Week 8A: Energy Metabolism (TCA Cycle and ETC)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Where does the TCA cycle occur in the cell?
Matrix of mitochondria
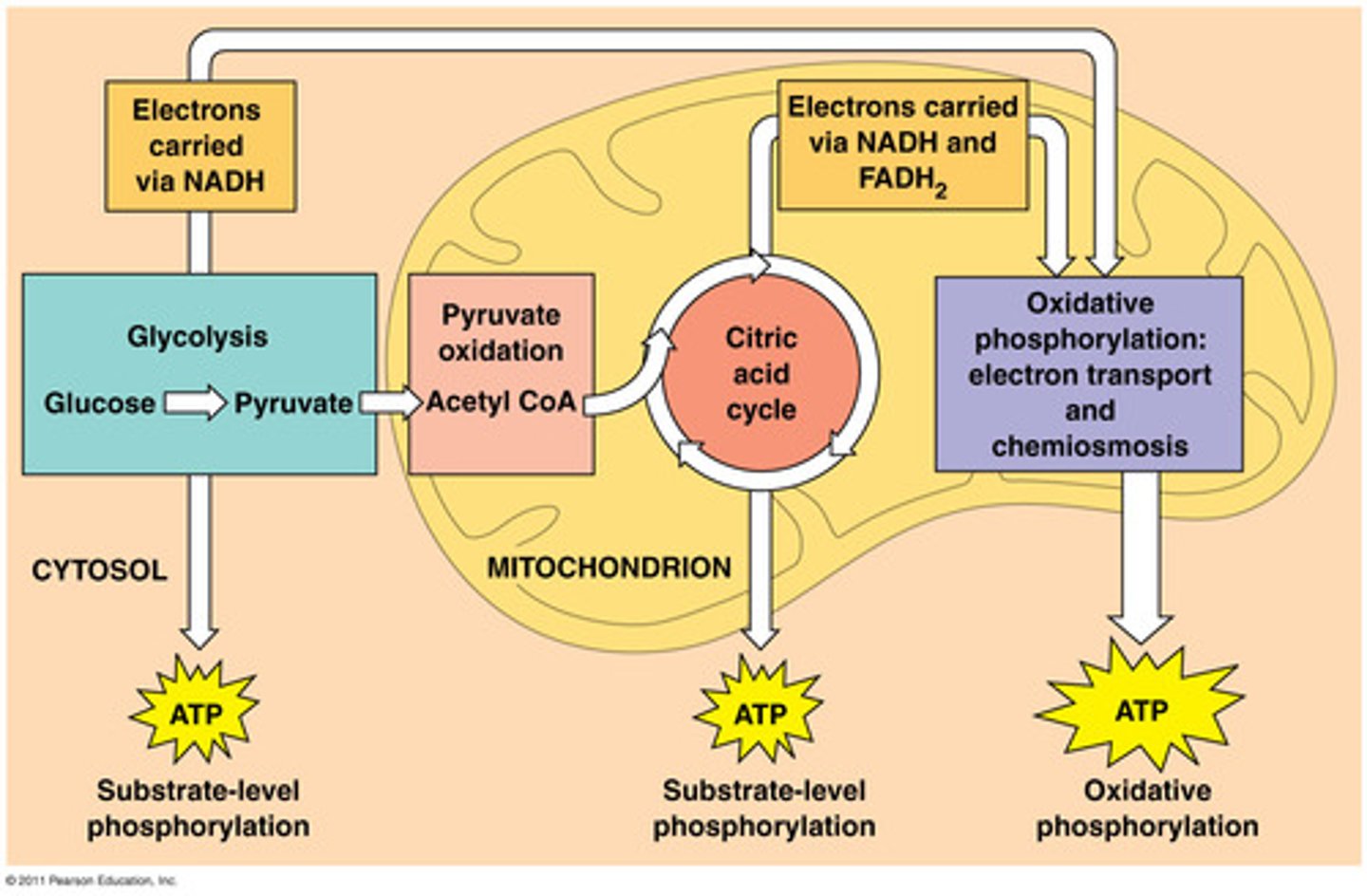
Where does the ETC occur in the cell?
Inner membrane of mitochondria (use of hydrogen gradient to generate ATP)
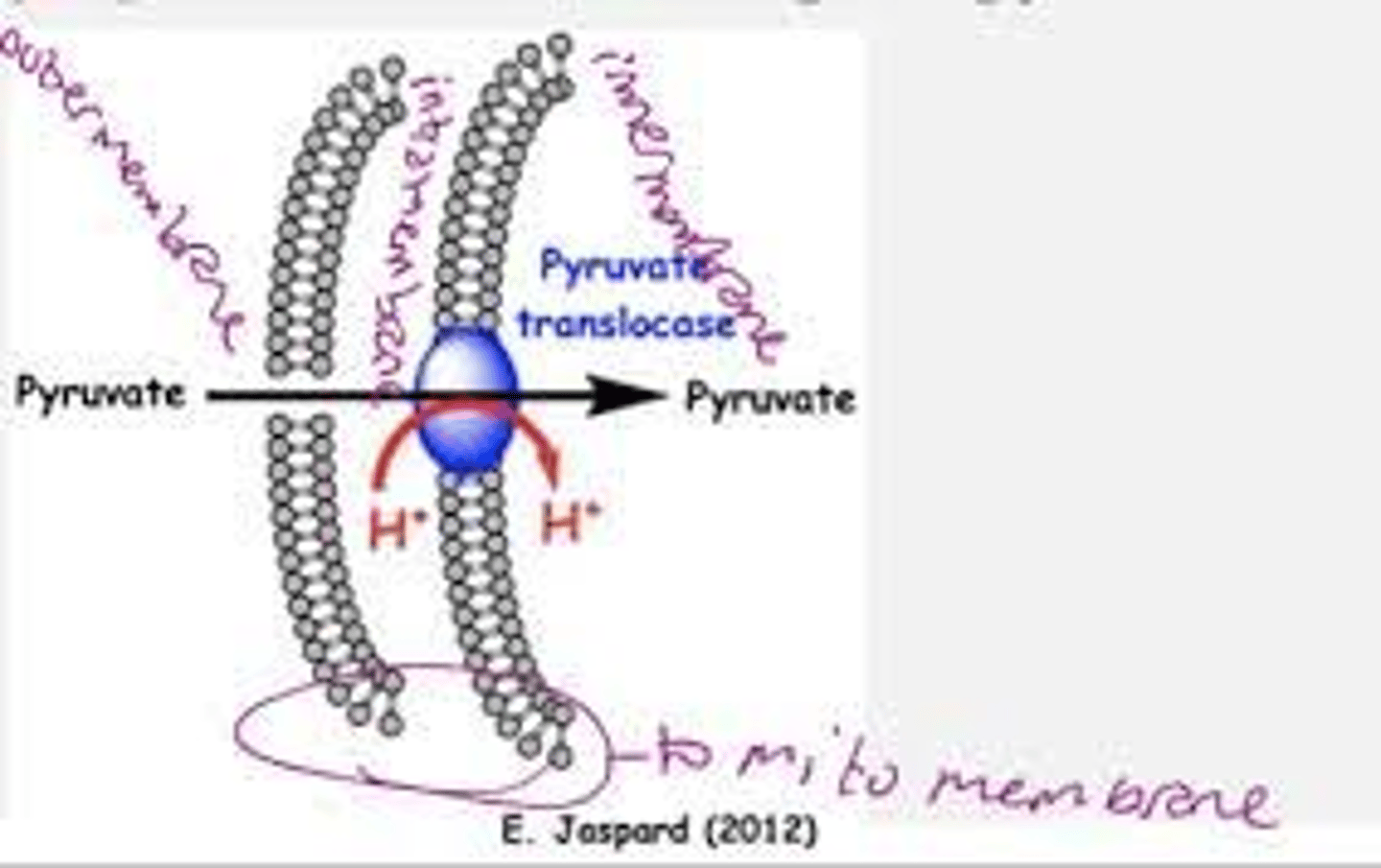
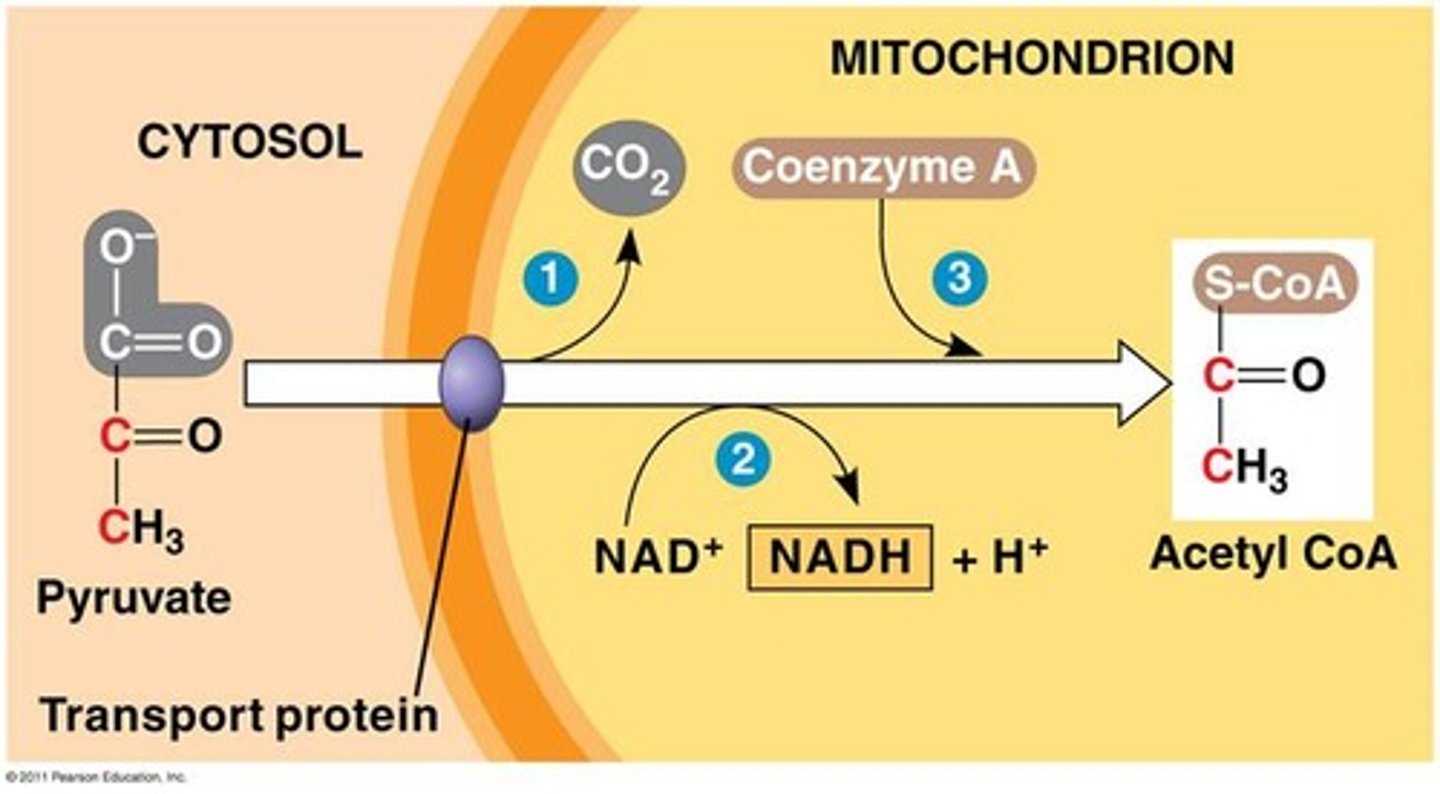
How does pyruvate enter the mitochondria?
Diffuses through outer membrane
Moves through inner membrane with aid of carrier proteins (not permeable to pyruvate)
Which enzyme converts pyruvate to acetyl-COA?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme complex (PDC)
Converts 3-carbon pyruvate to 2-carbon acetyl-CoA
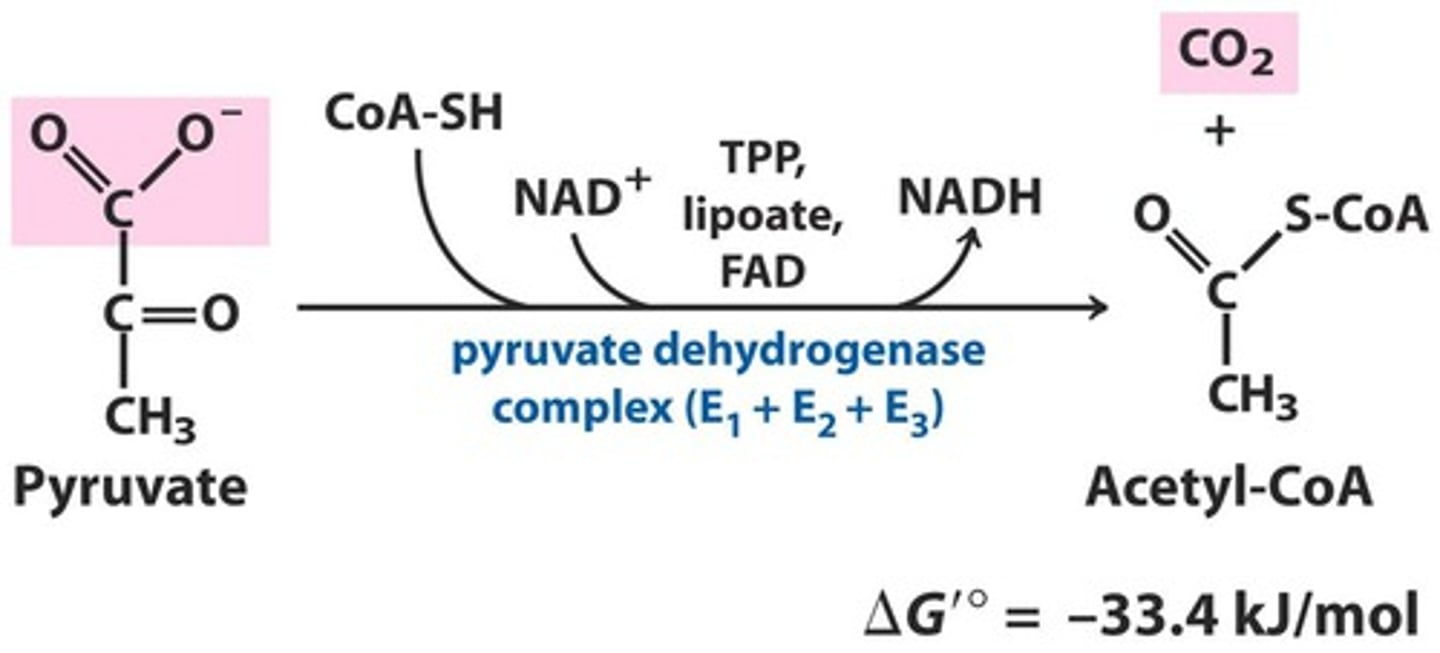
What are the products of converting pyruvate into acetyl-COA?
1 Acetyl-COA :0
1 NADH (Electron Carrier for ETC)
1 CO2
x2 for 1 glucose molecule
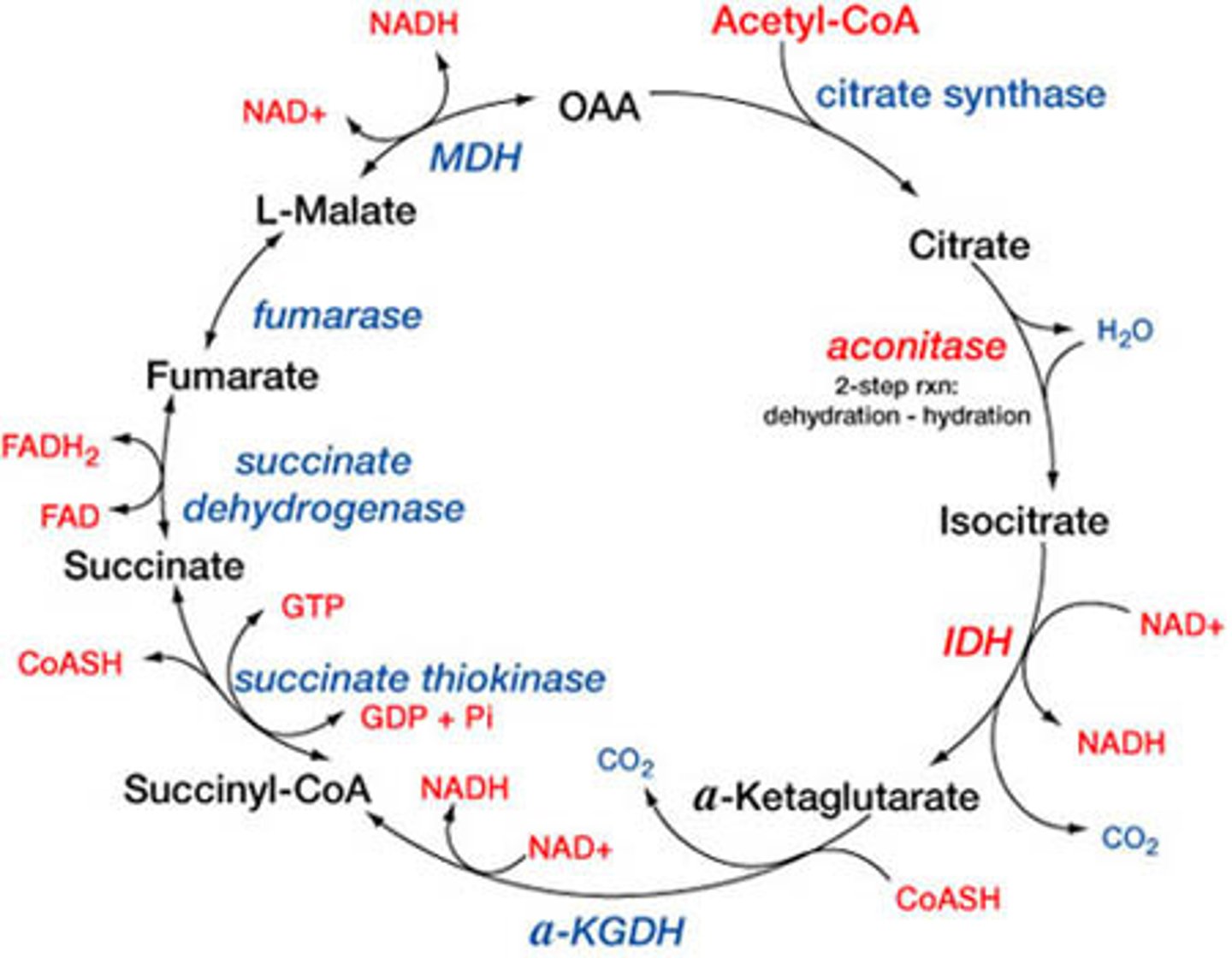
What is the first step of the krebs cycle?
Converting 4C oxaloacetate (end of krebs cycle) into 6C citrate with the addition of 2C acetyl-CoA
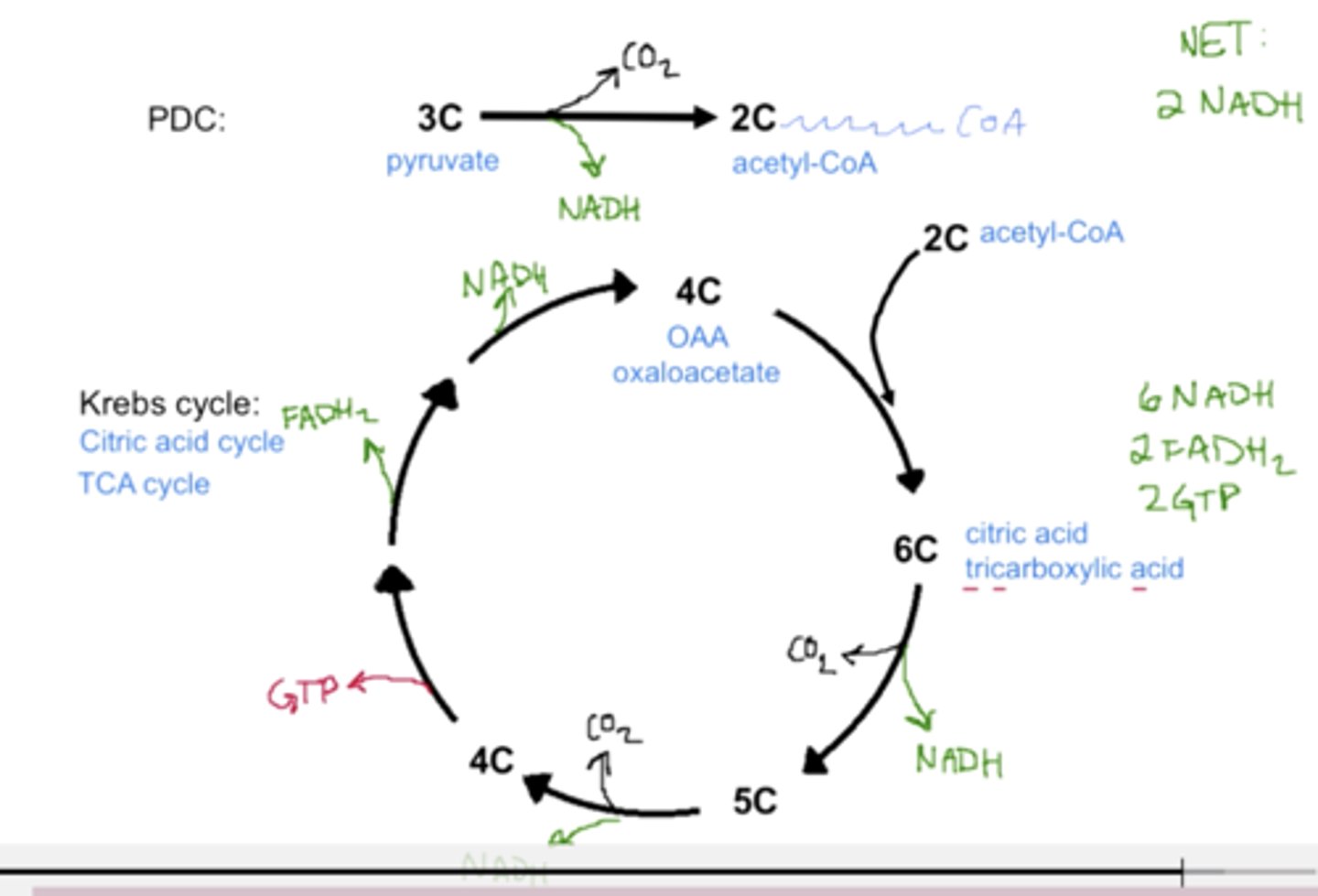
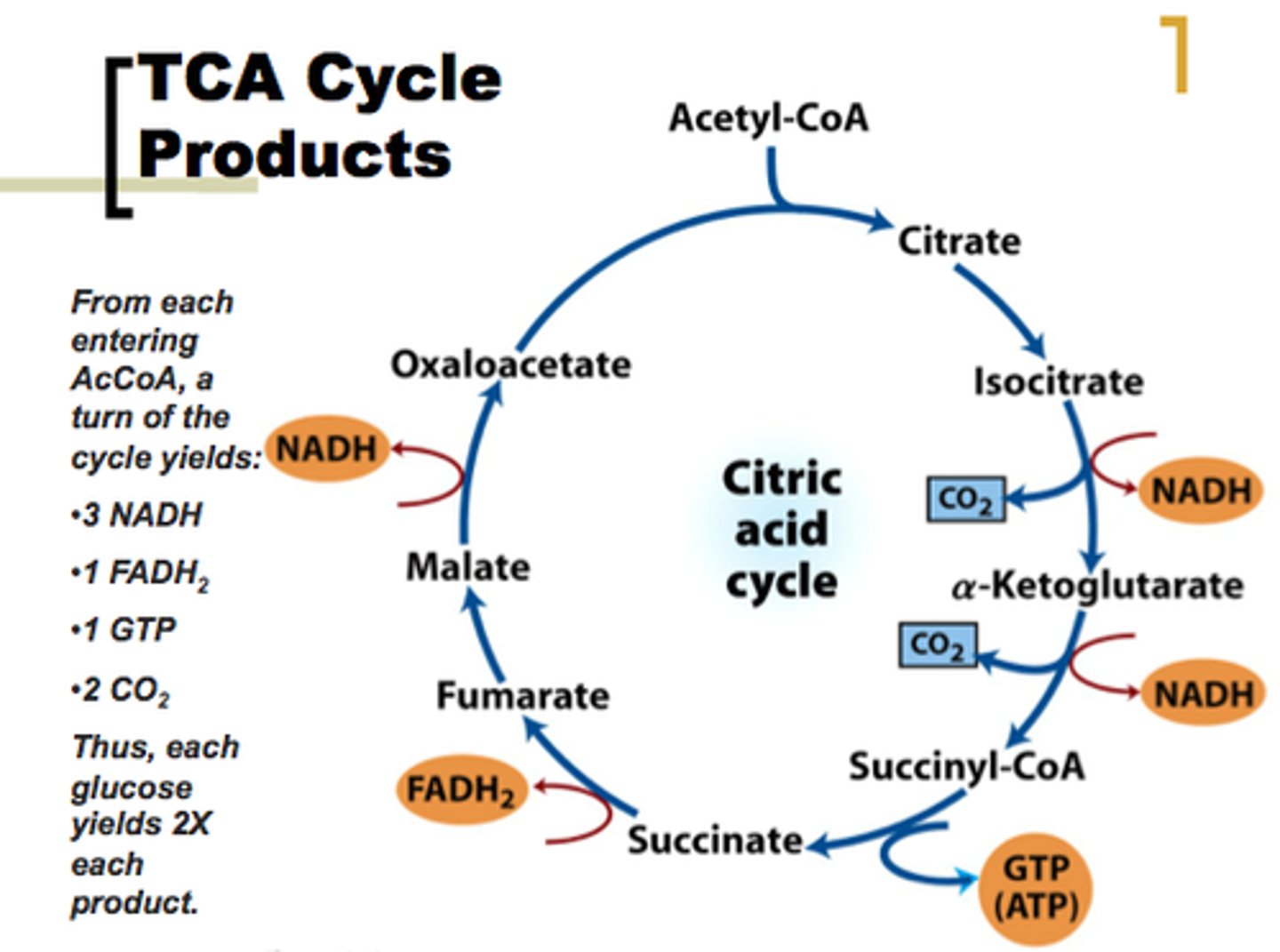
What are the products of the TCA cycle?
1 GTP
3 NADH (Electron Carrier for ETC)
1 FADH (Electron Carrier for ETC)
2 CO2 (waste products, exhaled by breathing)
x2 for 1 glucose molecule
Are the electron carriers oxidized or reduced during glycolysis and the TCA cycle?
Reduced (NAD+ -> NADH)
Is glucose oxidized or reduced during glycolysis and the TCA cycle?
Oxidized (breakdown of glucose to make energy)
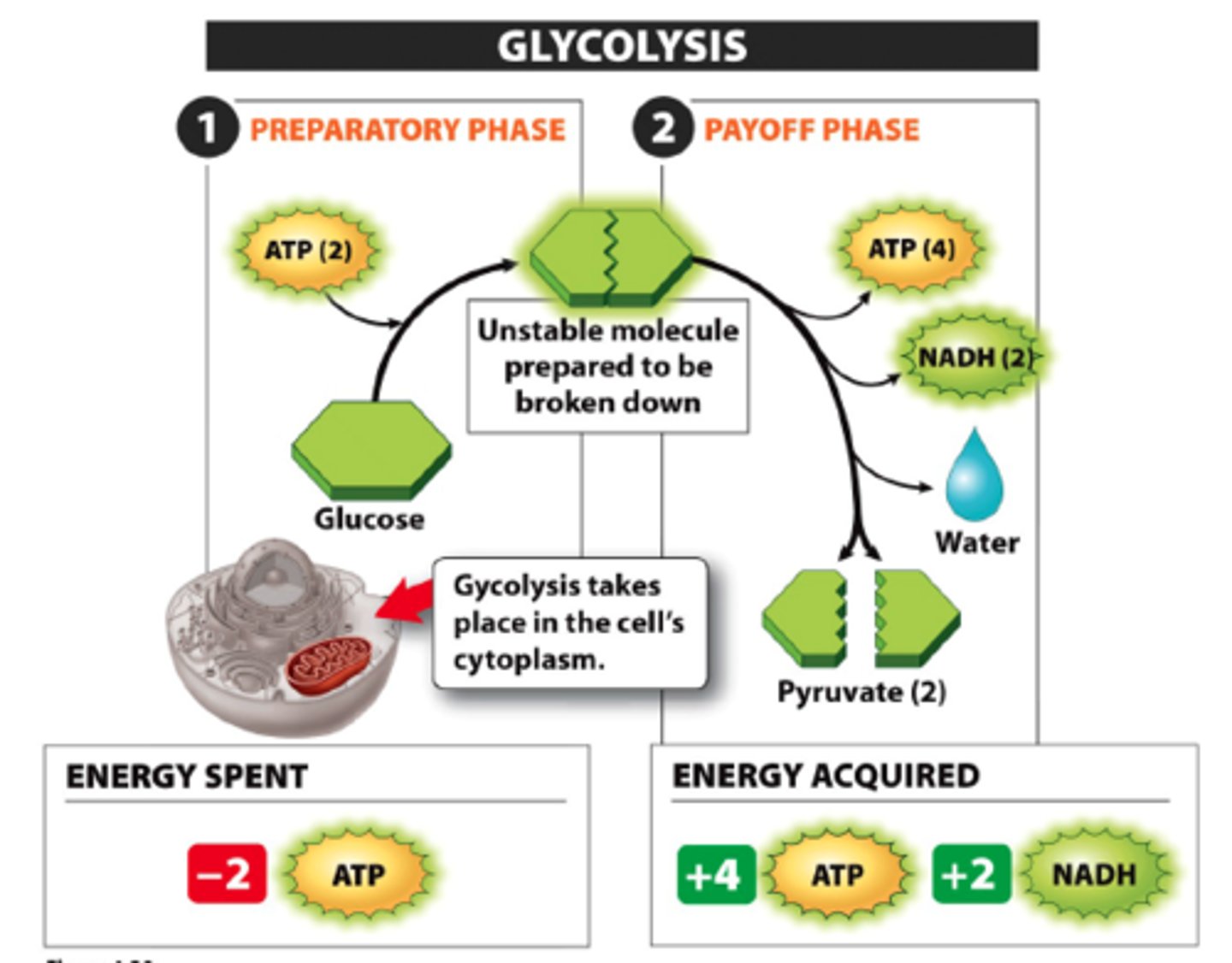
Are the electron carrier oxidized or reduced during the electron transport chain?
Oxidized (NADH -> NAD+ to generate ATP)
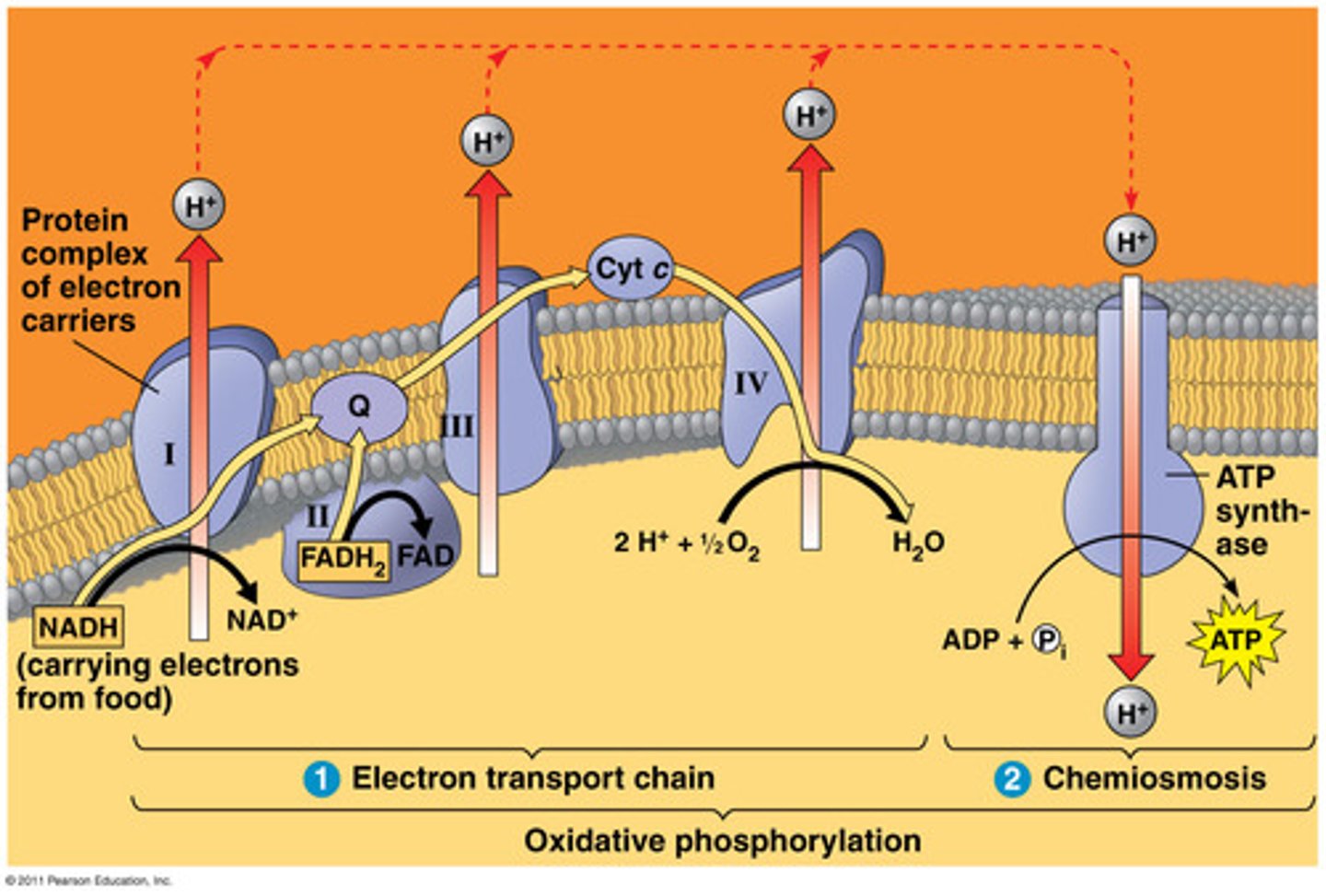
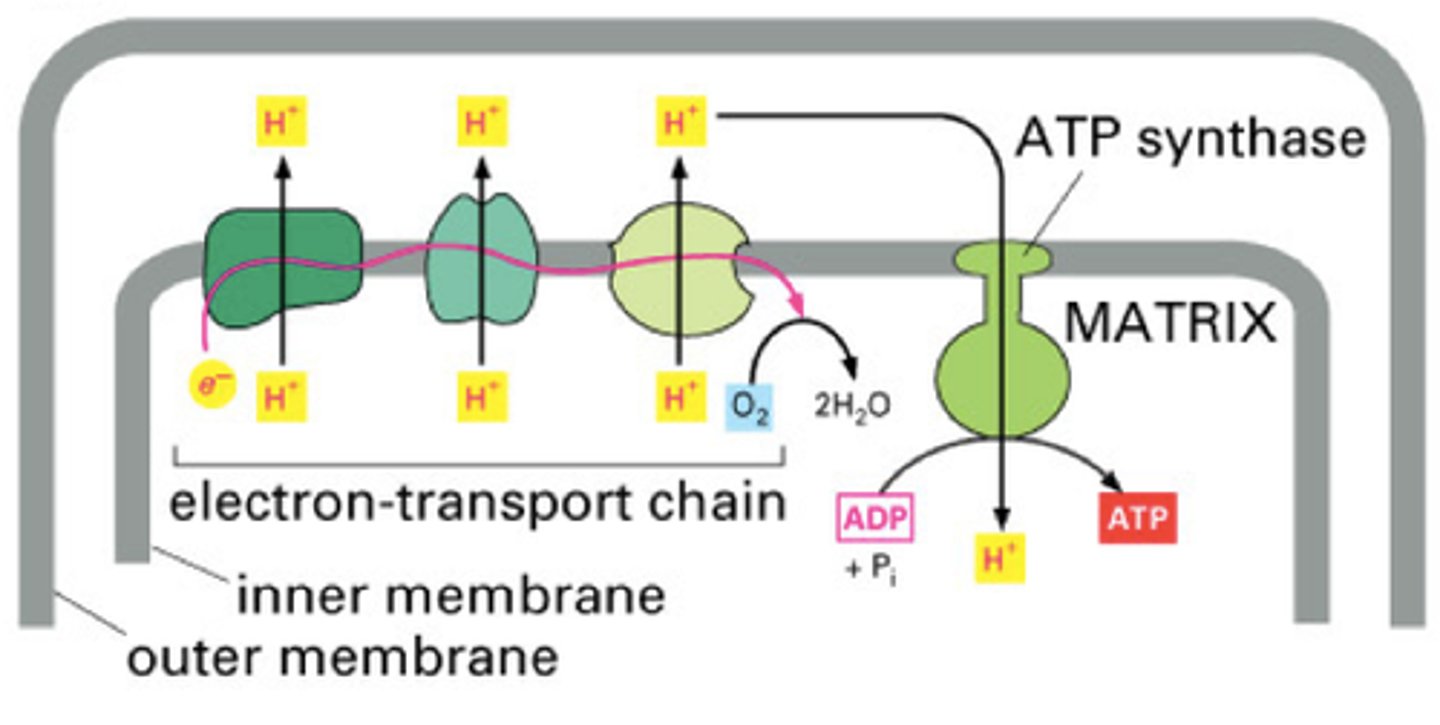
What process is responsible for producing ATP during the electron transport chain?
Oxidative phosphorylation
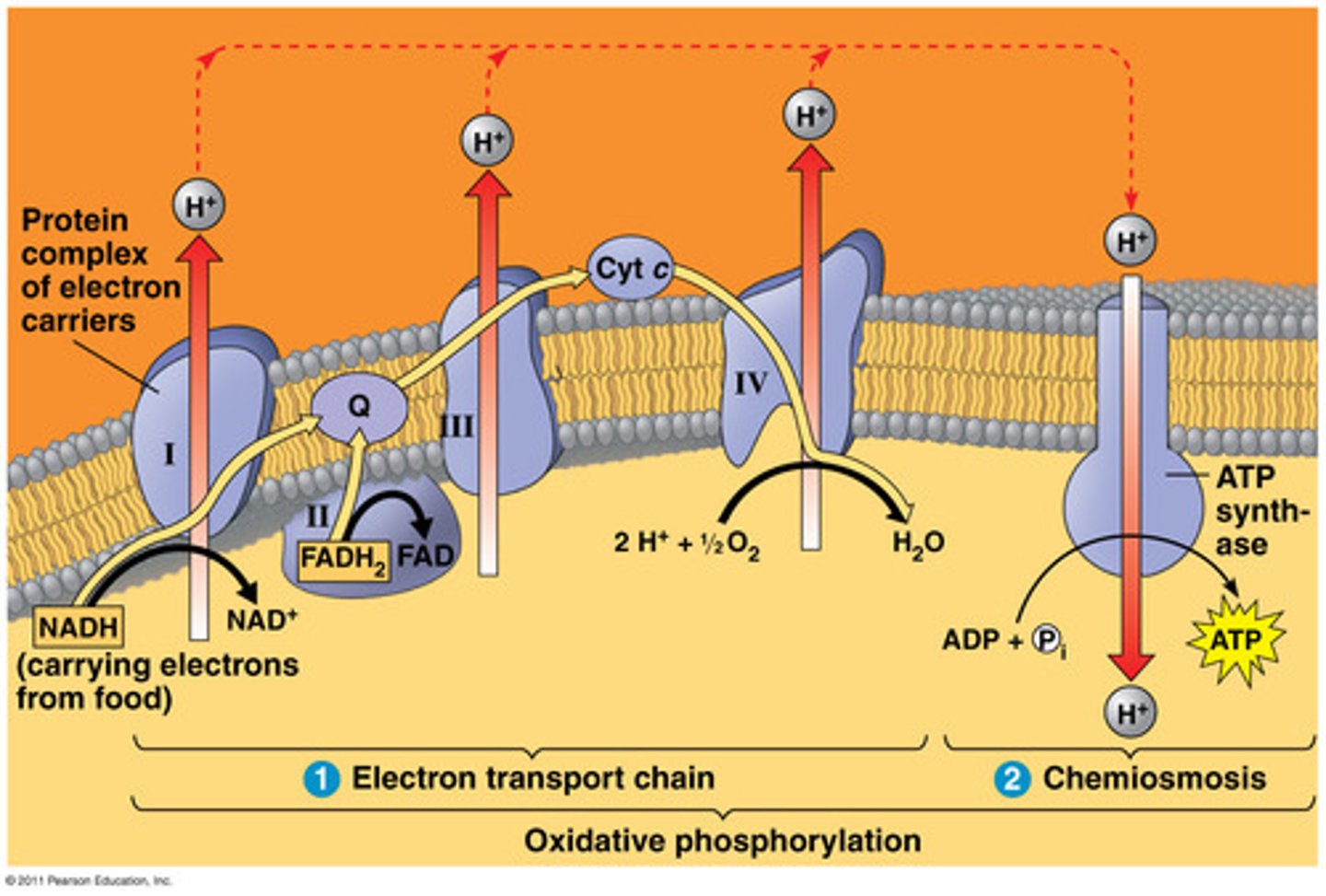
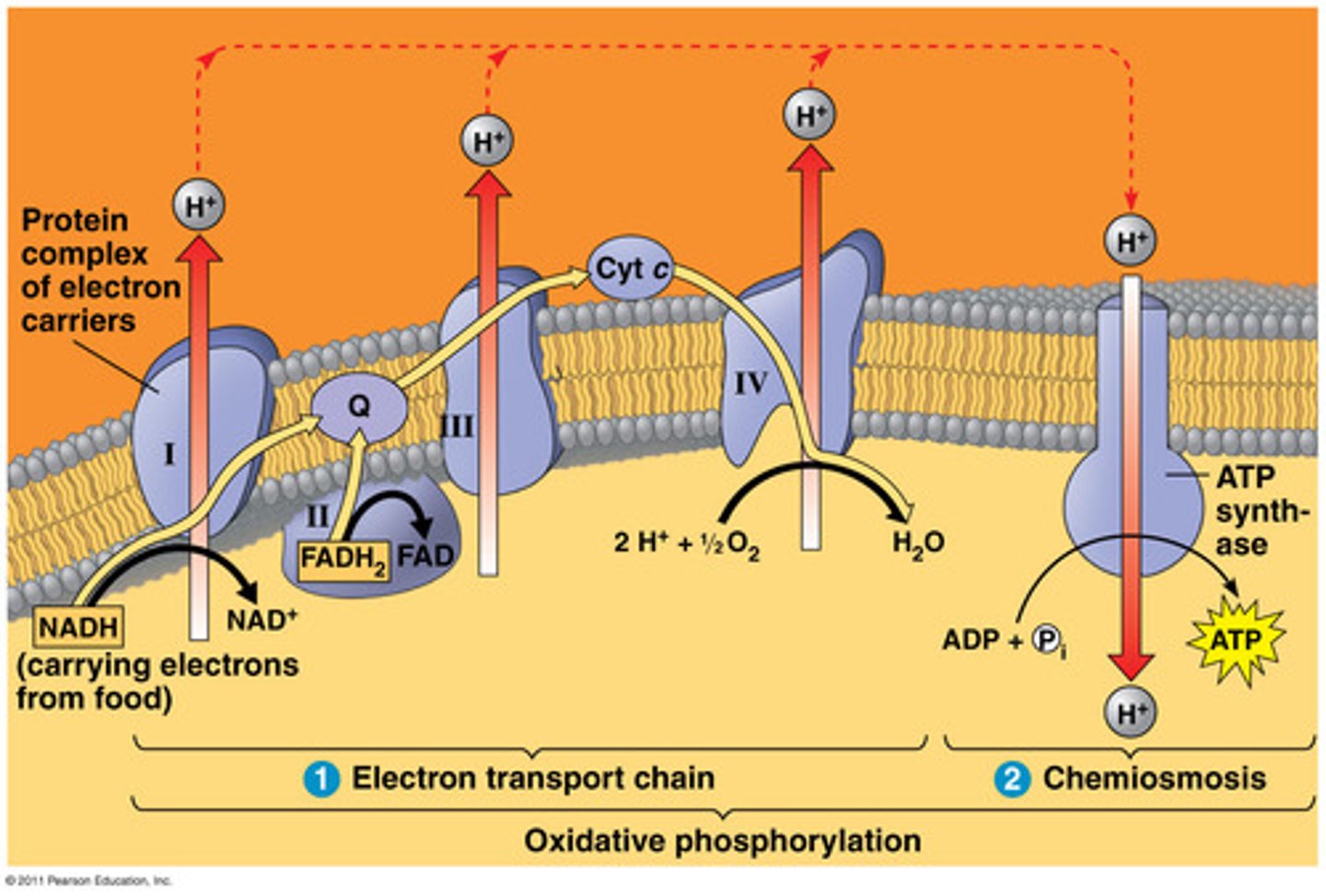
What occurs during the electron transport chain?
1. Electron carriers donate electrons to COMPLEX I of ETC (NADH -> NAD+ + H+ + e-)
2. This electron is used to power the complexes in the electron transport chain to move H+ out of the inner membrane
3. H+ moves back into the membrane through ATP synthase due to its concentration gradient (higher outside than inside)
4. This movement powers the ATP synthase to produce ATP, some energy is also released as heat
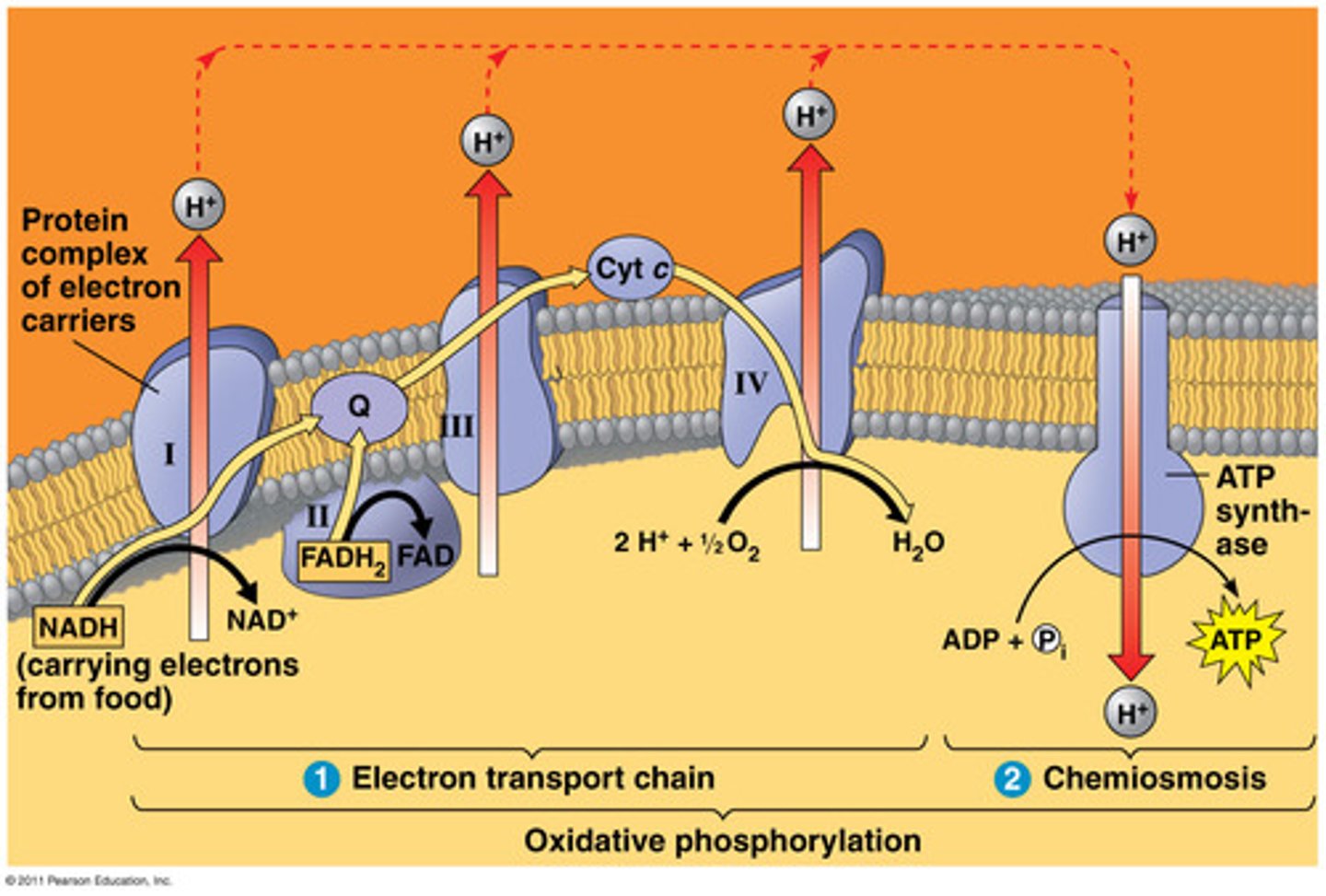
Why is oxygen required to power the electron transport chain?
Attracts the electron so that it moves it through the various complexes in the ETC
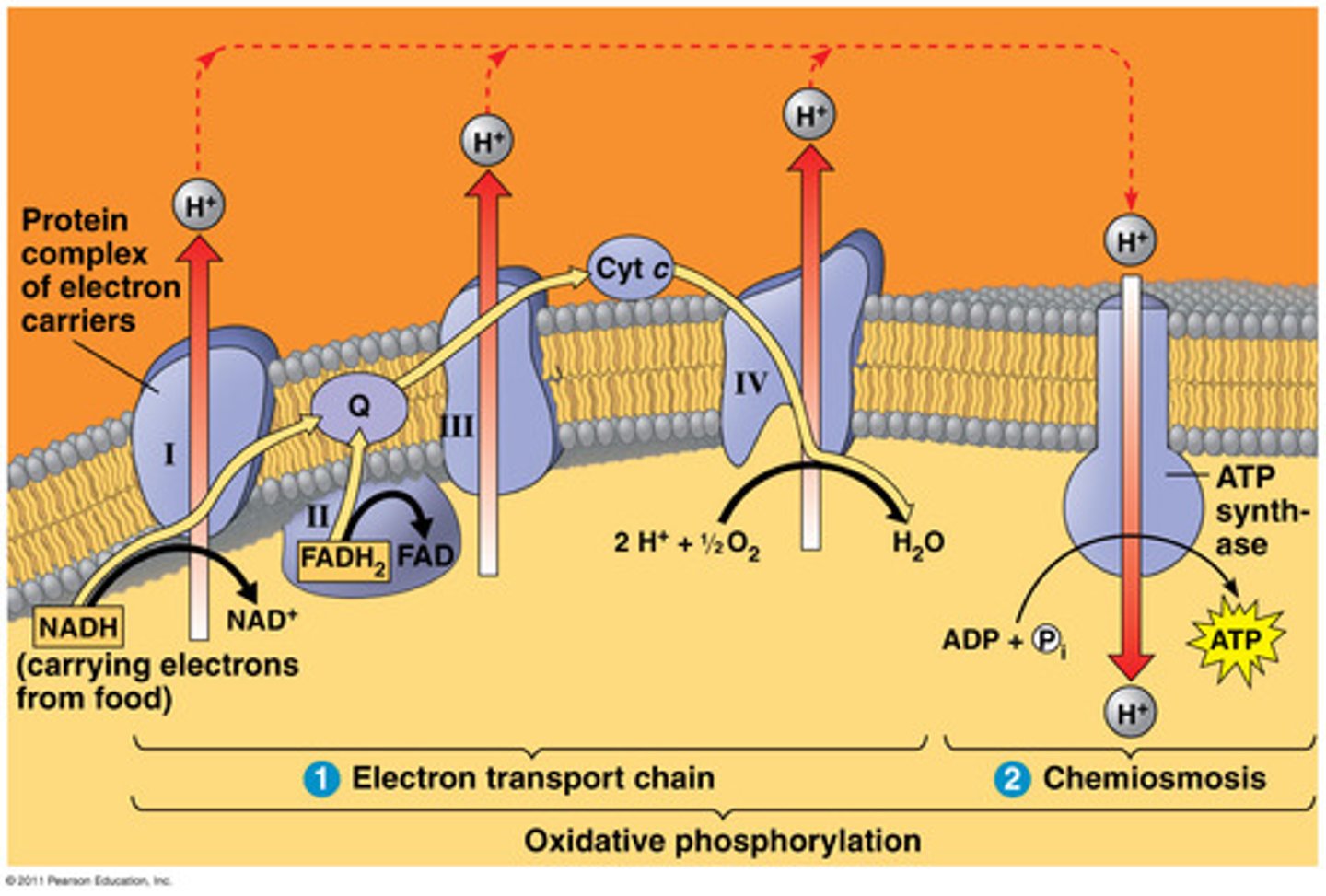
What are the products of the ETC?
ATP!!!
NAD+
FAD+
H2O (O2 -> H2O)
Heat
How much ATP and electron carriers are produced in glycolysis from 1 glucose molecule?
2 ATP + 2 NADH
How much ATP and electron carriers are produced by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from 1 glucose molecule?
2 NADH
How much ATP and electron carriers are produced in the TCA cycle from 1 glucose molecule
6 NADH
2 FADH
2 GTP
How much ATP is produced during the electron transport chain from 1 glucose molecule
2 NADH (gly) + 2 NADH (pdc) + 6 NADH (tca) = 10 NADH (x2.5 ATP per) = 25 ATP
2 FADH x 1.5 ATP per = 3 ATP
Total of 28 ATP produced during the electron transport chain
How much ATP/GTP is produced in the entire aerobic energy metabolism pathway from 1 glucose molecule?
28 ATP - ETC
2 GTP - TCA cycle
2 ATP - Glycolysis
Total = 32 ATP/GTP
What causes the TCA Cycle to be turned on?
Excess NAD+, means that energy is being used up very quickly
What causes the TCA Cycle to be turned off?
Excess NADH, means that there is an excess of potential energy in the cell
What occurs if a cell does not receive enough oxygen?
Cells need oxygen to efficiently produce ATP (via aerobic pathway)
Hypoxia (lack of o2 in cells) leads to decreased ETC< which leads to decreased ATP.
This causes calcium and sodium to accumulate in the cell, leading to cellular swelling as more water is being drawn into the cell. This causes the cell to be more permeable, amplifying the swelling until the cell dies
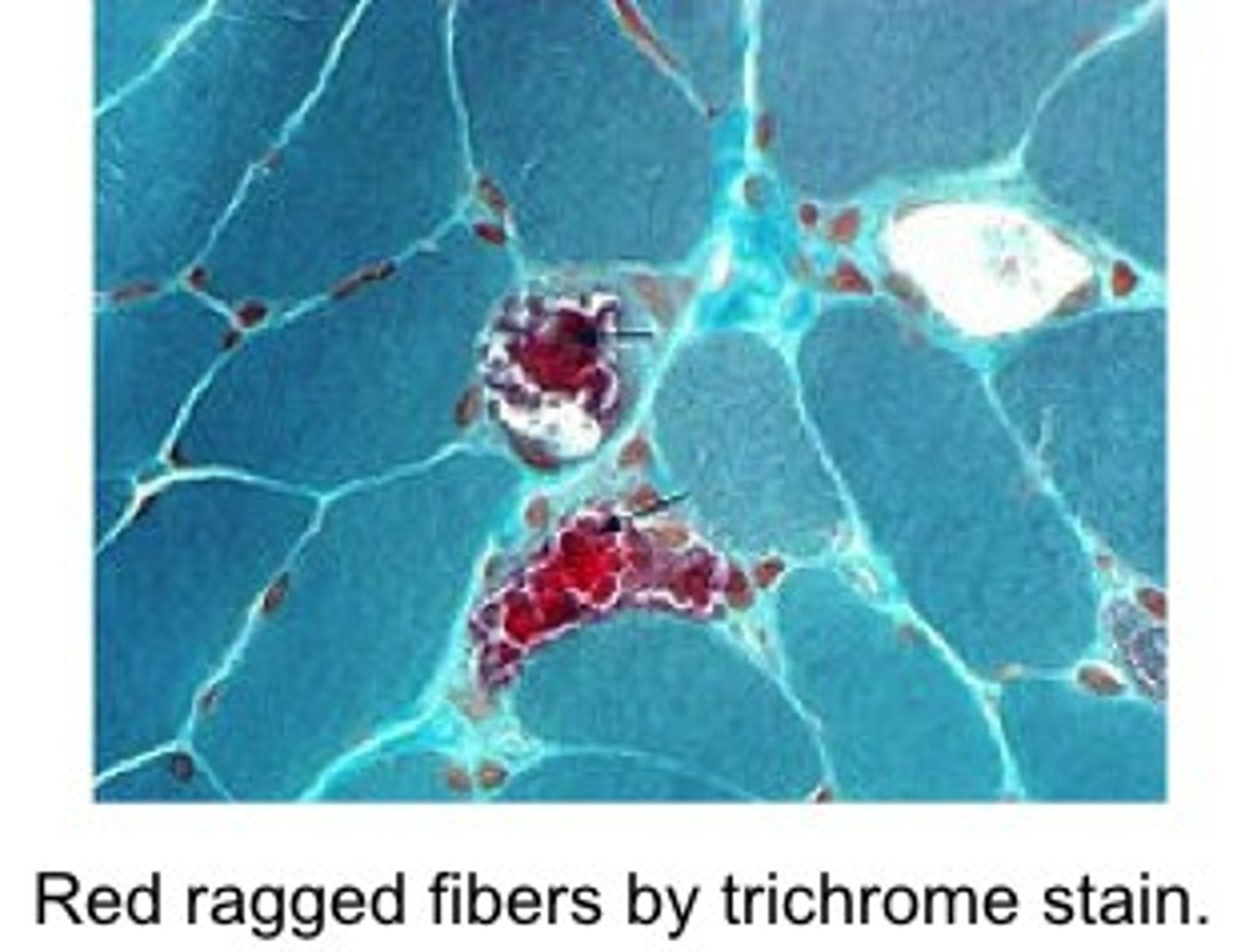
What is MERRF?
Myoclonic Epilepsy with Ragged Red Fibers
Caused by point mutation to mitochondrial tRNA tys, results in clumps of diseased mitochondria aggregating in muscle tissue, causing red clumps
Since mitochondria can not produce ATP, the nervous system and muscles are immediately implicated because they have the highest ATP requirements
How much ATP is produced by the oxidation of FADH?
1.5 ATP per
How much ATP is produced by the oxidation of NADH?
2.5 ATP per
Is acidosis or alkalosis more likely to occur during hypoxia (overuse of anerobic respiratory pathway)?
Acidosis due to production of lactate
What are 5 differences between aerobic and anerobic respiration?
Aerobic - O2 is required
Anerobic - No O2 is required
Aerobic - Occurs in mitochondria
Anaerobic - Occurs in cytoplasm
Aerobic - 32 ATP is produced
Anerobic - 2 ATP is produced
Aerobic - Occurs is slower
Anaerobic - Occurs faster