Unit 3: Module 11
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1
New cards
lesion
tissue destruction
2
New cards
Electroencephologram (EEG)
an amplified recording of the waves
of electrical activity sweeping
across the brain's surface. These
waves are measured by electrodes
placed on the scalp.
of electrical activity sweeping
across the brain's surface. These
waves are measured by electrodes
placed on the scalp.
3
New cards
CT (computed tomography) scan (CAT scan)
a series of X-ray photographs
taken from different angles and
combined by computer into a
composite representation of a slice
of the brain's structure.
taken from different angles and
combined by computer into a
composite representation of a slice
of the brain's structure.
4
New cards
PET (position emission tomography) scan
a visual
display of brain activity that detects
where a radioactive form of glucose
goes while the brain performs a
given task.
display of brain activity that detects
where a radioactive form of glucose
goes while the brain performs a
given task.
5
New cards
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
a technique that uses
magnetic fields and radio waves
to produce computer -generated
images of soft tissue
magnetic fields and radio waves
to produce computer -generated
images of soft tissue
6
New cards
MRI
shows brain anatomy
7
New cards
ventricles (def)
fluid filled brain areas
8
New cards
ventricles (fill-in-the-blank)
schizophrenic patients have enlarged _____________
9
New cards
fMRI (functional MRI)
a technique for revealing bloodflow
and, therefore, brain activity by
comparing successive MRI scans
and, therefore, brain activity by
comparing successive MRI scans
10
New cards
fMRI
shows brain function and structure
11
New cards
brainstem (def)
the oldest part and
central core of the brain, beginning
where the spinal cord swells as it
enters the skull; the ____________ is
responsible for automatic survival
functions.
central core of the brain, beginning
where the spinal cord swells as it
enters the skull; the ____________ is
responsible for automatic survival
functions.
12
New cards
brainstem (pic)
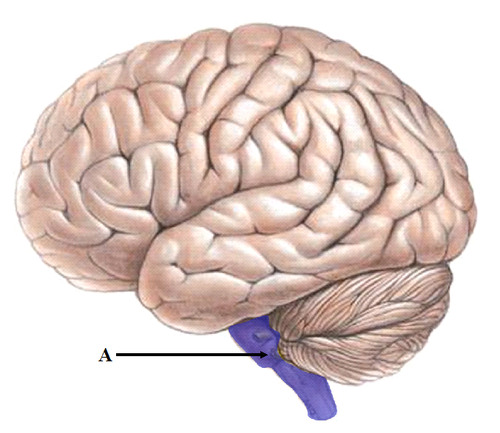
13
New cards
medulla (def)
the base
of the brainstem; controls heartbeat
and breathing
of the brainstem; controls heartbeat
and breathing
14
New cards
medulla (pic)
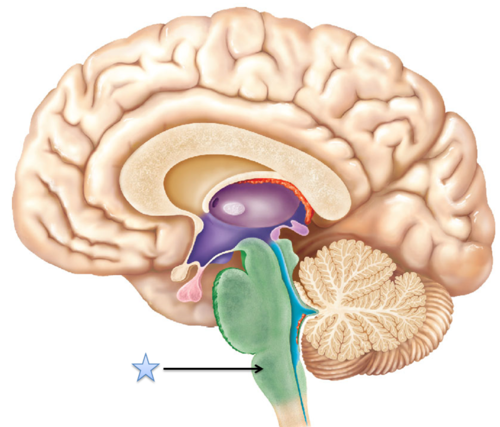
15
New cards
pons
above medulla; coordinates movements
16
New cards
pons (pic)
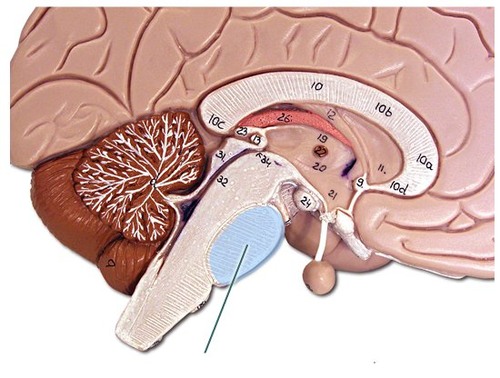
17
New cards
the brainstem (fill-in-the-blank)
_______________ is the crossover point between one side of the brain and the opposite side of the body
18
New cards
thalamus
the brain's sensory control center,
located on top of the brainstem;
it directs messages to the sensory
receiving areas in the cortex and
transmits replies to the cerebellum
and medulla.
located on top of the brainstem;
it directs messages to the sensory
receiving areas in the cortex and
transmits replies to the cerebellum
and medulla.
19
New cards
thalamus (pic)
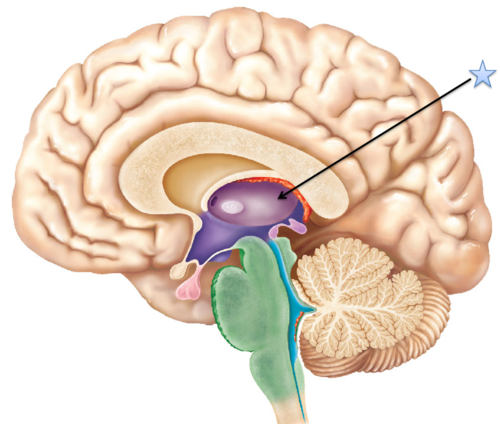
20
New cards
smell
thalamus receives info from all senses but ___________
21
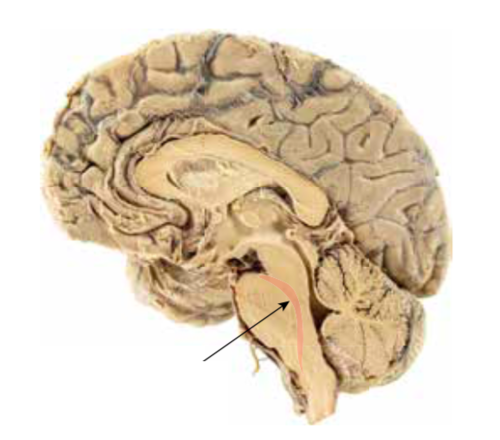
New cards
reticular formation
a nerve
network that travels through the
brainstem and thalamus and plays
an important role in controlling
arousal.
network that travels through the
brainstem and thalamus and plays
an important role in controlling
arousal.
22
New cards
reticular formation (pic)
23
New cards
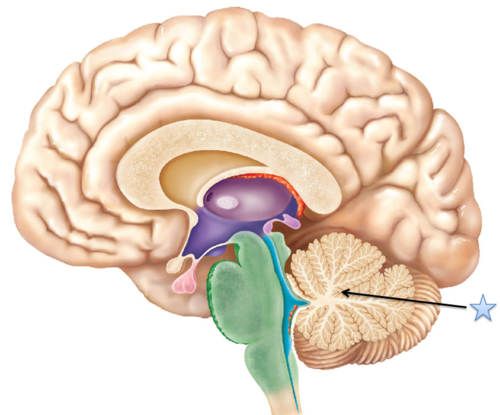
cerebellum (def)
the "little brain" at the
rear of the brainstem; functions
include processing sensory input,
coordinating movement output and
balance, and enabling nonverbal
learning and memory.
rear of the brainstem; functions
include processing sensory input,
coordinating movement output and
balance, and enabling nonverbal
learning and memory.
24
New cards
cerebellum (pic)
25
New cards
older
__________ brain functions occur without any conscious effort
26
New cards
limbic system (def)
neural system
(including the hippocampus,
amygdala, and hypothalamus)
located below the cerebral
hemispheres; associated with
emotions and drives.
(including the hippocampus,
amygdala, and hypothalamus)
located below the cerebral
hemispheres; associated with
emotions and drives.
27
New cards
hippocampus (def)
processes conscious memories
28
New cards
amygdala (def)
two lima-bean- sized neural clusters in
the limbic system; linked to emotion
the limbic system; linked to emotion
29
New cards
amygdala (fill-in-the-blank)
the _______________ is linked to aggression and fear
30
New cards
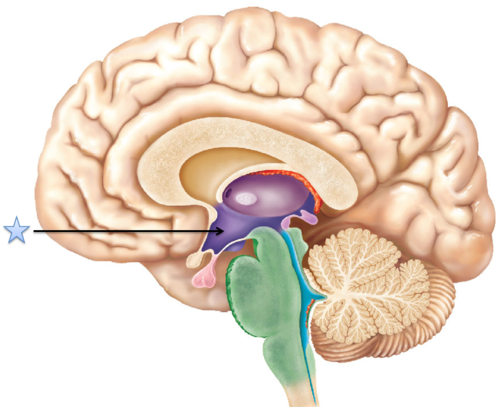
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several
maintenance activities (eating,
drinking, body temperature), helps
govern the endocrine system via
the pituitary gland, and is linked to
emotion and reward.
maintenance activities (eating,
drinking, body temperature), helps
govern the endocrine system via
the pituitary gland, and is linked to
emotion and reward.
31
New cards
hypothalamus (pic)
32
New cards
reward centers
hypothalamus has _____________
33
New cards
reward deficiency syndrome
a genetically disposed deficiency in the natural brain systems for pleasure and well-being that leads people to crave whatever provides that missing pleasure or relieves negative feelings