Taste and Smell
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
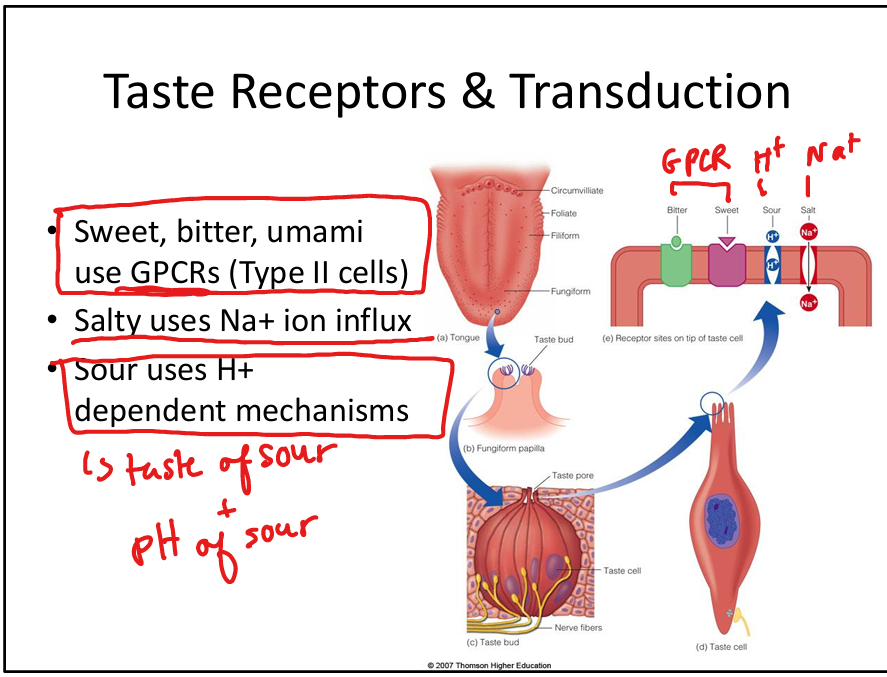
Describe the receptor types for taste.
Taste uses GPCRs for sweet, bitter, umami; ion channels for salty (Na+ influx) and sour (H+ mechanisms).

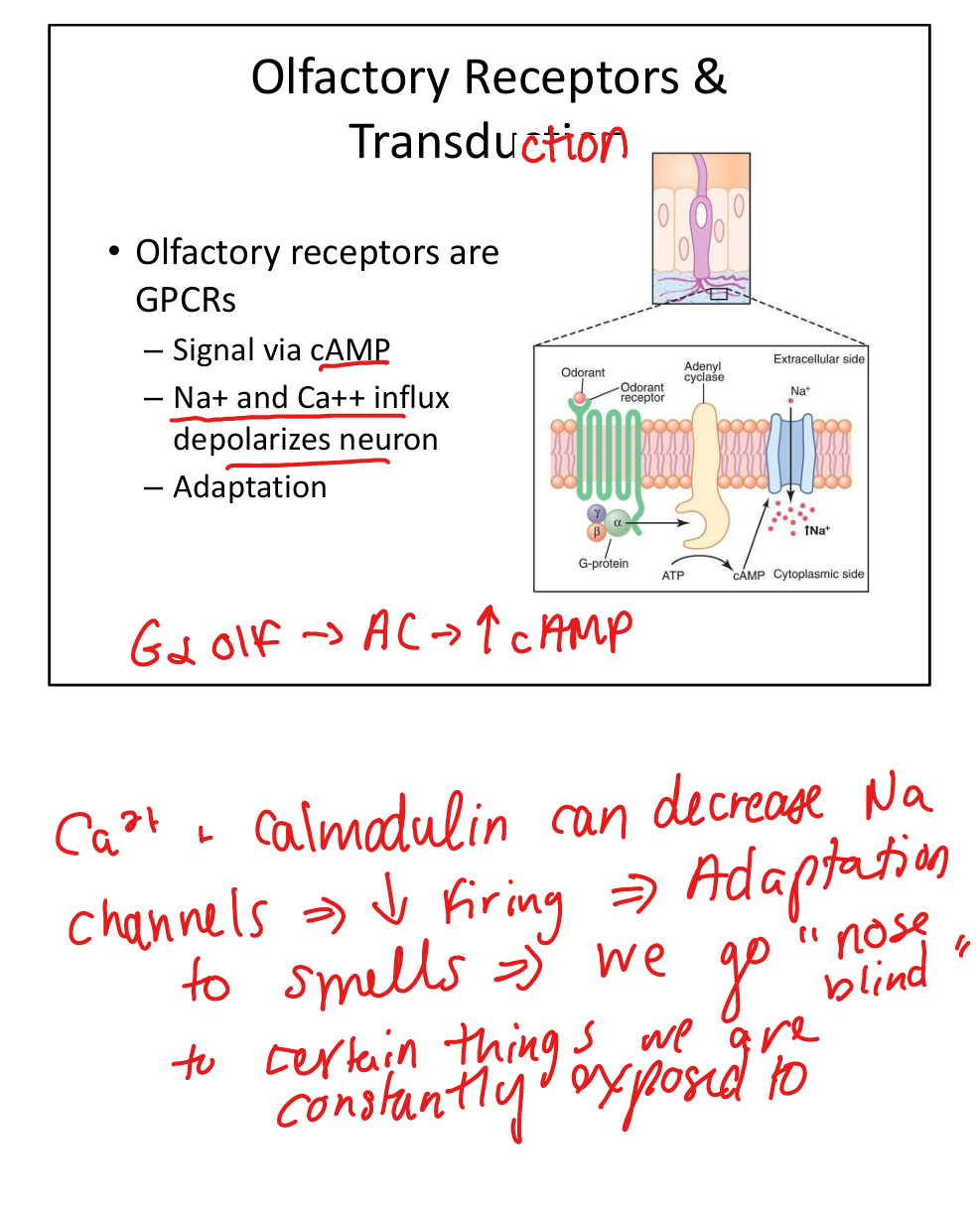
Describe the receptor types for smell.
Olfactory receptors are GPCRs that signal via cAMP, causing Na+ and Ca2+ influx and depolarization.

Which cranial nerves carry taste?
CN VII (anterior 2/3 tongue), CN IX (posterior 1/3), CN X (epiglottis/larynx/pharynx).
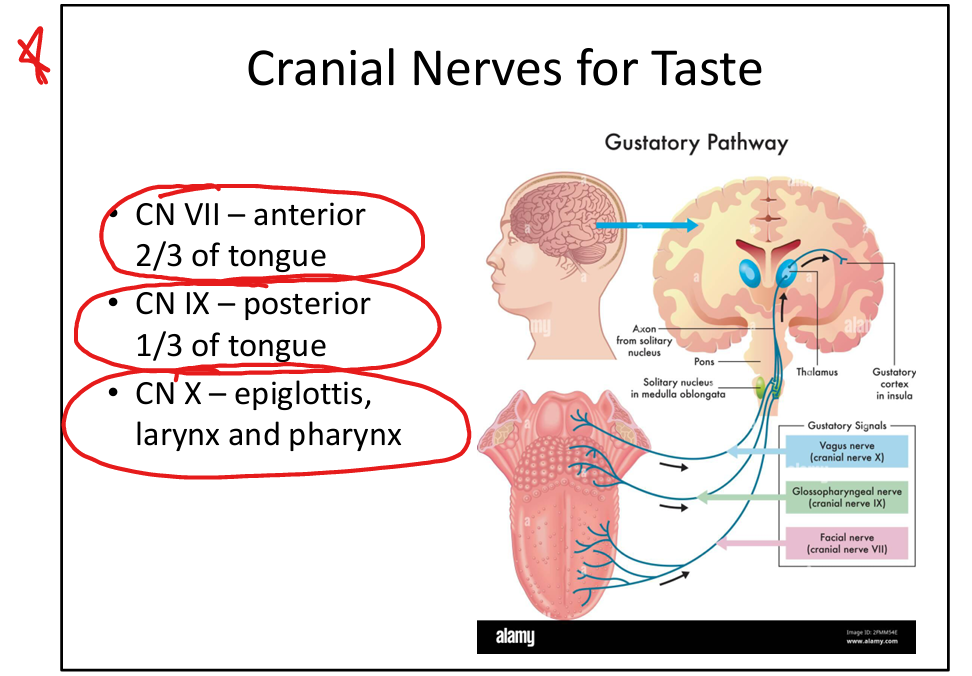

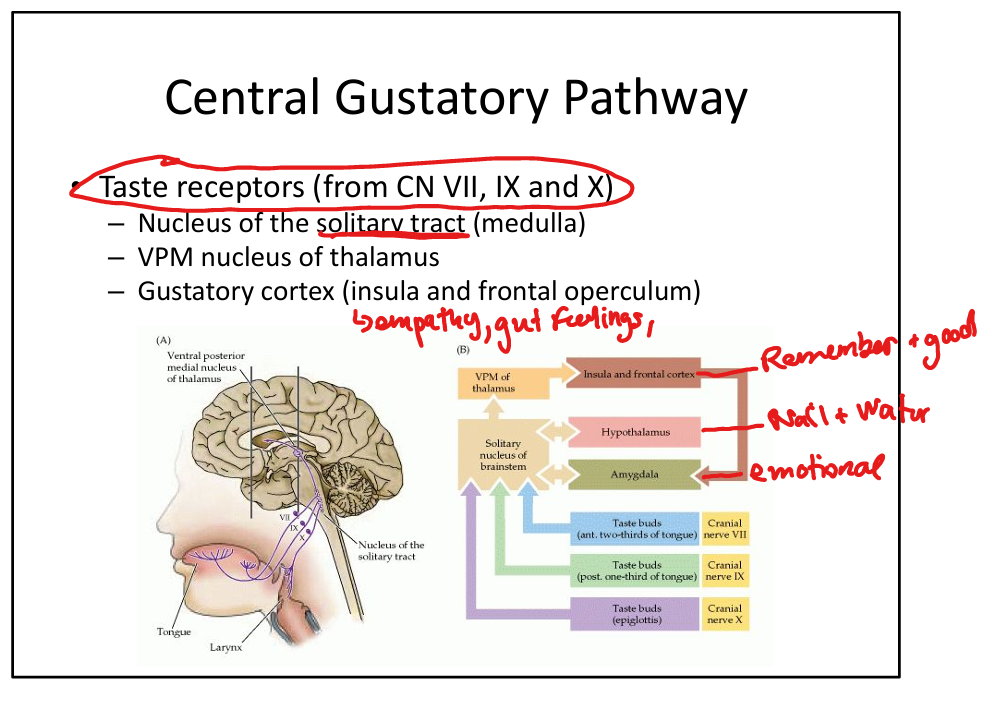
Where do taste pathways project after the solitary nucleus?
CN VII, IX, X>Solitary nucleus>VPM nucleus of the thalamus → gustatory cortex (insula + frontal operculum)>hypothalamus +amygdala

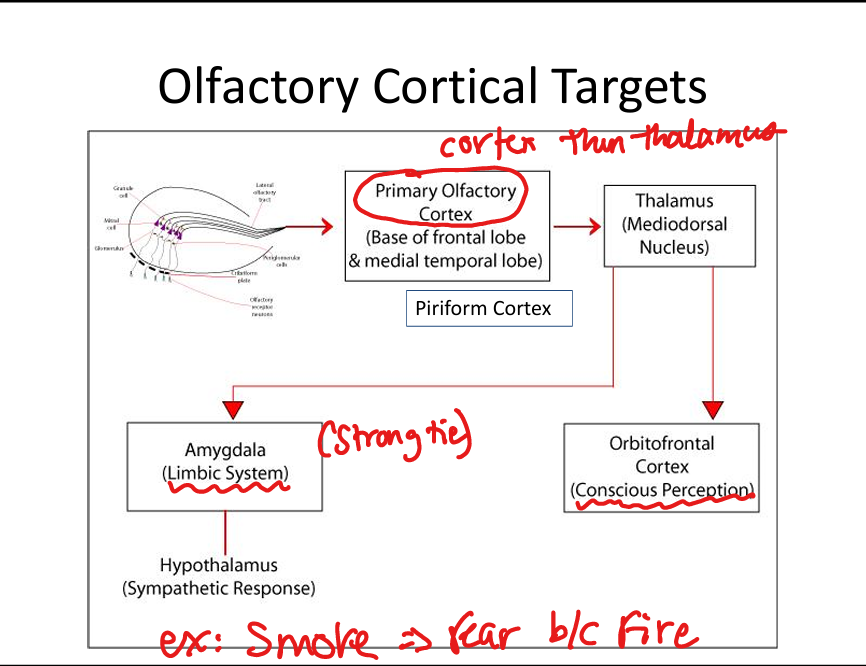
Where do olfactory receptor neurons project?
Through cribriform plate → olfactory bulb → olfactory tract→primary olfactory cortex→Thalamus→Orbitofrontal Cortex and Amygdala

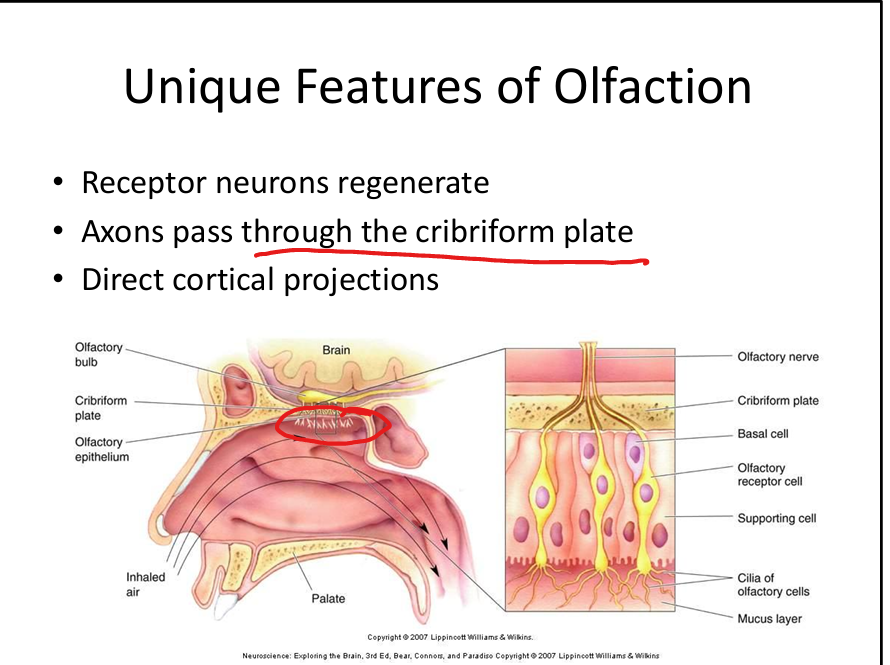
What makes olfaction unique among senses?
Receptor neurons regenerate; bypasses thalamus initially; direct cortical projections.

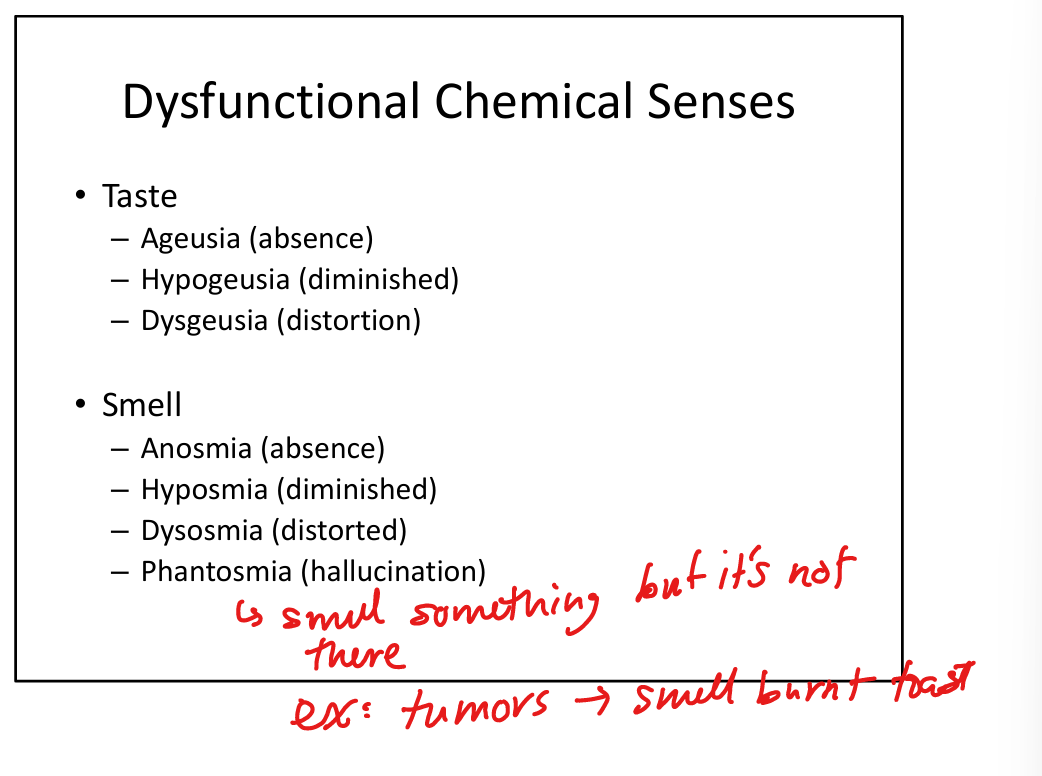
Define ageusia.
Complete loss of taste.
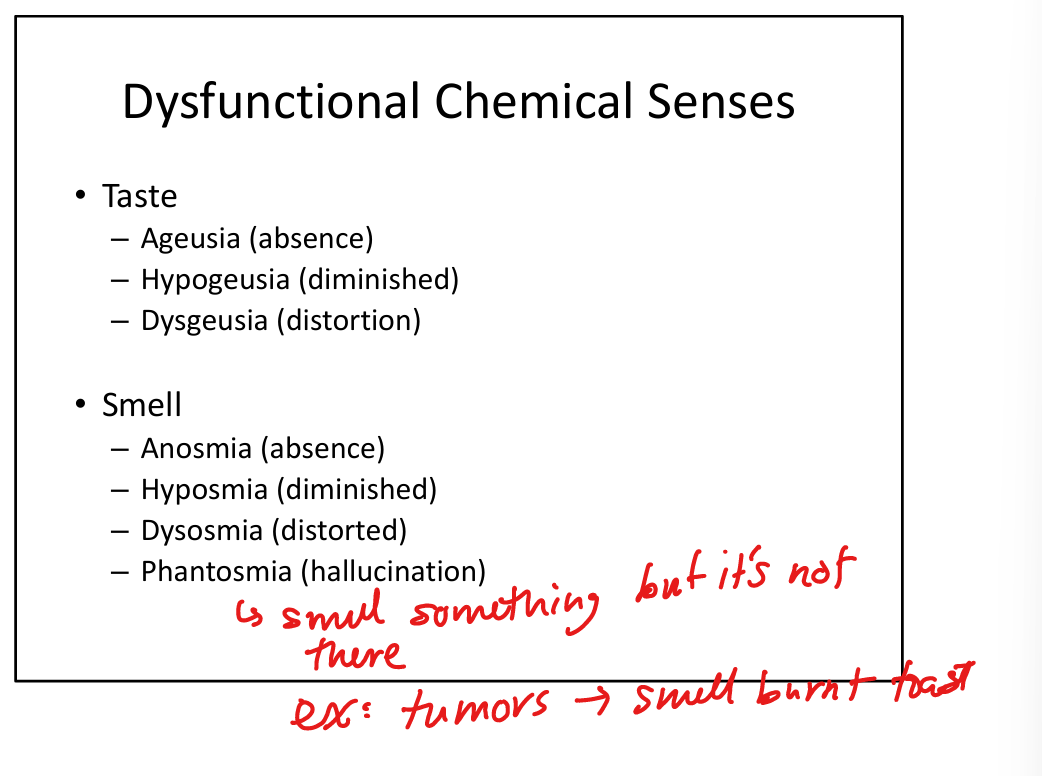

Define hypogeusia.
Reduced taste sensation.
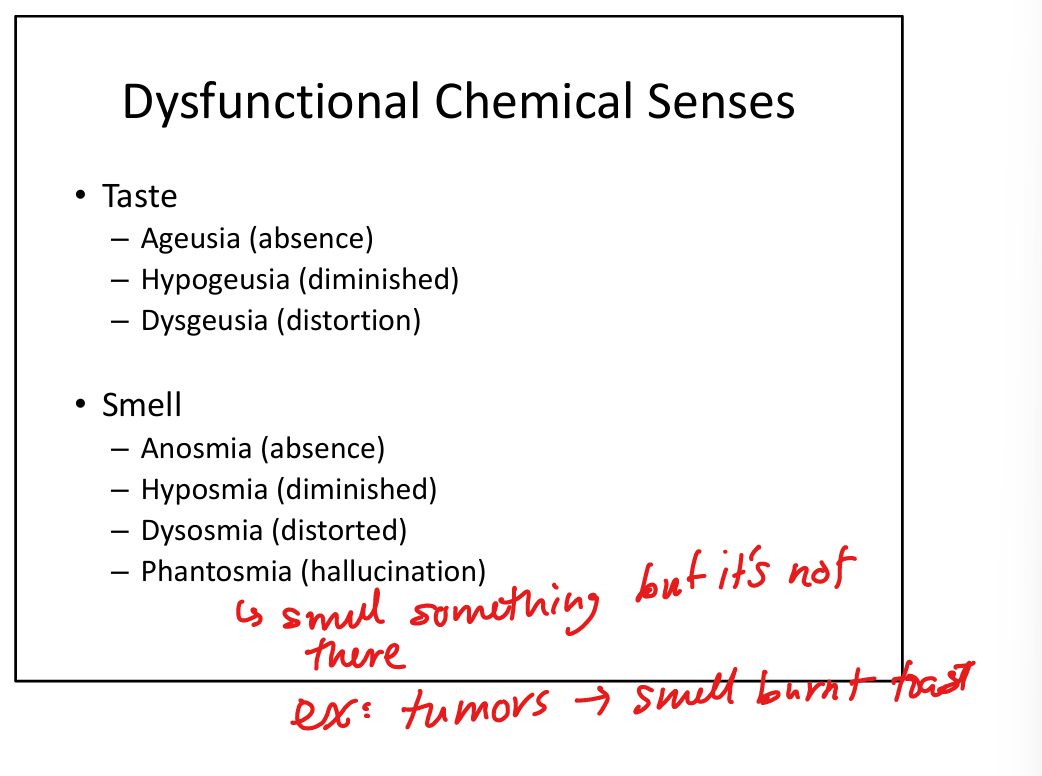

Define dysgeusia.
Distorted taste.
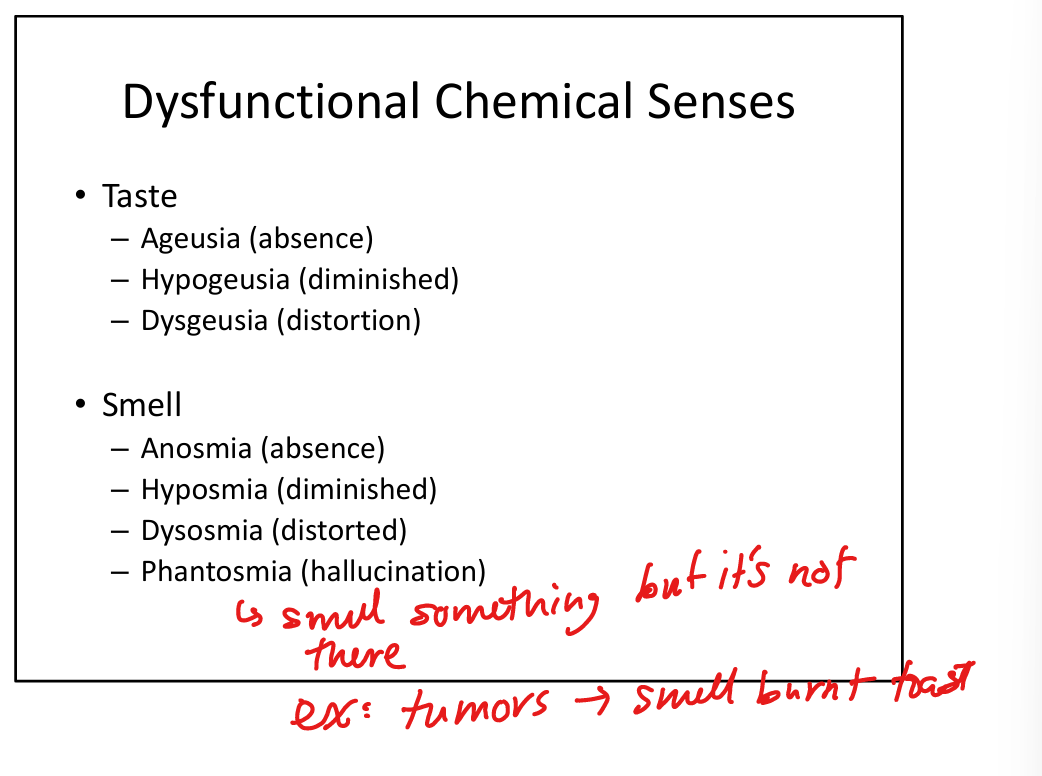

Define hyposmia.
Reduced smell.
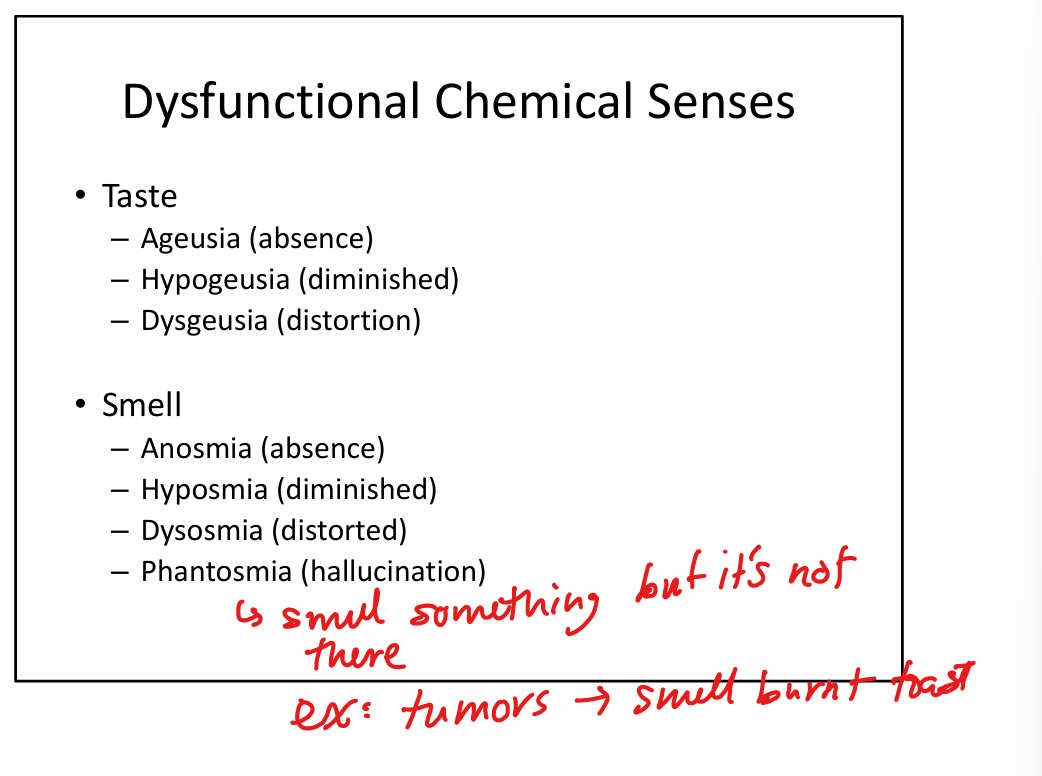

Define dysosmia.
Distorted smell perception.
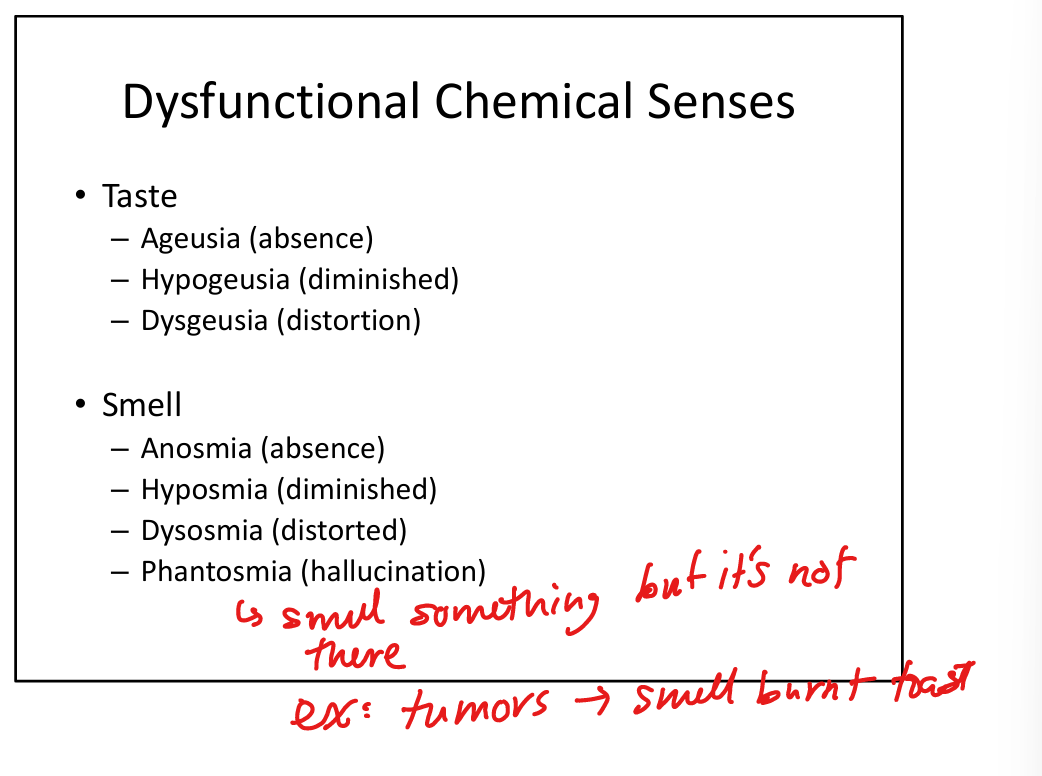

Define phantosmia.
Smell hallucinations (odor perceived without stimulus).

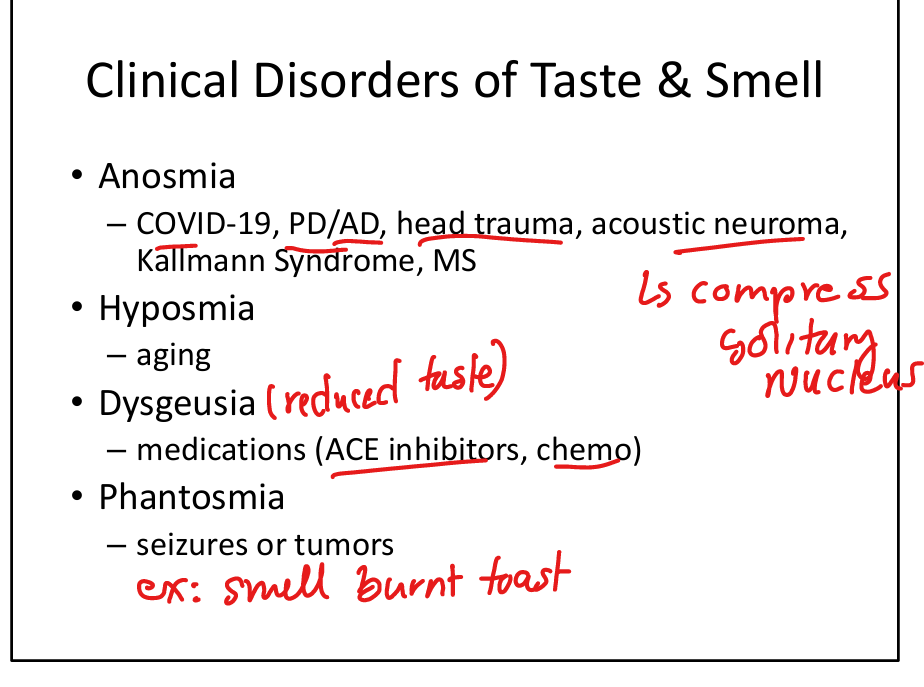
List causes of anosmia.
COVID‑19, Parkinson disease, Alzheimer disease, head trauma, acoustic neuroma, Kallmann syndrome, MS.
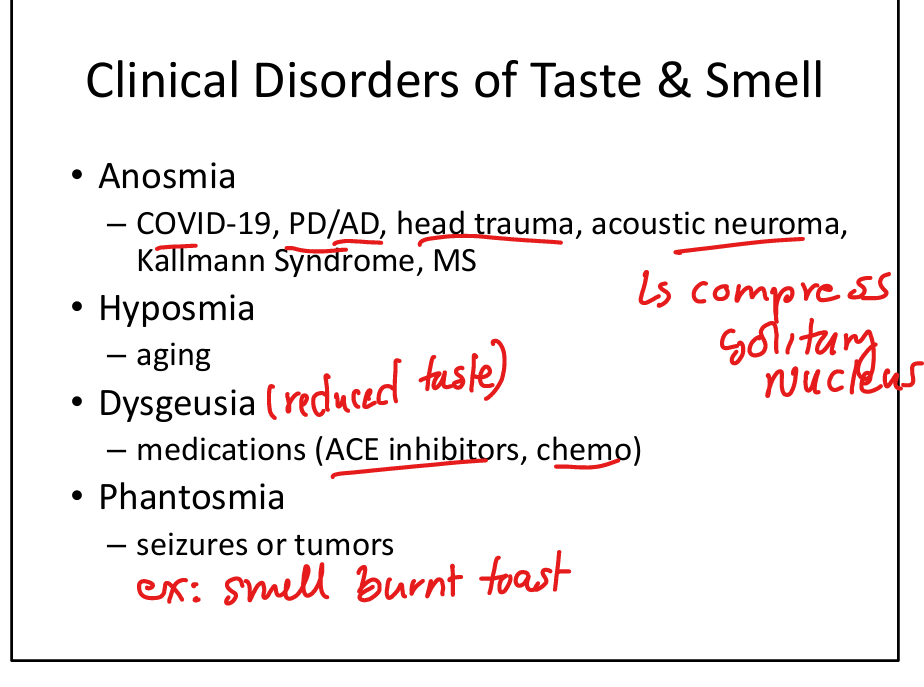

List causes of dysgeusia.
Medications (ACE inhibitors, chemotherapy).

Explain retronasal olfaction.
Odorants from the mouth reach nasal cavity during eating; major contributor to flavor perception.


What nerve adds “irritation” sensations like spicy or minty?
Trigeminal nerve (CN V).


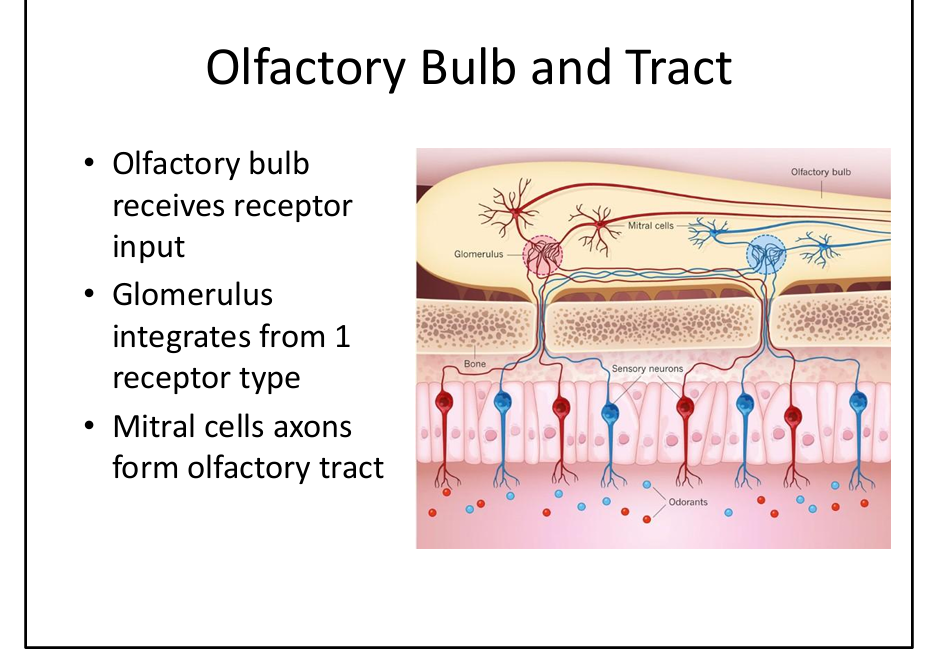
What is the role of the olfactory glomerulus?
Receives input from one receptor type; organizes odor coding.
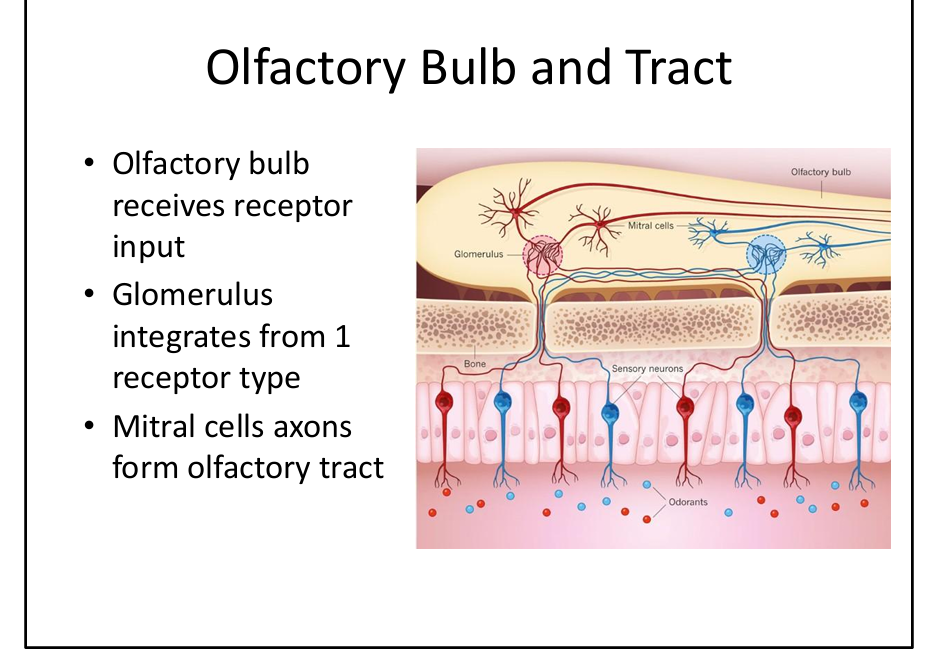

What is the role of mitral cells?
Second‑order neurons that form the olfactory tract.

What is the clinical significance of olfactory dysfunction?
Biomarker for neurodegenerative diseases (PD, AD); common after viral infections.
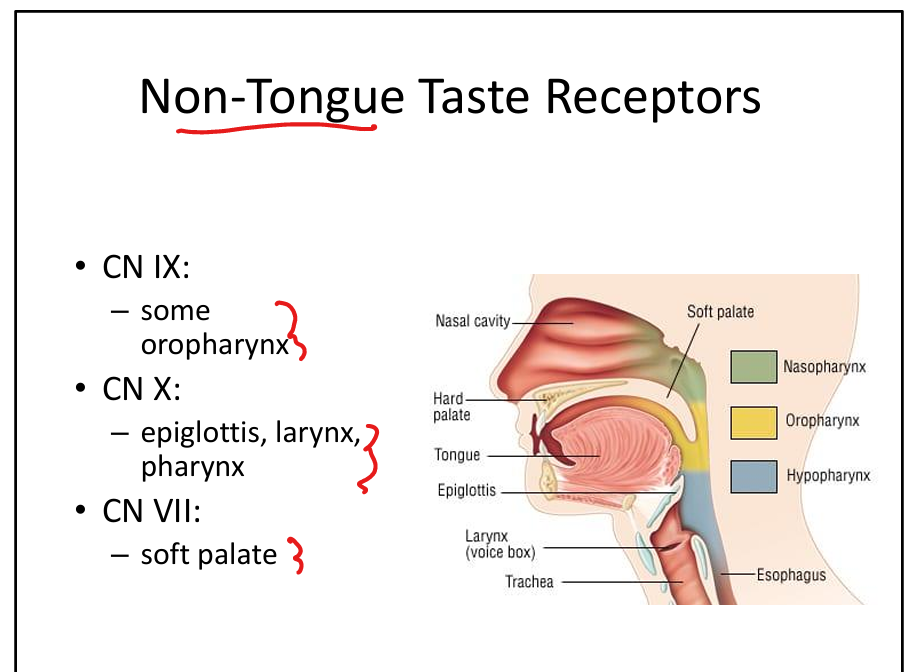
Which cranial nerve senses taste from the soft palate?
CN VII.
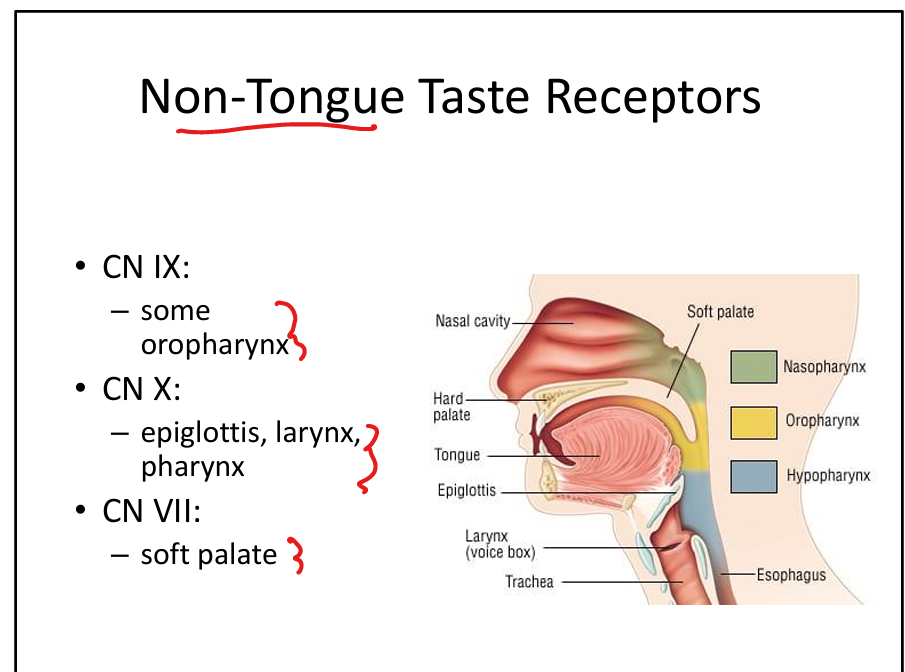

Which cranial nerve senses taste from the oropharynx?
CN IX.
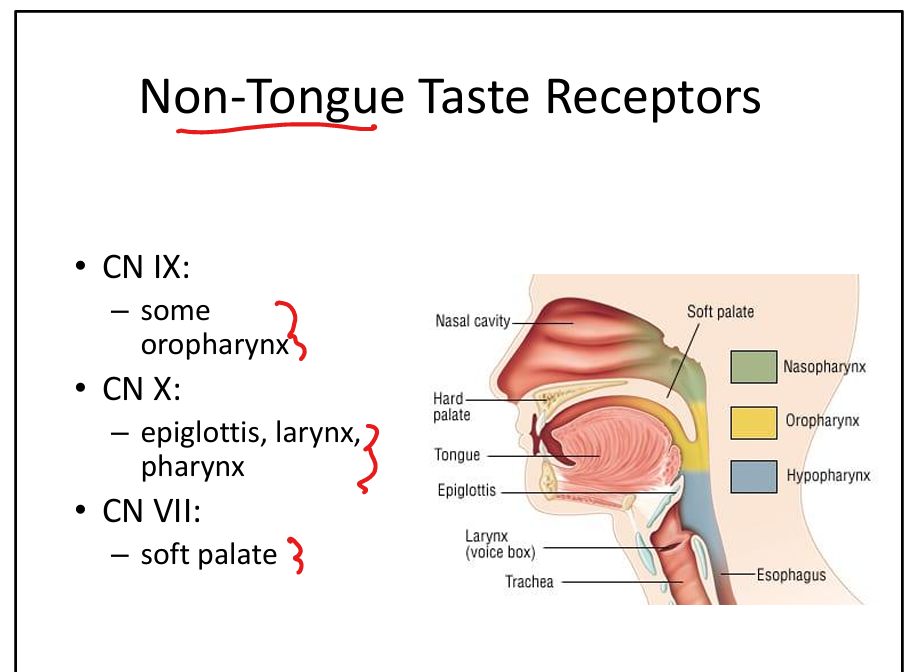

Which cranial nerve senses taste from the epiglottis?
CN X.