K2.1 collision theory
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
why may a theory be needed for bimolecular reactions
may otherwise need to extrapolate k to non-lab conditions e.g. combustion, atmosphere, space
may need to estimate k e.g. if there are too many reactions to measure
some reactions are just hard to measure, e.g. if there is no detection scheme (no absorption in UV/vis, no dipole moment etc), e.g. no LIF for detection but reaction too fast for other methods
how does collision theory work
uses sizes and velocities of A and B to calculate the number of collisions per second which is then related to the Arrhenius A factor
the fraction of collisions with sufficient energy to react will be related to Ea
assumptions of collision theory
reagents can be treated as hard spheres
atomic radii
no interactions between molecules
impenetrable spheres so no distortion on collision
use relative velocity and assume B is stationary
impact parameter
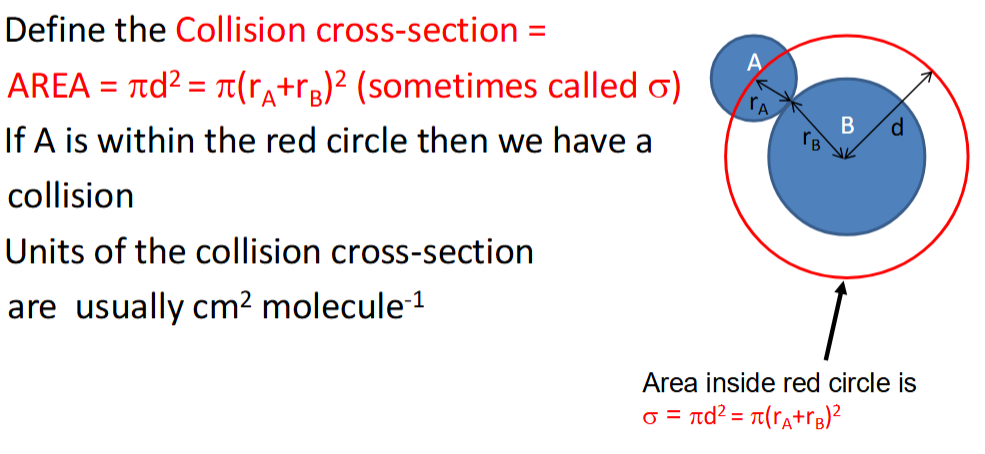
impact parameter, b, is defined as the closest perpendicular distance between the 2 centres at the point of collision
each collision has b somewhere between 0 and d

how is a collision defined
if b < d
collision cross section equation, symbol and units
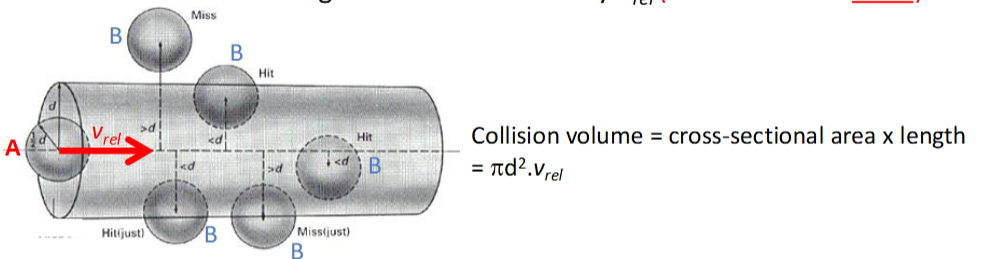
how is collision volume calculated
in 1 unit time (1 second), a collision volume is swept out by each moving A molecule which is moving at the relative velocity vrel
collision rate calculation for a single molecule and for the total collision rate
assumption for this calculation?
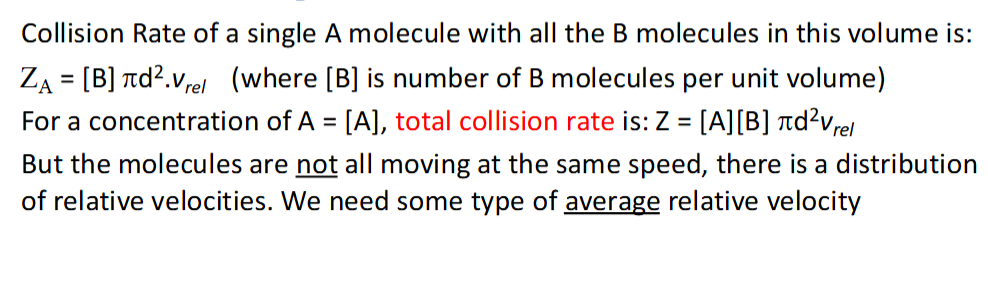
how is the assumption made in collision rate calculations corrected?
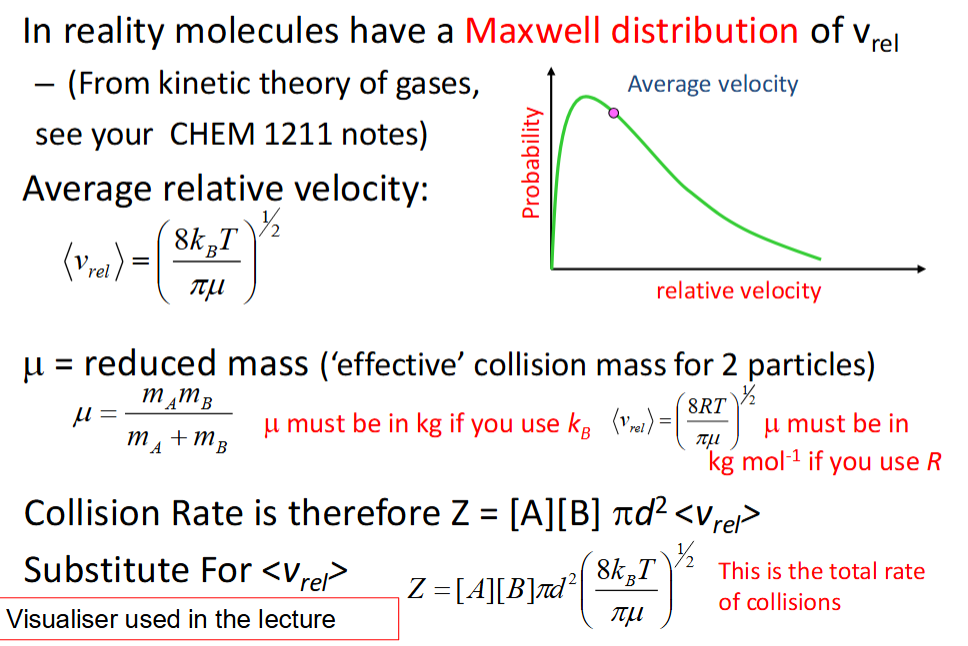
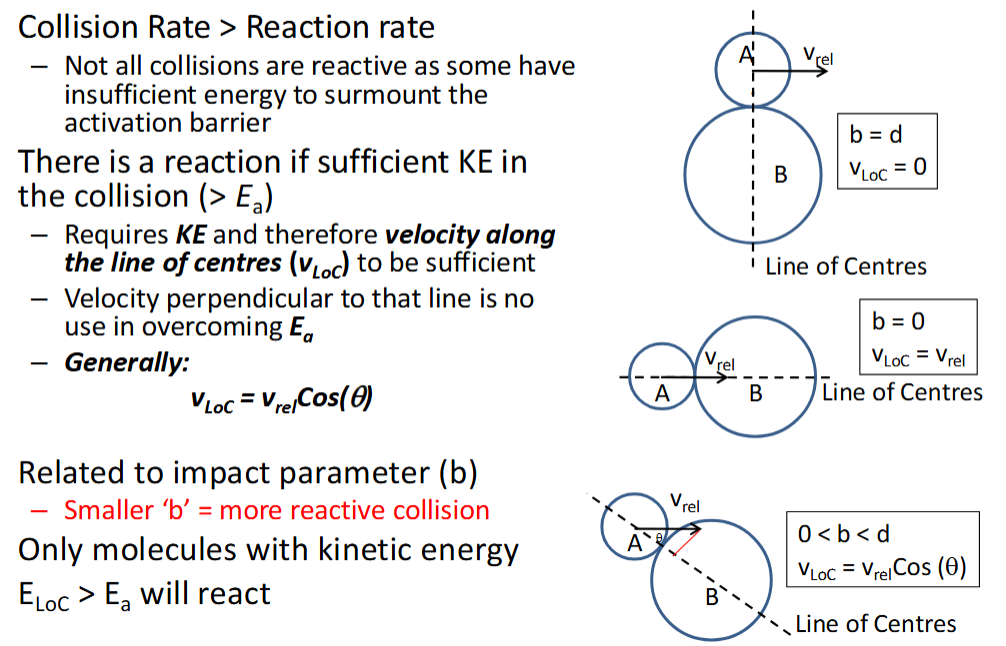
is collision rate greater than or less than reaction rate? why?
collision rate > reaction rate as not all collisions are reactive - some have insufficient energy to surmount the activation barrier
what is required for the collision to be reactive in terms of:
energy
velocity - give equation
relate to impact parameter
θ is the angle between vrel and the line of centres
how is reaction rate calculated from collision rate
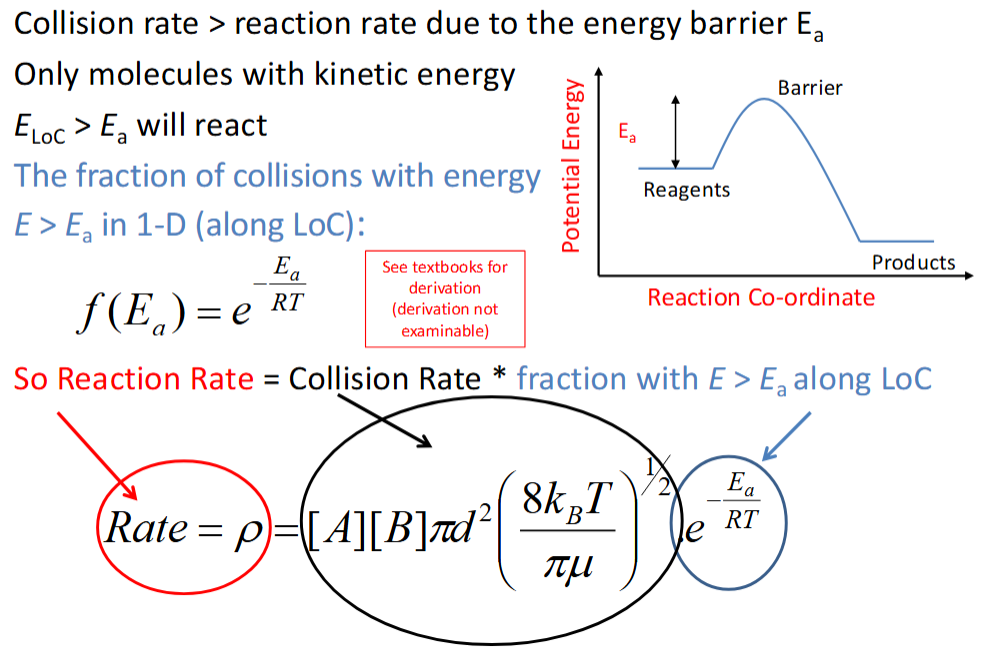
how is rate coefficient calculated from reaction rate
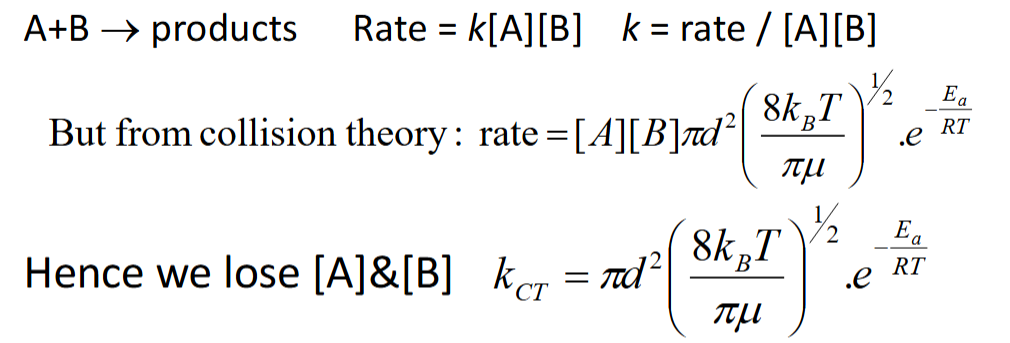
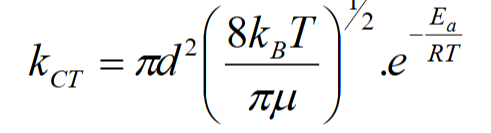
what can this equation be used to show
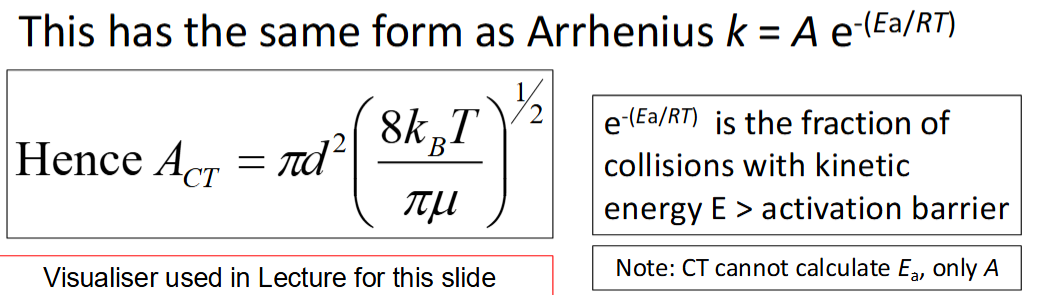
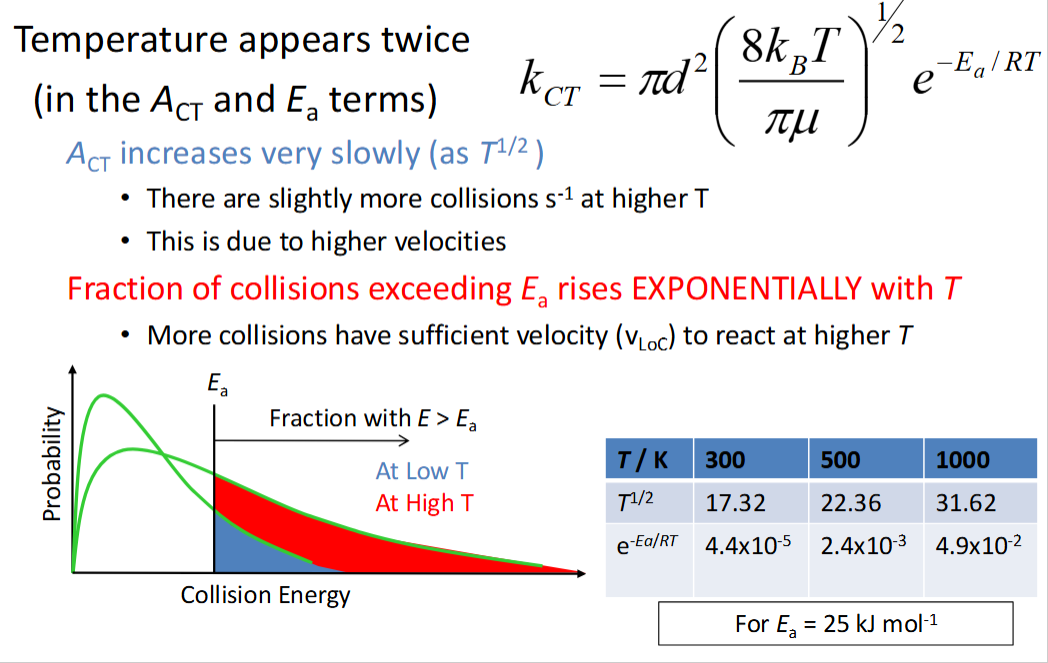
what is the temperature dependence of kCT?
how is AEXP determined
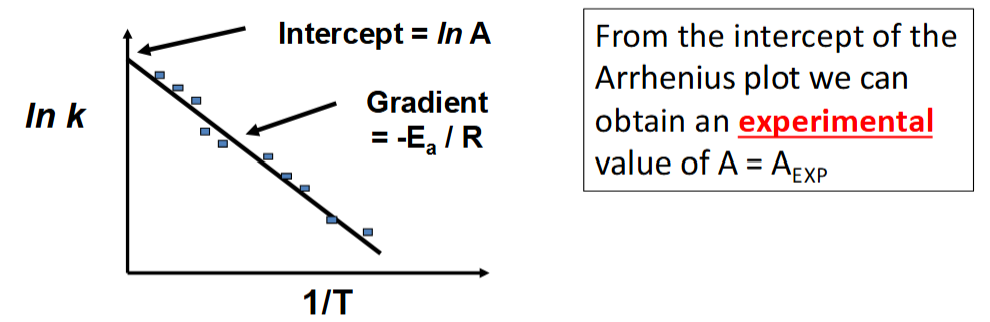
how are ACT and AEXP compared
how will they usually differ
CT usually overestimates the A factor by orders of magnitude - many collisions are ineffective as the reactive parts of the molecule do not collide due to incorrect orientation

exceptions to usual observation of ACT vs AEXP
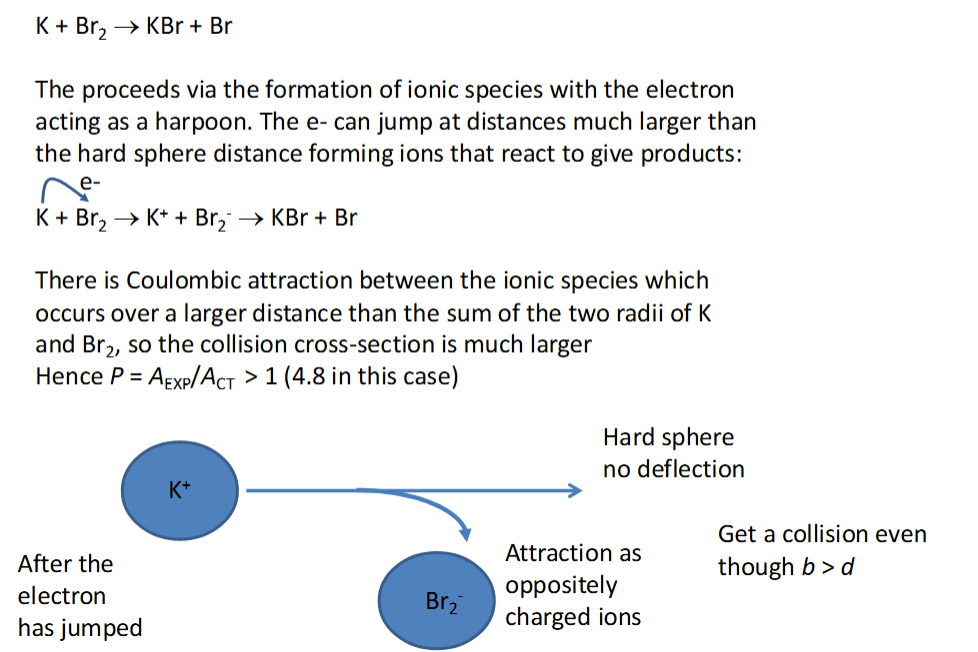
P can be > 1 - the Harpoon mechanism