e5
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
In the development of segmented animals, the earliest-acting acting of the genes listed are the
maternal effect genes
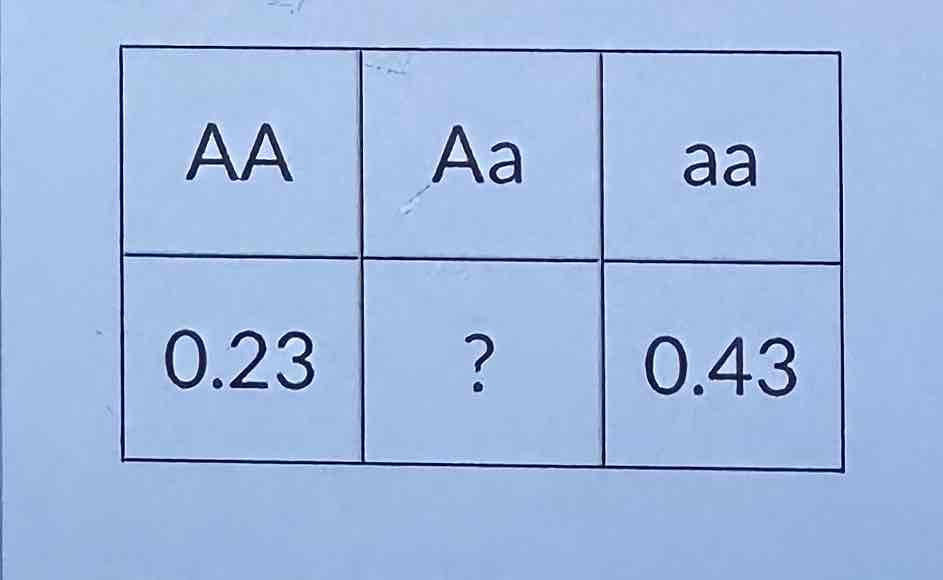
For the table above, what is the frequency of the A allele? Round your answer to the nearest 0.01
0.40
In Drosophila, bicoid mRNA is ____ in the anterior end of the egg by the ________
deposited; mother
Genetic drift is the result of
the random sampling of alleles during reproduction
In a Drosophila zygote, bicoid protein is present ____________, where the bicoid protein ____________ the zygote will develop head structures.
in a gradient, concentration is highest
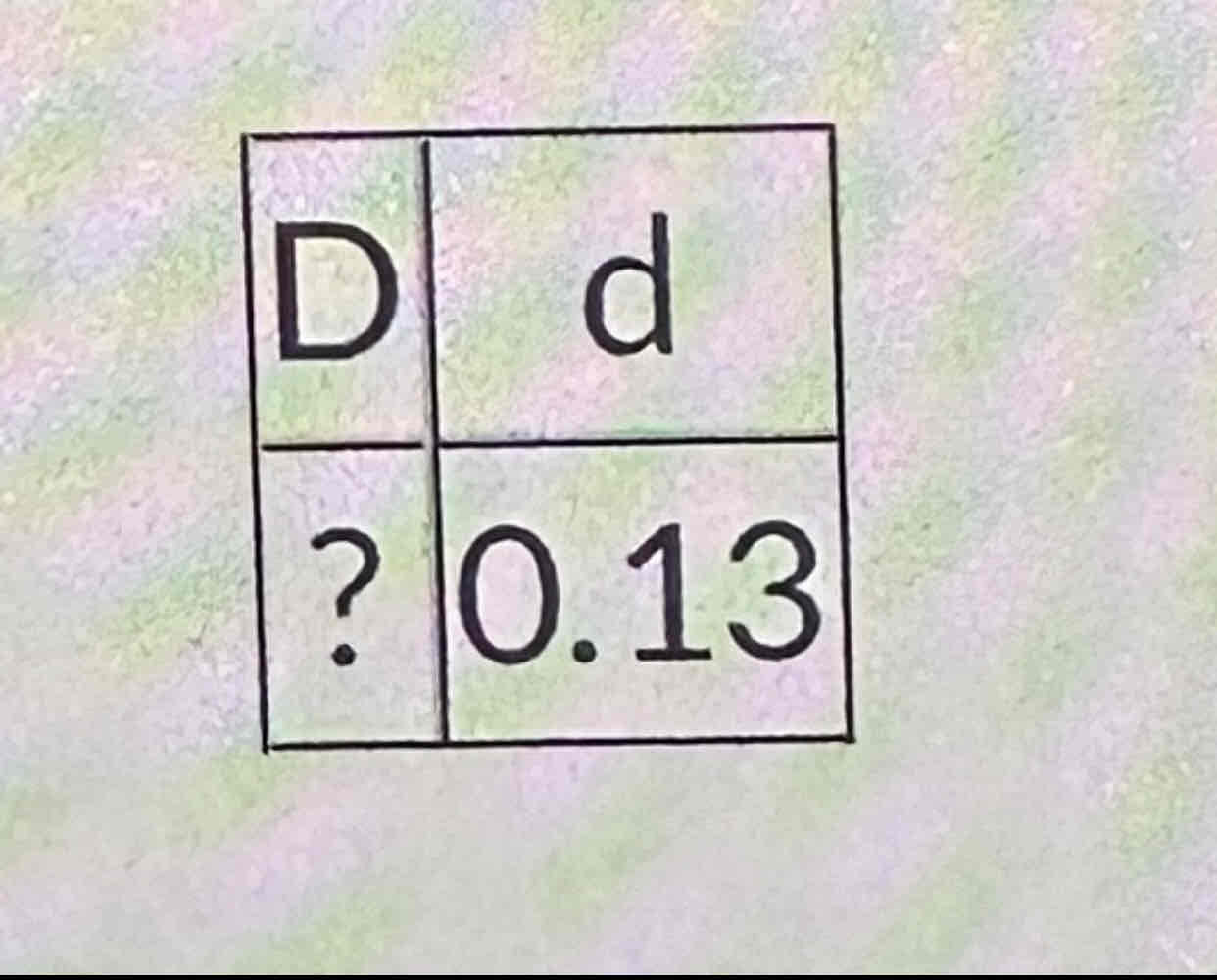
Fill in the table above, then answer: What is the Hardy-Weinberg expected frequency for the DD homozygote?” Round to the nearest 0.01
0.76
Oncogenic mutations in a proto-oncogene are typically __________; oncogenic mutations in a tumor-supressor gene are typically _______.
dominant; recessive
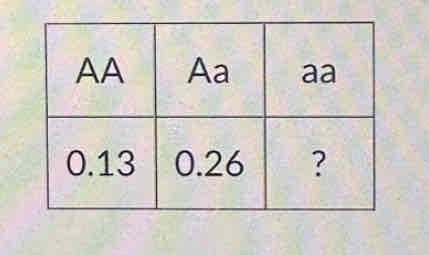
For the table above, what is the frequency of the a allele? Enter as a decimal number rounded to the nearest 0.01
0.74
A morphogen ________________________ that ______________ and impacts cells __________________________.
can be either a hormone or a protein; moves primarily by diffusion; in proportion to concentration
The normal function of oncogenes is often to
pass a signal from the cell surface to the nucleus
The normal function of tumor-suppressor genes is often to
control a cell-cycle checkpoint
This question is about genetic drift. Assume that drift is the only process acting on the population. At the start of your study, the frequency of the A allele in a population was 0.62. Today, the frequency of the A allele in the same population is 0.17. What is the probability that the A allele will eventually become fixed in the population? Enter your answer as a decimal number between 0 and 1, with two decimal places.
0.17
Which of the following is the best short definition for fitness in population genetics?
The genetic contribution to later generations
Estimating heritability by “elimination of variance components” normally requires
creation of a population of genetically identical individuals
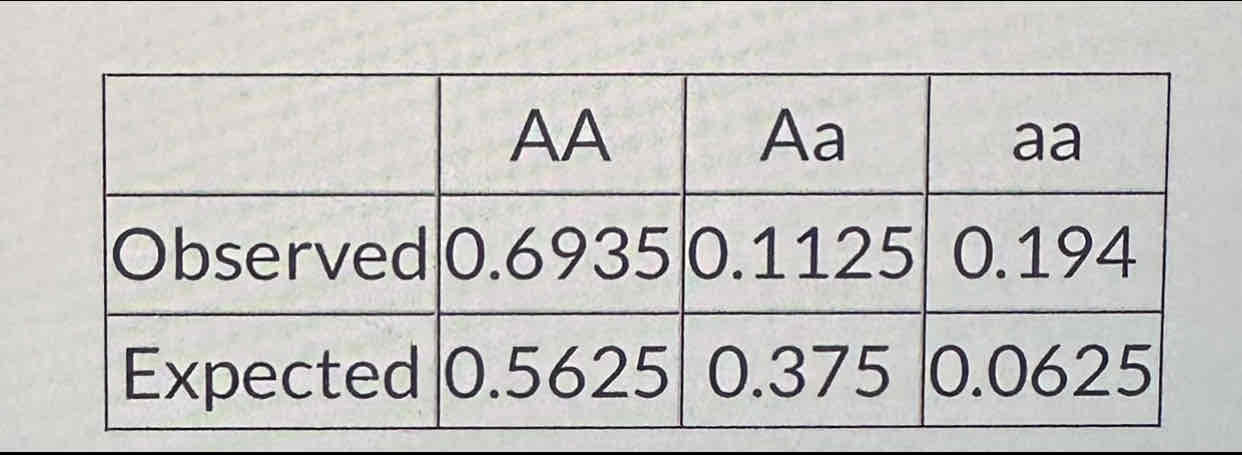
The table shows the observed H-W expected genotype frequencies for a population. What is the inbreeding coefficient for that population? Round your answer to the nearest 0.01
0.7
A grower has bred a new type of outbred heirloom tomato. She wants to know if it is worth the trouble to breed for increased fruit weight. In her original crop, the variance in fruit size was 142. She randomly selected the plant and self-crossed it for a few generations, eventually reaching a generation that was highly inbred. The variance for fruit size in the inbred population 57. What is the broad-sense heritability for fruit size in her original population of the new type of tomato?
0.60
For a normal distribution, what percentage of values fall between +/- 3 standard deviations? enter only numerals.
99
For a qualitative/complex/continuous trait, heritability is determined by
only the genetic component of variance
Finding the specific genes that contribute to a continuous trait phenotype is difficult. The current process is most like which of the following topics covered previously in this course?
Genome-Wide Association Studies
Homeotic genes control
the specific structure that are produced in a body segment
During normal operation, the ____________________ can be stopped at various _______________
cell cycle; checkpoints

For the genotypes in the table and the aspect of fitness measured, what is the relative fitness of the aa genotype?
0.14
In Drosphilia, bicoid
acts as a morphogen
__________ _________ possess homebox genes
Many animals; including humans
In the context of estimating broad-sense heritability, producing an inbred line allows
estimation of the environmental variance in the population
In corn, if plants with large kernels also produce higher sugar content, kernel size and sugar content are ___________ ___________
positively ; correlated
Estimating heritability by “elimination of variance components” describes a process by which one
“zeroes out” the genetic variance
Inbreeding does not
change allele frequencies
During the very earliest stages of embryonic development in segmented animals _______ __________ ______ act by ______ ___________
early transcription factors; binding to the promoter of genes for other transcriptions factors
Quantitative trait phenotypes are encoded by
normal Mendelian genes
Additive traits are those for which the contribution to the trait from each allele is ___ ______ by the genotype _________
not affected; at other loci
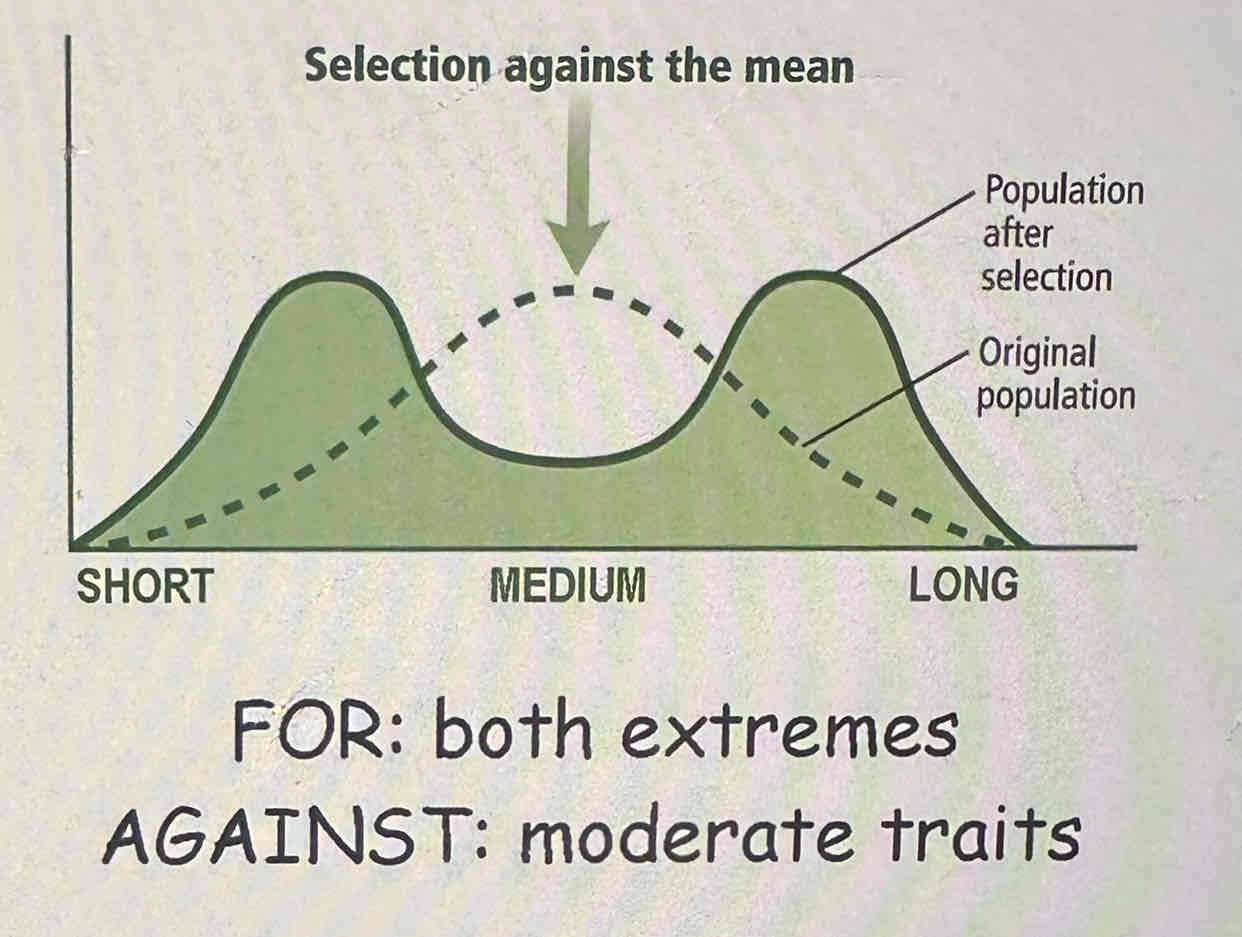
The graph is an illustration of
disruptive selection
Then phenotypes for quantitative traits are produced by the combination of ____ _____ _____ plus ________ effects
multiple contributing loci; environmental
An oncogene/proto-oncogene is active in
both normal and cancerous cells
Drift results in allele frequencies ____ ___ ____. From any one generation to the next, the “expected” _____ _____ ____ ____ __ ____
changing over time; allele frequencies remain the same
“Loss of heterozygosity” refers to
the second mutation in a two-step cancer progression model