
Sac like photosynthetic membrane that contains photosystems
How do plants get their nutrients?
Carbon from the air, nitrogen and phosphorus from the soil
Which nutrient requirement is the most difficult for plants to obtain?
Nitrogen
What converts to NADPH?
NADP+
When does NADP+ convert to NADPH?
When it’s full of electrons and a H+ ion, trapping sunlight in a chemical form
What is the first step of how energy from the sun becomes trapped by NADP+?
Sunlight hits chlorophyll in photosystems
What is the second step of how energy from the sun becomes trapped by NADP+?
Electrons in photosysems become highly energyized
What is the third step of how energy from the sun becomes trapped by NADP+?
NADP+ accepts and holds 2 high energy electrons and a hydrogen ion (H+)
What is the fourth step of how energy from the sun becomes trapped by NADP+?
NADP+ —> NADPH and sunlight is now trapped in chemical form
Which needs light to work?
Light Reaction
Where does the light reaction happen in a chloroplast?
Thylakoid membrane
Where does the Calvin cycle happen in the chloroplast?
Stroma
What are the light reaction inputs?
H2O, Sunlight, NADP+, ADP+P
What is the light reactions output?
O2, ATP, NADPH
What is the Calvin cycles inputs?
CO2, ATP, NADPH
What is the Calvin cycles output?
Glucose, NADP+, ADP+P
Photosynthesis is the key cellular process identified with what?
Energy production
What are the goals of photosynthesis?
Remove CO2 from the air, make food for plants in a form of sugar using CO2, and make O2 as a byproduct
What happens when chlorophyll absorbs light?
Energy is transferred to an electron and raises its energy
Why do plants appear green?
The colors the don’t absorb, the reflect
What is the balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6𝐶𝑂2 + 6𝐻2𝑂 + light energy → 𝐶6𝐻12𝑂6 + 6𝑂2
Compared to cellular respiration, photosynthesis is…
Endergonic - input light energy
How are cellular respiration and photosynthesis related?
Output for one reaction is the input for the other
What part of the chloroplast are photosystems found in?
Thylakoids
Which photosystems was discovered first?
Photosystem 1
Which Photosystem occurs first in the light reaction?
Photosystem 2
What does Photosystem 2 do in the light reaction?
Sends high energized electrons to Photosystem 1
What does Photosystem one do with electrons?
Provide energy to make ATP and NADPH
What does Photosystem 2 do with electrons?