lewis structure and lysozymes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
nucleophile
supplies electrons
electrophiles
accepts electrons
arrow rules
curved arrows show the direction of electron movement- pushing electrons
the base of the arrow begins at the original location of the pair of electrons
the head of the arrow points to the destination of the electrons
when does simultaneous making and breaking of sigma bonds occur
when a nucleophile approaches a carbon atom having a leaving group in a direction anti and rearward to the leaving group (substitution nucleophilic reaction) (the nucleophile does not have to attack the carbon)
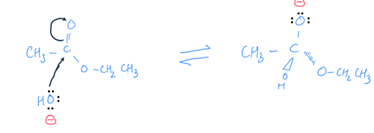
sigma bond making and pi bond breaking
condensation of a molecule and an ion into a single ion
1 curly arrow points from 1 of the lone pairs of electrons on the hydroxyl to the carbon and the other arrow from the C=O bond to the oxygen
C changes sp2 to sp3 hybrid state
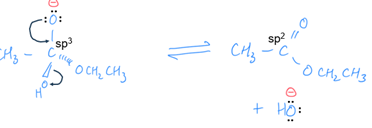
sigma bond breaking and pi bond making
one curly arrow points from 1 of the lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen to the C-O bond and the other arrow from the C-OH bond to the oxygen
lysozyme
an enzyme that is involved in the first line of defence against bacterial attacks that cleave peptidoglycan, the polysaccharide complex in the cell walls of gram-positive bacteria
the enzyme has little effect on gram negative bacteria
where are lysozymes found in humans
in most bodily secretions including tears and nasal mucus
history of lysozymes
the term lysozyme was by Fleming in 1922
the structure of hen egg-white lysozyme, determined in 1965 by x-ray crystallography, was the first to be determined for any enzyme
lysozyme structure
polypeptide chain: 129 amino acids, 4 s-s bridges
structure: 2 domains separated by a deep cleft
(left domain: a small beta sheet of mainly hydrophilic residues)
(right domain: hydrobic core surrounded by short alpha helices)
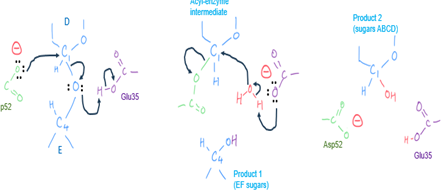
substrate: triNAG
the active site cleft binds 6 sugars (ABCDEF)
the glycosidic bond between the 4th and 5th sugar (D-E) is the bond broken in the reaction
lysozyme active site
lysozyme binds the peptidoglycan carbohydrate polyer so that a NAM ring is at side D and a NAG ring at site E in the binding site on the enzyme surface
the D-E glycosidic bond is close to the side chain of Glu35 and Asp52. Both have carboxylic acid side chains
Asp52
is in the carboxylate form as expected at pH 6 (optimum pH for lysozyme reaction)
Glu35
has an unusual raised pKa because it is in a hydrophobic microenvironment and is in the carboxylic acid form at pH 6
lysozyme mechanism
nucleophilic attack by Asp52 forms covalent acyl enzyme intermediate
Glu35 donayes a proton and sugars E-F diffuses away (first product)
attack by water: OH added to C1 of D and a proton to Glu35
sugars A-B-C-D are the 2nd product