Cell Structure
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Resolution
-min distance between two objects in which they can still be viewed as separate objects
-determined by the wavelength of light in a light microscope & by the wavelength of the electron beam in an electron microscope
Magnification
-How many times larger the image is compared to the object
-magnification= image size/actual size
Types of microscope
-light optical microscope
-transmission electron microscope
-scanning electron microscope
Eyepiece graticule
-small piece of glass with measurement scale etched on its surface that fits inside a microscope eyepiece
Calibrating the eyepiece graticule
-Line up the stage micrometer and eyepiece graticule whilst looking through the eyepiece
-Count how many divisions on the eyepiece graticule fit into one division on the micrometer scale
-Each division on the micrometer is 10μm, so this can be used to calculate what one division on the eyepiece graticule is at the current magnification
differential staining
-technique involving many different chemical stains being used to stain different parts of a cell in different colours
E.g. crystal violet and acetic orcein
Stage micrometer
-A microscope slide that has a ruler/scaled bar etched into it.
-The scale is usually 1mm long and has 100 divisions so each division is 10μm.
-It is used to calibrate the eyepiece graticule.
How does TEM work
-sample must thin and stained
-beam of electrons passes through the sample used to create an image
-focused using electromagnets in a vacuum
TEM evaluations
-Highest revolving power
-High magnification
-Extremely thin specimens required
-Complex staining method
-Specimen must be dead
-Vacuum required
How does SEM work
-Beam of electrons pass across the sample used to create an image of the surface of the sample
-Focussed using electromagnets
SEM evaluation
-High resolving power
-High magnification
-Thick specimens unusable
-Complex staining method
-Specimen must be dead
-Vacuum required
what can you see with TEM
2D image of details within organelles
what can you see with SEM
3D image of the surface of cells and organelles
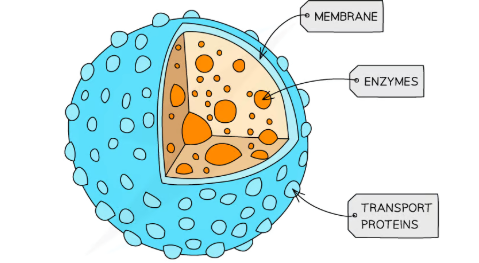
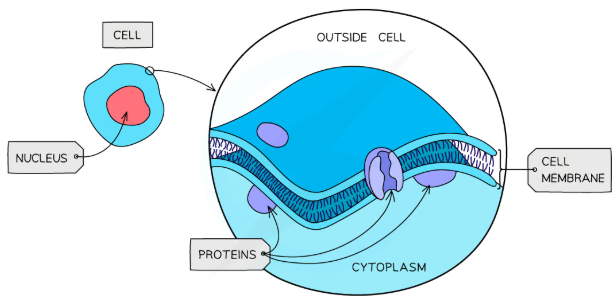
plasma membrane structure
Phospholipid bilayer with embedded intrinsic and extrinsic proteins
plasma membrane structure diagram

plasma membrane function
-Maintain structural integrity
-act as a barrier
-control passage of substances in and out of the cell
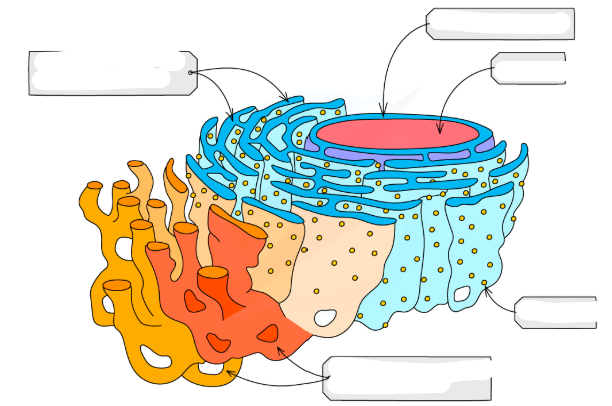
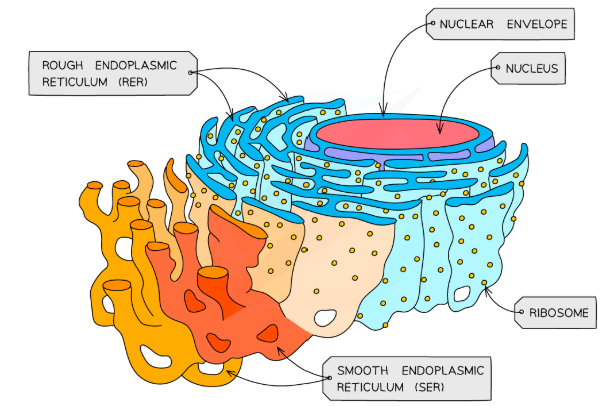
Nucleus structure
-Surrounded by a double membrane nuclear envelope with nuclear pores
-contains chromosomes with proteins bound, linear DNA
-Contains nucleolus to synthesise ribosomes
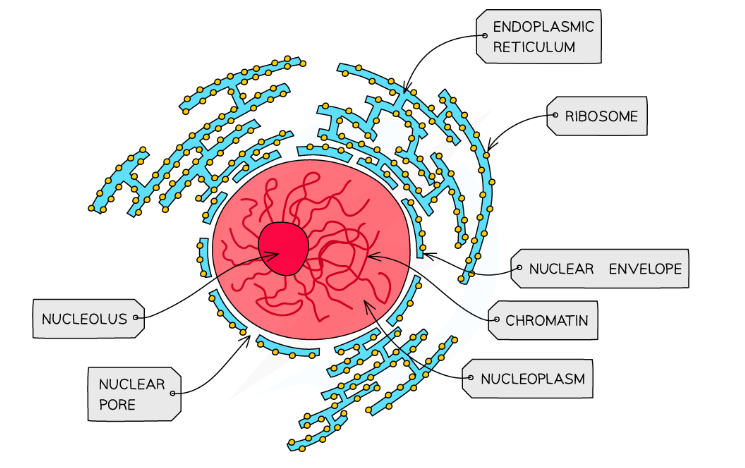
Nucleus function
contains DNA
site of transcription and primary mRNA splicing
Site of DNA replication
Nucleolus makes ribosomes
Nuclear pore allows movement of substances to/from cytoplasm
cilia structure
hair like projections out of cell
cilia function
-Can be mobile or stationary
-Mobile cilia help move substances in a sweeping motion
-Stationary cilia are important in sensory organs, such as the nose
flagella structure
whip like structure
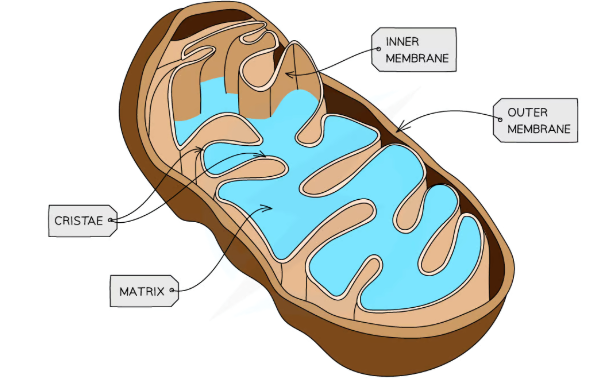
mito structure
-dbl membrane with inner membrane folded into cristae
-Fluid-filled centre called matrix
-70S ribosomes in matrix
-Small, circular DNA
-Enzymes in matrix
mito function
site of aerobic respiration
atp production
centriole structure
-made of microtubules
-occur in pairs to form a centrosome
centriole function
-involved in production of spindle fibre
-organisation of chromosomes in cell division
lysosome structure
Vesicles formed from the golgi apparatus and which contain hydrolytic enzymes
lysosome function
-type of golgi vesicle that releases lysozymes to hydrolyse pathogens/cell waste products
cytoskeleton structure
-network of fibres found within the cytoplasm all over a cell
-Consists of microfilaments, microtubules and intermediate fibres
-Microfilaments are responsible for cell movement
-Microtubules are responsible for creating a scaffold-like structure
cytoskeleton function
-mechanical strength to cells
-maintain the shape and stability of a cell
-forms a network for organelles to move around the cell on
ribosome structure
Small organelles in cells made up of protein and rRNA
Ribosomes are made up of a small and large subunit (80S size in eukaryotes)
ribosome function
Site of protein synthesis
Site of translation in protein synthesis
RER structure
-RER = rough endoplasmic reticulum
-System of membranes with bound ribosomes that is often continuous with the nucleus
RER function
The site of protein synthesis (translation)
SER structure
SER = smooth endoplasmic reticulum
System of membranes with no bound ribosomes
SER function
Create, store and transport lipids chand carbohydrates
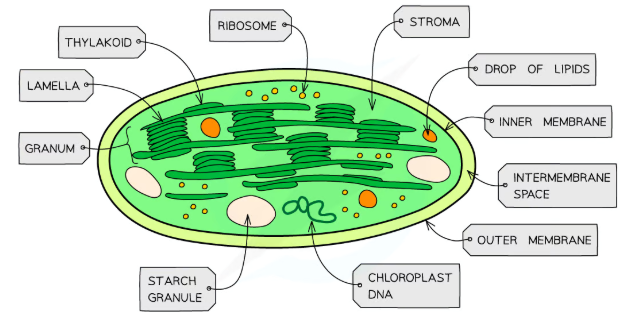
chloroplast structure
-double membrane bound organelle
cell wall structure
-found in plants, algae and fungi
-plants: made of polysaccharide cellulose
-fungi: made of chitin
-bacteria: peptidoglycan
cell wall function
-provides structural strength to cells
-prevents cells from bursting from osmotic pressures
-provides shape, support and structure
organelles involved in secretion of protein
-Polypeptide chains synthesised in the RER
-chains are packaged into vesicles to be sent to the golgi apparatus via the cytoskeleton
-they are to be modified
-from the golgi they are package into secretory vesicles carry the protein to the cell membrane
-to be released via exocytosis
contrast prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic cells are smaller
Prokaryotes have no membrane-bound organelles
Prokaryotes have smaller 70S ribosomes
Prokaryotes have no nucleus-circular
DNA is not associated with histones
Prokaryotic cell wall made of peptidoglycan instead of cellulose/chitin
Possible extra organelles of prokaryotes
Plasmids: loops of DNA
Capsule surrounding the cell wall: gives protection from the immune system
Flagella: locomotion
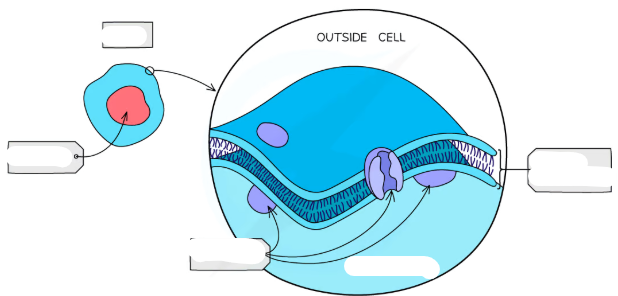
lysosome structure diagram