Renewables Concept Questions
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Smart Grid – Definition
A smart grid is an electricity network that uses two-way digital communication, automation, and advanced control systems to manage power flow. It integrates renewable energy sources, adapts to peak load conditions, and improves reliability, efficiency, and power quality by monitoring and responding to grid conditions in real time.
Difference between Micro-Grid, Distributed Generation, Islanded Systems
Micro-grid: Has its own energy management system and can operate grid-connected or islanded (EMS and Grid Connected)
Distributed Generation: Injects power into the grid but does NOT manage local loads (Grid connected, No EMS)
Islanded Energy System: Not connected to the grid; must manage its own voltage and frequency (No Grid, EMS)
Why smart grids are increasingly needed with EV growth
EV charging creates large peak demands. Smart grids manage charge timing and power levels, prevent overloads, and can even use EV batteries for support via vehicle-to-grid services.
What is AA-CAES (Advanced Adiabatic Compressed Air Energy Storage)?
It stores the heat generated during air compression and later reuses it for reheating during expansion. This avoids burning extra fuel, improves efficiency, and makes storage cleaner.
Advantages & disadvantages of Superconducting Magnetic Energy Systems (SMES) + Definition
Stores Energy in magnetic field generated by a DC current flowing through a superconducting coil kept at cryogenic temperature. Energy can be released instantly by adjusting the current.
Advantages: Fast response time, deep discharge possible, no environmental hazards.
Disadvantages: High cost and maintenance, reduced efficiency due to cooling process, high daily energy loss (1–2%).
Advantages & disadvantages of Flywheels + Definition
Heavy rotor spins at high speed in low friction environment. When energy is needed, the kinetic energy of the spinning rotor is converted back into electricity.
Advantages: Low Maintenance and long lifespan (20 years), almost no carbon emissions, fast response times, no toxic components
Disadvantages: High cost, limited capacity, high self-discharge.
Advantages & disadvantages of Lead-Acid Batteries
Advantages: Cheap, mature tech, high surge capability, recyclable.
Disadvantages: Heavy, short lifetime, toxic materials, corrosion.
Advantages & disadvantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Advantages: Very high energy density, high voltage per cell, low energy loss.
Disadvantages: Expensive, degrades even unused, flammable if exposed to moisture.
Advantages & disadvantages of Pumped Hydro Storage (PSH) + Definition
Uses two reservoirs at different heights. Water is pumped up during low demand and released back down through a turbine during high demand.
Advantages: Mature tech, huge amounts of energy storage, high overall efficiency, fast response, inexpensive method
Disadvantages: Few potential sites, huge environmental impact, requires a significant water source.
Advantages & disadvantages of Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) + Definition
Electricity is used to compress air into underground caverns. During discharge, the air is reheated and expanded through a turbine.
Advantages: Large energy storage, relatively inexpensive, fast response, AA-CAES capable of 70% efficiency.
Disadvantages: Requires sealed caverns, limited duration (about a day), not fully developed, competes with other storage needs (natural gas, hydrogen)
Difference between conventional batteries & redox-flow batteries
Conventional batteries store energy in electrodes and electrolyte inside the cell.
Redox-flow batteries store energy in external electrolyte tanks; power depends on cell stack size, energy depends on tank size.
Four types of ocean energy
Tidal Lagoon: Uses rising/falling tides like a hydro dam but in an estuary. Large volumes of water are held back then released twice a day as the tides rise and fall. Water flows through a turbine and generates electricity.
Wave Energy: Captures up and down surface wave motion to drive a power conversion device (hydraulic, pneumatic, direct drive).
Ocean Current (Tidal Stream): Underwater turbines capture steady currents similar to wind turbines. Water is 800 times denser so currents carry substantial power.
Ocean Thermal (OTEC): Uses warm/cold water temperature difference to run a heat engine and produce steam that turns a turbine.
Compare Wave vs Tidal Energy
Wave energy varies with weather; tidal energy is predictable and stable. Wave devices float offshore; tidal systems use underwater turbines and barrages.
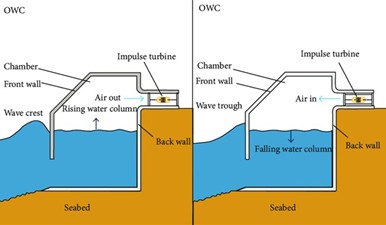
Working principle of Oscillating Water Column (OWC)
Waves move water up/down in a chamber, pushing and pulling air through a turbine. The same turbine spins during both inflow and outflow.
Difference between gasification and pyrolysis
Pyrolysis
Heats biomass without oxygen at lower temperatures to produce biochar and bio-oil (solid and liquid products).
Gasification
Uses limited oxygen or steam at high temperatures to convert biomass into syngas (CO and H₂) for power generation, hydrogen, or liquid fuels.
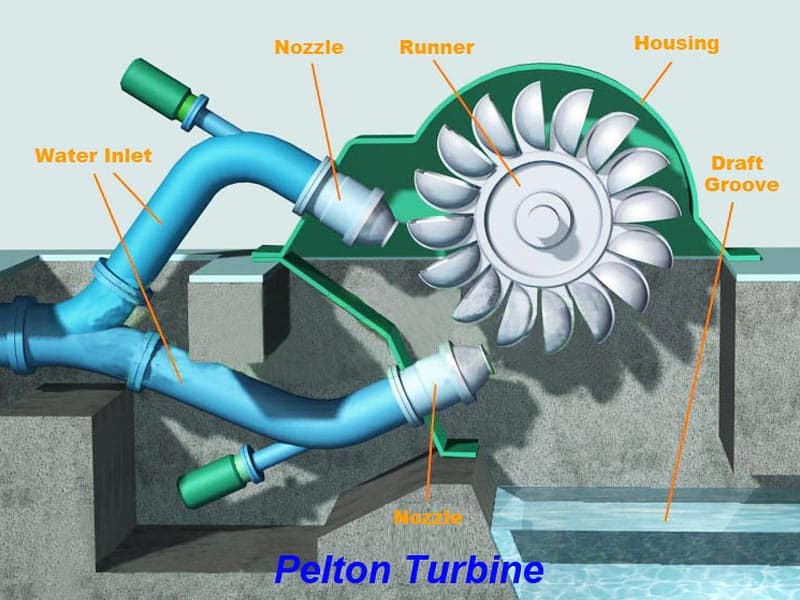
Explain Pelton Turbine
Impulse turbine for very high head, low flow. Water jets hit spoon-shaped buckets and reverse direction, transferring momentum efficiently.
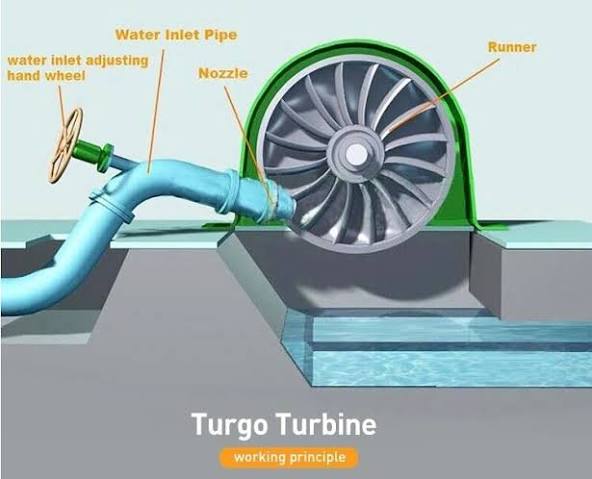
Explain Turgo Turbine
Impulse turbine for medium-high head, moderate flow. Water strikes at an angle and passes through the runner, allowing higher rotational speed and compact design.
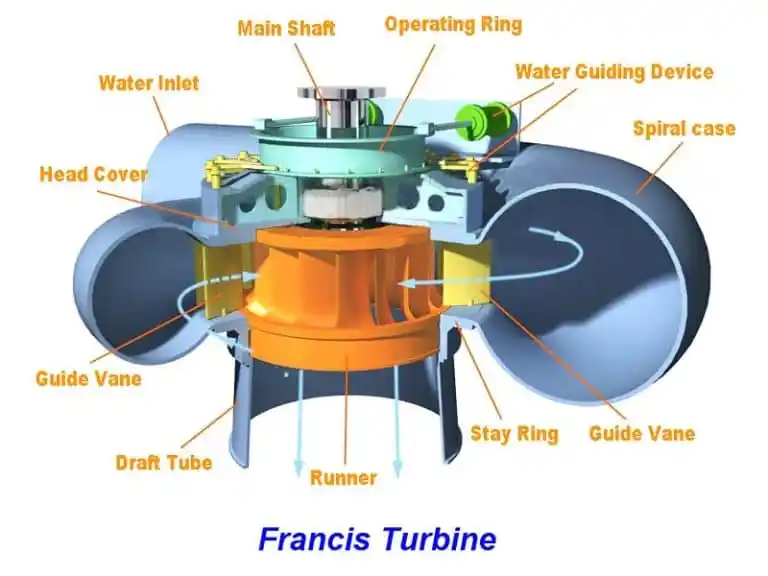
Explain Francis Turbine
Reaction turbine for medium head and flow. Water enters radially via adjustable guide vanes and flows inward/downward. Most common turbine in the world. Very efficient and widely used in damns and large hydro plants.
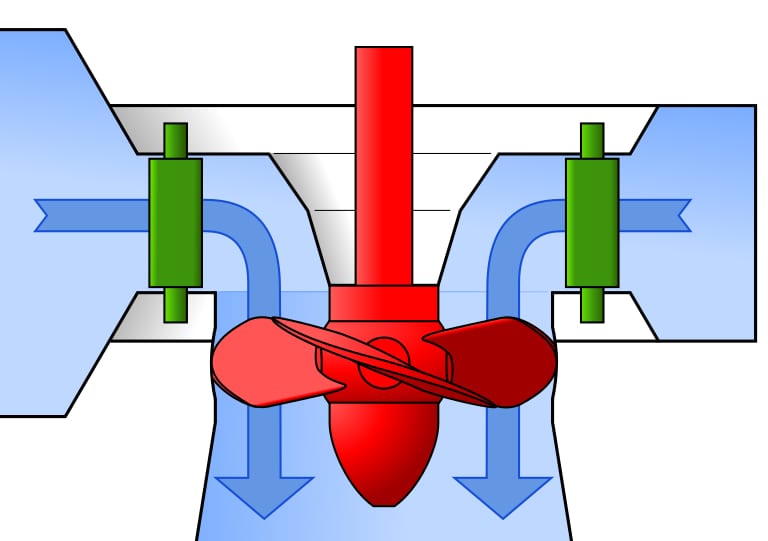
Explain Kaplan Turbine
Reaction turbine for low head, high flow. Works like a ship’s propeller in reverse. Adjustable blades give high efficiency across wide flow ranges. Good for rivers and run-of-river plants.
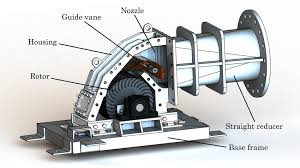
Explain Crossflow Turbine
Impulse turbine for low–medium head, variable flow. Water passes through runner twice, making it simple, robust, and tolerant of debris.
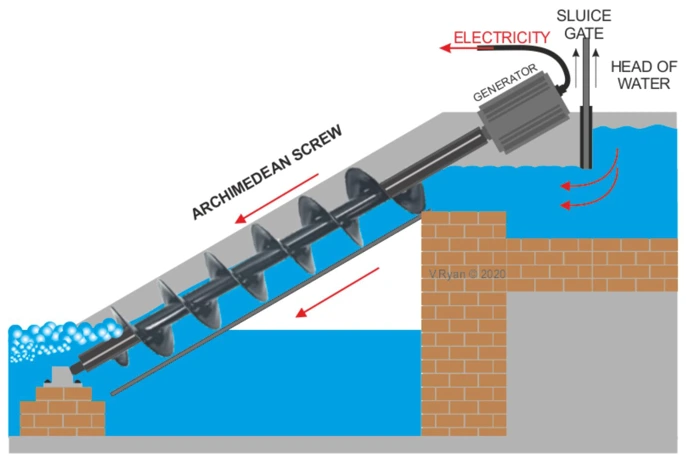
Explain Archimedes Screw Turbine
Low-head turbine for very high flow. Water turns a screw, generating power; extremely fish-friendly and used in old mills and channels.
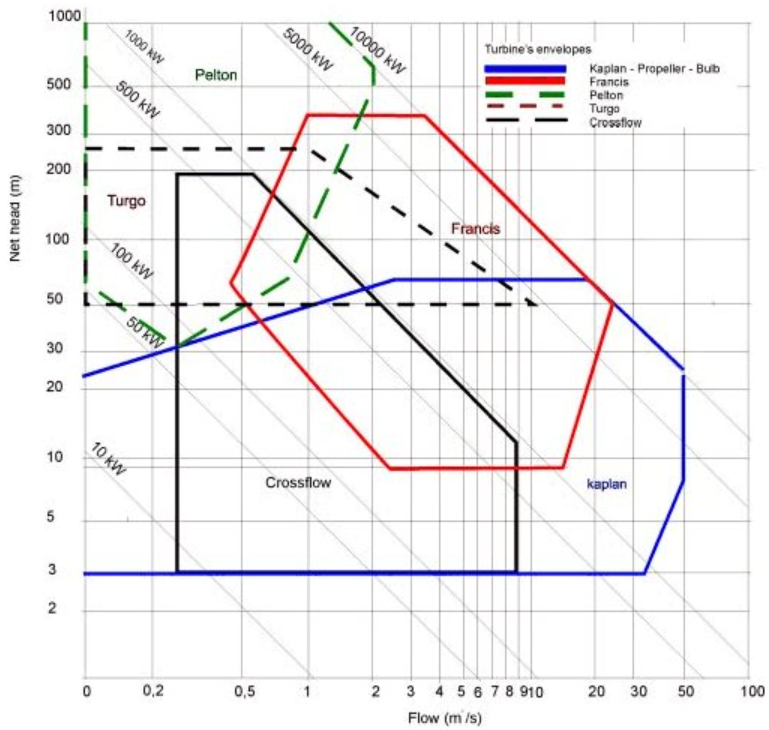
Which hydropower turbines suit 100 m head & 1 m³/s flow?
Francis is the best match; Pelton and Turgo also work. Crossflow is borderline.
Why do we prefer 3-blade wind turbines?
Two blades cause vibration and balance problems; four blades cost more with little gain. Three blades give the best balance of stability, efficiency, and cost.
Benefits of the wind turbine pitch system
Adjusts blade angle to control power output, improve efficiency at varying wind speeds, and protect the turbine by feathering blades during storms.
Compare Parabolic Trough CSP vs Linear Fresnel CSP
Parabolic Trough: Higher efficiency, higher temperatures, but higher cost and maintenance.
Linear Fresnel: Cheaper, simpler, easier to maintain, but lower efficiency.
Explain Stirling Engine CSP
A parabolic dish focuses sunlight onto a receiver heating gas in a Stirling engine. Expanding gas drives a piston and generator. Very efficient but requires precise tracking and more maintenance.
Explain Concentrated Photovoltaics (CPV)
Mirrors or lenses concentrate sunlight onto ultra-high-efficiency PV cells. Requires dual-axis tracking and strong direct sunlight.
Explain Power Tower CSP
Heliostats focus sunlight onto a central tower receiver, heating molten salt for high-temperature steam and integrated thermal storage.$