1. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Investigate different cellular structures, including but not limited to, Examining a variety of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are cells?
The smallest structural and functional unit of a living organism. can be either prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
How do you know if a cell is prokaryotic?
A cell is prokaryotic if it does NOT have a nucleus, or any other membrane bound organelles (this doesn’t include ribosomes).
What size are prokaryotic cells?
0.1 to 5.0 micrometres.
What are the four main structures in all prokaryotic cells?
The cell membrane, the cytoplasm, ribosomes, genetic material.
Where is genetic material found in prokaryotic cells?
Found in a large loop (the bacterial chromosome) and as small circular structures (plasmids).
What are some sub structures in prokaryotic cells?
Cell wall, pili, fimbriae, flagella, and a capsule.
What are pili in prokaryotic cells?
Hair-like structures on the cell surface that allow the cell to adhere to surfaces.
What are fimbriae in prokaryotic cells?
Hair-like structures, often shorter than pili.
What are flagella in prokaryotic cells?
whip-like tail to provide locomotion.
What is a capsule in prokaryotic cells?
Layer of complex carbohydrates outside the cell wall, protects the cell.
Are organisms with prokaryotic cells unicellular or multicellular?
Organisms are only unicellular.
How do prokaryotic cells undergo cell division?
Binary fission.
What are the two main groups prokaryotic cells can be divided into?
bacteria and archaea
Bacteria
Widespread and can either be harmful or beneficial.
Archaea
Live in harsh environments, subjected to extreme conditions such as hydrothermal vents and hot springs.
How do you know if a cell is eukaryotic?
A cell is eukaryotic if it has a nucleus and membrane bound organelles (e.g., mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum).
What size are eukaryotic cells?
10 to 100 micrometers.
Do eukaryotes contain membrane-bound organelles?
Yes. Each organelle has a specific function and carries out all the biochemical processes and reactions of the cell (such as respiration and photosynthesis in plant cells).
What are so organisms with eukaryotic cells?
Animals, plants, fungi, (multicellular) and amoeba proteus (unicellular).
Are organisms with eukaryotic cells unicellular or multicellular?
Can be either unicellular or multicellular.
How do eukaryotic cells undergo cell division?
Mitosis and meiosis
Similarities in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Has a cell membrane that regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Contains cytoplasm, where cellular processes occur
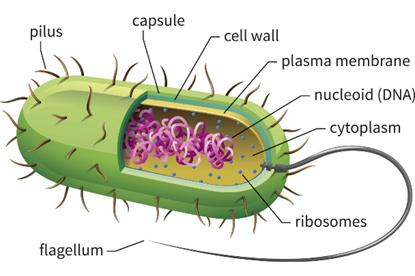
What type of cell is this? (prokaryotic or eukaryotic)
A prokaryotic cell.
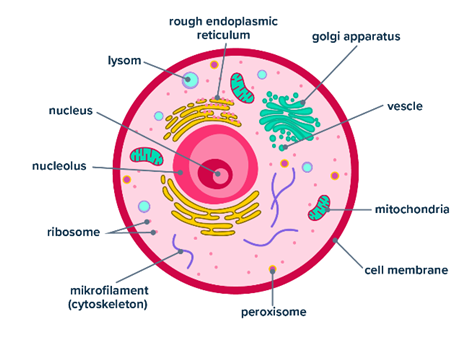
What type of cell is this? (prokaryotic or eukaryotic)
A eukaryotic cell.