Cyberspace and Network Security 🔐
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Digital Technology Unit 1: Digital Technology (Core)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Cyber crime
using a computer to commit a crime
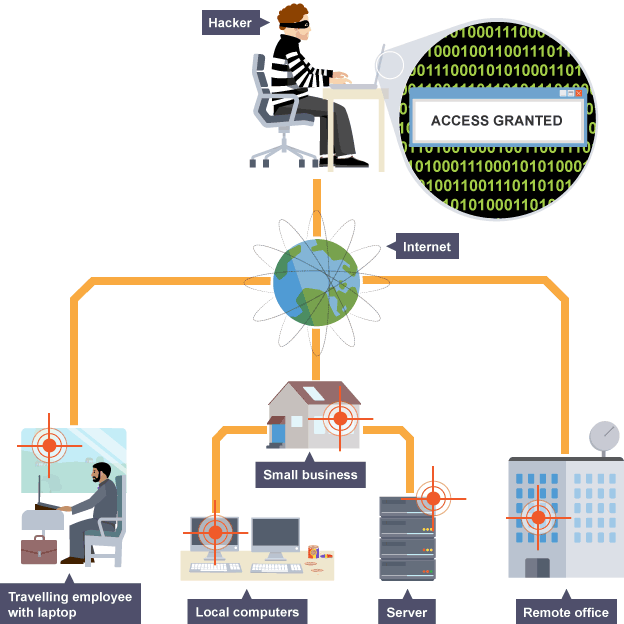
Hacking
gaining unauthorised access to computer system with intention of corrupting and stealing data or other illegal purposes
Pornography
often used to hide malware when downloaded or the distribution of illegal forms
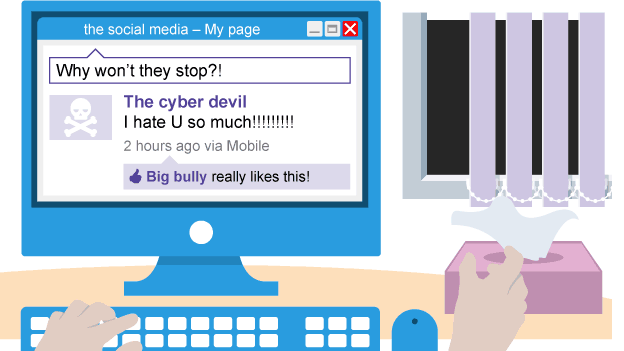
Cyber stalking
online stalking; repeatedly using computer to frighten or harass others e.g inappropriate comments
Data theft
illegal copying or taking of personal data with the intent of gaining confidential information, used for identity fraud e.g passport applications

Denial of service (DoS)
attack to prevent network from functioning by flooding it with useless traffic, users are unable to access
Digital forgery
intentionally creating falsely altered files or documents with intent of misleading others e.g qualifications
Cyber defamation
intentionally damaging reputation of person or organisation with false information over the internet
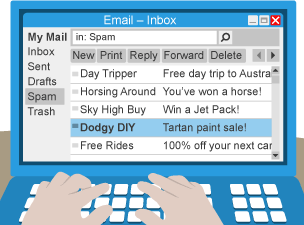
Spamming
bulk sending unsolicited messages to large numbers of internet users indiscriminately to overload their inbox
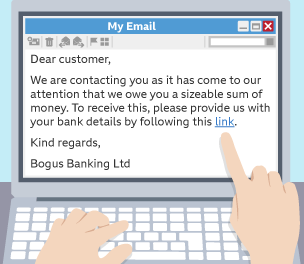
Phishing
Sending emails, appearing to be from reputable companies, to persuade people to disclose private information e.g fake hyperlinks
Malware
malicious software downloaded onto someone’s computer and designed to gain access to or damage it
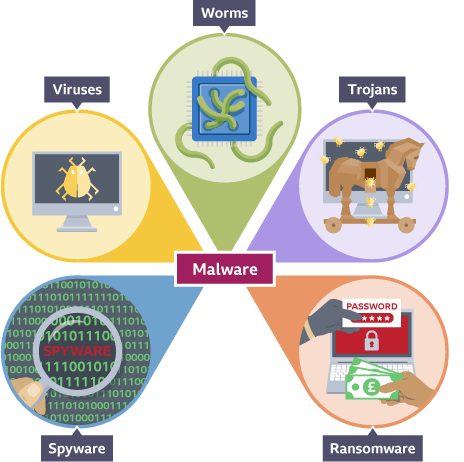
Virus
gains access to device and replicates, attaching onto other files to hide
can copy personal data, delete files or slow down devices when a condition is met
Trojan horse
gains entry in ‘disguise’ by misleading users of its true intentions
tricks into downloading/ installing program that does serious damage
Worm
spreads by replicating itself but works on its own without a host program/ file
requires bandwidth causing slower data transmission speeds
Keylogger
records keystrokes performed by user to steal personal information
saves as file and sends to hacker secretly
Spyware
secretly installed on computer
tracks user activities to gather personal information e.g bank details
Protecting networks
using encryption, passwords, levels of access, backup and firewalls
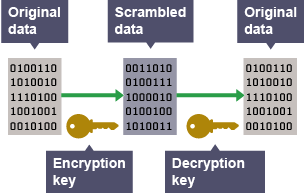
Encryption
using special software to encode or ‘scramble’ data with a key before transmission so it’s unreadable if intercepted
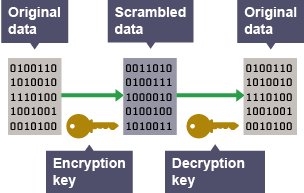
Encryption key
used to unscramble data when arriving at destination
Why use encryption
Helps identify authentic users
Prevents alteration of message
Prevents unauthorised users from reading message
Usernames and passwords
users are allocated unique ID and password which is checked against database when logging on

Secure passwords
weak passwords are easy to guess so should have mix of letters, numbers and special characters
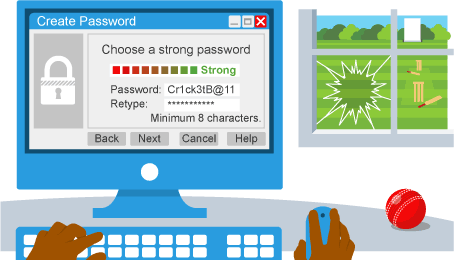
Updating passwords
must be regularly updated to enhance security and accounts can be disabled after unsuccessful attempts
Access levels
different levels linked to user ID which can be ‘read only’, ‘read and copy’ or ‘read and write’
Why use access levels
prevents unauthorised users accessing or altering sensitive information they don’t need
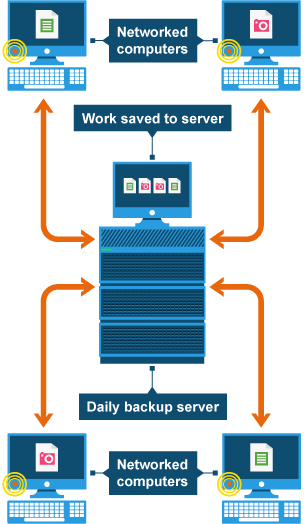
Backups
used to recover data when lost or corrupted by storing a copy that can be loaded, usually automatically scheduled
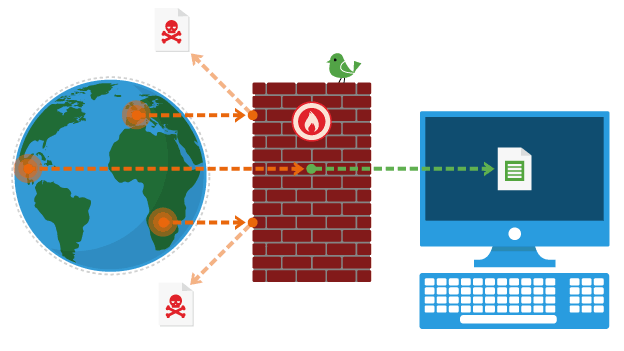
Firewalls
monitor and filter data entering or leaving networks by blocking what doesn’t comply with set rules
Data transfer
transmitting data from point to point easily over the internet, using a digital signal
How does data transfer work
files are stored on web server and can be accessed by any computer using an internet connection, although not very secure so we use transfer protocols
Communication protocols
agreed standards of rules for sending or receiving data on network, managing its speed, size and error checking
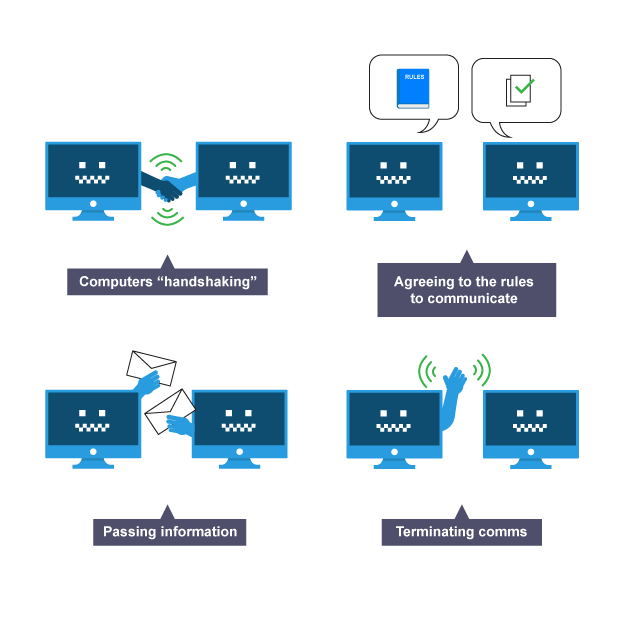
Packet switching
data packets travel between computers from one router to the next
File transfer protocol (FTP)
uses data encryption, allowing users to download or upload files from web servers securely over internet
Hypertext transfer protocol (http)
used by WWW to transfer webpages over the internet, defining how messages are formatted and transmitted
How are webpages requested
http sends command to web sever on behalf of user requesting webpage
If webpage can’t be located
will report an error e.g 404 page not found
Hypertext transfer protocol secure (https)
uses secure socket layer (SSL) to ensure data is transmitted securely via encryption
Indicator of https
padlock icon displayed on screen, mainly in financial applications