Quantitative Week 4 Lecture Observational Study Design
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What are two different of analytical studies?
Experimental Studies
Observational Studies
What is an obervational study design?
When researchers are looking at the effect of some type of intervention, risk, a diagnostic test or treatment, without trying to manipulate who is or who is not exposed
What study design allows testing of hypotheses about the association of specific risk factors and outcomes?
Observational study design
What study design cannot make inferences about the cause and effect relationship?
Observational study design
What are 4 different types of observational studies?
Cohort
Case-control
Cross-sectional
Ecological
What kind of observational study is it if observations are made looking forward?
Prospective
What kind of observational study is it if observations are made from existing data?
Retrospective
What kind observational study is it if observations are made at one point in time?
cross-sectional
What are the pros of prospective observational studies?
Can identify diagnosis and confounders clearly at outset
intervention can be more clearly documented
temporal sequence of onset and outcome
What are cons of prospective observational studies?
Can be expensive
Not as precise
What are the pros of retrospective observational studies?
Data already available
Often involves large numbers
What are cons of retrospective studies?
Definitions may change over time
Follow-up times may be inconsisten
What is a cohort study?
exposure oriented
researcher observes the intervention but do not control it
following a group of subjects (cohort) who are likely to develop a certain outcome
What are two types of cohort studies?
Prospective cohort studies
Retrospective cohort studies
Prospective cohort studies:
cohort is identified and followed over time to see what happens
Retrospective cohort studies
cohorts are defined from a previous point in time and information is collected about the outcome
What study can track the same groups of people over extended period of time?
cohort studies
What study has a powerful strategy for defining incidence and investigating potential causes of an outcome before it occurs?
Cohort studies
What study provides informations about timiing of outcome and identifies potential contributing factors?
Cohort studies
What is a case control observational study?
researchers identify individuals with existing health issue or condition, or cases along with a similar group without the condition or controls
What are the cases and controls classified as in the case control observational study?
Cases are classified as having the disorder and controls are chosen as the comparison group
What kind of study is it when the researcher looks backward in time of previously collected data to determine if the groups differ with respect to their exposure histories or the presence of specific characteristics that may put a person at risk for developing the condition of interest?
Case control observational study
What kind of study is outcome oriented and conducted after outcome has occured?
Case control observation studies
What is the objective of case control observational studies?
To identify variables that may predict the outcome
What do the cases and controls consist of in an case control observational study?
Case=a group that has the outcome
Control=a group free of the outcome
Once the case and controls are identified in the study, what do the researchers look for?
After the case and controls are identified, the researchers look back in time to learn what subjects were exposed to that might predict the outcome
What is the study direction or trajectory/pathyway of case control observational study?
Researchers start with an end point and work backward, figuring out what might of caused that outcome
In a case control observational study, once researchers start with an end point and work backward, figuring out what might have cause that outcome, what can this process help to identify?
Can note any differences in risk factors or exposures that emerge between the two groups which can help suggest what may have led to the outcome in some people
What are cross-sectional studies?
observational studies designed to collect data on an outcome and exposure/treatment variables of interest at one point in time
What type of observational study can analyze associations between variables?
cross-sectional observational studies
What type of observational study looks at data from a particular group at one specific period of time?
Cross-sectional observational studies
What kind of study occurs when researchers observe and record information about something present in the population without manipulating any variables or interventions?
Cross-sectional observational studies
What are ecological studies?
An observational study defined by the level at which data is analyzed, namely at the population level or group level, rather than individual level
What do ecological studies compare?
this observational study compares large groups of people instead of individuals for differences in things such as cancer rates
What makes ecological studies valuable?
They can be done easily and quickly by using population data that has already been collected while seeking associations between potential risk factors and various disease outcome
True/False: some observational studies do not have control a control group and look at associations between variables while other observational studies use controls to make comparisons between groups
True
What is an example of historical control groups?
ex) clients in the previous 6 months
What are concurrent control groups?
clients in another department or similar organization
What kind of control is the following scenario:
Hospital system implements a new policy to address pressure injury to see if it made a difference
Looked at pressure injury rates 6 months prior to the policy and compared to rates 6 months after the policy was implemented
Historical control
What kind of control is the following scenario:
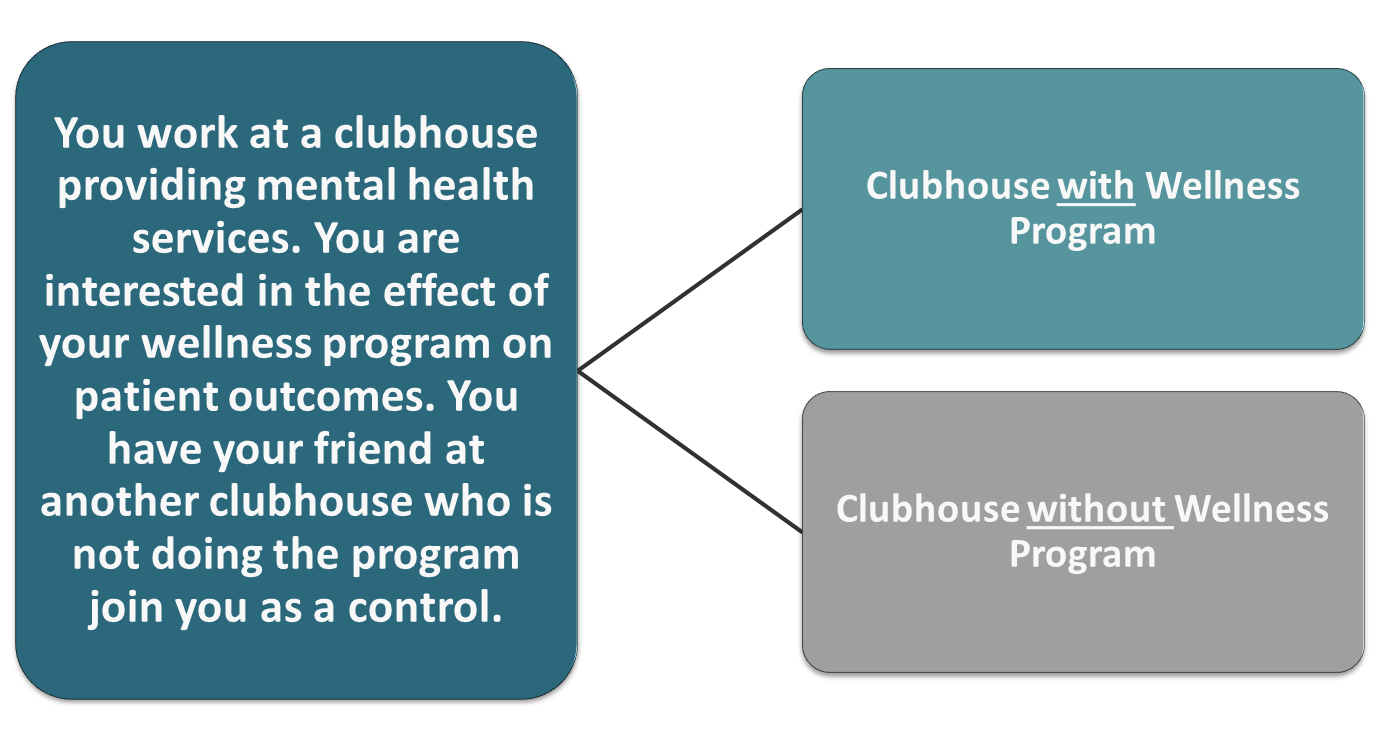
Concurrent Control
What is internal validity?
The extent to which the results reflect the truth about what happened within just this study
What is external validity?
The extent to which the results reflect the truth about what may happen OUTSIDE this study, but in similar situations
What type of validity determines the extent to which any observed difference between exposure and control groups is attributable to the exposure?
Internal Validity
What is internal validity evaluated by?
-sample identification and selection process
-exposures and covariates are clearly defined
-results are not due to confounding variables
True/False: Internal Validity is necessary for external validity
True
What type of validity determines the extent to which study results are applicable to people who were not part of the study?
External Validity
What is external validity evaluated by?
-sample similarity to target population
-setting
-protocol of study
What are some protocols of study addressed in understanding the external validity of a study?
Unrealistic for real practice situations
Resources (e.g money, time, space)
Equipment
What is a confounding variable?
A confounding variable is a factor that influences both the cause and the potential effect that unaccounted for
What is the consequence of confounding?
The consequence of confounding is that the estimated association is not the same as true effect
The actual data collected may be correct, but the subsequent effect attributed to the exposure of interest is actually caused by something else
What are the conditions needed to be met for a variable to be a true confounder?
-relationship with the exposure
-relationship with the outcome even in the absence of the exposure
-not on the causal pathway
-uneven distribution in comparison groups-more likely to occur in non-random designs
What may be a confounder in the following scenario: initial association between alcohol consumption and lung cancer
Confounded by smoking, which is associated with alochol use and an independent risk factor for lung cancer (i.e the more you drink, the more you smoke)
Are there confounders in the following example":
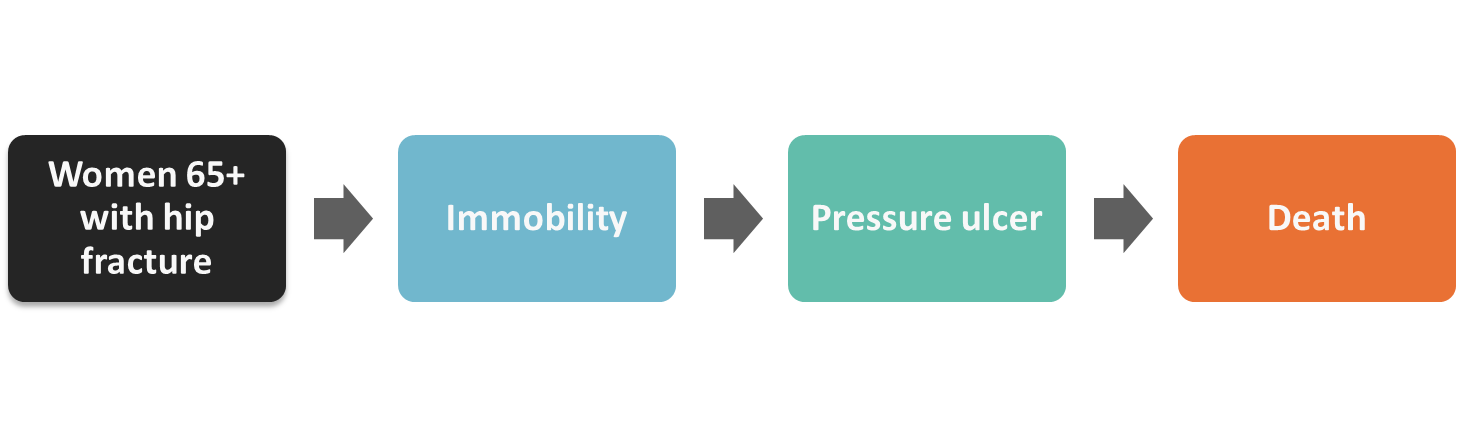
No confounder!
Causal Chain
What is a type of common confounder?
Co-intervention
What is a co-intervention?
Participants receive other interventions at the same time as the intervention of interest
Why are co-interventions a common problem in rehabilitation studies?
Because they are common confounders, clients may typically receive intervention from multiple care providers, but this may not be the same across all participants (e.g one client gets OT/PT/SLP, another gets OT/PT)
Whatis bias?
Bias is a result of a systematic error in study design
What should be eliminated or minimized whenever possible in research?
Bias
What cannot be controlled for statistically?
Bias
What are the most relevant sources of bias?
Sampling or Selection Bias
Maturation Bias
Measurement Bias
Response Bias
Convience Bias
Sampling or Selection Bias
Unless the sampling method ensures that all members of the universe or reference population have the same probability of incusion in the sample, bias is possible
Maturation Bias:
The effect might be due to changes that have occured naturally over time, not because of the intervention
Measurement Bias
Systematic error arising from inaccurate measurement (or classification) of subjects on the study variables
In measurement bias, how can systematic errors occur?
Can occur if measure is:
-not administered in a standardized way
-not valid for your sample
-lacks sensitivity to change
Response Bias
Differences between individuals who choose to respond and those that choose not to respond
Convenience Bias
When a sample is taken from individuals that are conviently available
True/False: Confounders can be statistically controlled for, but bias can not be
True
true/false: once bias is present, there is no way to adjust for it in the resuls
True
Advantage or disadvantage of observational study: Collect data when and where an event or activity is happening
Advantage of Observational Study designs
Advantage or disadvantage of observational study: Does not rely on people’s willingness or ability to provide information
Advantage of observational study designs
Advantage or disadvantage of observational study designs: Allows researcher to directly see what people do rather than relying on what people say they did
Advantage of observational study designs
Advantage or disadvantage of observational study: Provides practical application
Advantage of observational study designs
Advantage or disadvantage of observational study: Provides detailed insights
Advantage of Observational Study Designs
Advantage or disadvantage of observational study: Can be completed quickly and inexpensively
Advantage of Observational Study Design
Advantage or disadvantage of observational study: Susceptible to bias-people may perform better when they know they are being observed
Disadvantge of Observational Study Design
Advantage or disadvantage of observational study: Cannot control for bias and confounding
Disadvantage of Observational study design
Advantage or disadvantage of observational study: Can be time consuming compared to other data collection methods
Disadvantage of Observational Study Designs
Advantage or disadvantage of observational study: Can be susceptible to subjectivity
Disadvantage of Observational Study Design
Advantage or disadvantage of observational study: Can have ethical considerations regarding researcher involvement and influence
Disadvantage of Observational Study Design