Protein Synthesis Lecture Notes
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms and concepts related to protein synthesis, gene expression, and mutations.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Gene
A short segment of DNA that encodes the information to produce a single polypeptide.
Genome
The complete set of genetic information (all the genes) of an organism.
Chromosome
A DNA molecule packaged with proteins; carries many genes. Bacteria typically have one circular chromosome, eukaryotes multiple linear ones.
Genetic Code
The set of rules that translate mRNA codons (triplets of nucleotides) into specific amino acids or stop signals.
Genetics
The study of heredity and variation in organisms, including how DNA differences lead to phenotypic differences.
Genotype
The precise nucleotide sequence (genetic makeup) of an individual organism.
Phenotype
The observable physical or biochemical traits of an organism, determined by its genotype.
One Gene–One Polypeptide Hypothesis
Concept that each gene contains the instructions to make one specific polypeptide chain.
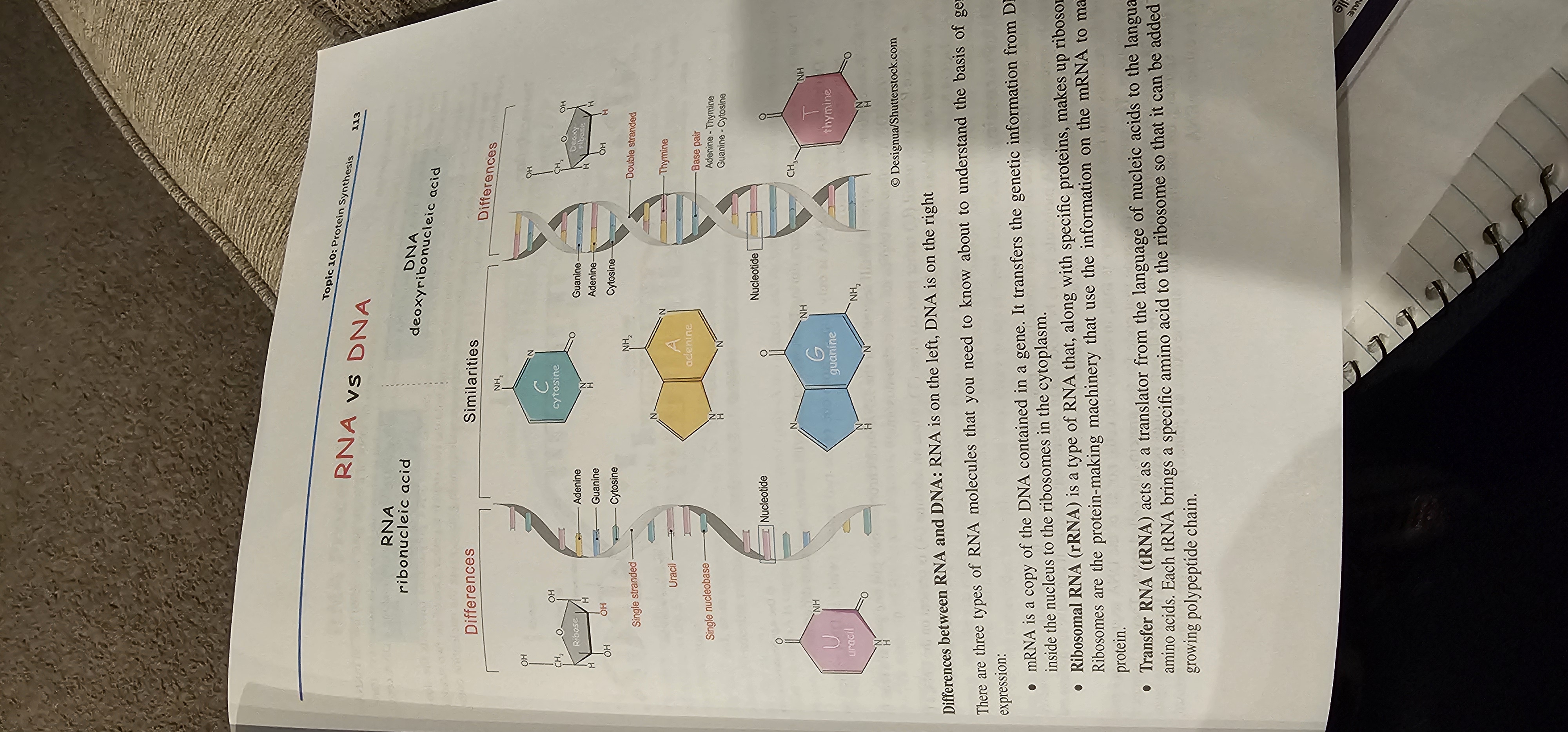
DNA
A double-stranded nucleic acid using deoxyribose sugar and the bases A, T, C, G; stores hereditary information.
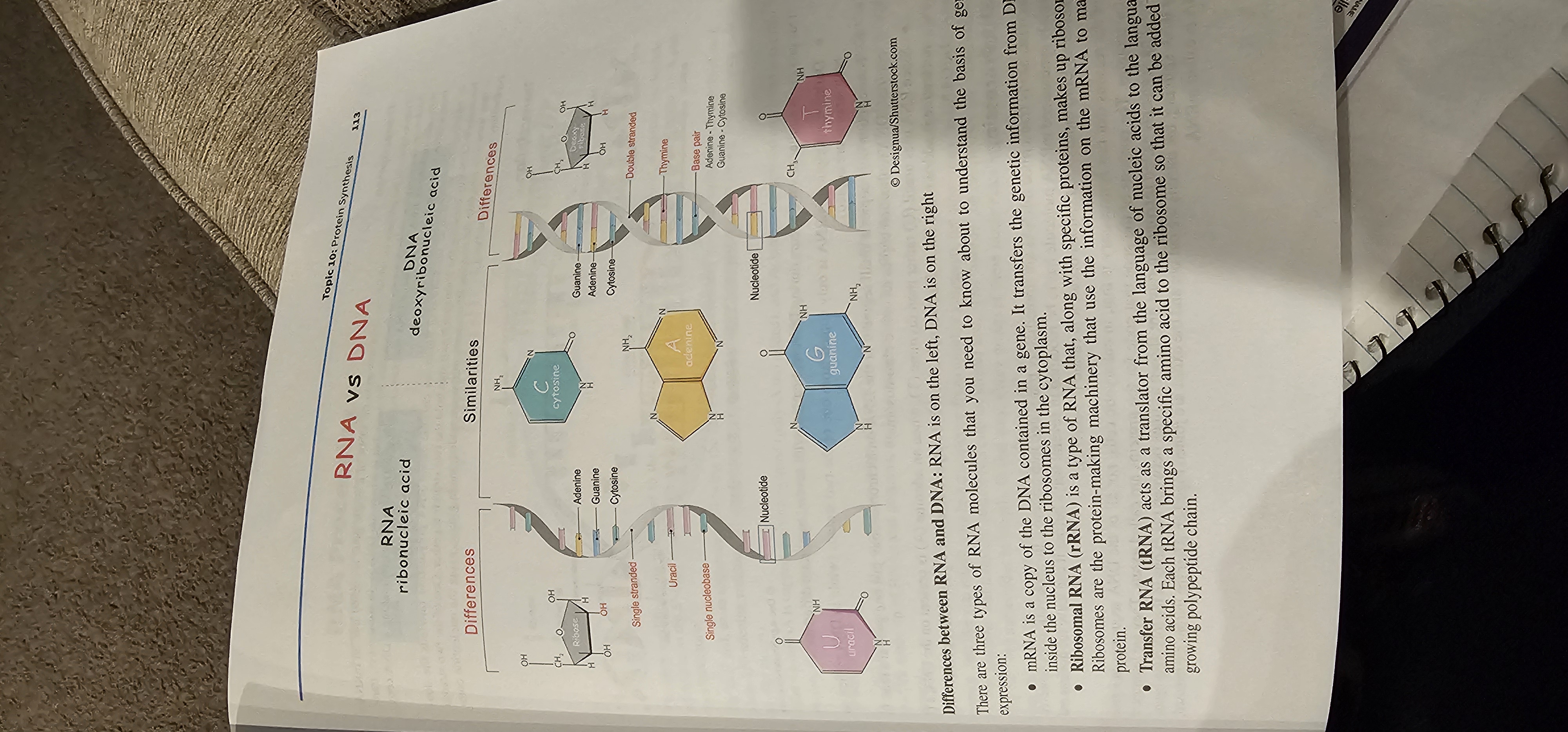
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid using ribose sugar and the bases A, U, C, G; functions in gene expression.
mRNA (Messenger RNA)
An RNA copy of a gene that carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
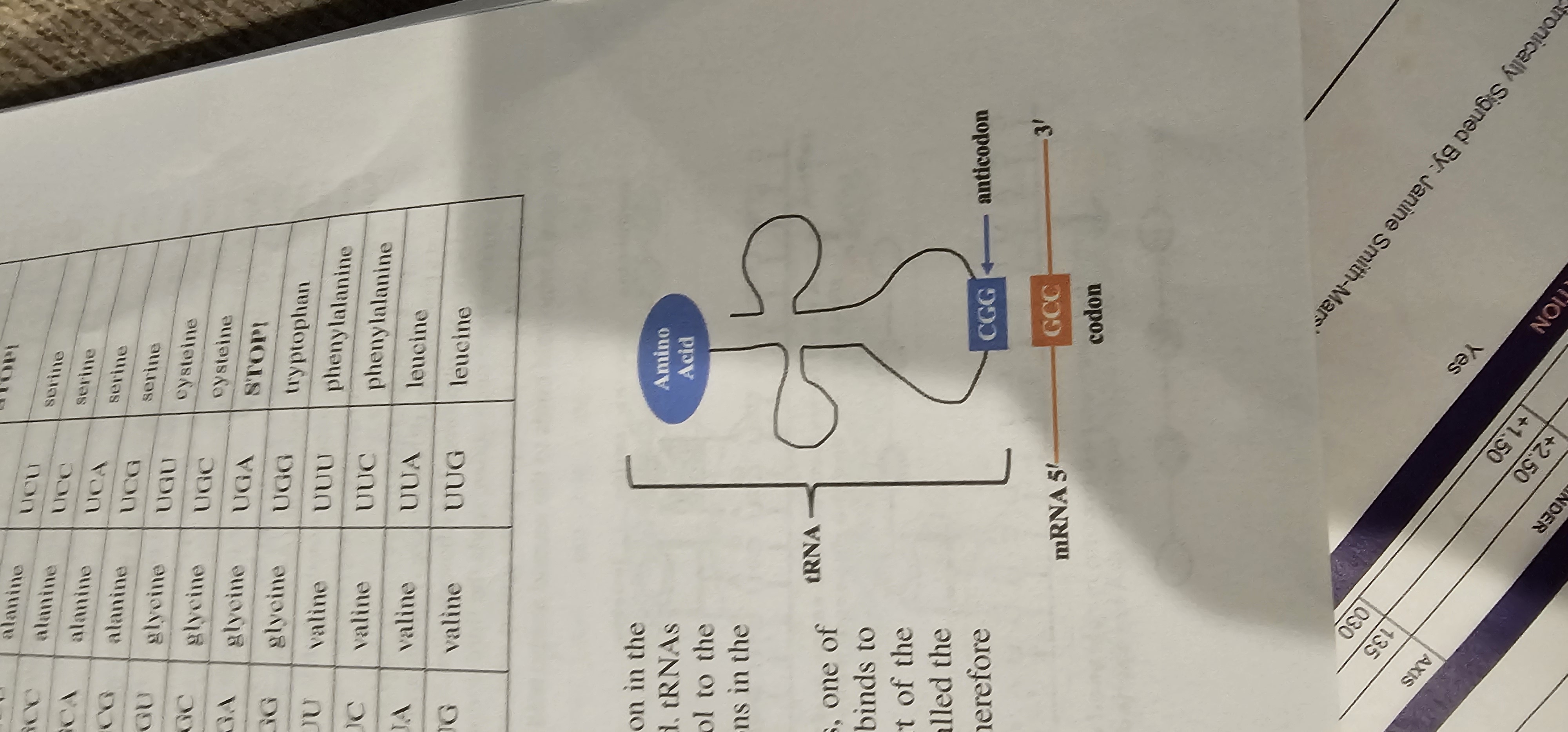
tRNA (Transfer RNA)
Adapter RNA that brings specific amino acids to the ribosome and pairs its anticodon with mRNA codons.
rRNA (Ribosomal RNA)
RNA molecules that, with proteins, compose ribosomes, the sites of protein synthesis.
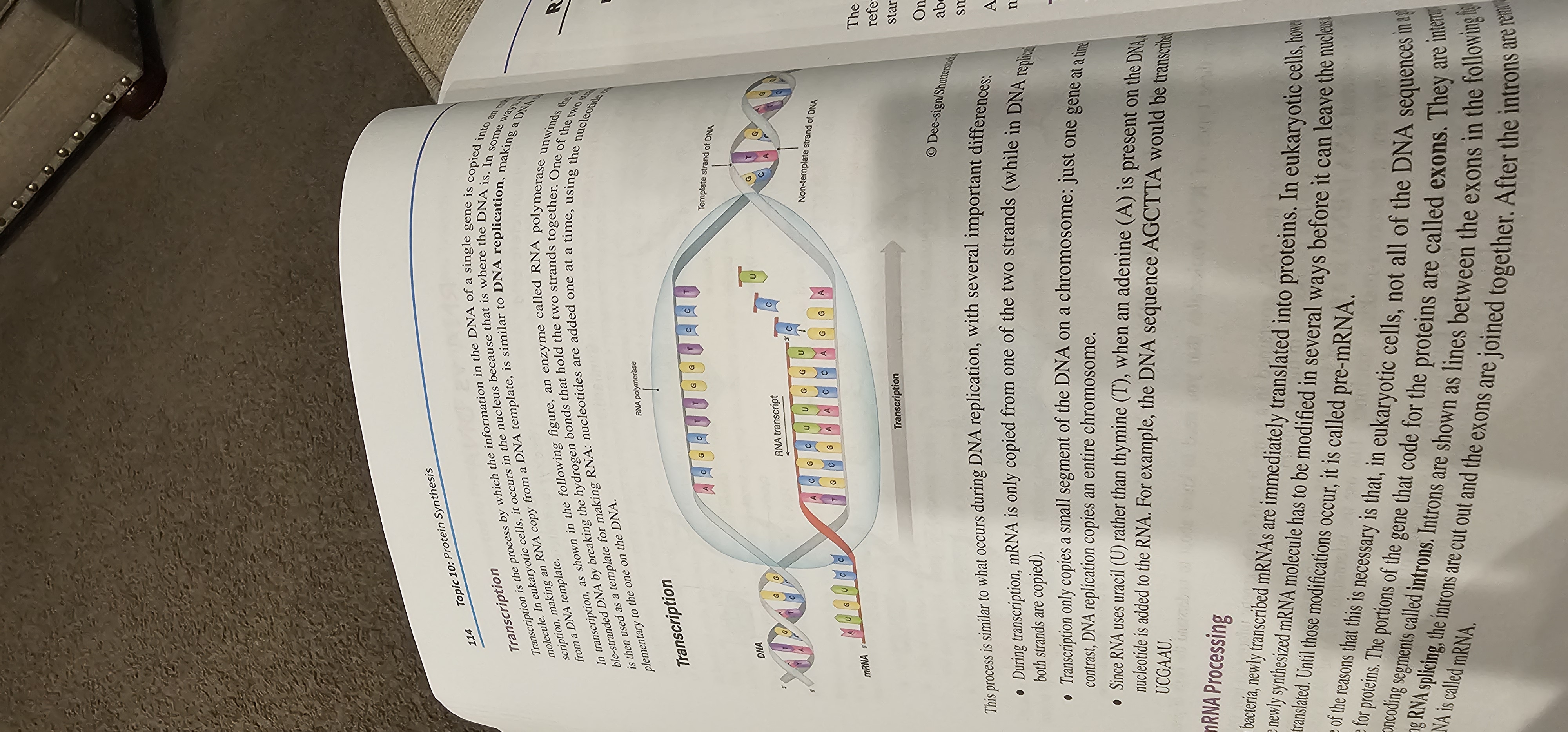
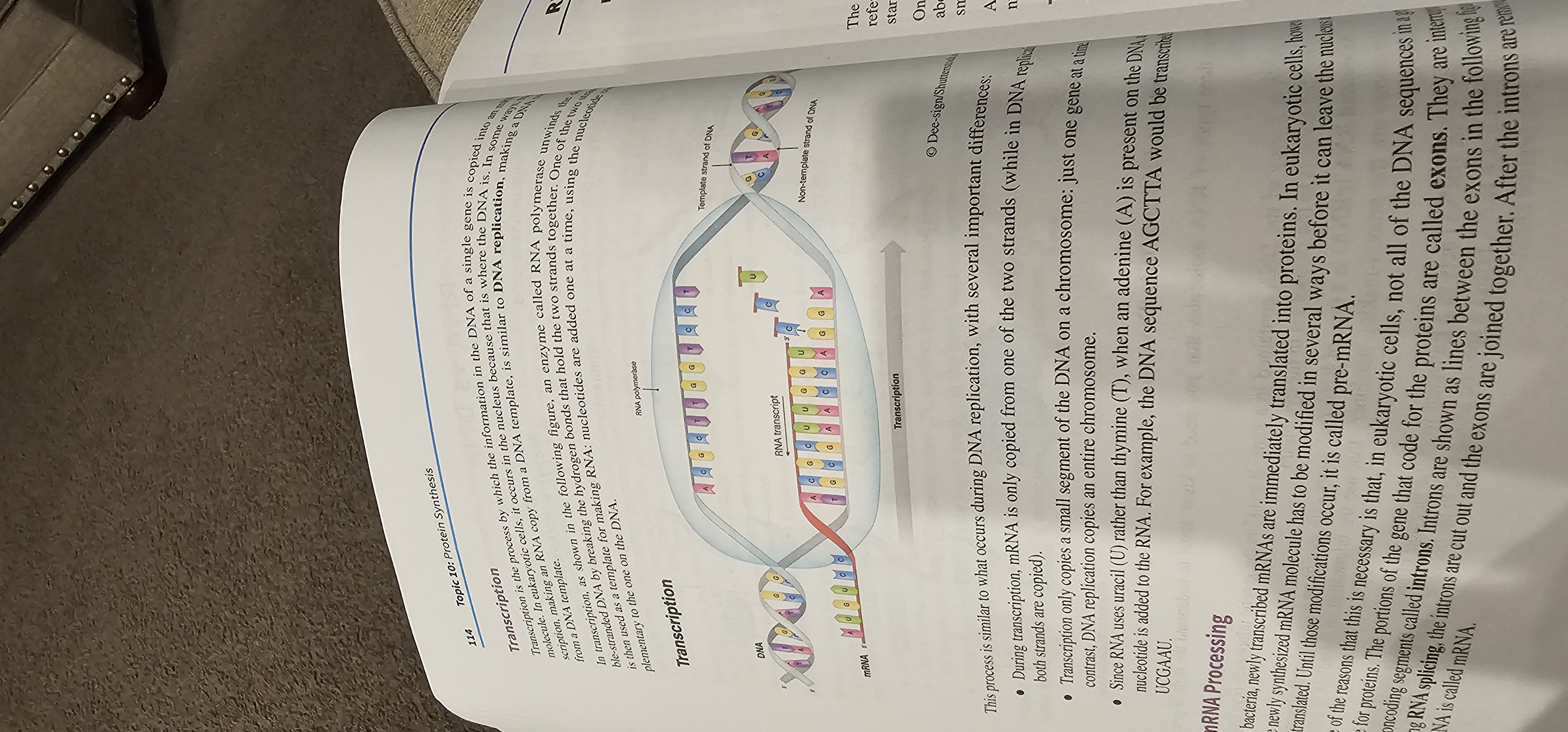
Transcription
Process in which RNA polymerase makes an RNA copy (mRNA) of a DNA template; occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotes.
Translation
Process in which ribosomes decode mRNA into a specific sequence of amino acids, forming a polypeptide; occurs in the cytoplasm.

Central Dogma
The directional flow of genetic information: DNA → RNA → Protein.

RNA Polymerase
The enzyme that unwinds DNA and synthesizes RNA during transcription.
RNA Processing
Eukaryotic modifications of pre-mRNA: 5′ capping, splicing out introns, and addition of a 3′ poly-A tail.
Exon
A coding sequence in a gene that remains in mature mRNA after splicing.
Intron
A non-coding sequence in a gene removed from pre-mRNA during splicing.
5′ Cap
A modified nucleotide added to the 5′ end of eukaryotic mRNA that aids ribosome binding and mRNA stability.
Poly-A Tail
A stretch of ~250 adenines added to the 3′ end of eukaryotic mRNA that protects it from degradation.
Codon
A sequence of three mRNA nucleotides that specifies an amino acid or a stop signal during translation.
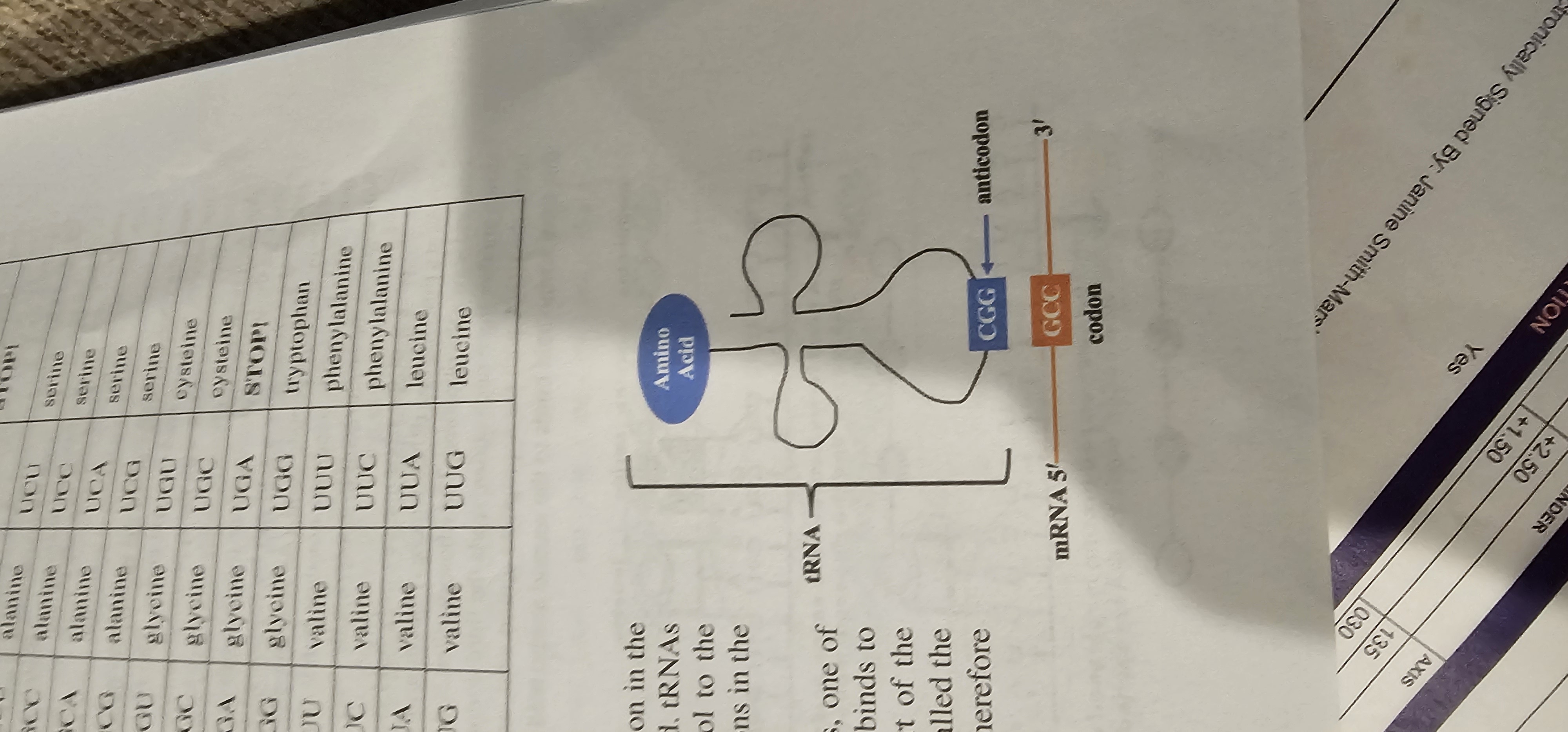
Anticodon
A three-nucleotide sequence on tRNA complementary to an mRNA codon.
Start Codon
The AUG codon that signals initiation of translation and codes for methionine.
Stop Codon
One of three mRNA codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) that signal termination of translation.
Ribosome
A two-subunit molecular machine of rRNA and proteins that orchestrates translation.
Reading Frame
The grouping of mRNA nucleotides into consecutive, non-overlapping codons beginning at the start codon.
Gene Regulation
Control of gene expression levels, often by turning transcription on or off in response to environmental changes.
Housekeeping Proteins
Essential proteins continuously produced because their genes are constitutively expressed.
Promoter
DNA sequence upstream of a gene where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription.
Mutation
A permanent change in a DNA nucleotide sequence.
Point Mutation
A mutation involving a single nucleotide substitution in DNA.
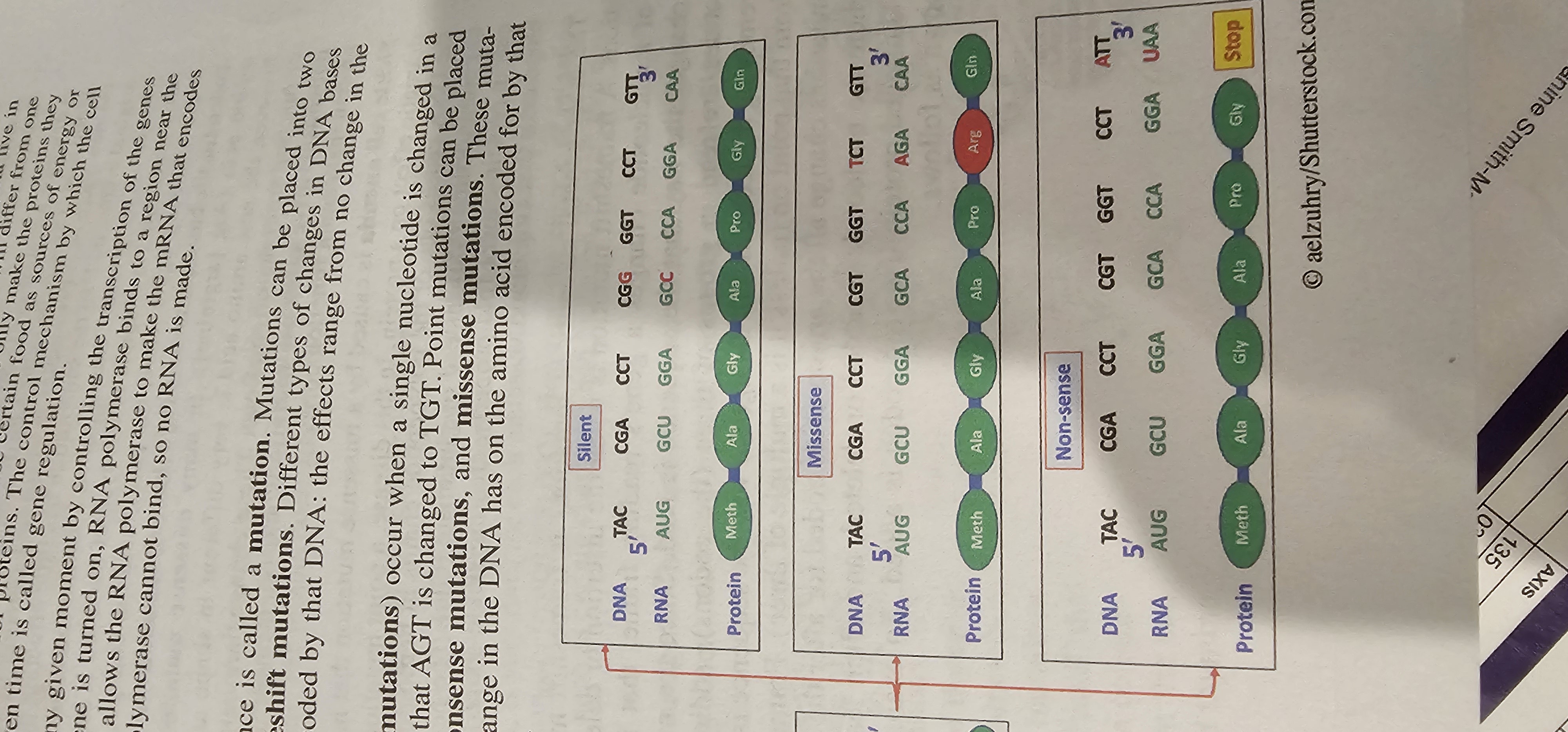
Silent Mutation
Point mutation that changes a codon but not the encoded amino acid, leaving the protein sequence unchanged.
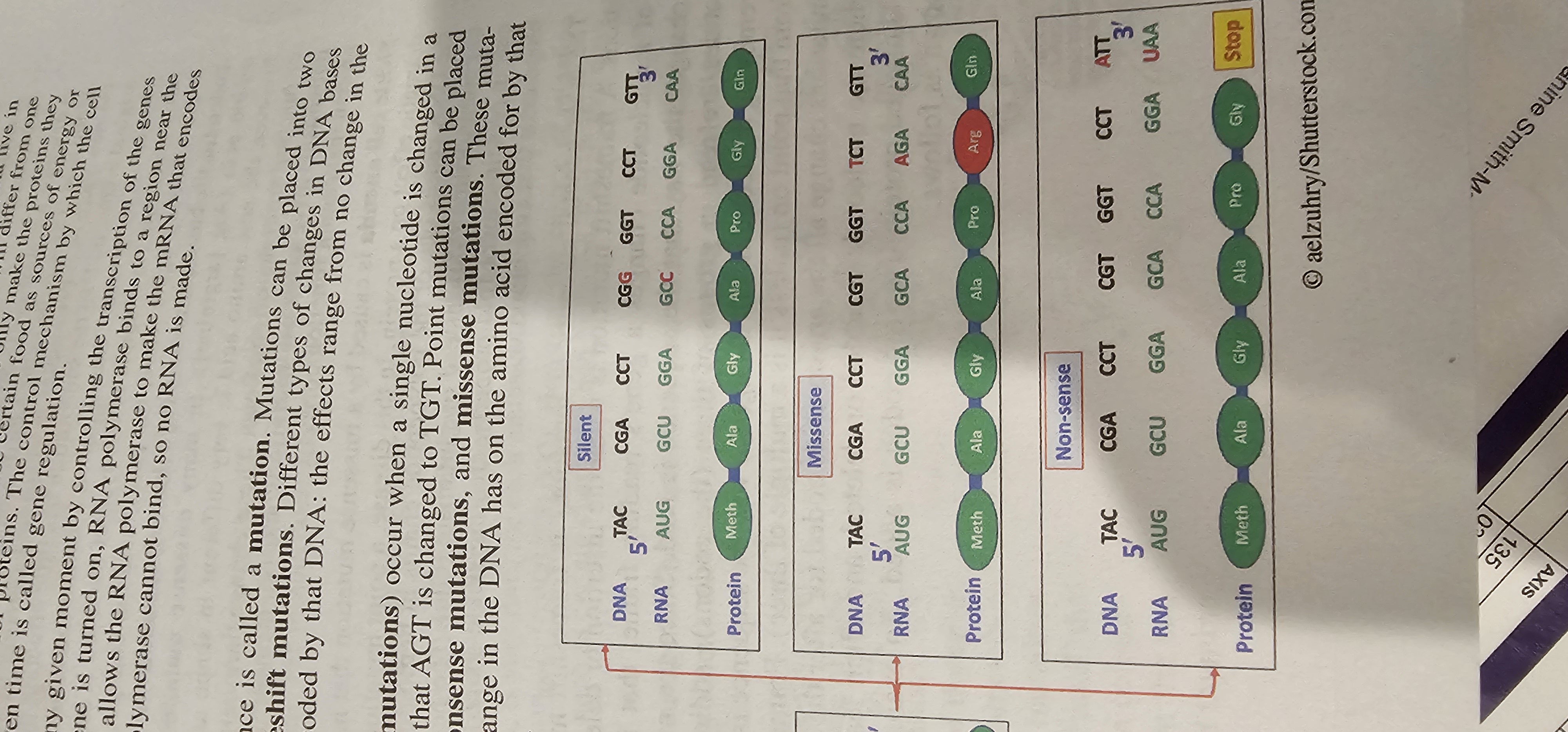
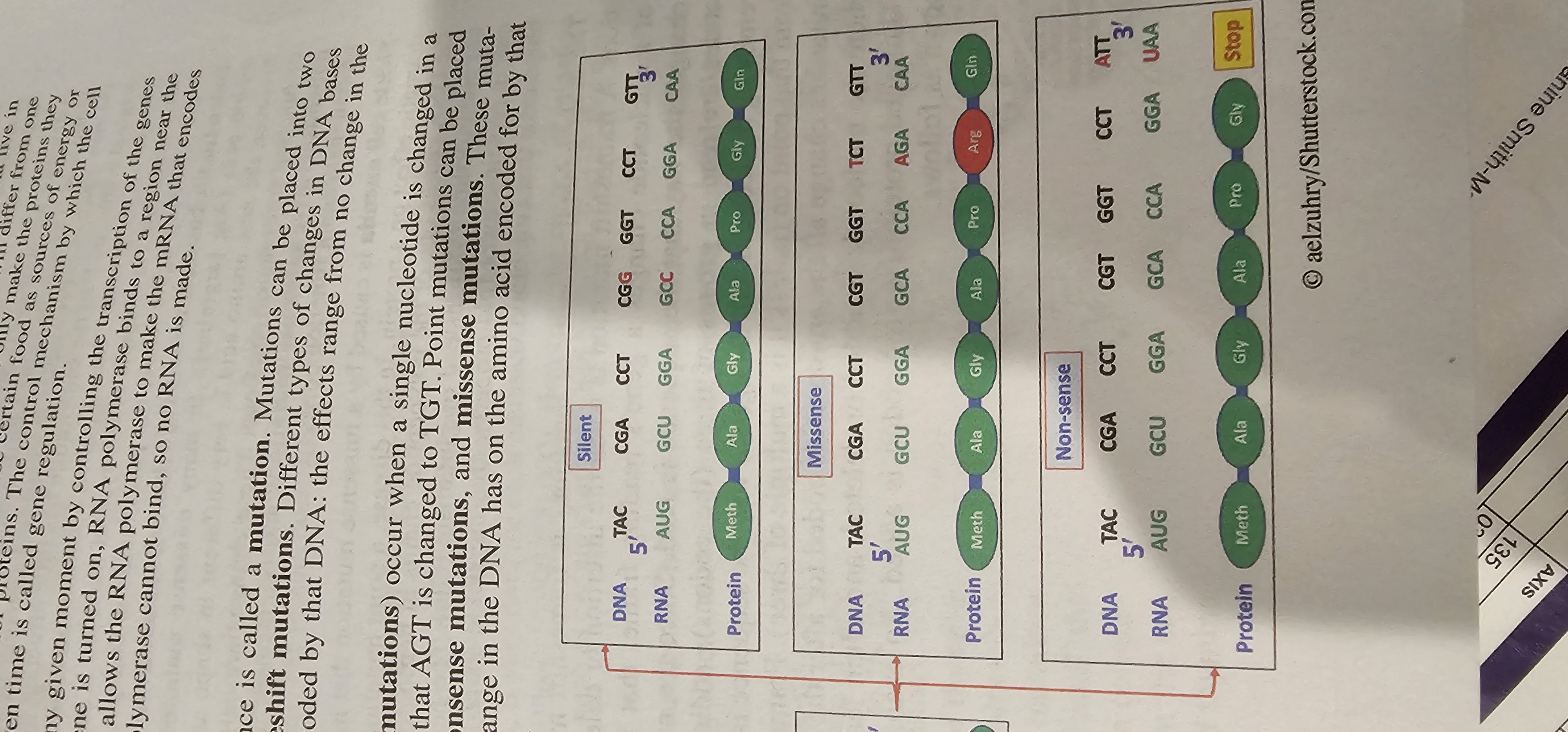
Missense Mutation
Point mutation that replaces one amino acid with another in the protein sequence.
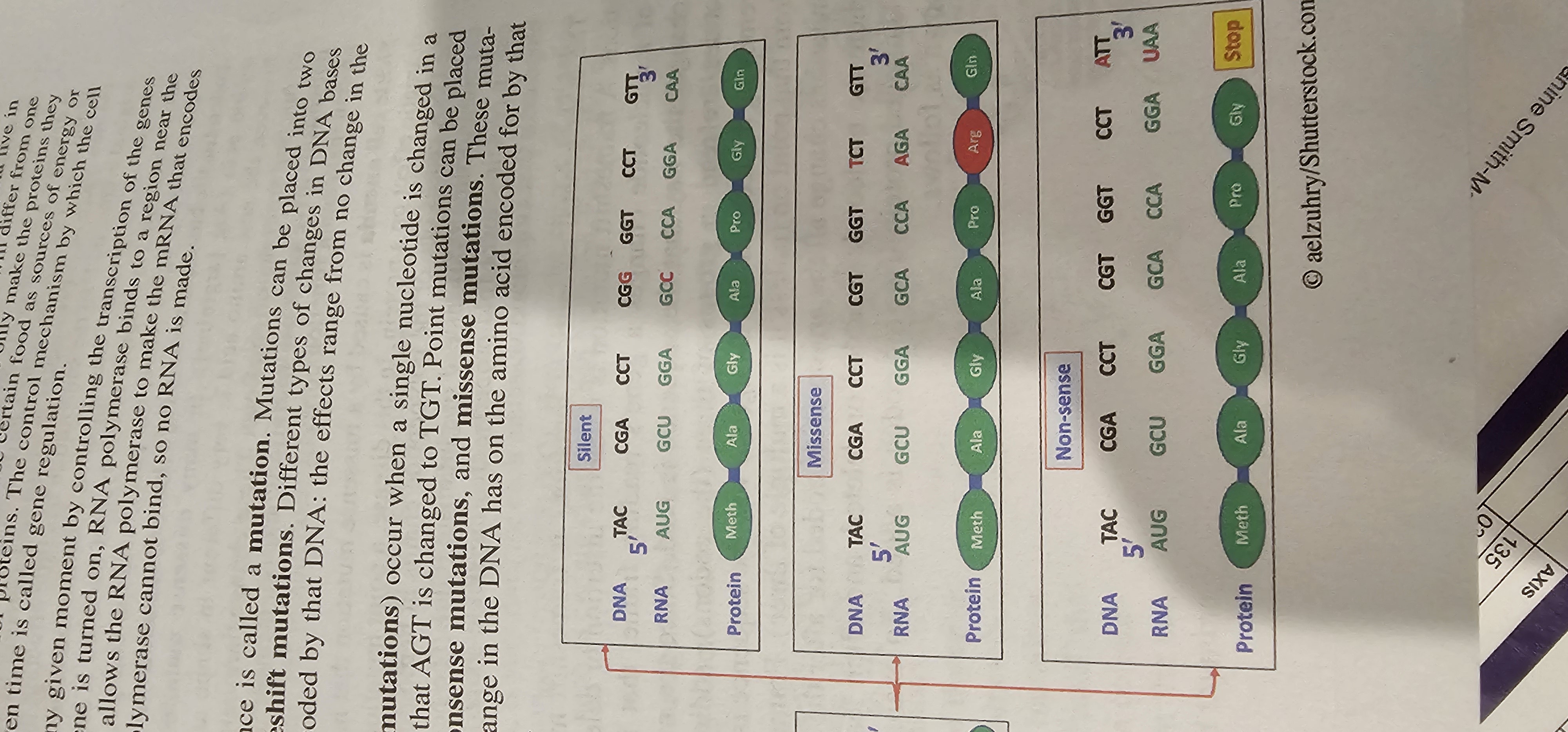
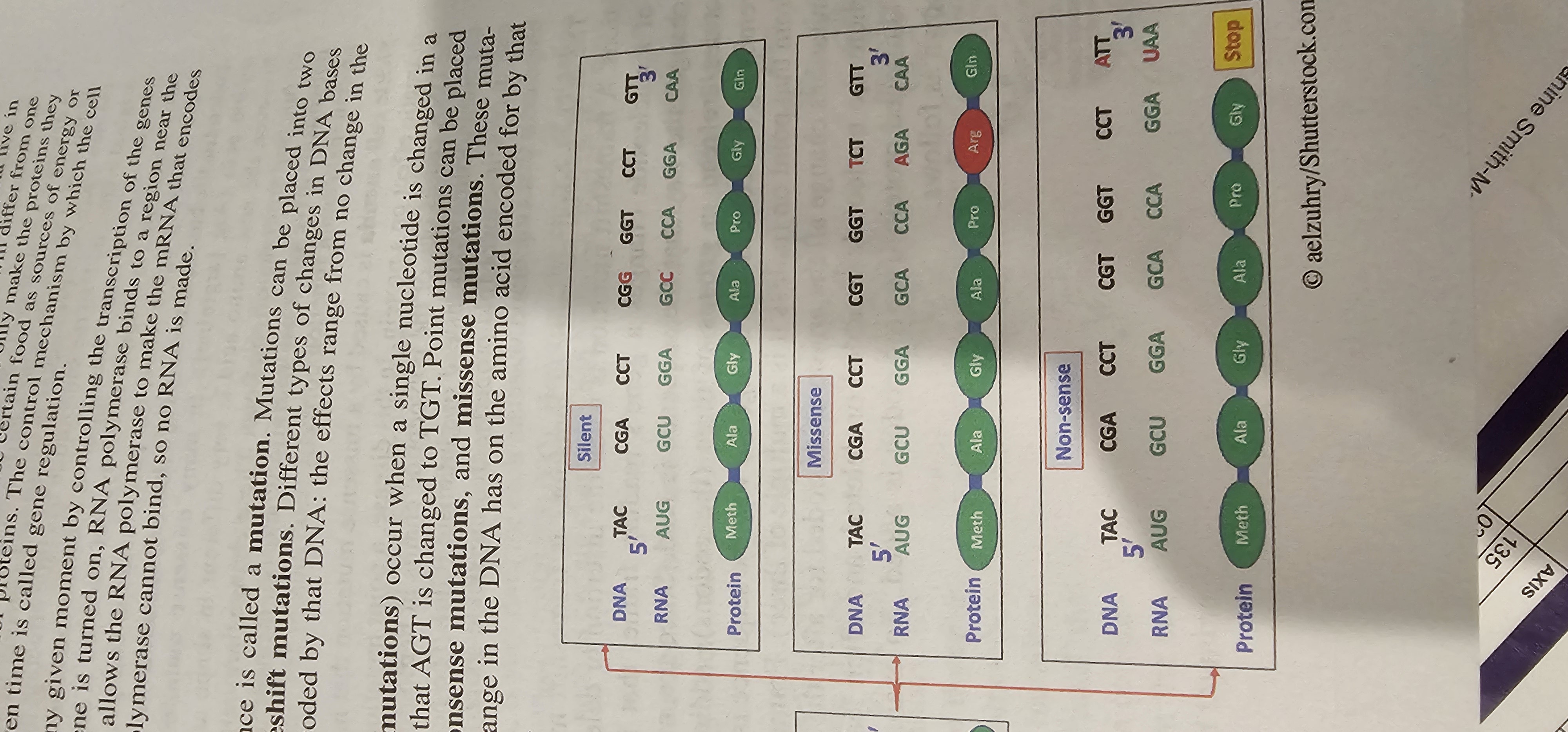
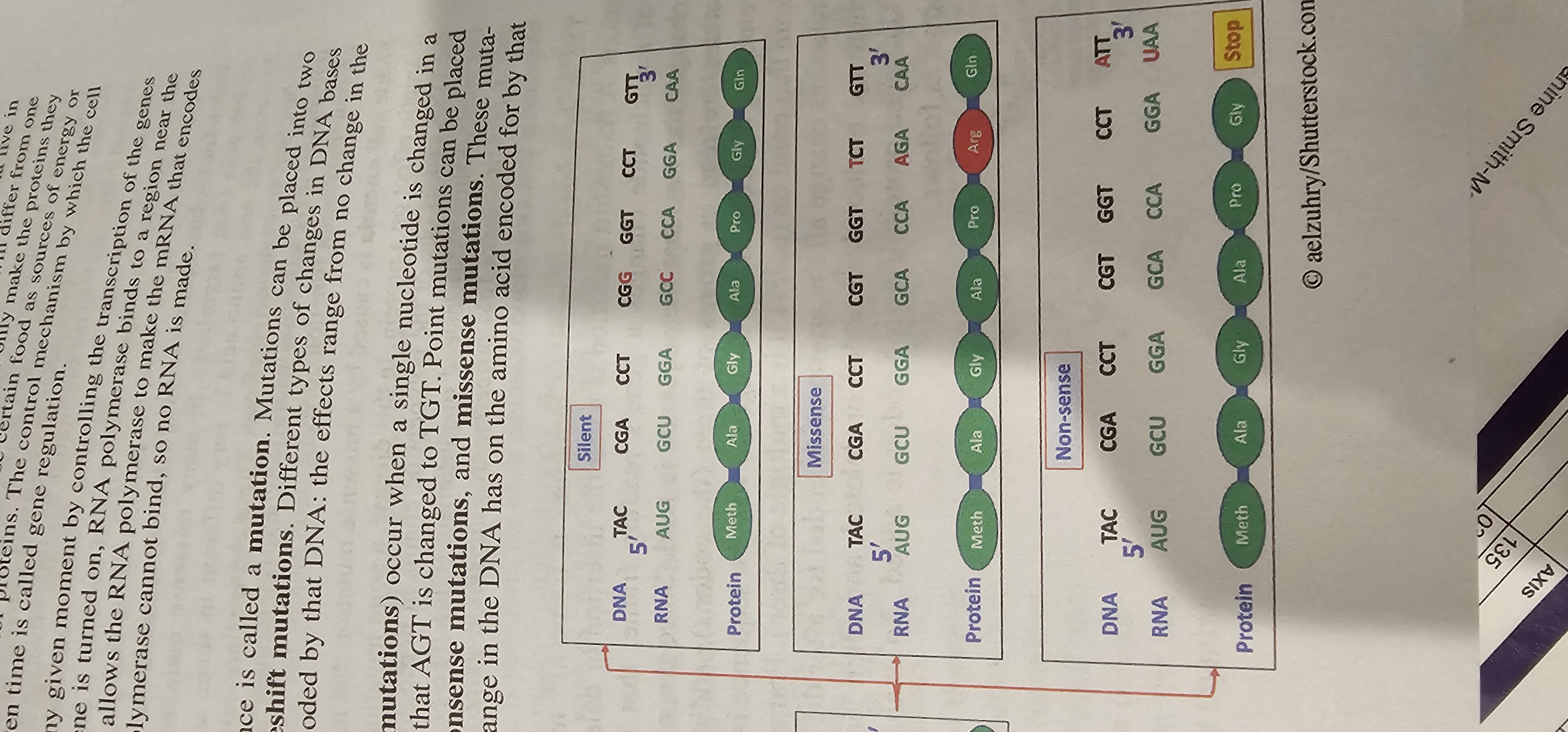
Nonsense Mutation
Point mutation that converts an amino-acid codon into a stop codon, producing a truncated polypeptide.
Frameshift Mutation
Insertion or deletion of nucleotides that alters the reading frame, changing downstream amino-acid sequence.
Mutagen
An agent (chemical or radiation) that increases the frequency of mutations in DNA.
Carcinogen
A substance capable of causing cancer; many carcinogens are mutagens.
Spontaneous Mutation
A rare DNA change arising without external influence, often due to DNA polymerase errors.
Thymine Dimer
Covalent linkage of adjacent thymines caused by UV light, leading to replication errors and mutations.
Ames Test
Bacterial assay that detects mutagenic chemicals by measuring reversion mutations in histidine-requiring Salmonella.
Auxotroph
A mutant organism requiring a nutrient supplement (e.g., histidine) that the wild type can synthesize.