Acid-Base Imbalances
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
197 Terms
intracellular fluids (ICF)
inside the cells
extracellular fluids (ECF)
outside the cells
interstitial
intravascular (plasma)
transcellular
electrolyte composition in ICF & ECF
electrolyte composition varies between ICF & ECF, but concentration is nearly the same
fluid compartments of the body
plasma - 3 L
interstitial fluid - 10 L
intracellular fluid - 28 L
1 L of water weighs…
2.2 pounds (1kg)
body weight change is an excellent indicator of
overall fluid volume loss or gain
cations vs anions
cations - positively charged
anions - negatively charged
ICF prevalent cation and anion
cation - K+
anion - PO43-
ECF prevalent cation and anion
cation - Na+
anion - Cl-
diffusion
movement of molecules across a permeable membrane from high to low concentration
facilitated diffusion
uses carrier to help move molecules
active transport
process in which molecules move against concentration gradient
external energy is needed for this process
osmosis
movement of water “down” concentration gradient from region of low solute concentration to one of high solute concentration
across semipermeable membrane
requires no outside energy sources
osmotic pressure
amount of pull required to stop osmotic flow of water
osmolarity vs osmolality
osmolarity → measures the total mOsm/L of solution
osmolality → measures the number of mOsm/kg of water
how to calculate the plasma osmolality
plasma osmolality = (2 x Na) + (BUN / 2.8) + (glucose / 18)
normal plasma osmolality
between 280 and 295 mOsm/kg
greater than 295 mOsm/kg =
water deficit
less than 275 mOsm/kg =
water excess
isotonic
same as cell interior → same osmolarity
hypotonic
solutes less concentrated than in cells/hypoosmolar → lower osmolarity
hypertonic
solutes more concentrated than in cells/hyperosmolar → increased osmolarity
effects of water status on RBC
hypotonic → RBC swell
isotonic → normal
hypertonic → RBC shrink
hydrostatic pressure
force of a fluid in a compartment
blood pressure generated by hearts contraction
oncotic pressure
pressures exerted by colloids (ex. proteins such as albumin)
fluid movement in capillaries amount and direction is determined by
capillary hydrostatic pressure
plasma oncotic pressure
interstitial hydrostatic pressure
interstitial oncotic pressure
edema is caused by
shifts of plasma to interstitial fluid
elevation of venous hydrostatic pressure
decreased in plasma oncotic pressure
elevation of interstitial oncotic pressure
first spacing
normal distribution
second spacing
abnormal accumulation of interstitial fluid (edema)
third spacing
fluid is trapped where it is difficult or impossible for it to move back into cells or blood vessels (burns, blisters)
hypothalamic-pituitary regulation
osmoreceptors in hypothalamus sense fluid deficit or increase
deficit stimulates thirst and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) releases
decreased plasma osmolality (water excess) suppresses ADH release
increase in plasma osmolarity or decreased in circulating blood volume =
stimulation of ADH
what is renal regulation
when the kidneys regulate fluid and electrolyte balance
adjusts urine volume
selective reabsorption of water and electrolytes
what are renal tubules sites of
sites of action of ADH and aldosterone
adrenal cortical regulation
releases hormones to regulate water and electrolytes
hormones include ….
glucocorticoids (cortisol)
mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
cardiac regulation of water balance
natriuretic peptide are antagonists to the RAAS
hormones made by cardiomyocytes in response to increased atrial pressure
they suppress secretion of aldosterone, renin, and ADH to decrease blood volume and pressure
GI regulation of water balance
oral intake accounts for most water
small amounts of water are eliminated by GI tract in feces
diarrhea and vomiting can lead to significant fluid and electrolyte loss
for geriatric pts, structural changes in kidneys decrease ability…
to conserve water
for geriatric pts, hormonal changes include a
decrease in renin and aldosterone and increase in ADH and ANP
for geriatric pts subcutaneous tissue loss leads to..
increased moisture loss
fluid and electrolyte imbalances are directly caused by
illness or disease (burns or heart failure)
result of therapeutic measures (colonoscopy preparation, diuretics)
what is hypovolemia
ECF volume deficit
abnormal loss of body fluids
inadequate fluid intake
plasma to interstitial fluid shift
dehydration
loss of pure water without corresponding loss of sodium
hypervolemia
fluid volume excess
excess intake of fluids
abnormal attention of fluids
interstitial-to-plasma fluid shift
what is the most common clinical manifestation of fluid volume excess (hypervolemia)
weight gain
interprofessional care for hypovolemia
correct underlying cause and replace water and electrolytes
orally
blood products
balanced IV solutions
interprofessional care for hypervolemia
remove fluid without changing electrolyte composition or osmolality of ECF
diuretics
fluid restriction
restriction of sodium intake
removal of fluid to treat ascites or pleural effusion
nursing diagnoses for ECF volume deficit
fluid imbalance
impaired cardiac output
acute confusion
potential complication of ECF volume deficit
hypovolemic shock
nursing diagnoses for ECF volume excess
fluid imbalance
impaired gas exchange
impaired tissue integrity
activity intolerance
disturbed body image
potential complications of ECF volume excess
pulmonary edema
ascites
what are sodium imbalances typically associated with
parallel changes in osmolality
sodium plays a major role in..
ECF volume and concentration
generating and transmitting nerve impulses
muscle contractility
regulating acid-base
hypernatremia
high serum sodium may occur with inadequate water intake, excess water loss, or sodium gain
what does hypernatremia cause
hyperosmolality leading to cellular dehydration
what is the primary protection against hypernatremia
thirst
symptoms of hypernatremia
dehydration
postural hypotension
weakness
tachycardia
thirst
why is hypernatremia manifested in the central nervous system
dehydration of brain cells
shrinkage of cells
what changes in mental status can hypernatremia cause
drowsiness
restlessness
confusion
lethargy
seizures
coma
nursing diagnoses for hypernatremia
electrolyte imbalances
fluid imbalances
risk for injury
potential complications: seizures and coma
treatment for hypernatremia
primary water deficit → replace fluid orally or IV with isotonic or hypotonic fluids
excess sodium → dilute with sodium-free IV fluids and promote sodium excretion with diuretics
hyponatremia
results from loss of sodium-containing fluids and/or from water excess
clinical manifestations of hyponatremia
mild → headache, irritability, difficulty concentrating
more severe → confusion, vomiting, seizures, coma
nursing diagnoses for hyponatremia
electrolyte imbalance
risk for injury
acute confusion
potential complications: seizures and coma
treatments for hyponatremia if the cause is water excess →
fluid restriction may be only the only treatment
loop diuretics
demeclocyline
severe symptoms (seizures) → give small amounts of IV hypertonic saline solution (3% NaCl)
treatments for hyponatremia if the cause is abnormal fluid loss
fluid replacement with isotonic sodium-containing solution
encouraging oral intake
witholding diuretics
drugs that block vasopression (ADG)
Convaptan (Vaprisol)
Tolvaptan (Samsca)
potassium is necessary for.. (MAJOR ICF CATION)
resting membrane potential of nerve and muscle cells
cellular growth
maintenance of cardiac rhythms
acid-base balance
sources of potassium
protein-rich food
fruits and vegetables
salt substitutes
potassium medications (PO, IV)
stored blood
what is potassium regulated by
the kidneys
what is hyperkalemia caused by
impaired renal excretion
shift from ICF to ECF
massive intake of potassium
some drugs
hyperkalemia is most common in what disease?
renal failure
manifestations of hyperkalemia
dysrhythmias
fatigue, confusion
tetany, muscle cramps
weakened or paralyzed skeletal muscles
abdominal cramping/diarrhea
nursing diagnoses for hyperkalemia
electrolyte imbalance
activity intolerance
impaired cardiac output
potential complication: dysrhythmias
how do you stabilize cardiac cell membranes in hyperkalemic pts
IV calcium gluconate
how do you force K+ from ECF to ICF
by IV insulin with dextrose and an alpha agonist or sodium bicarbonate
hypokalemia causes
increased loss of K+ via the kidneys or gastrointestinal tract
increased shift of K+ from ECF to ICF
Dietary K+ deficiency (rare)
renal losses from diuresis
manifestations of hypokalemia
cardiac most serious
skeletal muscle weakness (legs)
paralysis
weakness of respiratory muscles
respiratory arrest
decreased GI motility
hyperglycemia
what increases digoxin toxicity
low K+ level
nursing diagnoses for hypokalemia
electrolyte imbalance
activity intolerance
impaired cardiac output
potential complication: dysrhythmias
how to give IV KCl
always dilute
never push K+ or bolus
do not exceed 10 mEq/hr
must use an infusion pump
what is the function of calcium
formation of teeth and bone
blood clotting
transmission of nerve impulses
myocardial contractions
muscle contraction
what are the most common causes of hypercalcemia
hyperparathyroidism causes 2/3 cases
rest is caused by malignancy
how is calcium obtained
dietary intake
needs vitamin D to absorb
what affects calcium levels
changes in pH and serum albumin affect levels
what is calcium balance controlled by and what do they do
parathyroid hormone - increases bone resorption, GI absorption, and renal reabsorption of calcium
calcitonin - increases calcium deposition into bone, increases renal calcium excretion, and decreases GI absorption
manifestations of hypercalcemia
fatigue, lethargy, weakness, confusion
hallucinations, seizures, coma
dysrhythmias
bone pain, fractures, nephrolithiasis
polyuria, dehydration
nursing diagnoses of hypercalcemia
electrolyte imbalance
acute confusion
impaired physical mobility
potential complication → dysrhythmias
nursing interventions for hypercalcemia
low calcium diet
increased weight-bearing activity
increased fluid intake
hydration with isotonic saline infusion
biphosphonates
calcitonin
hypocalcemia is caused by
decreased production of PTH
multiple blood transfusion
alkalosis
increased calcium loss
manifestations of hypocalcemia
positive trousseau’s or chvostek’s signs
laryngeal stridor
dysphagia
numbness and tingling around the mouth or in the extremities
dysrhythmias
paresthesia, circumoral numbness
monitor pts with thyroidectomy for…
hypocalcemia
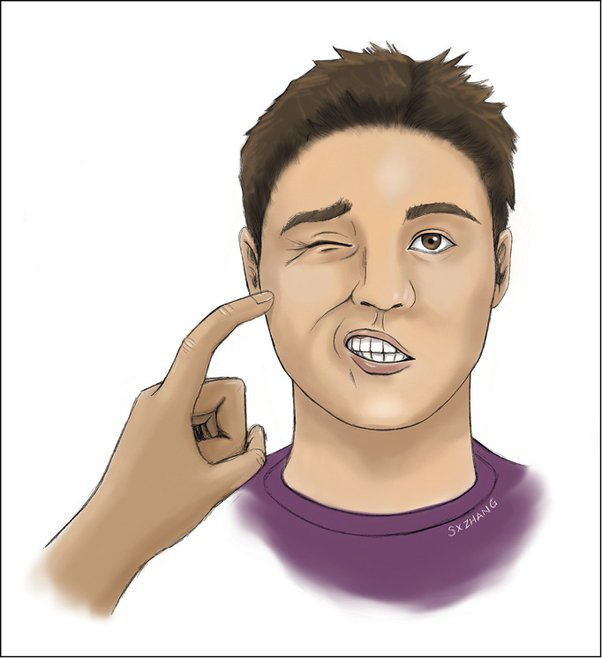
chovstek’s sign

Trousseau sign
nursing diagnoses for hypocalcemia
electrolyte imbalance
impaired breathing
activity intolerance
potential complication : fracture, respiratory arrest
treatment for hypocalcemia
treat cause
calcium and vitamin D supplements
IV calcium gluconate
rebreathe into paper bag
treat pain and anxiety to prevent hyperventilation → induced respiratory alkalosis
what does phosphate do
primary anion in ICF
essential to function of muscle, red blood cells, and nervous system
involved in acid-base buffering system, ATP production, cellular uptake of glucose, metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and facts
serum levels of phosphate is controlled by…
parathyroid hormone
maintenance of phosphate requires….
adequate renal functioning
phosphate has a reciprocal relationship with…
calcium
What causes hyperphosphatemia
acute kidney injury or chronic kidney disease
excess intake of phosphate or vitamin D
hypoparathyroidism