AP Macroeconomics - Unit 3
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Aggregate Demand
The quantity demanded of all goods and services at different price levels, ceteris paribus
Aggregate Supply
The quantity supplied of all goods and services at different price levels, ceteris paribus
Automatic Fiscal Policy (Non-Discretionary Fiscal Policy)
Changes in the government expenditures and/or taxes that occur automatically without (additional) congressional action
Budget Deficit
A shortfall of tax revenue from government spending
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
Decrease in government spending and/or increase in taxes to reduce economic growth
Crowding Out
The decrease in private expenditures that occurs as a consequence of increased government spending or the financing needs of a budget deficit
Discretionary Demand-Side Fiscal Policy
Deliberate changes of government expenditures and/or taxes to achieve particular economic goals
Expansionary Demand-Side Fiscal Policy
Increases in government expenditures and/or decreases in taxes to achieve particular economic goals
Fiscal Policy
Changes in government expenditures and/or taxes to achieve economic efficiency
Inflationary Gap
The condition where the Real GDP the economy is producing is greater than the Natural Real GDP and the unemployment rate is less than the natural unemployment rate
Interest Rate Effect
The changes in household and business buying as the interest rate changes
International Trade Effect (Net Export Effect)
The change in foreign sector spending as the price level changes.
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
The ratio of the change in consumption to the change in disposable income.
1 - MPS
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
The ratio of the change in saving to the change in disposable income.
1 - MPC
Menu Costs
The cost of changing prices
Multiplier
The number that is multiplied by the change in autonomous (new) spending to obtain the overall change in total spending
Public (National) Debt
The total amount the federal government owes its creditors
Real Balance Effect
The changes in the purchasing power of dollar-dominated assets that results from a change in the price level
Recessionary Gap
The condition where the Real GDP the economy is producing is less than the Natural Real GDP and the unemployment rate is great than the natural unemployment rate
Say's Law
Supply creates its own demand. Production creates demand sufficient to purchase all goods and services produced.
Short-Run Equilibrium
The condition that exists in the economy when the quantity demanded of Real GDP equals the (short-run)quantity supplied of Real GDP. Shown by where the AD curve intersects the SRAS
Stagflation
The simultaneous occurrence of high rates of inflation and unemployment
Supply-Side Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy centered on tax reductions targeted to aggregate supply so that real GDP increases with very little or no inflation. The main justification is that lower taxes on individuals and firms increase incentives to work, save, invest, and take risks
Autonomous Change in Aggregate Spending
Is an initial rise or fall in aggregate spending that is the cause, not the result, of a series of income in spending changes
Wealth Effect
The change in the consumer spending caused by the altered purchasing power of consumer assets
Monetary Policy
The central banks use the changes in the quantity of money or the interest rate to stabilize the economy
Aggregate Supply Curve
Shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output supplied in the economy
Nominal Wage
Dollar amount of the wage paid
Sticky Wages
Nominal wages that are slow to fall even in the face of high unemployement and slow to rise even in the face of labor shortages
Short-run Aggregate Supply Curve
relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output supplied that exists in the short run, the time period when many production costs can be taken as fixed
Long-run Aggregate Supply Curve
shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output supplied that would exist if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible
Potential Output
the level of real GDP the economy would produce if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible
AD-AS model
aggregate supply curve and aggregate demand curve are used together to analyze economic fluctuations
Short-run Macroeconomic Equilibrium
when the quantity of aggregate output supplied is equal to the quantity demand
Short-run Equilibrium Aggregate Price Level
the aggregate price level in the short run macroeconomic equilibrium
Short-run Equilibrium Aggregate Output
is the quantity of aggregate output produced in the short-run macroeconomic equilibrium
Demand Shock
An event that shifts the aggregate demand curve
Supply Shock
An event that shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve is a supply shock
Long-run Macroeconomic Equilibrium
when the point of short-run macroeconomic equilibrium is on the long-run aggregate supply curve
Output Gap
percentage difference between actual aggregate output and potential output
Self-Correcting
When the shocks to aggregate demand affect aggregate output in the short run, but not the long run
Stabilization Policy
The use of government policy to reduce the severity of recessions and rein in excessively strong expansion
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
Increases aggregate demand
Lump-Sum Taxes
are taxes that don't depend on the taxpayers income
Tax Multiplier
tax increase = -MPC / MPS; tax cut MPC / MPS. Always 1 less than comparable spending multiplier.
Recognition Lag
The time it takes for policy makers to recognize the existence of a boom or a slump.
Administrative Lag
The time it takes for Congress to agree on a course of action with the president.
Operational Lag
Spending/planning takes time to organize and execute (changing taxing is quicker).
Crowding-Out Effect
Government spending might cause unintended effects that weaken the impact of the policy.
Net Export Effect
Works through international trade to reduce the effectiveness of fiscal policy.
Beliefs of Classical Theory
1. A change in AD will not change output even int he short run because prices of resources (wages) are very flexible.
2. AS is vertical so AD can't increase without causing inflation.
Classical Theory
The economy self-adjusts to deviations from its long-term growth trend. No government involvement is required.
Beliefs of Keynesian Theory
1. A decrease in AD will lead to a persistent recession because prices of resources (wages) are NOT flexible.
2. Increase in AD during a recession doesn't cause inflation.
Keynesian's 3 Ranges of Aggregate Supply Curve
1. Keynesian Range - Horizontal at low output.
2. Intermediate Range - Upward sloping
3. Classical Range - Vertical at physical capacity
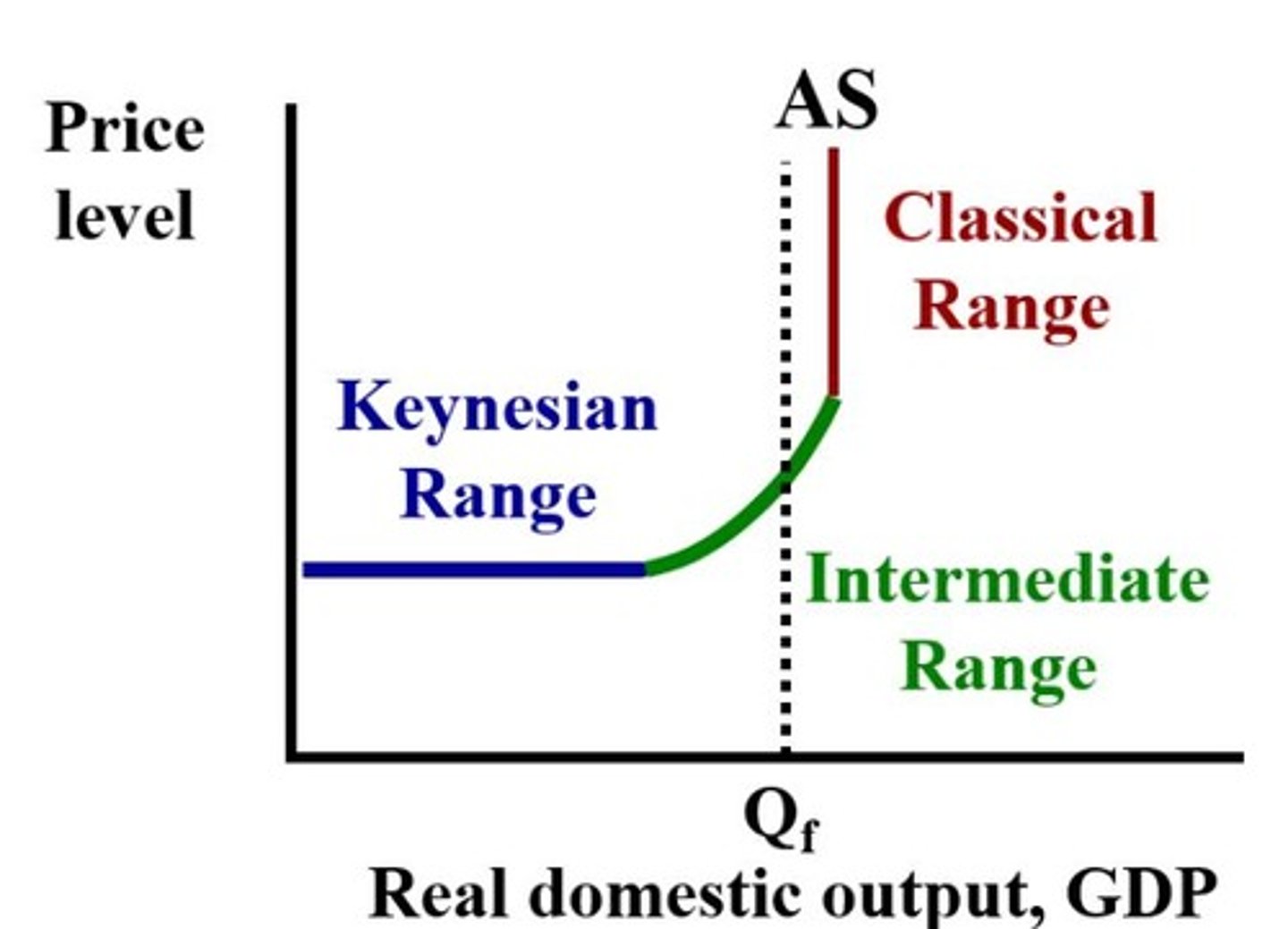
Keynesian Range of Keynesian AS Curve
Shifts of the aggregate demand curve in this range lead to changes in the aggregate output, but not changes in price level.
Intermediate Range of Keynesian AS Curve
The positively-sloped segment of the Keynesian aggregate supply curve that reflects the trade-off between aggregate output and the price level. Shifts of the aggregate demand curve in this range lead to changes in both aggregate output and the in price level.
Classical Range of Keynesian AS Curve
The vertical segment of the Keynesian aggregate supply curve that reflects the independence of full-employment aggregate output (or gross domestic product) to the price level. Shifts of the aggregate demand curve in this range lead to changes in the price level, but not changes in aggregate output.
Aggregate Demand Curve
Shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output demanded by households, businesses, government and the rest of the world (C+I+G+Xn).