Cardiovascular System
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Structure of the Cardiovascular System
Heart Anatomy
Location: Located in the mediastinum, between the lungs, behind the sternum.
Chambers:
Right Atrium (RA): Receives deoxygenated blood from the body.
Right Ventricle (RV): Pumps blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
Left Atrium (LA): Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
Left Ventricle (LV): Pumps oxygenated blood to the body via the aorta.
Heart Valves
Ensure one-way blood flow:
Atrioventricular (AV) Valves:
Tricuspid Valve (RA → RV)
Mitral (Bicuspid) Valve (LA → LV)
Semilunar Valves:
Pulmonary Valve (RV → Pulmonary artery)
Aortic Valve (LV → Aorta)
Continue..
Blood Vessels
Arteries: Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart (except the pulmonary artery).
Veins: Return deoxygenated blood to the heart (except the pulmonary veins).
Capillaries: Microscopic vessels where gas and nutrient exchange occurs.
Coronary Circulation
Coronary Arteries: Supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle.
Coronary Veins: Remove deoxygenated blood from the heart.
Physiology of the Cardiovascular System
Cardiac Cycle
Consists of systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation) phases:
Diastole: Heart relaxes, AV valves open, ventricles fill with blood.
Systole: Ventricles contract, semilunar valves open, blood is ejected to the lungs and body.
Heart Sounds (Auscultation)
S1 ("Lub"): Closure of AV valves (beginning of systole).
S2 ("Dub"): Closure of semilunar valves (end of systole).
S3 (abnormal in adults): May indicate heart failure.
S4: Suggests stiff ventricles (e.g., hypertension, ischemic heart disease).
Cardiac Output (CO)
The volume of blood pumped per minute.
CO = Stroke Volume (SV) × Heart Rate (HR)
Normal: 4-8 L/min
Blood Pressure (BP)
Force exerted by circulating blood on vessel walls.
Normal BP: ~120/80 mmHg.
Regulated by: Autonomic nervous system, hormones (e.g., renin-angiotensin system), blood volume.
Pulse
Represents heartbeats per minute.
Normal Resting Heart Rate (RHR): 60-100 bpm.
Physical Assessment of the Cardiovascular System
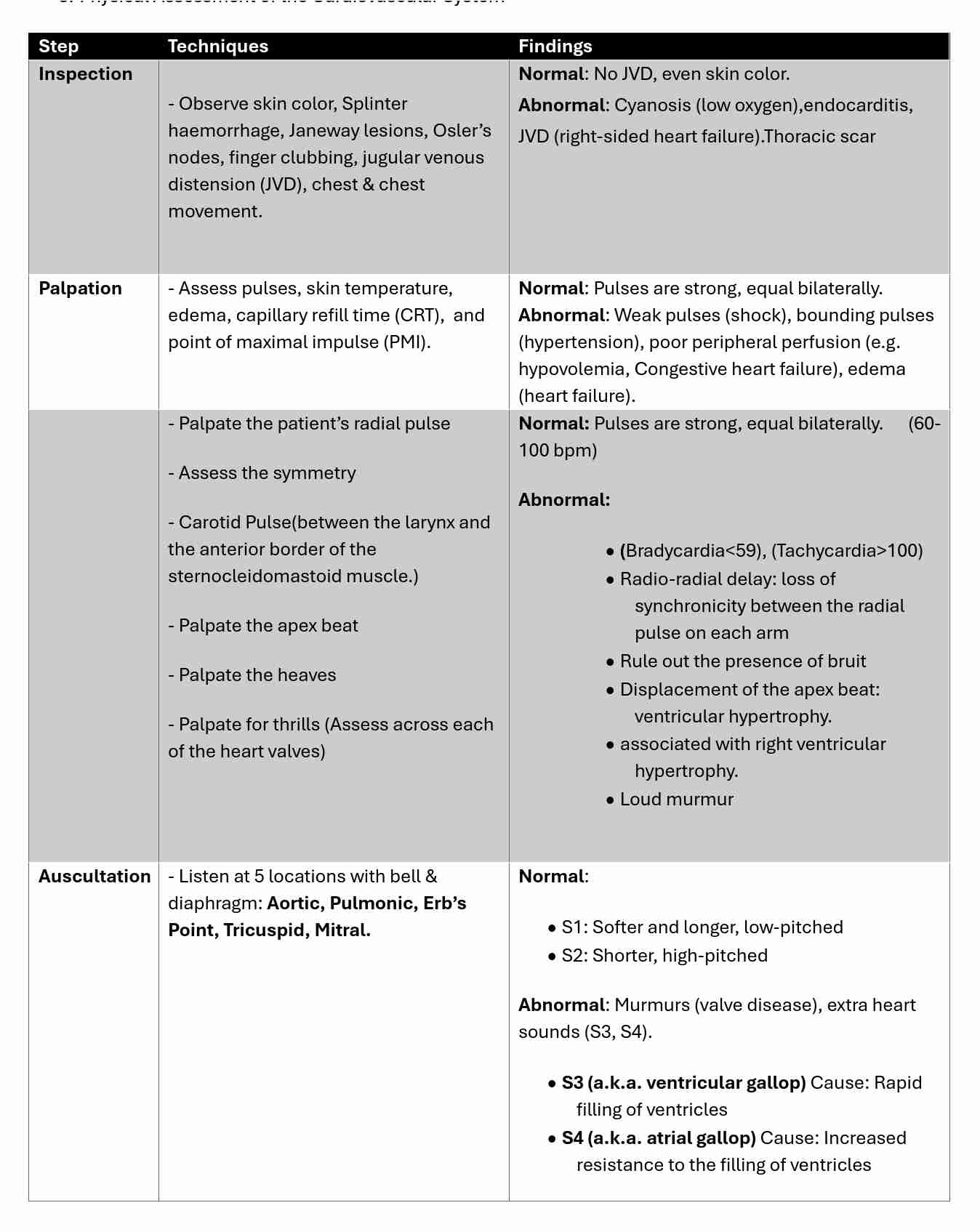
Auscultation Landmarks
Aortic Valve → 2nd right intercostal space (ICS), right sternal border.
Pulmonic Valve → 2nd left ICS, left sternal border.
Erb’s Point → 3rd left ICS, left sternal border (best place to hear S2).
Tricuspid Valve → 4th left ICS, left sternal border.
Mitral Valve (Apical Pulse) → 5th ICS, midclavicular line.
patient’s pulse
0 = pulse not palpable or absent
+1 = weak, thready
+2 = normal
+3 = slight increase
+4 = bounding
Differentiating Normal & Abnormal Findings
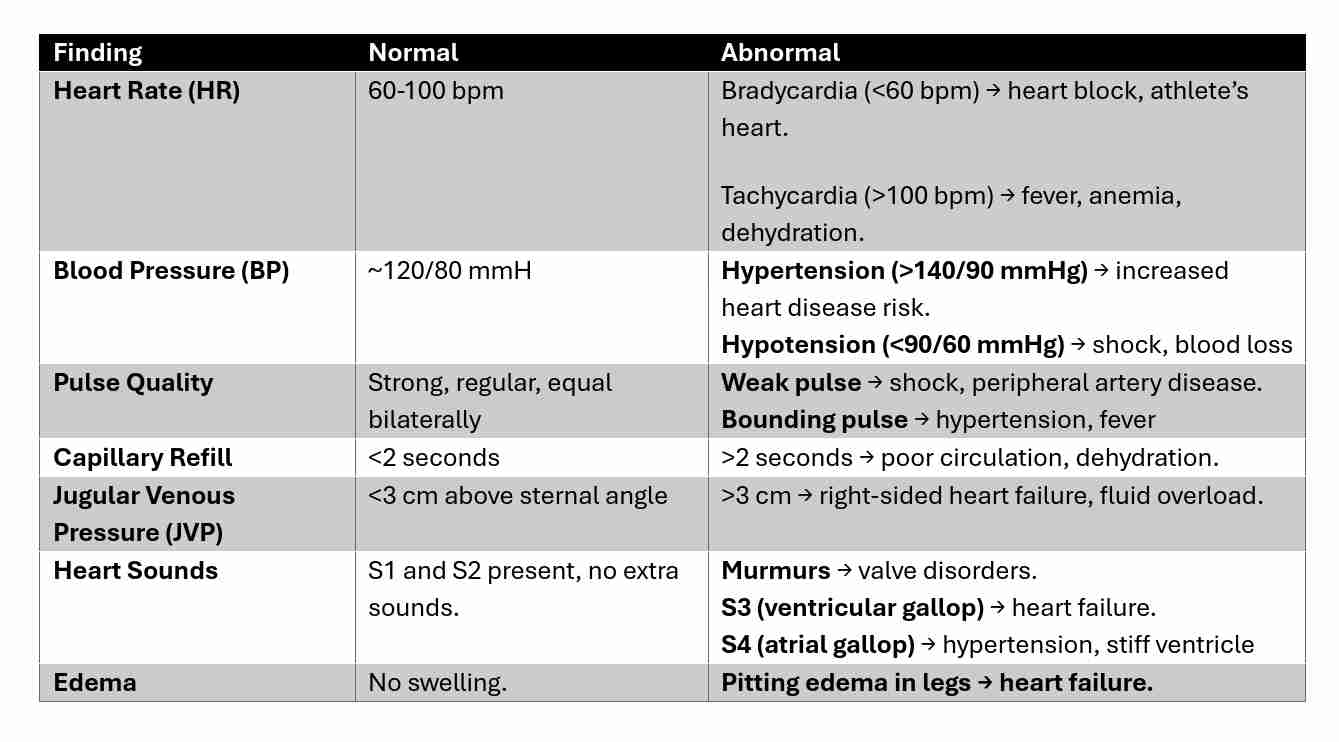
Analyzing Findings from Interviews, General Survey & Physical Exam
Interview Findings:
Chief complaints: chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, swelling (edema).
History of hypertension, diabetes, smoking, alcohol use, family history of heart disease.
General Survey:
Skin tone (cyanosis, pallor), breathing effort, edema, overall health status.
Physical Exam Analysis:
Chest pain + ST-segment elevation on ECG → Myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Bradycardia + Syncope → Heart block.
Tachycardia + Hypotension + Cold skin → Shock.
JVD + Pitting Edema + Crackles in lungs → Congestive Heart Failure.
Weak pulses + Delayed capillary refill → Poor circulation, dehydration, shock.