Lab 7 Histology || Muscle tissue, Nervous tissue, Membranes, and the Integumentary system
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are muscle tissue
are highly cellular tissues that use ATP to generate force to produce contractions
Muscle cells are called
muscle fibers
as these cells have an elongated shape.
The cytoplasm of the muscle cell is referred to as the
sarcoplasm
cell membrane of the muscle cell is referred to as the
sarcolemma
three types of muscle tissue found in the human body
skeletal muscle tissue, smooth muscle tissue and cardiac muscle tissue
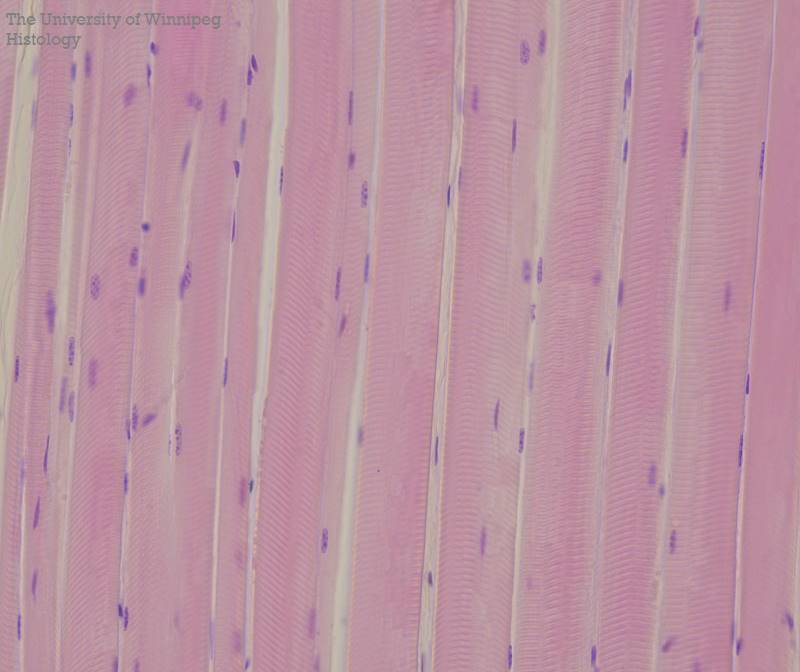
What does skeletal muscle tissue have?
muscle fibers: long, thick cylindrical cell
multiple peripherally located nuclei
obvious transverse bands (striations)
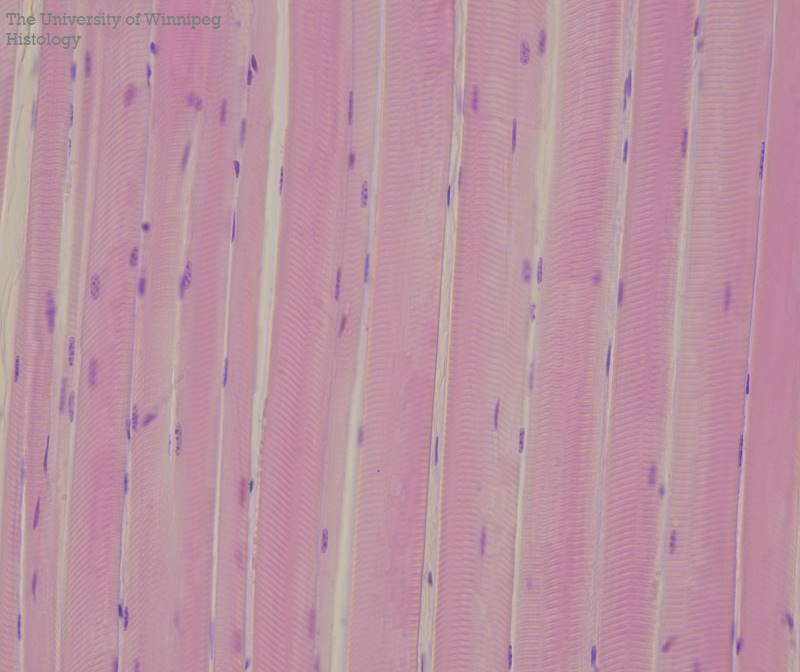
Where is skeletal muscle tissue located
within skeletal muscles (organs that also contain connective tissues and nervous tissue)
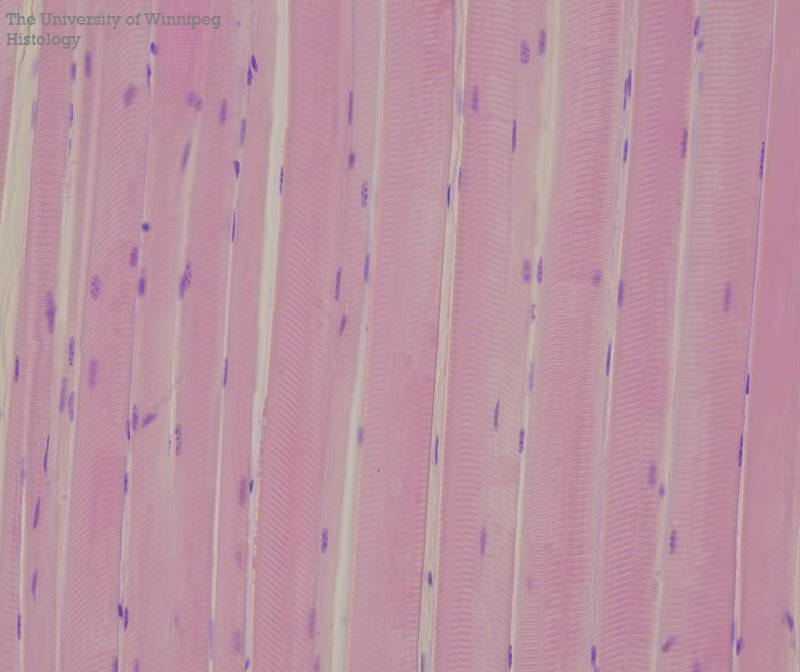
Skeletal muscles are attached to what? what does it do?
bones and when these muscles contract, movement of the skeleton occurs. The contraction of skeletal muscle is consciously controlled hence it is called voluntary muscle.
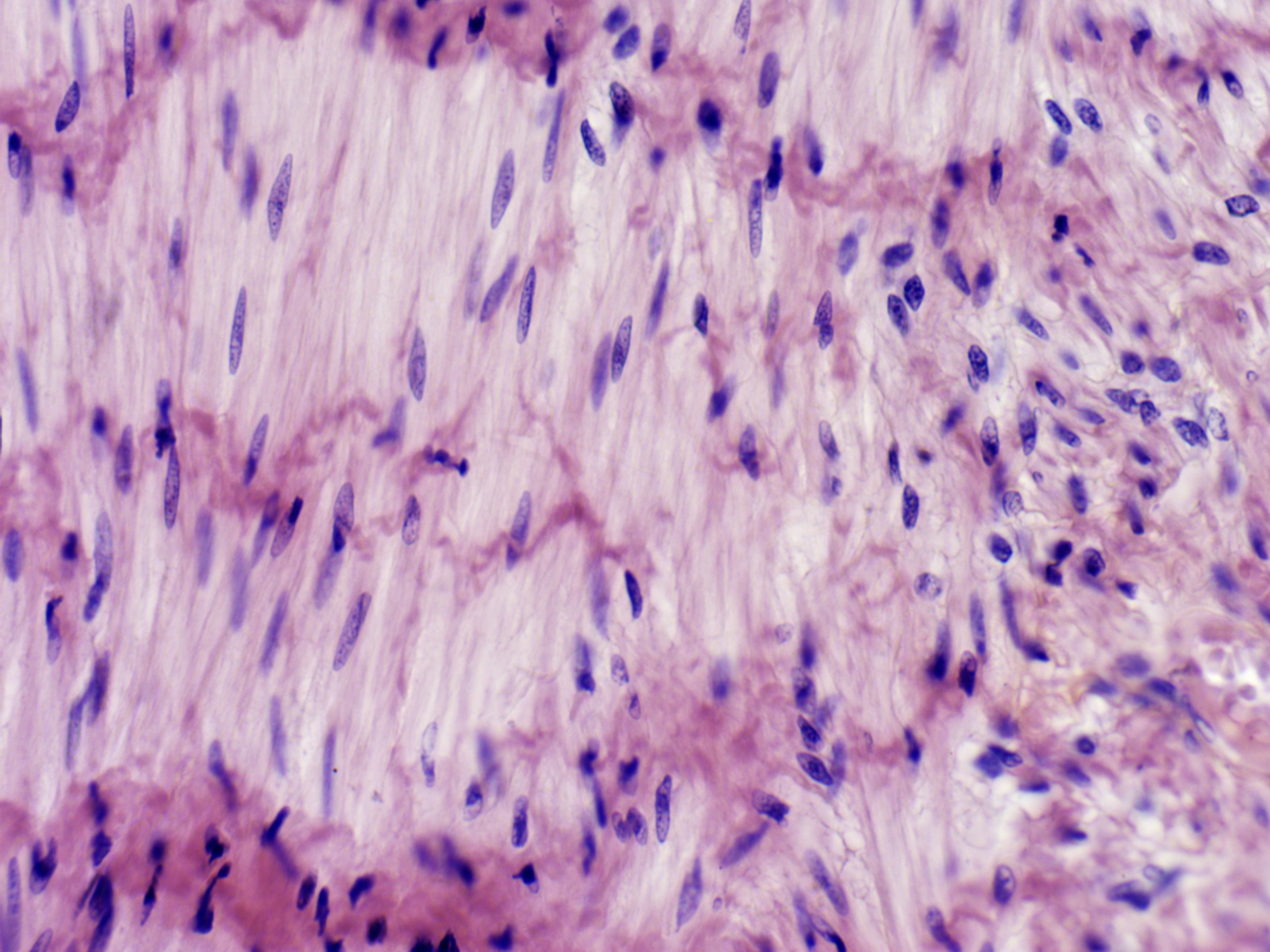
How to identify a smooth muscle tissue?
individual fibers are shorter spindle-shaped cells with tapered ends
cells are tightly packed in a sheet-like arrangement
Each cell has a single, oval nucleus that is centrally located at the thickest portion of the fiber.
There are no visible striations within the sarcoplasm of the smooth muscle fibers
In an area where the tissue has been cut in cross section, the smooth muscle fibers appear as discs of cytoplasm with a central nucleus
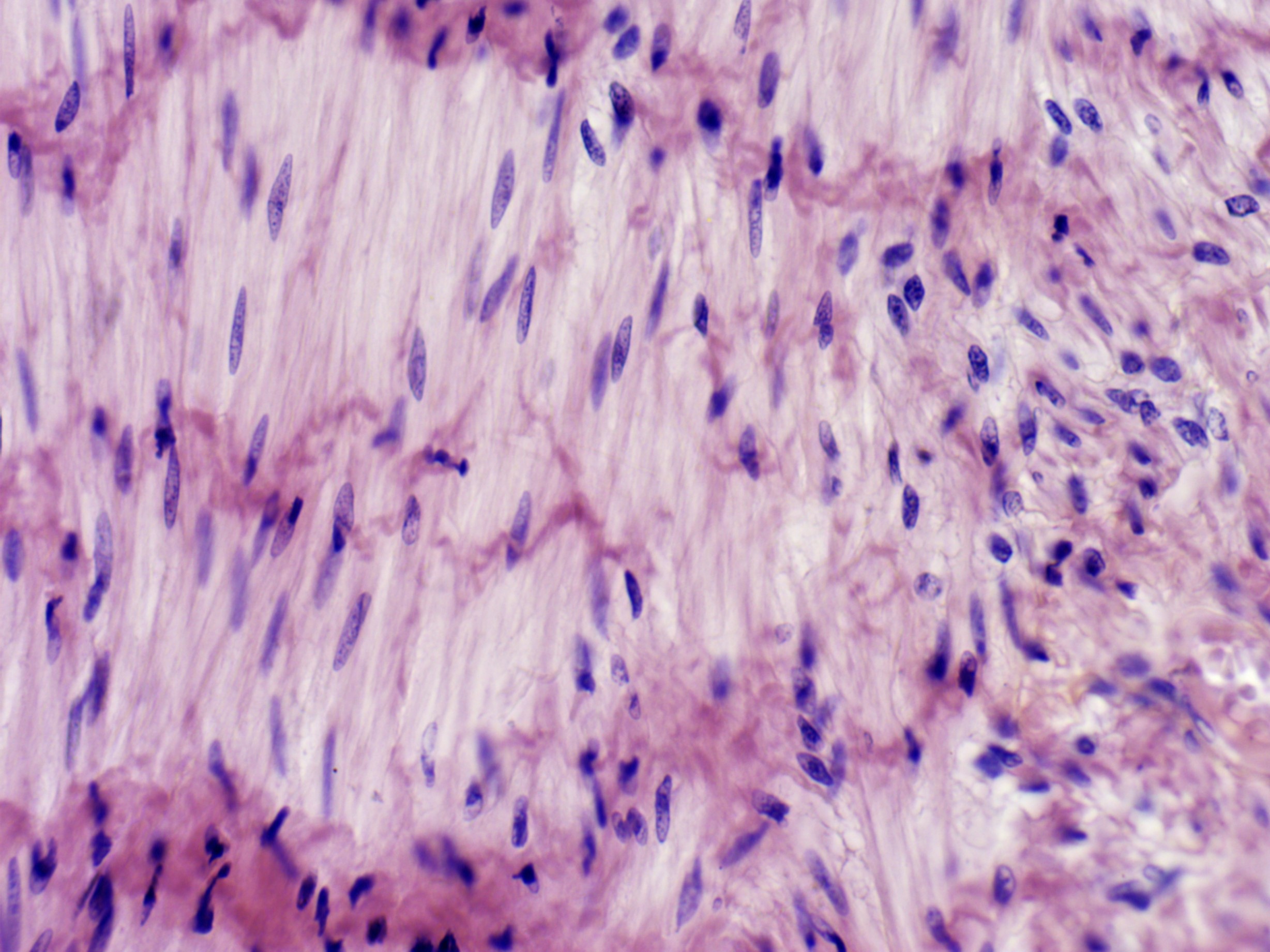
Where is smooth muscle tissue primarily located?
within the walls of hollow organs, such as blood vessels and organs of the digestive, urinary, respiratory and reproductive tracts.
What does smooth muscle tissue do?
The contraction of smooth muscle tissue moves materials along internal passageways and regulates the diameter of blood vessels and respiratory tracts. Smooth muscle contractions are involuntary, “not consciously controlled”.
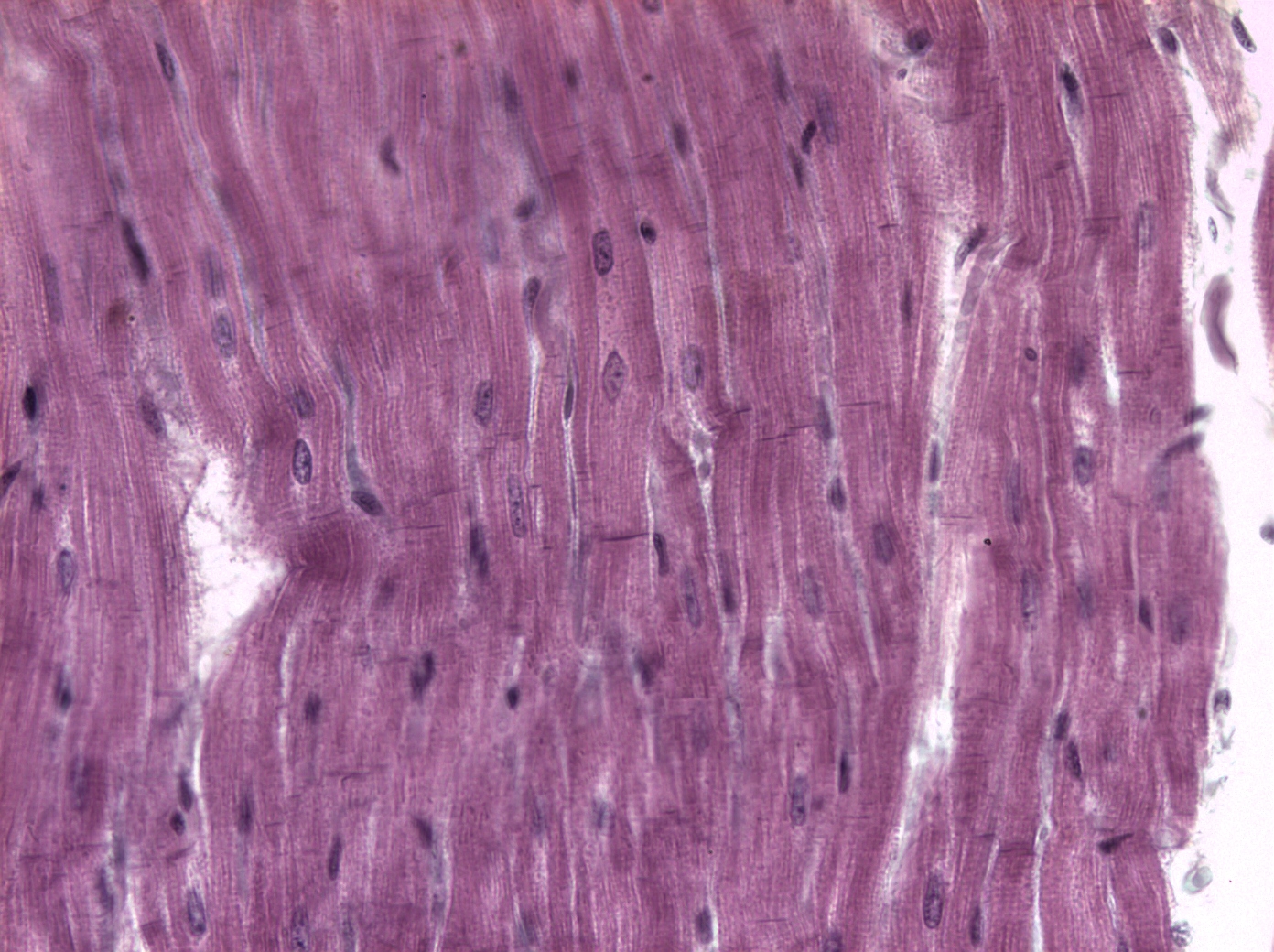
How to identify a cardiac muscle tissue?
The cells of cardiac muscle tissue, like skeletal muscle fibers, possess visible striations
one nucleus and is shorter in length
The nucleus is oval and centrally located within the cell
characterized by cells that branch in an irregular pattern and cells join end-to-end by special regions called intercalated discs.
define intercalated discs
regions where the cell membranes of adjacent cells contact each other and contain desmosomes and gap junctions.
the specialized cells of a cardiac muscle tissue have a function that does what?
These specializations of the cell allow for cohesion and rapid electrical conduction, respectively
coordinated contraction of all the cardiac muscle cells is necessary for the efficient pumping of blood.
where is the cardiac muscle tissue located?
Cardiac muscle tissue is located only in the walls of the heart and is involuntarily controlled. The contraction of this tissue circulates the blood throughout the body.
What is the nervous system?
organ system which regulates the activity of other body systems
two major divisions of the nervous system
the central nervous system (which consists of the brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (which consists of all nervous tissue outside the brain and spinal cord).
Nervous tissue contains two main cell types
neurons and the more numerous supportive neuroglial cells
What are neurons
which are the “structural and functional” units of nervous tissue. Neurons, the largest and most prominent cells of nervous tissue, are specialized cells that convert stimuli into electrical signals called action potentials or nerve impulses.
This electrical information is rapidly conducted to other neurons, to muscle tissue or to glands.
basic structure of a “typical” neuron includes the
cell body (soma), dendrites and the axon.
The cell body of a typical neuron consists of?
nucleus, which has a conspicuous nucleolus, and the surrounding cytoplasm.
The cytoplasm of a neuron contains
many organelles, such as mitochondria, ribosomes, and Nissl bodies
What is Nissl bodies?
which are aggregations of rough endoplasmic reticulum
what is neurofibrils?
bundles of protein filaments within the cytoplasm
which are important elements of the cytoskeleton
Extending from the cell body of the neuron are various numbers of tapering, branched processes known as
dendrites
dendrites
function to receive stimuli or information from other neurons
Another type of cytoplasmic process extending from the cell body is the
axon
what is axon
specialized to conduct information to other cells and is often referred to as a nerve fiber because it may be very long and slender.
The axon may be covered with a fatty sheath called
myelin
myelin
which protects and insulates the axon and also increases the speed of conduction of nerve impulses
the difference of myelin sheath between peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system
In the peripheral nervous system, axons are often covered by a myelin sheath formed by Schwann cells. In the central nervous system, the myelin sheath is formed by oligodendrocytes.
what are Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes
are types of neuroglia cells
what is nodes of Ranvier
There are small gaps in the myelin sheath where the plasma membrane of the axon is exposed.
they enable the nerve impulse to jump from node to node, hence increasing the speed at which an impulse travels.
telodendrites (axon terminals)
are the fine branched endings of the axon.