Biochem - Lecture 5 Learning Objectives
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all of the learning objectives for the 5th lecture about tertiary and quaternary structures and protein folding
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
amphipathic alpha helix
an alpha helix with opposing polar and nonpolar faces that are oriented along the helix's long axis
tertiary structure
all aspects of a 3-D folding of peptide chains
quaternary strutcure
arrangement in space of 2 or more polypeptides
motif
short, conserved sequence of amino acids that are important for protein function
domain
structurally independent folding units with distinct tertiary structures but are all a part of the same polypeptide chain
what are the 3 principles guiding folding of water-soluble globular proteins?
minimization of solvent-accessible surface area
maximization of Hydrogen bonding within a protein
chiral effect
what is minimization of solvent-accessible surface area?
burying as many hydrophobic groups as possible within the protein to decrease the amount of them touching the water
what is maximization of hydrogen bonding within a protein?
polar backbone groups and side chains tend to be either in contact with water or hydrogen bonding with other protein groups in order to maximize the amount of hydrogen bonding
what is the chiral affect?
the tendency of extended backbone structural arrangements to be right-handed as a result of having all L configuration amino acids
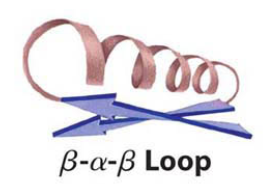
beta alpha beta loop
protein that is a beta conformation connected to an alpha helix connected to a beta conformation, all connected by loops
beta barrel
beta conformation wraps around

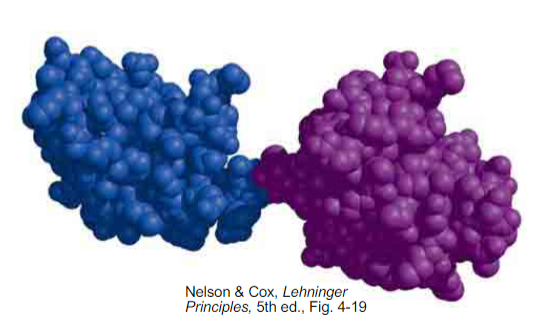
how many domains are in this protein?
2
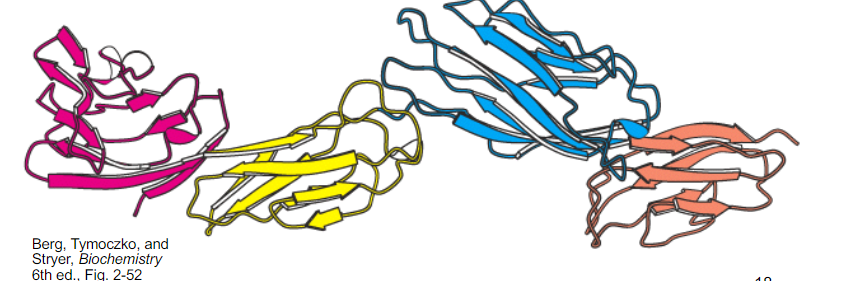
how many domains in this protein?
4
myoglobin structure
made of 70% alpha helices, with the remaining 30% being mostly turns and loops, with no beta sheets or conformations at all
immunoglobulin structure
this is made up of entirely beta strands with loops and no alpha helixes. Has 4 domains
immunoglobulin fold
a protein domain that is made up of two antiparallel beta sheets
alpha beta barrel protein
parallel 8-stranded beta barrel on interior, surrounded by alpha helices
structure of globular protein embedded in lipid bilayer
hydrophobic residues are on the outside and hydrophilic on the inside, creating a channel for water to pass through
subunit
each polypeptide in a multichain protein
rotational axis of symmetry
an imaginary line through a molecule where, if rotated by a specific angle (360°), the molecule appears identical to its original structure
denaturation
unfolding or breaking of a protein
renaturation
process of restoring a denatured protein
homometric
has identical subuinits
heterometric
has different subunits
2-fold symmetry
if you rotate 180° about the axis, the protein will look as though it never moved
3-fold symmetry
if you rotate 120° about the axis, the protein will look as though it never moved
delta G folding
change in free energy between unfolded structure and folded structure
is the delta G folding large or small between the unfolded structure and the folded structure?
very small
loss of 1 or 2 hydrogen bonds might do what to equilibrium of a protein?
it might shift equilibrium from folded state to unfolded state
is the folded form of a protein in a higher
or lower free energy state than the unfolded state?
lower free energy state, meaning it is more stable and energetically favorable
what four things contribute to enthalpy change in folding?
electrostatic effects
solvation/desolvation of charged residues
Van der Waals interactions
steric factors
what two things contribute to entropy change in folding?
hydrophobic effect
conformational entropy
what is conformational entropy?
a major force that opposes protein folding, it is defined as the entropy associated with the number of conformations that a molecule has
is entropy lost or gained due to the conformational entropy?
entropy is lost due to the molecules having less ability to move around (meaning less disorder)
what is the affect of beta-mercaptoethanol on proteins?
it reduces the disulfide bonds in a protein (reducing agent)
what is the affect of urea on proteins?
urea is a denaturing agent, so it disrupts the noncovalent bonds within the protein that stabilize its structures (structures become be stabilized)
what was Anfinsen’s experiment?
he took denatured ribonuclease (RNase) and in one experiment he removed the urea and then oxidized it. In the other he first oxidized the RNase, then he removed the urea
what did Anfinsen find in his experiment?
he found that if you remove urea first and then oxidize it, you still get fully active RNase, but if you reverse the process and oxidize it and then remove the urea, you do not get active RNase
what was the general conclusion drawn from Anfinsen’s experiment?
the native tertiary structure is determined entirely by the primary structure of a protein and is most stable under native (physiological) conditions
cross-beta structure
protein strands are aligned side by side and form hydrogen bonds to create a stable sheet-like structure that is characteristic in many proteins that misfold
what do cross-beta structures lead to the formation of?
amyloid plaques
amyloid plaques
built up clumps of proteins in the brainwha
what disease can cross-beta structures and amyloid plaques cause?
Alzheimer disease
what is the name of the peptide that aggregates extracellularly in Alzheimer disease?
amyloid-beta peptide
what is the name of the protein that’s the source of the peptide that aggregates extracellularly in Alzheimer diease?
amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP)
what is the general type of secondary structure of the aggregate in the amyloid fibers?
beta sheet structure