Upper & Lower Extremity PE Techniques + Assignments
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
loss of active & passive ROM (esp. external rotation)
- diagnosis: adhesive capsulitis/frozen shoulder
- how: active ROM (flexion, extension, abduction, & adduction), passive ROM, & then keeping elbow close to side, move arm out to externally rotate
+ = no active or passive ROM
drop arm test
- diagnosis: rotator cuff pathology
- how: ask patient to raise arm out to side, & apply minimal downward pressure
+ = cannot hold arm out at 90º of abduction (arm drops w/ pressure)
neer test
- diagnosis: rotator cuff tear (or impingement syndrome/tendinitis)
- how: rotate hands out (palms facing out) & bring arms up
+ = weakness or pain
hawkins test
- diagnosis: rotator cuff tear (or impingement syndrome/tendinitis)
- how: flex shoulder & elbow to 90º, support elbow & internally rotate humerus
+ = pain
maintained passive ROM, but loss of active ROM =
rotator cuff tear
empty can test
- diagnosis: specifically, supraspinatus pathology (rotator cuff)
- how: arms up w/ thumbs down & palms out, apply downward pressure while patient attempts to resist
+ = pain or weakness
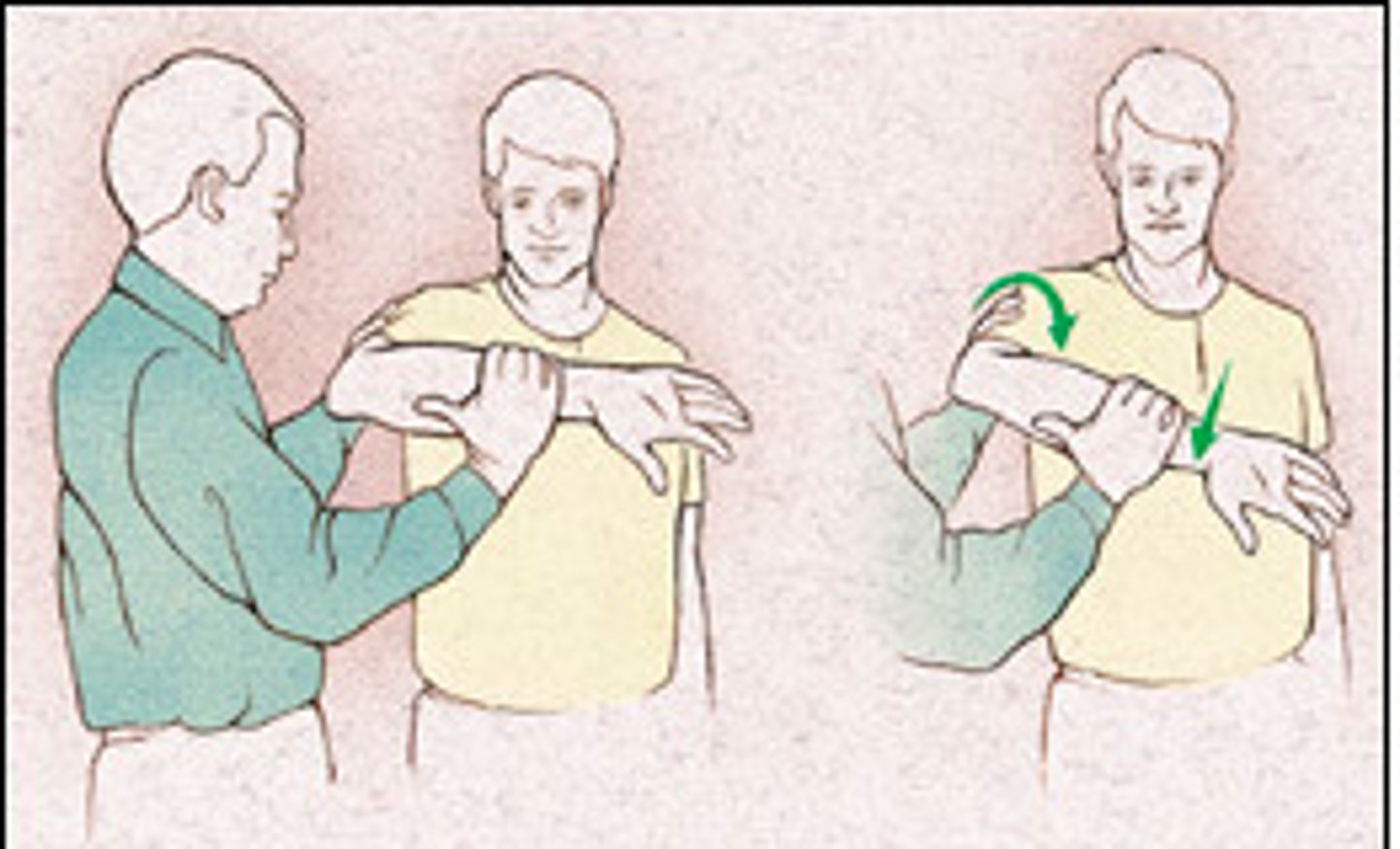
test of infraspinatus & teres minor
- diagnosis: specifically infraspinatus or teres minor pathology (rotator cuff )
- how: elbow in at side, support elbow, apply pressure at distal forearm (you are trying to internally rotate arm), ask patient to attempt to maintain position against your resistance
+ = unable to do or pain
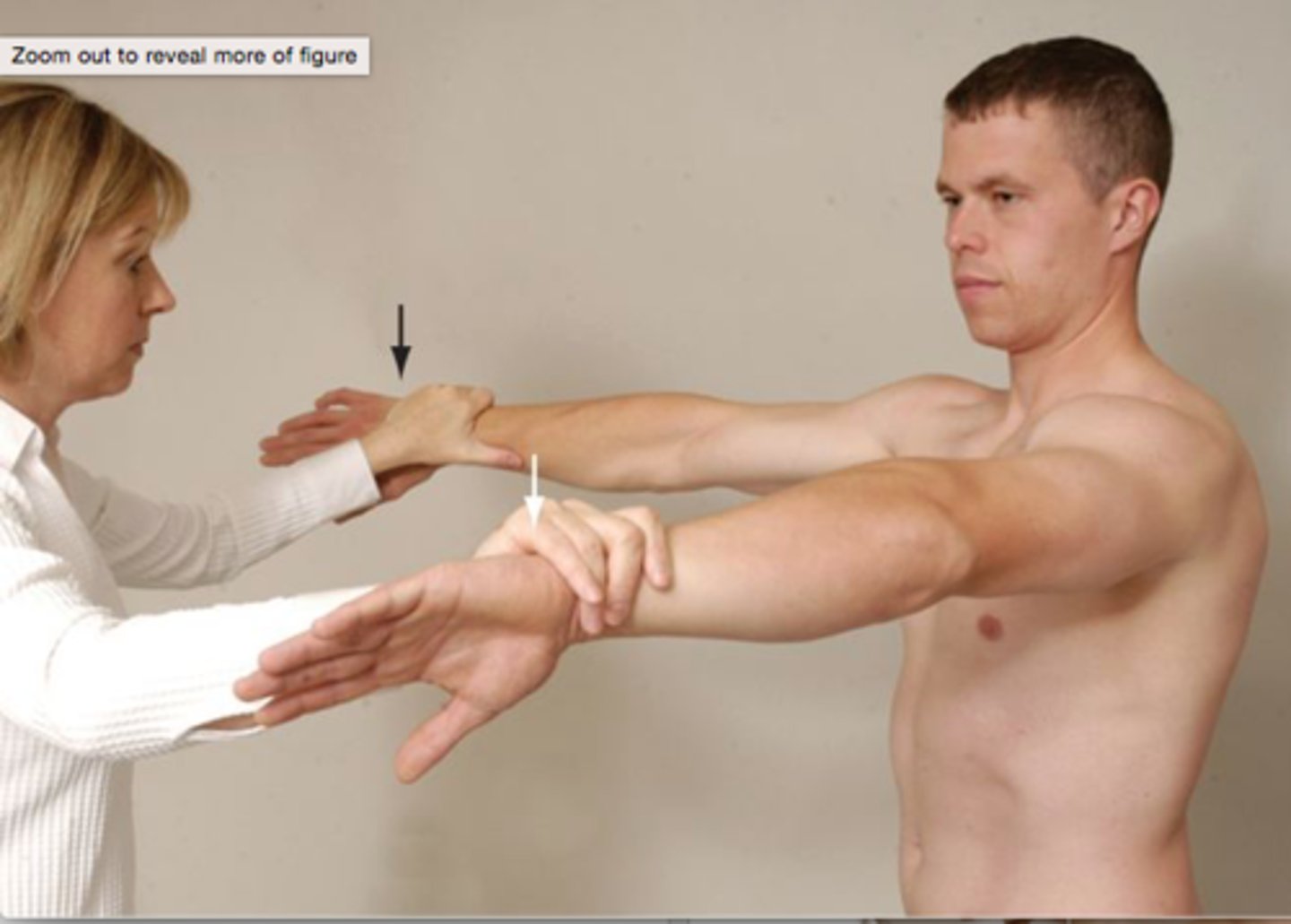
hornblower's test
- diagnosis: specifically, teres minor pathology (rotator cuff)
- how: w/ arm abducted & elbow flexed 90º, ask patient to externally rotate arm against resistance
+ = inability to maintain externally rotated position & arm drops to neutral position
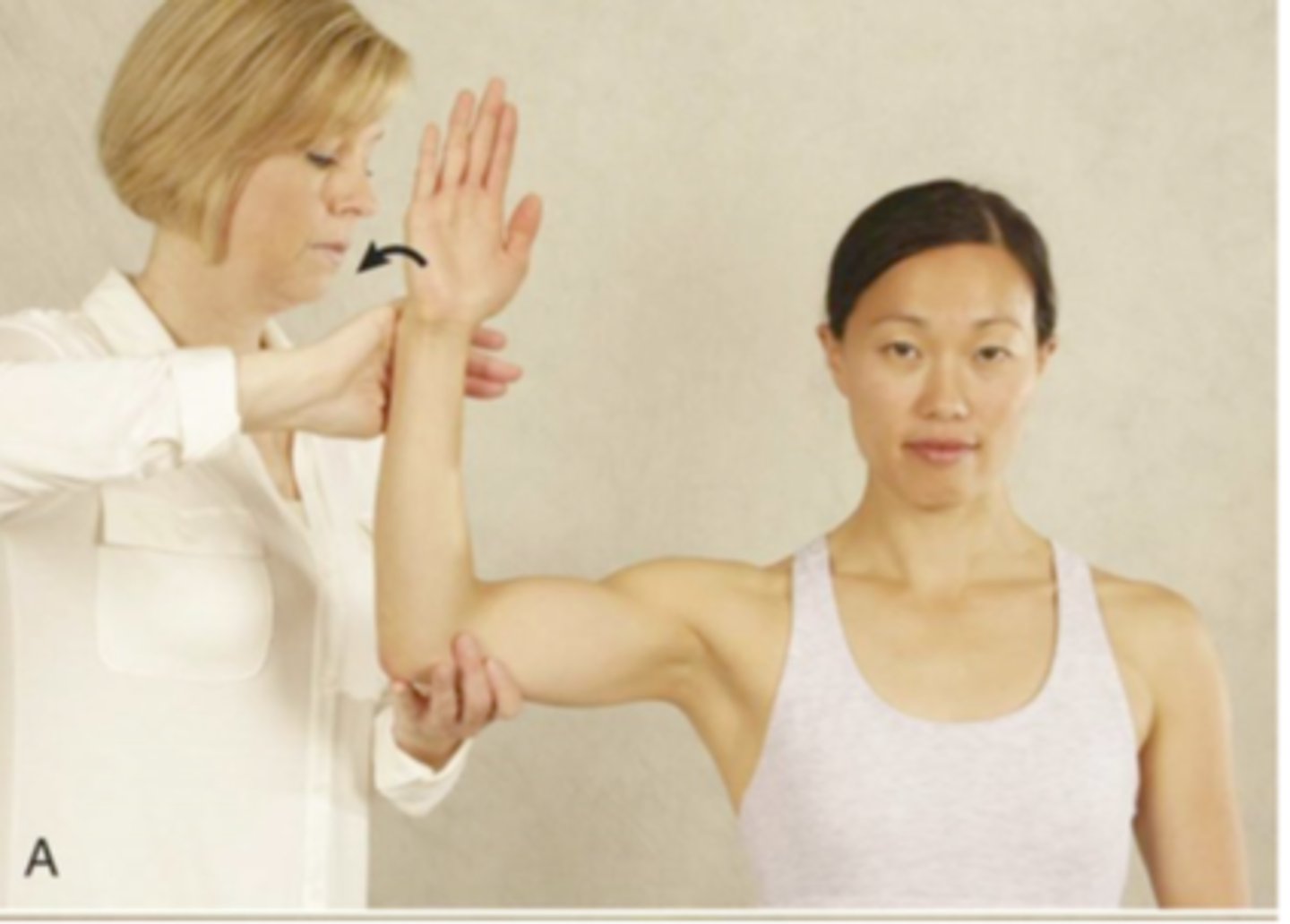

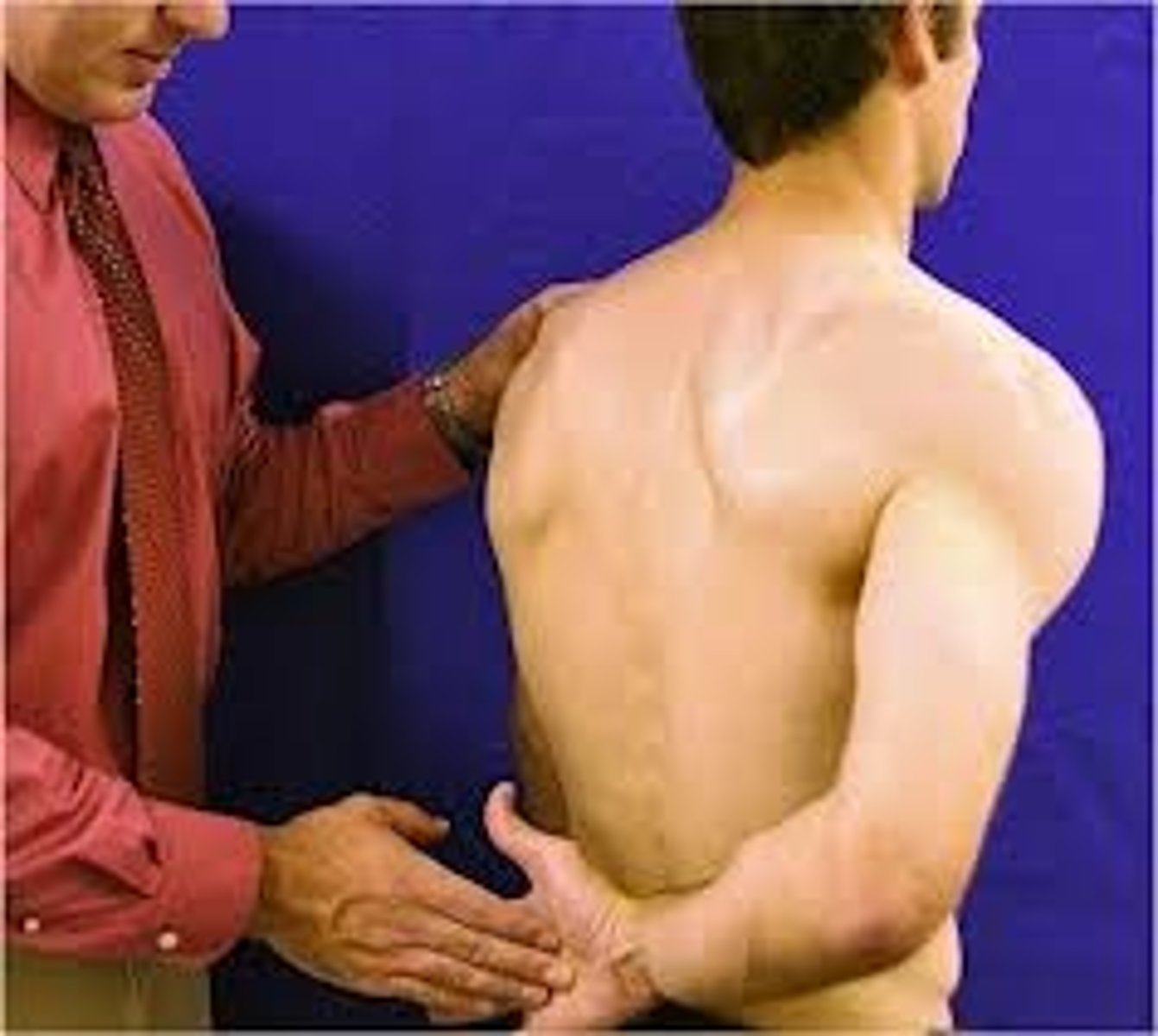
lift-off test
- diagnosis: specifically, subscapularis pathology (rotator cuff)
- how: ask patient to place hand behind back w/ palm facing away from the body, & lift it away from the back against your resistance
+ = pain, weakness, or unable to do
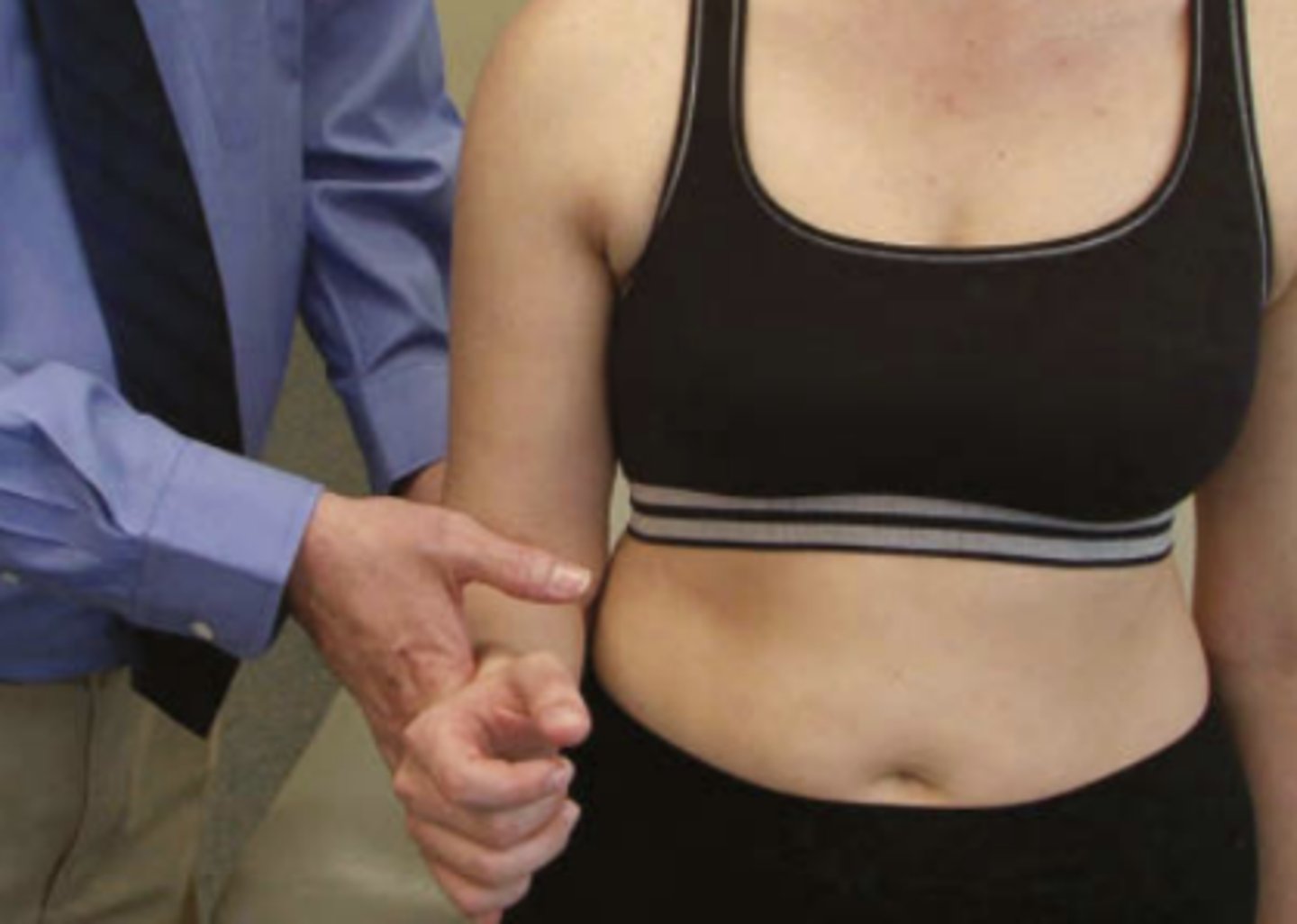
sulcus sign
- diagnosis: inferior shoulder instability (usually young pts with multidirectional instability)
- how: ask patient to relax arm down at side (close to body), & pull down an arm
+ = visible sulcus (gap between acromion & humeral head)
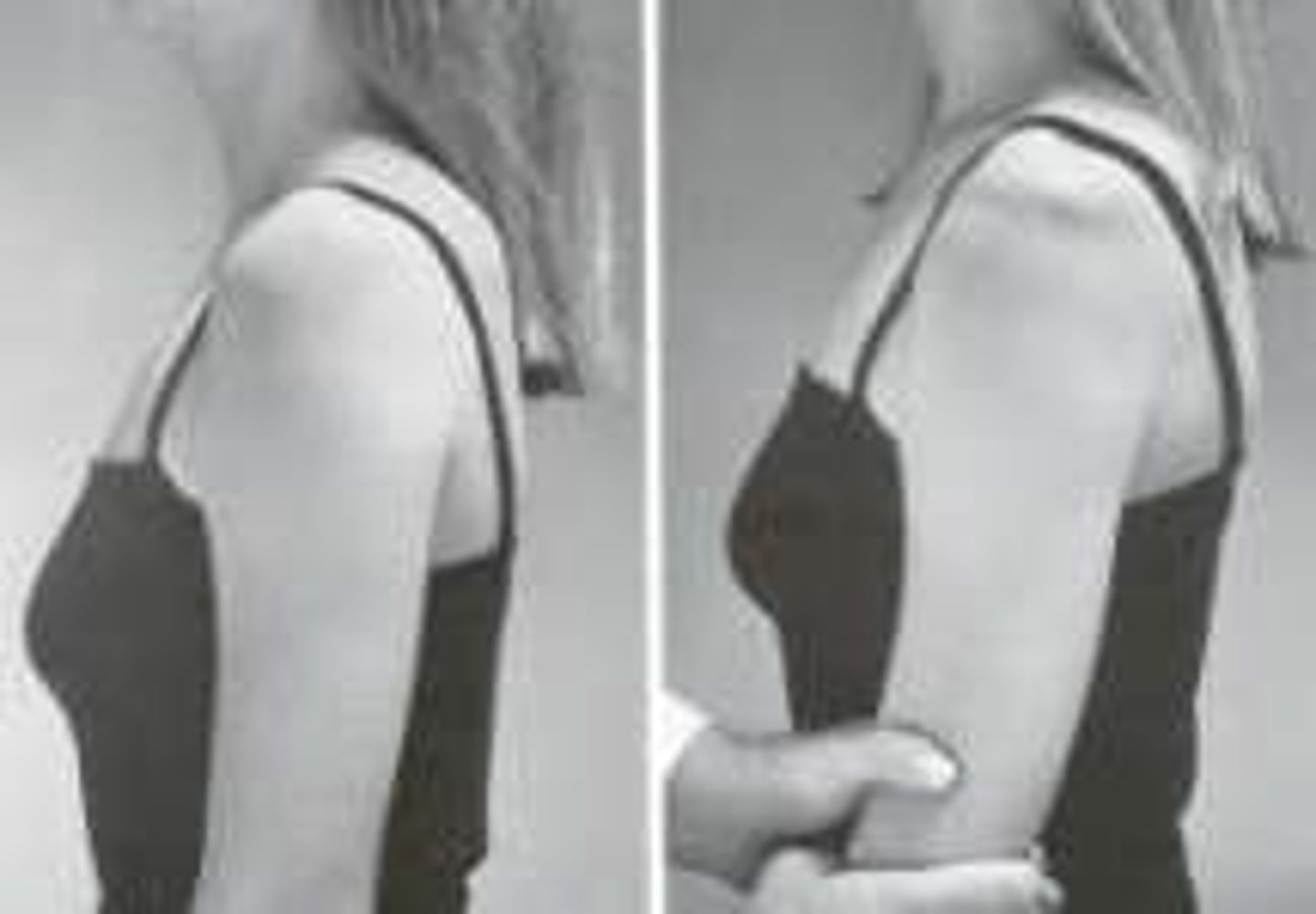
jerk test
- diagnosis: posterior shoulder instability
- how: arm & elbow flexed 90º & max internal rotation, adduct arm across body while applying axial load at elbow to push humerus in posterior direction
+ = posterior dislocation/subluxation (humeral head may be felt to "jerk" or "clunk" back into the joint as the arm is then horizontally abducted)
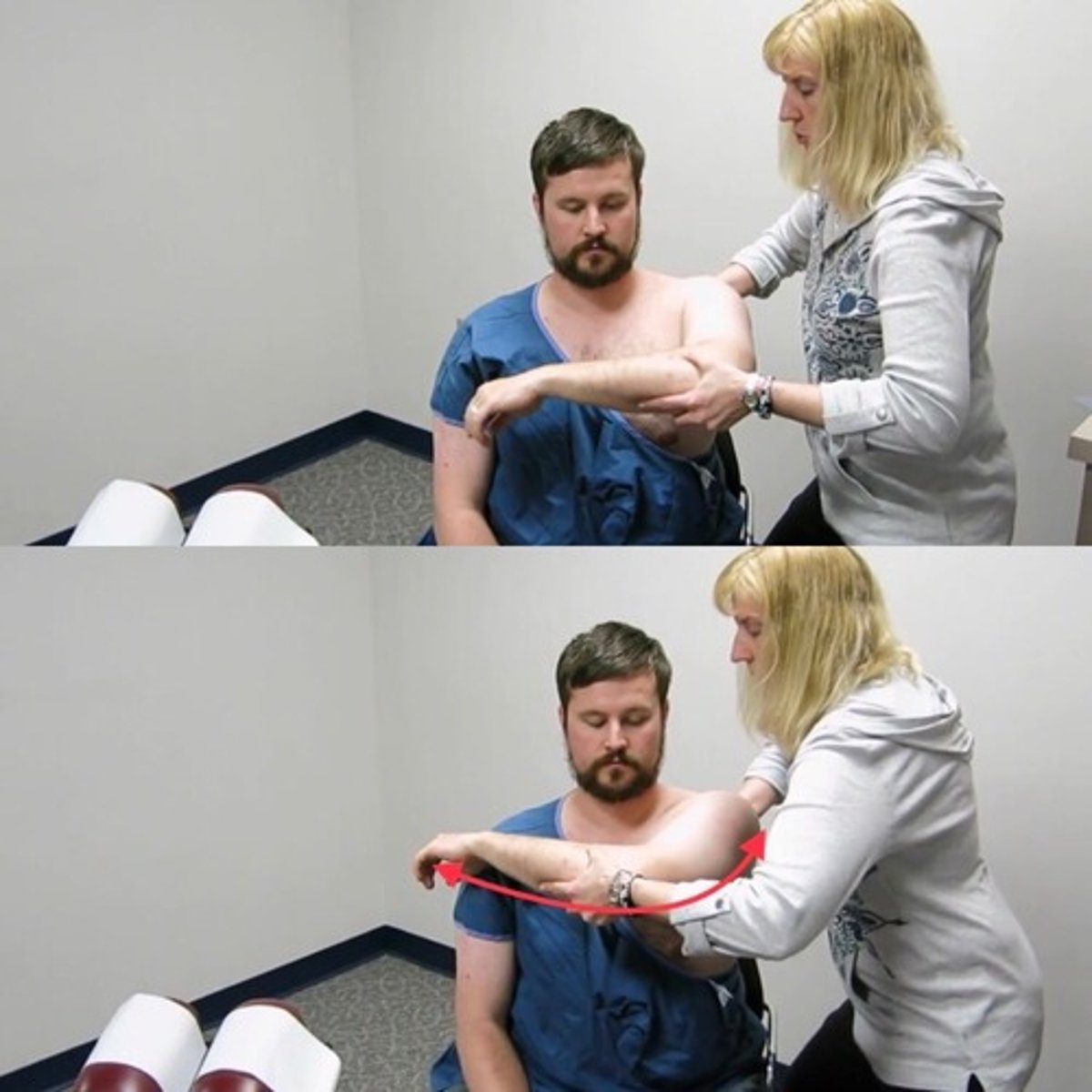
apprehension test (shoulder)
- diagnosis: anterior shoulder instability
- how: patient supine, arm abducted & elbow flexed 90º, gently externally rotate forearm to 90º
+ = pt displays apprehension, grimace, or pain (some type of reaction to indicate sense of impending dislocation)
crank test
- diagnosis: SLAP lesion/labral tear
- how: patient supine, abduct arm to 160º, flex elbow to 90º, apply axial pressure, & IR/ER arm (trying to grind labrum)
+ = pain or click
clunk test
- diagnosis: SLAP lesion/labral tear
- how: pt supine w/ shoulder flexed 180º, elbow flexed 90º, & hand pointing toward floor, hold elbow in place, grasp hand & use it to internally rotate shoulder
+ = pain w/ internal rotation
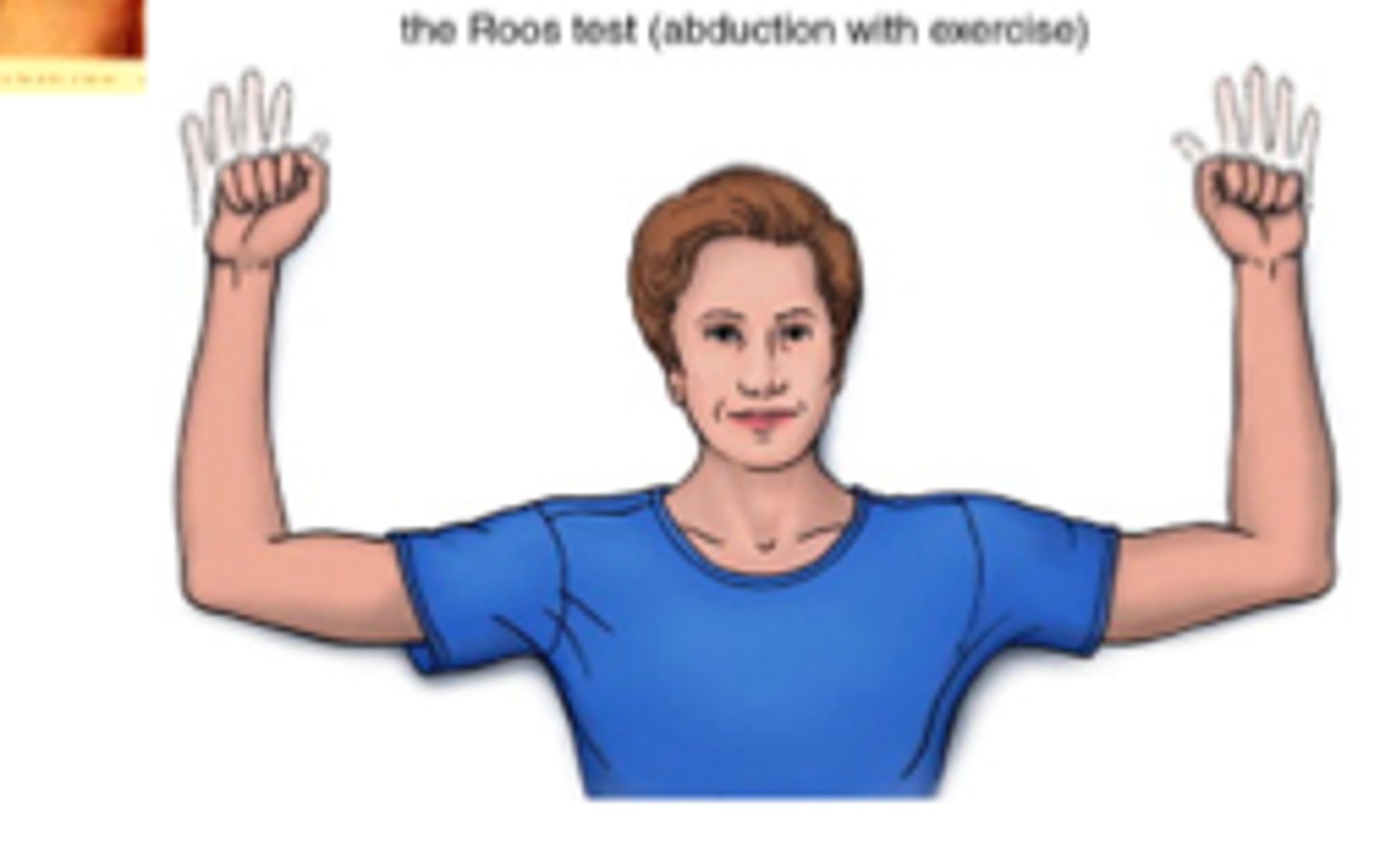
EAST test
- diagnosis: thoracic outlet syndrome
- how: both shoulders abducted to at least 90º, ask patient to open & close fists for 3 mins
+ = reproduction of neurologic &/or vascular symptoms
- or inconclusive = fatigue w/o neurologic or vascular symptoms
lifting weight w/ palms up & resisted pronation =
medial epicondylitis
1 multiple choice option
lifting weight w/ palms down & resisted supination =
lateral epicondylitis
1 multiple choice option
elbow flexion test
- diagnosis: ulnar nerve compression (cubital tunnel)
- how: "I don't know" position, hold for 3-5 mins
+ = tingling, numbness, or paresthesia in ulnar nerve distribution
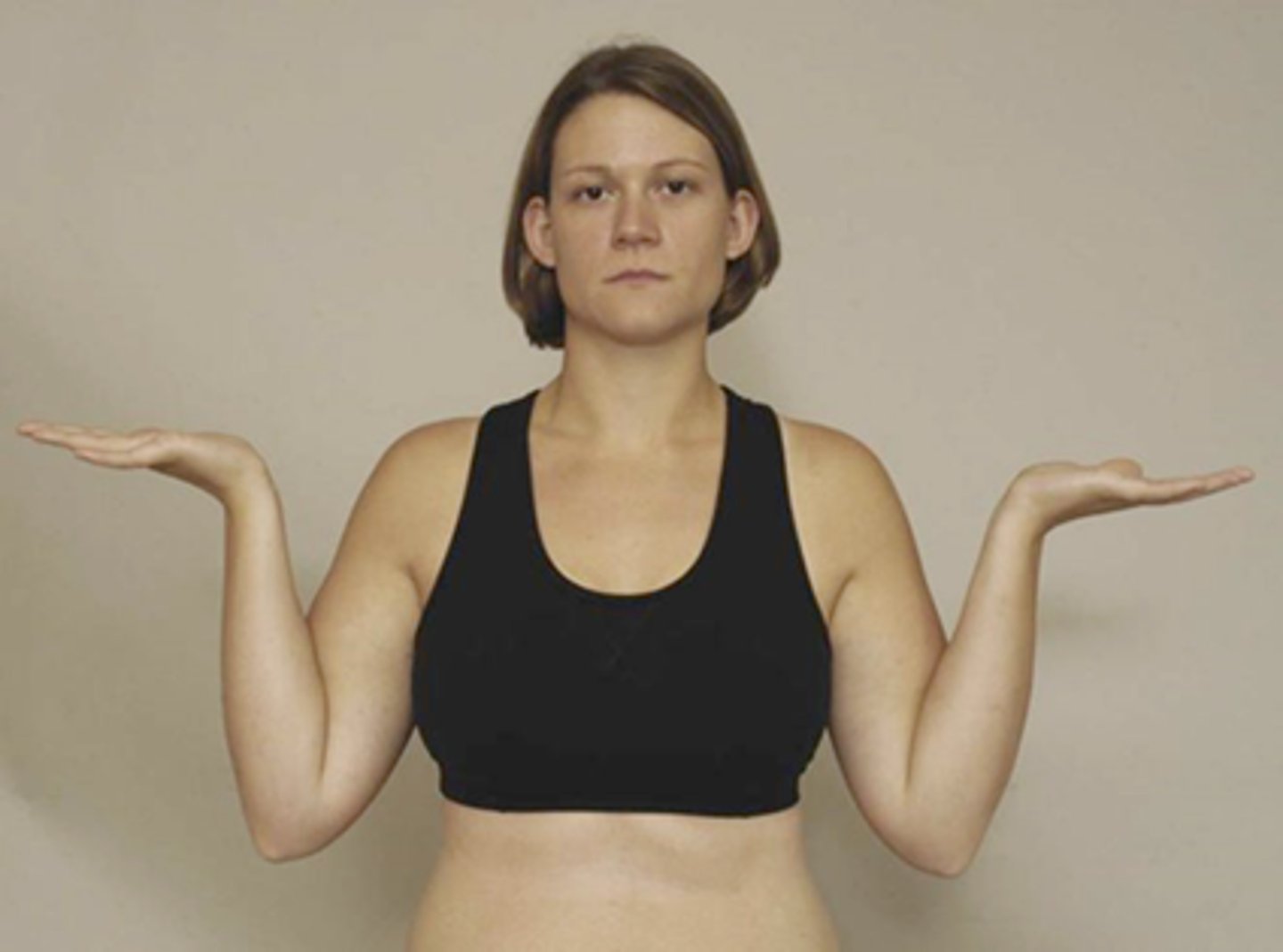

middle finger resistance test
- diagnosis: posterior interosseous nerve compression (radial tunnel)
- how: apply pressure to 3rd digit proximal interphalangeal joint
+ = unable to do
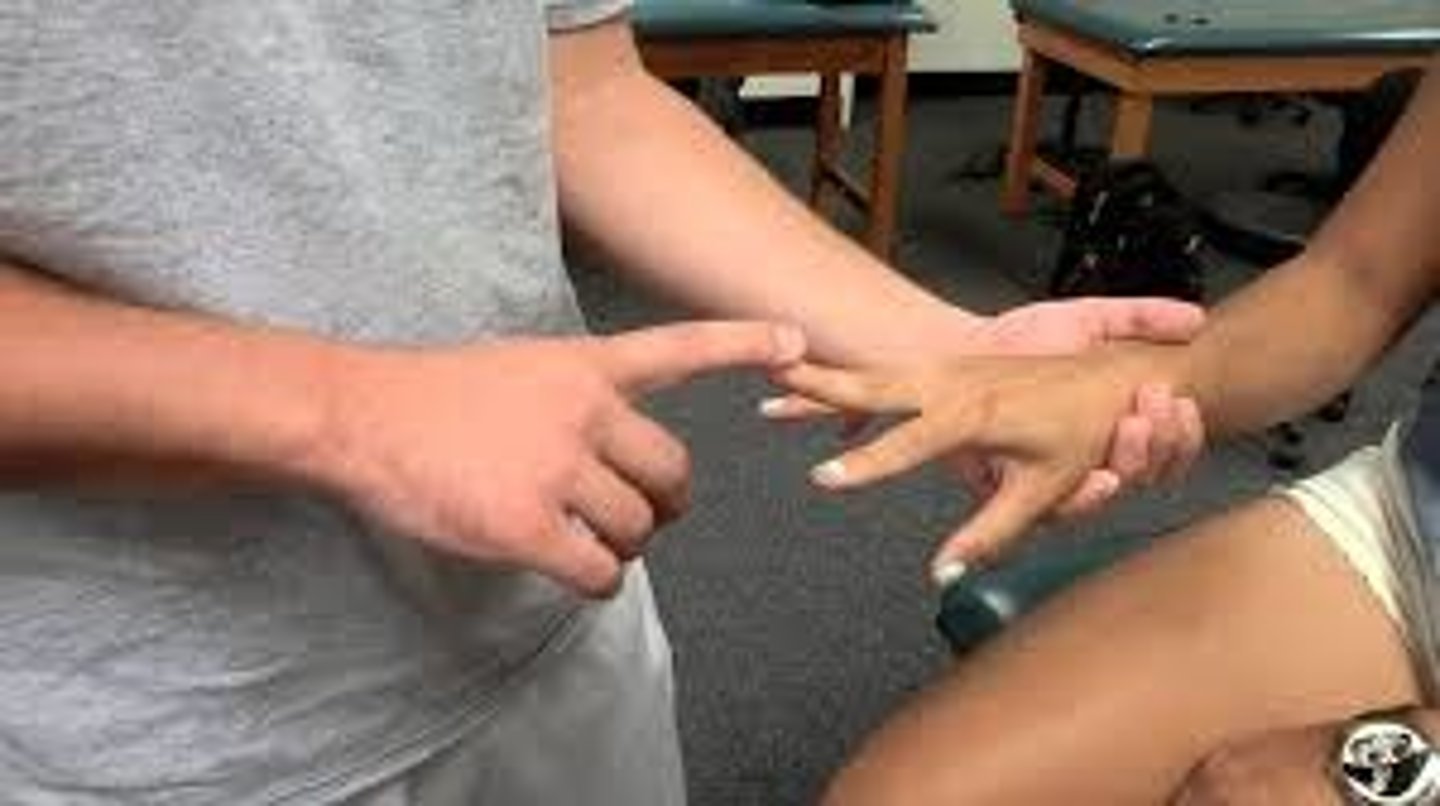
phalen test
- diagnosis: median nerve compression (carpal tunnel)
- how: elbows relaxed in extension, & allow gravity flexion of the wrists
+ = numbness or tinging in distribution of median nerve w/i 60 secs
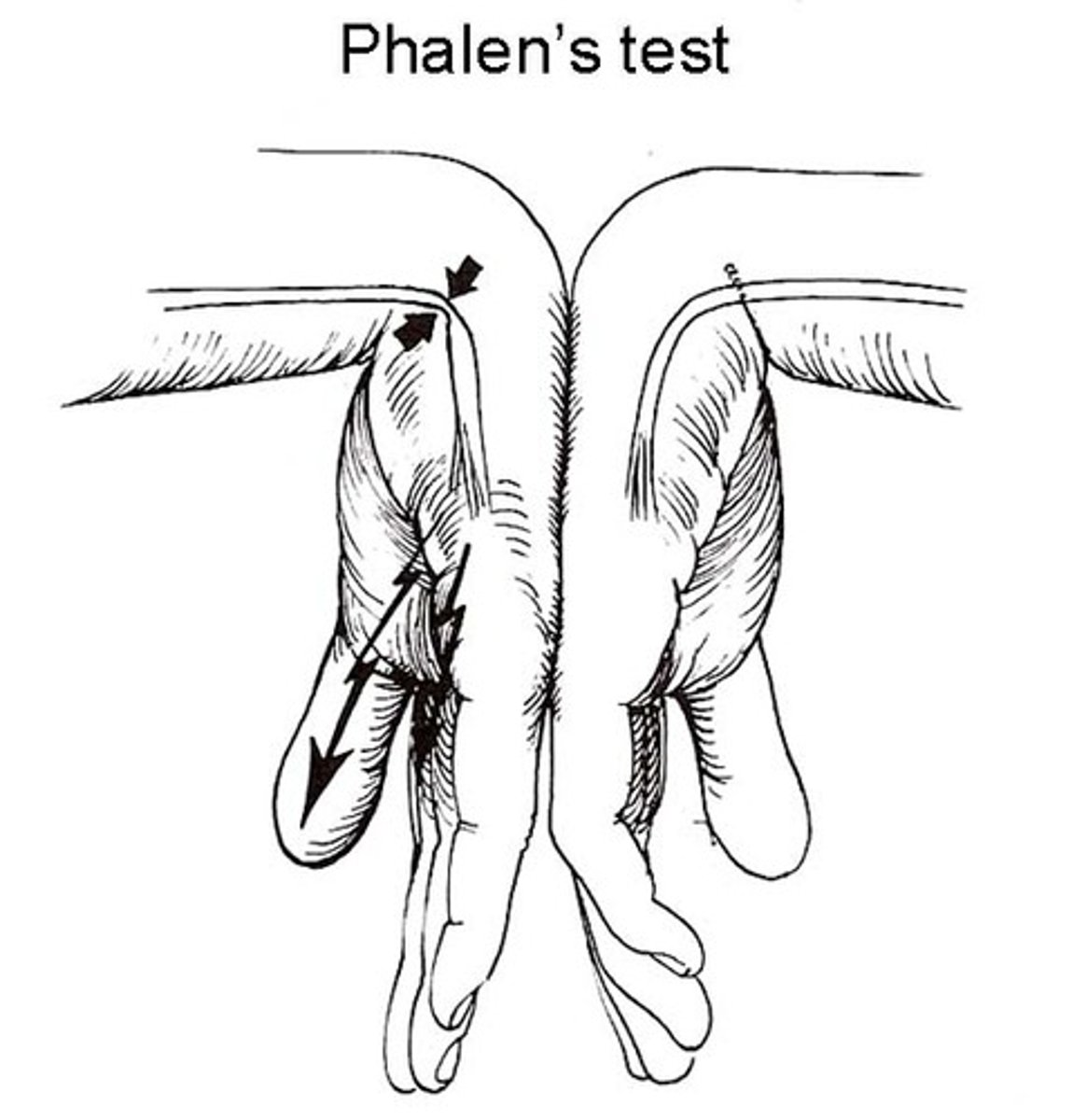
tinel sign (wrist)
- diagnosis: median nerve compression (carpal tunnel)
+ = reproduction of symptoms
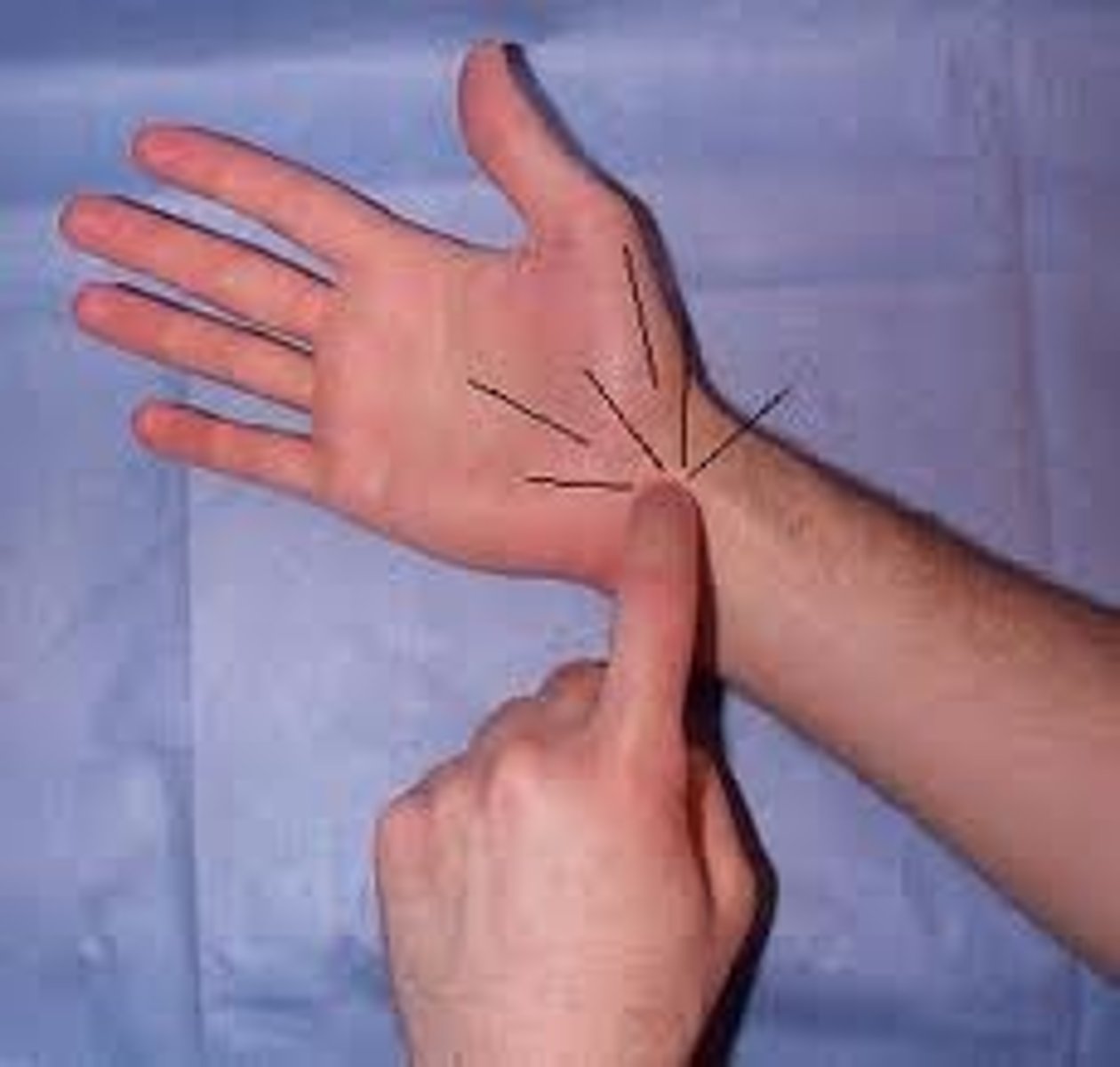
compression test (wrist)
- diagnosis: median nerve compression (carpal tunnel)
+ = reproduction of symptoms
how can you evaluate sensory function of the median nerve?
tip of thumb on volar aspect (palm side)
how can you evaluate sensory function of the radial nerve?
dorsum of thumb & web space
how can you evaluate sensory function of the ulnar nerve?
tip of little finger on volar aspect (palm side)
finkelstein test
- diagnosis: dequervain tenosynovitis
- how: make fist w/ thumb inside fingers, push into ulnar deviation
+ = pain
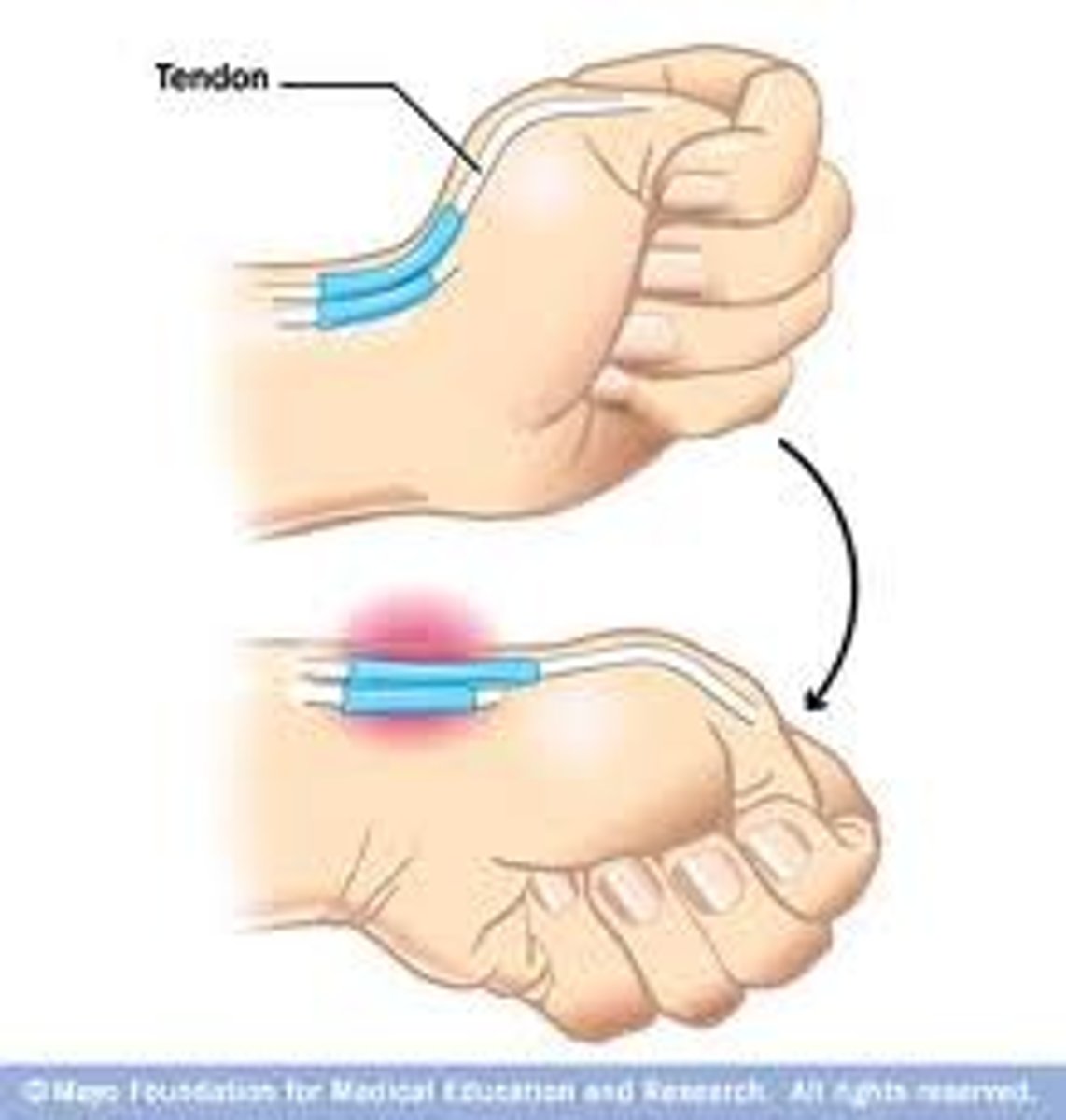
mallet finger test
- diagnosis: injury to extensor tendons
- how: isolate extensor tendon by holding finger at middle phalanx, instruct patient to actively extend DIP joint
+ = unable to extend DIP joint
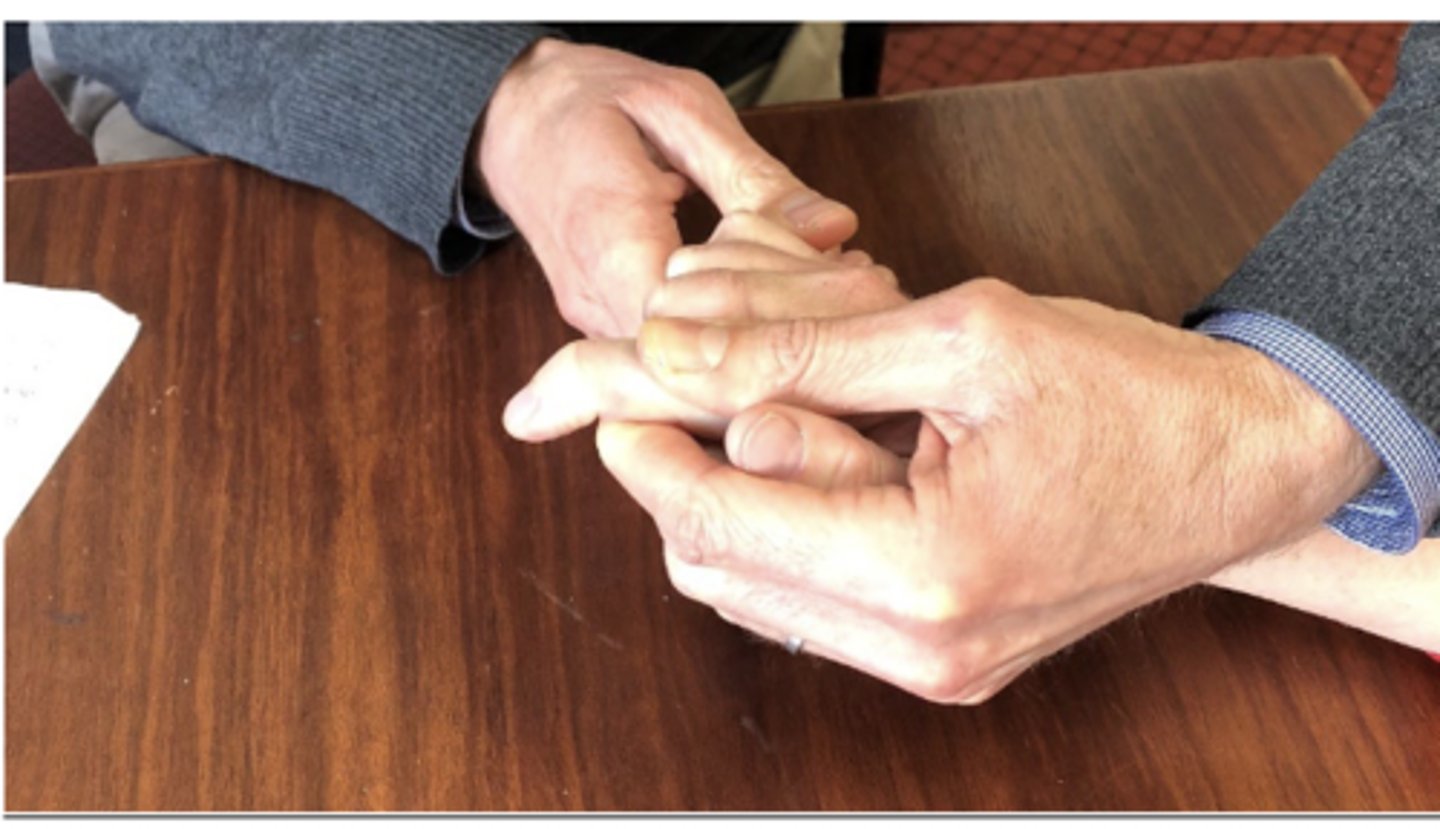
trendelenburg sign
- diagnosis: weakness of hip abductors (gluteus medius)
- how: stand 1st on one leg & then the other
+ = abductor weakness in stance leg if opposite iliac crest drops
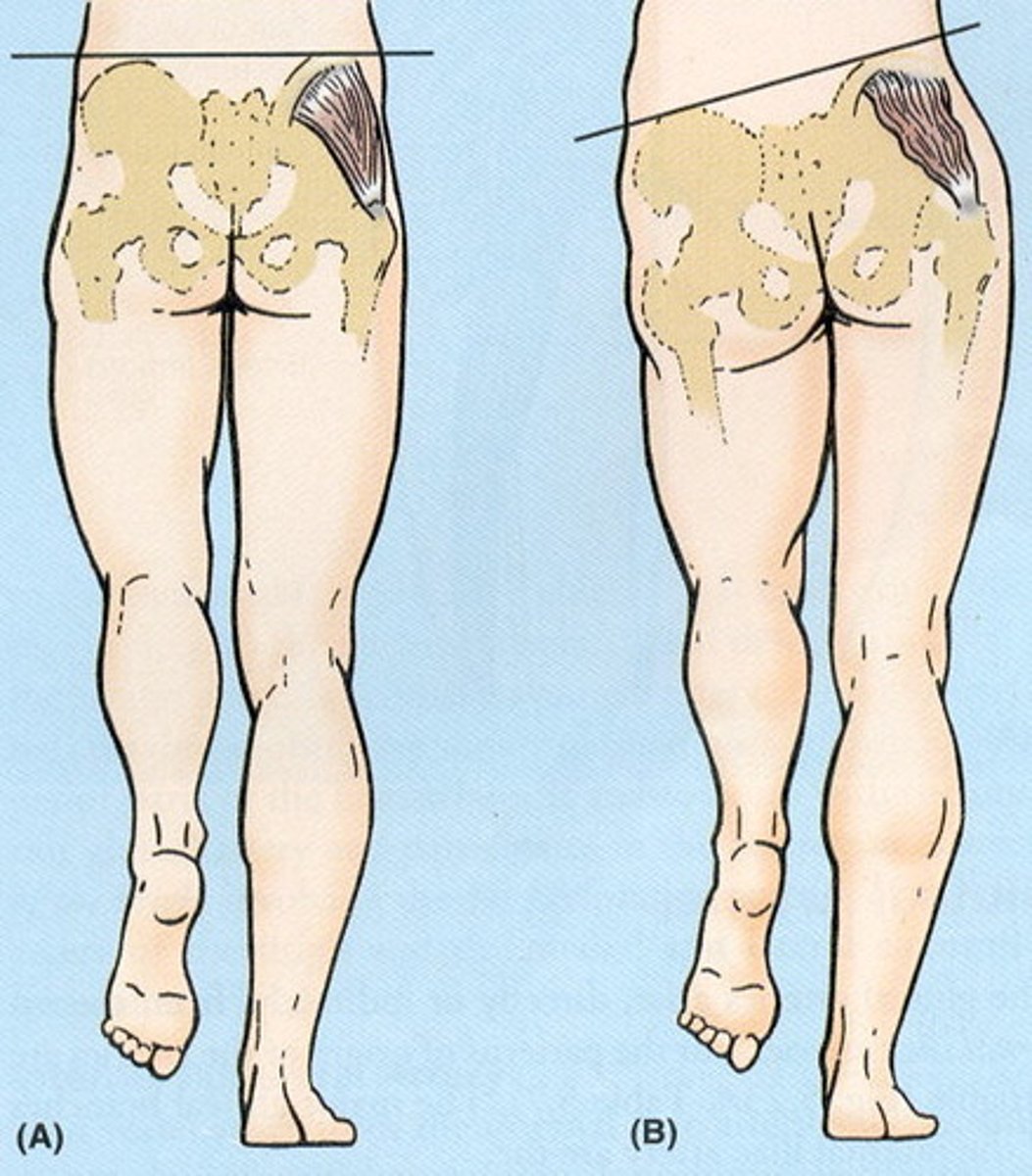
FABER test
- diagnosis: SI joint pathology
- how: patient supine, place foot on opposite knee, stabilize pelvis w/ hand on opposite ASIS, press down on affected side
+ = pain (could also be normal)
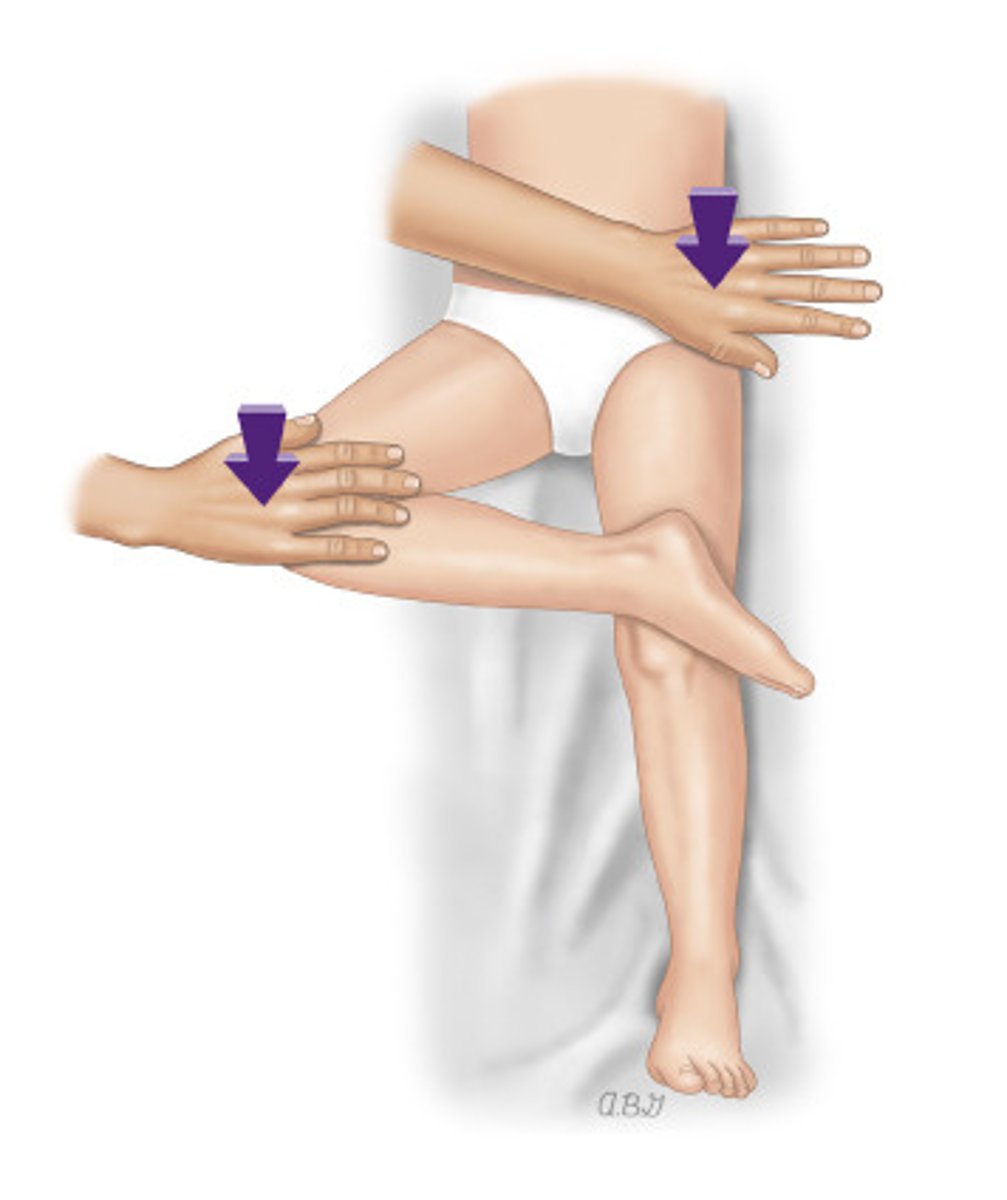
log roll test
- diagnosis: acetabular or femoral neck (hip) pathology
- how: patient supine, IR/ER the relaxed lower extremity
+ = anterior hip or groin pain (particularly w/ internal rotation); will be negative w/ snapping hip
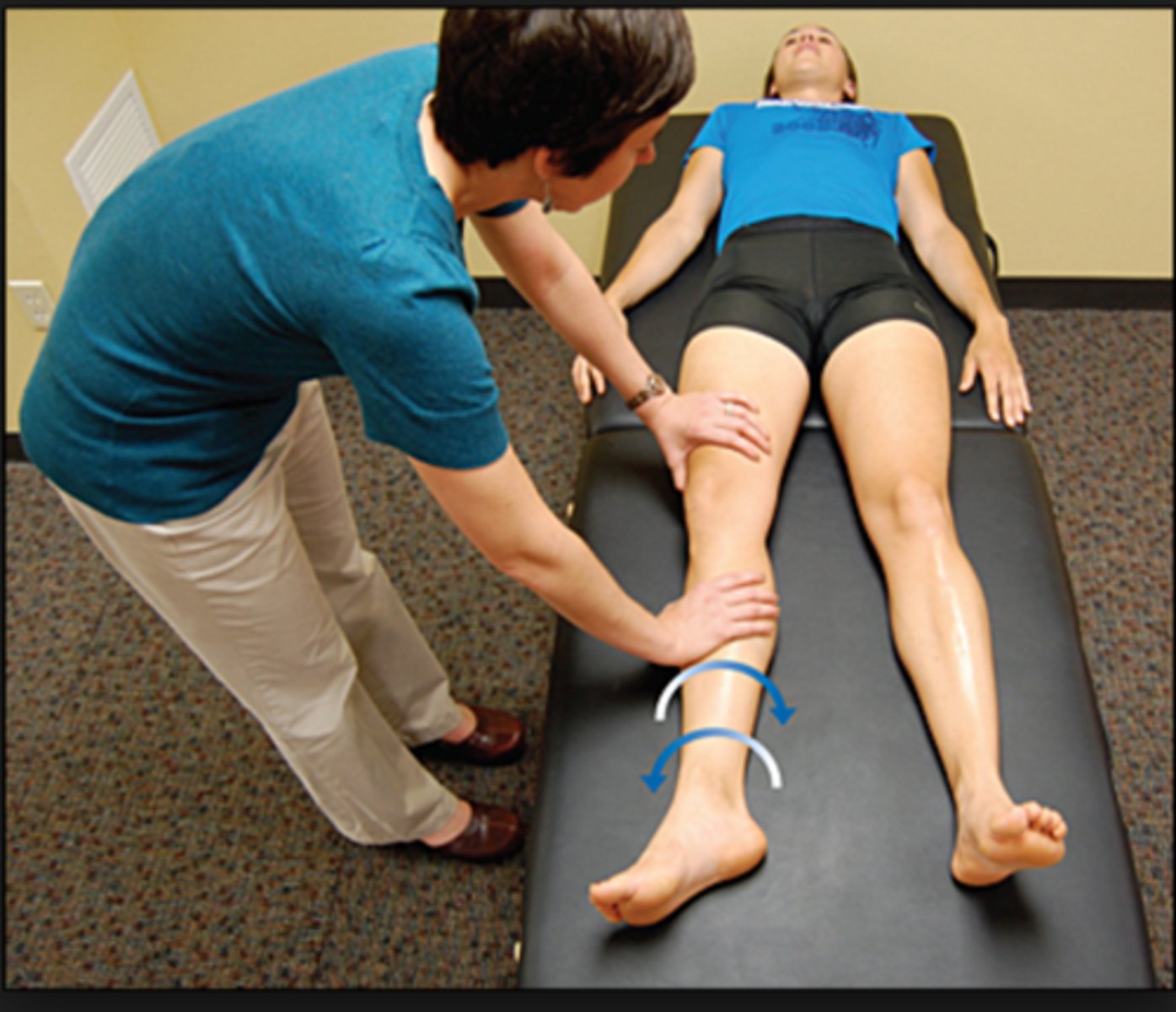
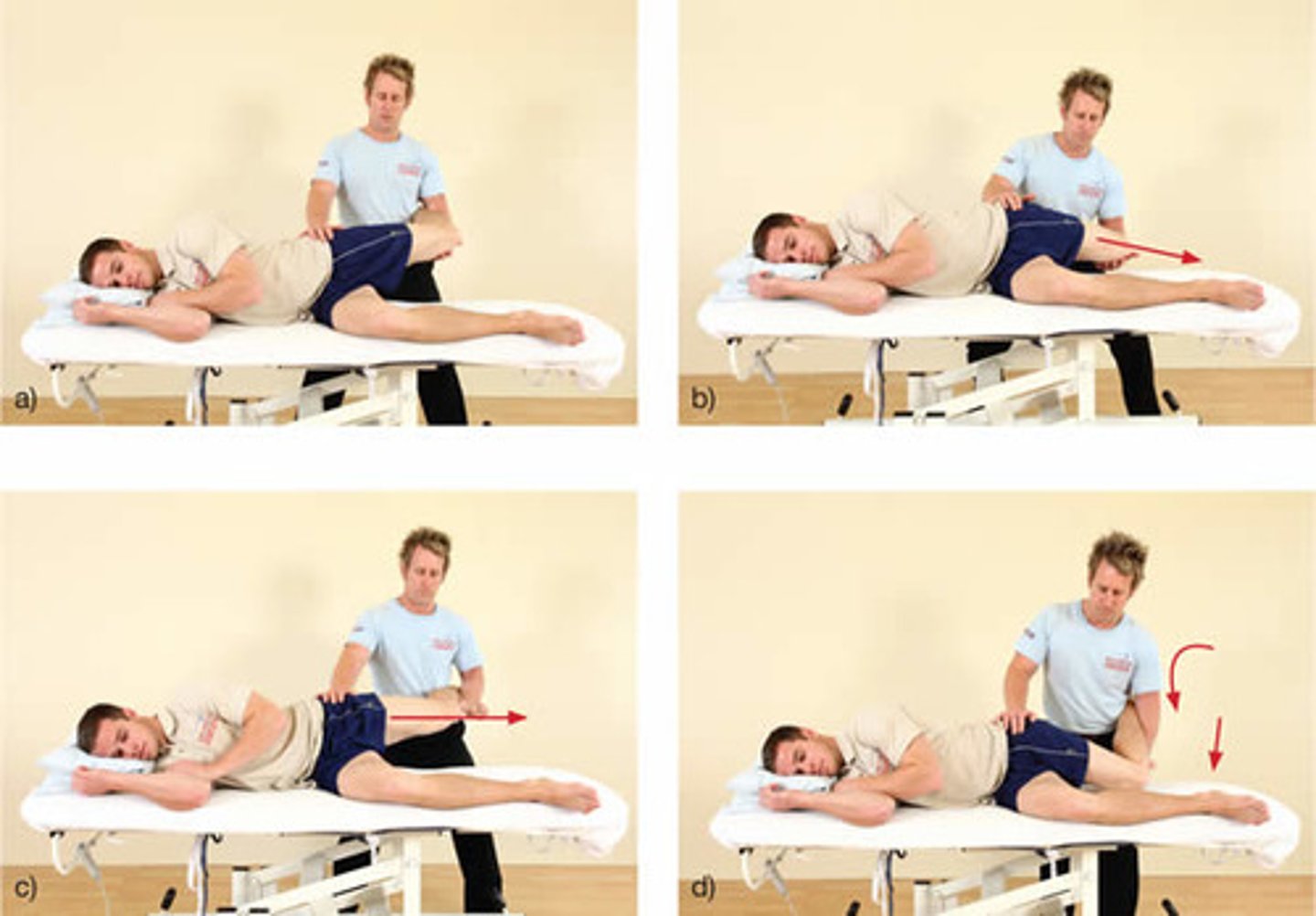
ober test
- diagnosis: TFL &/or IT band tightness or external snapping hip
- how: see photo
+ = extremity stays elevated (should drop to level of other knee on table)
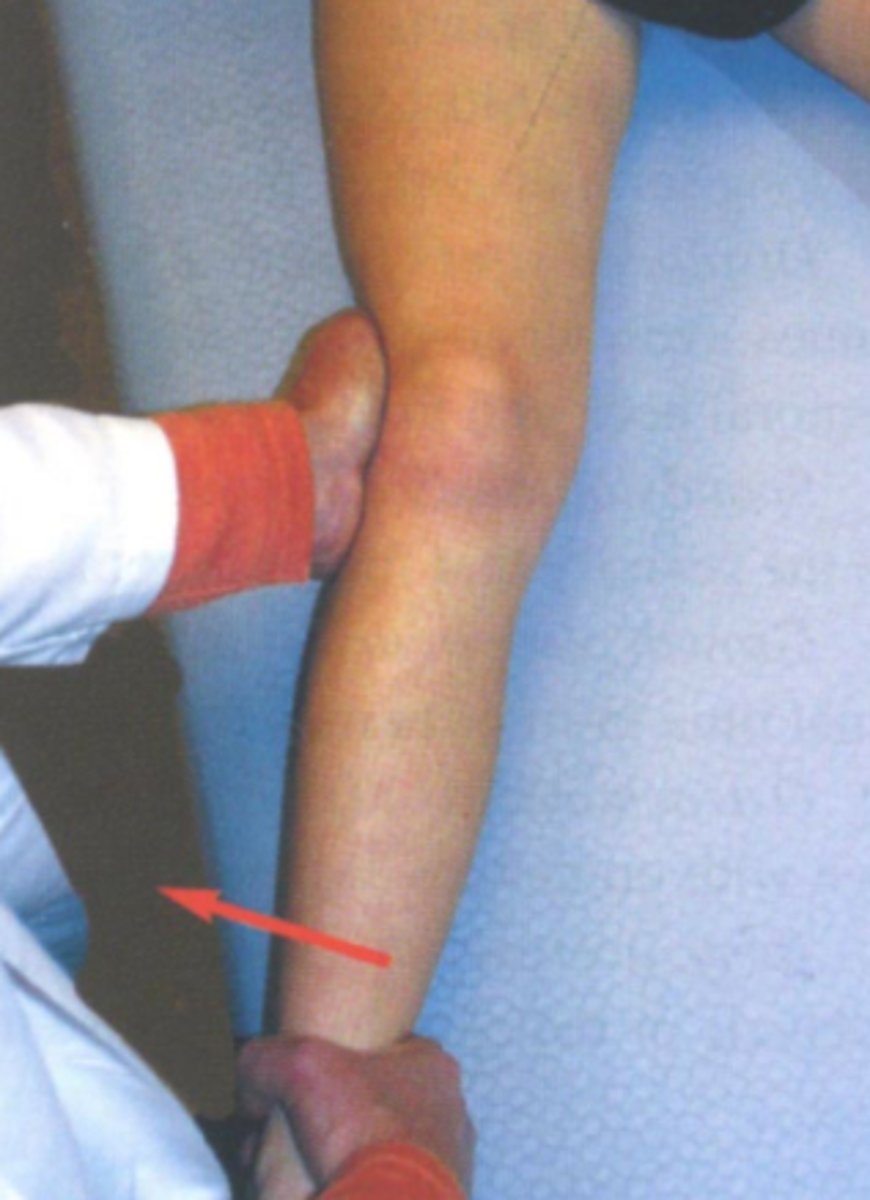
valgus stress test
- diagnosis: medial collateral ligament pathology
- how: apply valgus stress to both knees (once extended & once in 30º of flexion)
+ = affected joint opens medially
varus stress test
- diagnosis: lateral collateral ligament pathology
- how: apply varus stress to both knees (once extended & once in 30º of flexion)
+ = affected joint opens laterally
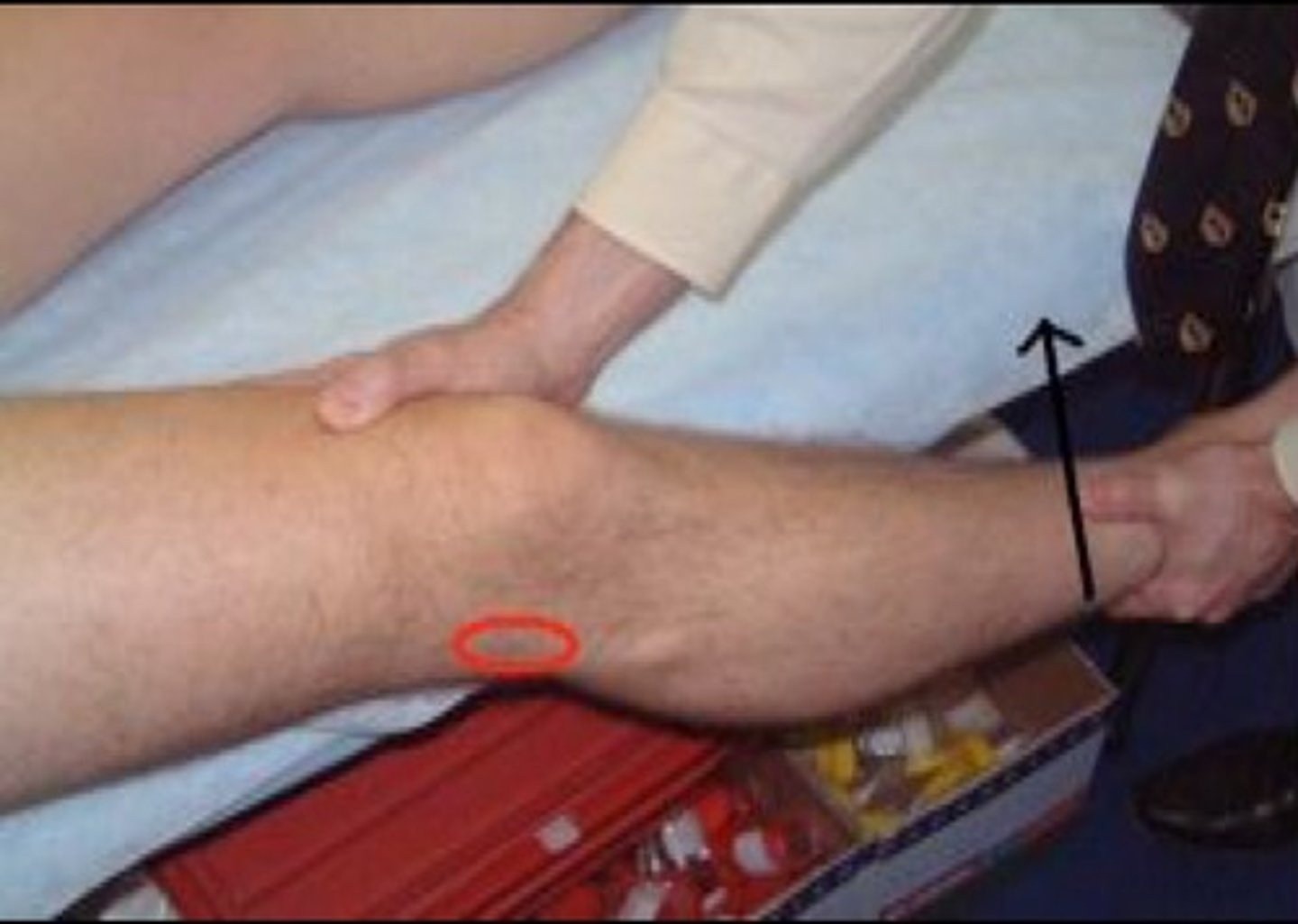
lachman test
- diagnosis: ACL pathology
- how: patient supine, thigh supported & relaxed, flex knee to 30º, stabilize distal femur w/ one hand & attempt to translate tibia anteriorly
+ = increased tibial translation &/or absence of firm end point
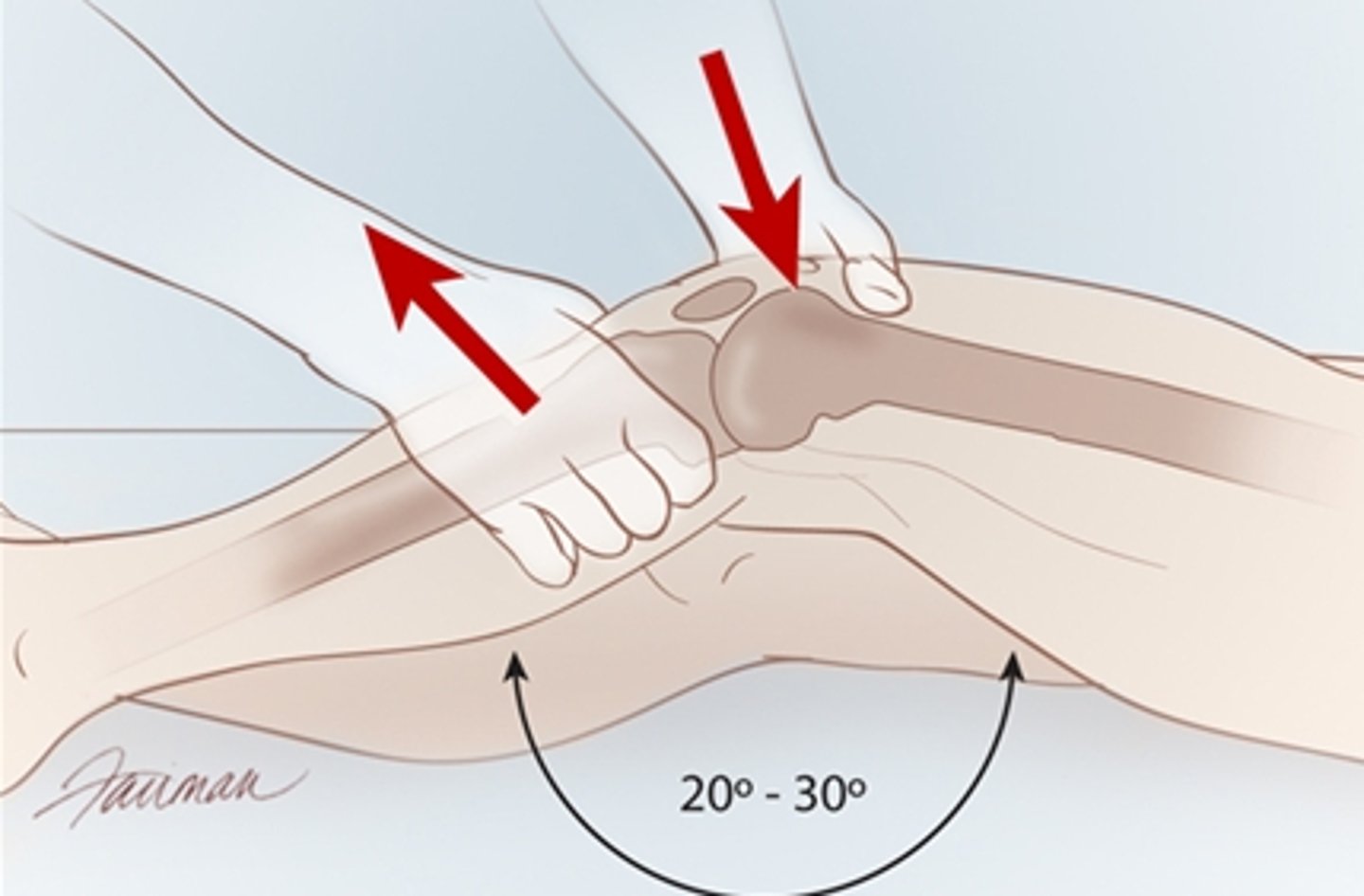
anterior drawer test
- diagnosis: ACL pathology
- how: patient supine, knee flexed to 90º, stabilize patient's leg by sitting on foot, grasp proximal tibia w/ both hands & thrust tibia anteriorly
+ = anterior translation of tibia (not as sensitive as lachman's)
posterior drawer test (gravity sag sign)
- diagnosis: PCL pathology
- how: patient supine, foot supported on table, knee flexed to 90º, grasp proximal tibia w/ both hands & push posteriorly
+ = posterior translation of tibia
joint line tenderness
- diagnosis: meniscal tear
- how: palpate joint line
+ = tenderness
mcmurray test
- diagnosis: medial vs lateral meniscal tear
- how: patient supine, bend knee 90º, rotate knee inward & fully extend, rotate knee outward & fully extend
+ w/ external rotation = medial meniscus
+ w/ internal rotation = lateral meniscus
mcmurray test positive w/ external rotation = ________ meniscus
medial meniscus
1 multiple choice option
mcmurray test positive w/ internal rotation = ________ meniscus
lateral meniscus
1 multiple choice option
J sign
- diagnosis: patellar instability
- how: patient sitting on side of bed, extend knee
+ = arc movement of patella
patellar grind test
- diagnosis: patellar instability
- how: one hand superior to patella, push patella inferiorly, & ask patient to tighten quads against patella resistnace
+ = grinding sound
apprehension test (knee)
- diagnosis: patellar instability
- how: patient supine, knee relaxed in 20º of flexion & draped across thigh, using thumbs, apply gentle directed pressure to displace patella laterally
+ = becomes apprehensive & contracts quad to avoid further displacement
squeeze test
- diagnosis: tibiofibular syndesmosis injury
- how: patient supine, squeeze mid portion of the tibia & fibula
+ = pain
test for lisfranc injury
- diagnosis: disruption of tarsometatarsal joints
- how: stabilize the calcaneus w/ one hand, rotate &/or abduct the forefoot w/ the other hand
+ = pain (severe = midfoot fracture; minimal = ankle sprain)
severe pain when stabilizing the calcaneus & rotating or abducting the forefoot =
a. ankle sprain
b. midfoot fracture
b. midfoot fracture
1 multiple choice option
minimal pain when stabilizing the calcaneus & rotating or abducting the forefoot =
a. ankle sprain
b. midfoot fracture
a. ankle sprain
1 multiple choice option
thompson test
- diagnosis: achilles tendon rupture
- how: patient prone, squeeze calf
+ = foot does NOT plantarflex
dependent rubar test
- diagnosis: charcot foot vs. cellulitis or osteomyelitis
- how: elevate the symptomatic foot above heart for 1 minute
+ for cellulitis = foot loses redness
+ for charcot foot = foot remains red
foot is elevated for 1 min & loses redness
a. cellulitis
b. charcot foot
a. cellulitis
1 multiple choice option
foot is elevated for 1 min & remains red
a. cellulitis
b. charcot foot
b. charcot foot
1 multiple choice option
seated straight-leg raise test
- diagnosis: sciatic lesion
- how: distract patient, lift foot & extend knee
+ = pain or lean back
supine straight leg raise test
- diagnosis: lumbar disc herniation
- how: patient supine, raise leg w/ knee extended
+ = pain in the leg (not the back)
hoover's sign
- diagnosis: malingering
- how: patient supine, place hand under the non-paralyzed heel, ask patient to elevate the paralyzed leg
+ = no pressure felt under non-paralyzed heel
signs of malingering =
+ hoover's sign
or
negative seated straight leg w/ + supine straight leg
reverse straight leg raise test
- diagnosis: L1 to L4 nerve root pathology
- how: patient prone, lift hip into extension while keeping knee straight
+ = pain in anterior thigh
patellar reflex = ___ nerve root
L4
2 multiple choice options
achilles reflex = ___ nerve root
S1
2 multiple choice options
reduction of nursemaid's elbow
- what: radial head dislocation
- how: place thumb over radial head, grasp hand, quickly extend arm in supination & flex it
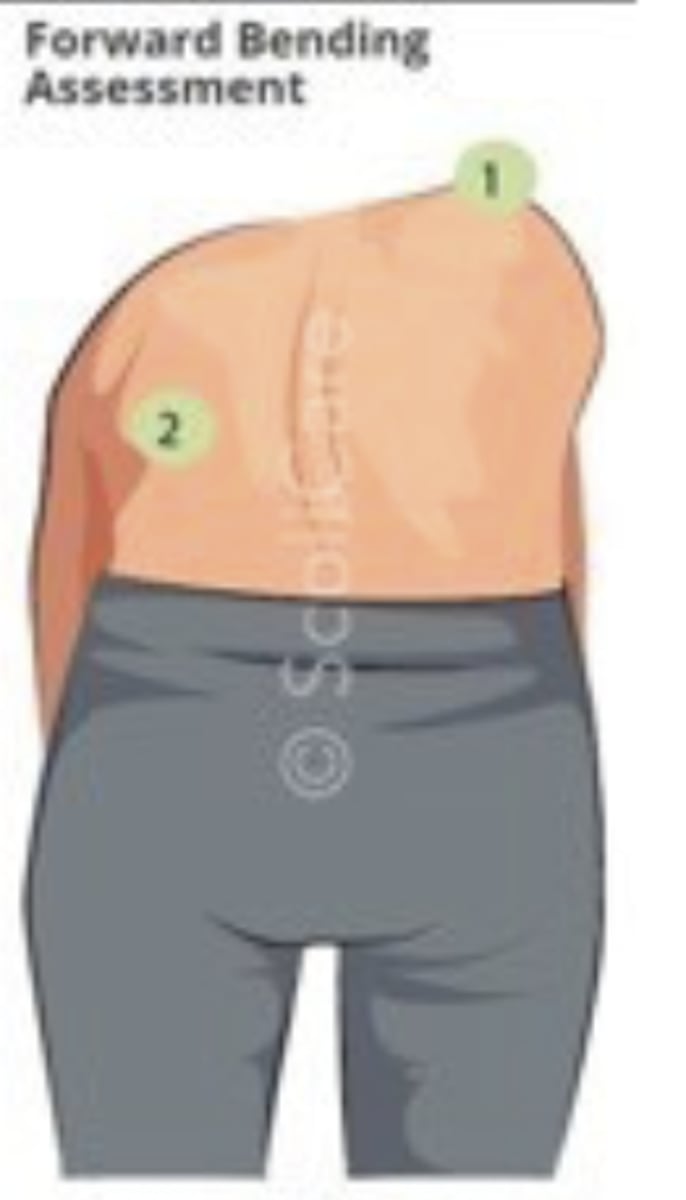
forward bending test
- diagnosis: scoliosis
- how: ask patient to bend forward & touch toes, observe from behind
+ = scapular prominence

how is limb length measured?
from ASIS to medial malleolus
internal hip rotation
- diagnosis: SCFE, LCPD, or femoral anteversion
- how: patient supine, knees flexed 90º, hip in extension, rotate lower extremities outward
+ for femoral anteversion = internal rotation exceeds external rotation by >/= 30º (usually > 65º)
+ for SCFE or LCPD = < 45º
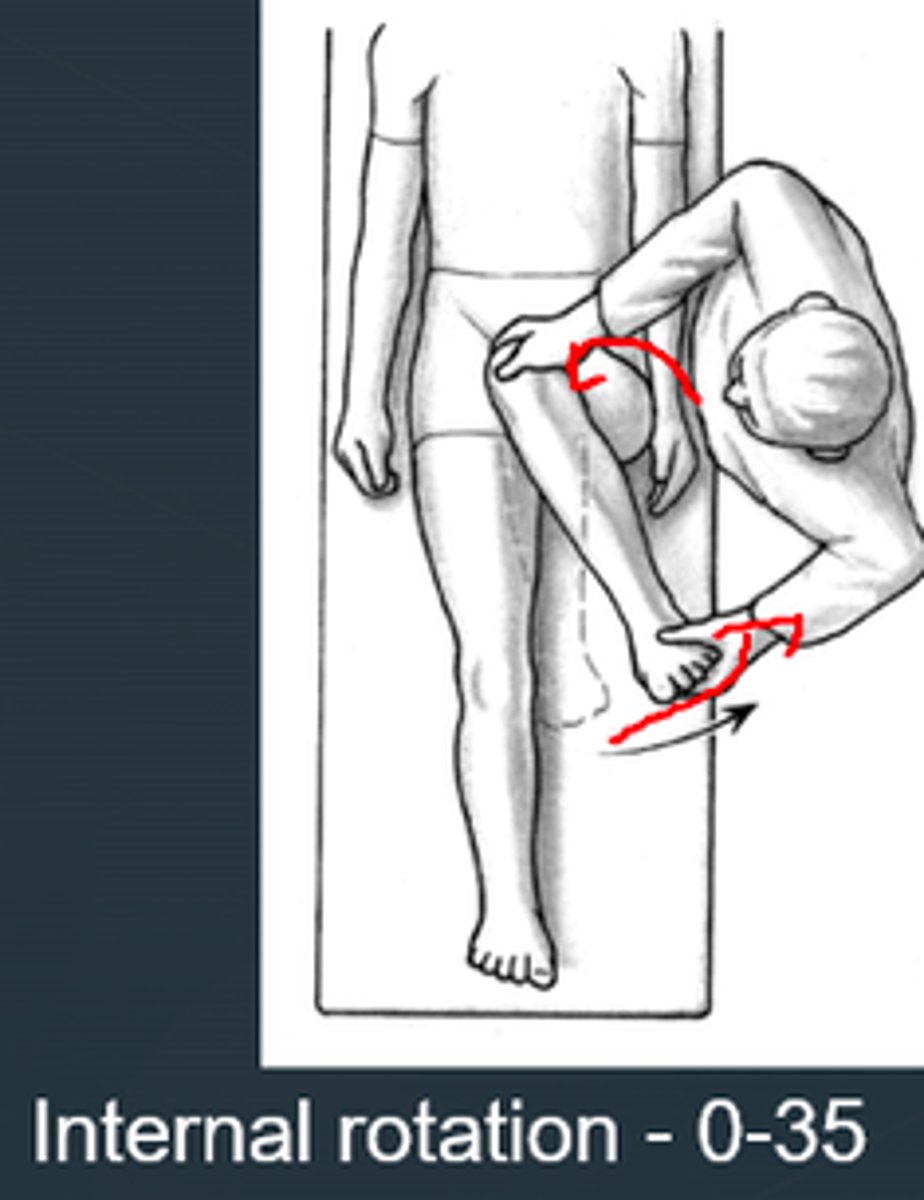
internal rotation of hip exceeds external rotation by >/= 30º
a. SCFE or LCPD
b. femoral anteversion
b. femoral anteversion
1 multiple choice option
internal rotation of hip is < 45º
a. SCFE or LCPD
b. femoral anteversion
a. SCFE or LCPD
1 multiple choice option
thigh foot angle
- diagnosis: tibial torsion (can be external or internal)
- how: patient prone, knee flexed 90º, measure axis of foot relative to axis of thigh
+ = > 10-15º
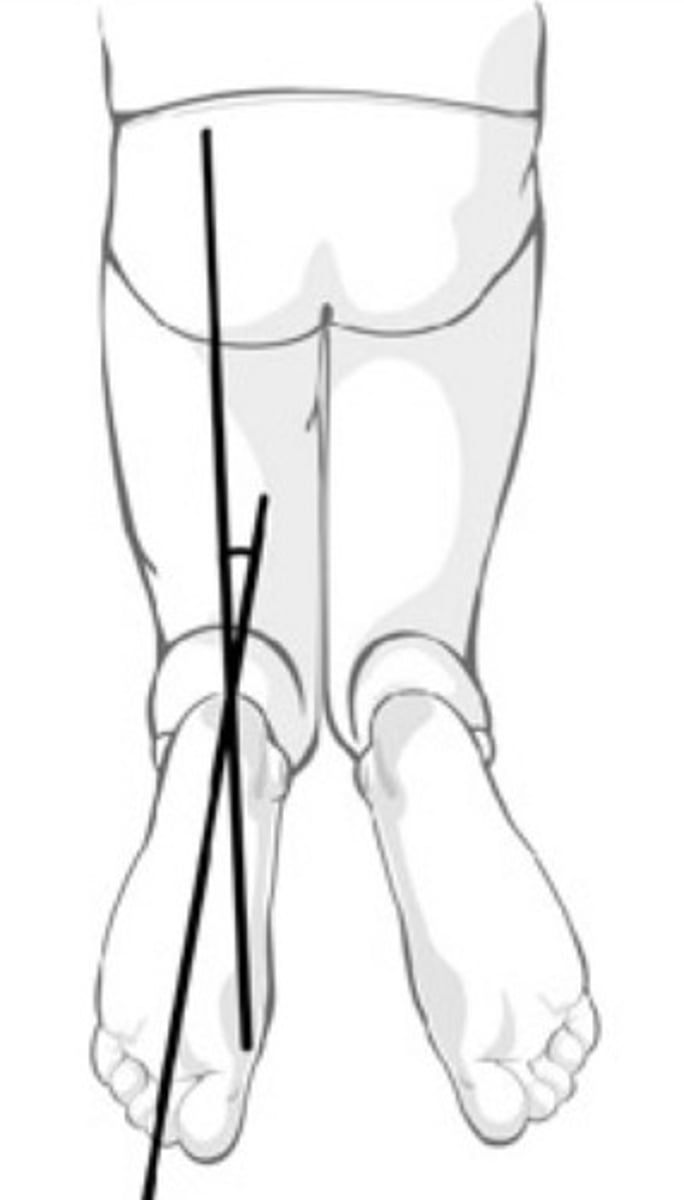
barlow test
- diagnosis: DDH
- how: flex knees, keep in adduction & apply posterior pressure
+ = hip dislocates
ortolani test
- diagnosis: DDH
- how: abduct knees, & while bringing back together, apply anterior pressure
+ = reduces already dislocated hip
galleazi test
- diagnosis: DDH
- how: flex knees, feet flat on table, observe if knees are same height
+ = not same height
SLAP lesion/labral tear tests =
crank or clunk tests
rotator cuff tests =
- drop arm
- neer
- hawkins
- maintained passive ROM, but loss of active
- empty can (supraspinatus)
- attempt to maintain position while pressure is applied to try to internally rotate arm (infraspinatus or teres minor)
- hornblower's (teres minor)
- lift off (subscapularis)
ACL tests =
- lachman
- anterior drawer
meniscus tests =
- joint line tenderness
- mcmurray
patellar instability tests =
- J sign (patellar tracking)
- patellar grind
- apprehension
DDH tests =
- barlow
- ortolani
- galleazi
explain the pathophysiology of acute compartment syndrome:
intracompartment pressure > vascular perfusion pressure (20 mmHg) = cascade of physiologic events
- ↑ pressure = ↑ muscle damage = swelling, ↑ compartment pressure, + muscle necrosis
- most common cause = trauma
6 P's of compartment syndrome
Pain
Pallor
Paresthesias
Paresis
Poikilothermia
Pulselessness
how is the pain described in acute compartment syndrome (ACS)?
- disproportionate to injury
- intolerable when stretching muscles of traumatized area
which 2 of the 6 P's of acute compartment syndrome are considered late findings & may indicate irreversible soft-tissue damage?
- pulselessness
- paresis
if you are suspecting possible compartment syndrome in a patient,
how much time can pass from the time of trauma to the time when irreversible damage begins?
8 hrs
3 multiple choice options
modality w/ the highest radiation
CT
3 multiple choice options
- increases contrast when evaluating joint pathology
- enhances the differentiation of tissues around the joint
- often combined w/ CT or MRI
arthrography
3 multiple choice options
utilizes an IV radioactive agent that localizes in areas of increased bone activity
scintography/bone scan
3 multiple choice options
commonly indicated after an inconclusive XR when an occult/stress fracture or early osteonecrosis is suspected
MRI
3 multiple choice options
initial modality for the evaluation of bone or joint pain
radiographs (XRs)
3 multiple choice options
useful in guiding difficult joint aspirations (other than US)
CT
3 multiple choice options
best modality for tendons, ligaments, menisci, & spinal cord
MRI
3 multiple choice options
very safe but quality & interpretation is technician & radiologist dependent
US
3 multiple choice options
what is the usual cause of cervical radiculopathy in young adults?
herniation of a cervical disk (nucleus pulposus) that entraps the root as it enters the foramen
what is the usual cause of cervical radiculopathy in older adults?
cervical spondylosis
- combo of foraminal narrowing d/t vertical settling of the disk space & arthritic involvement of the uncovertebral joint
s/s of cervical radiculopathy
- unilateral neck/radicular pain w/ assoc. numbness & paresthesias in the UE distribution of the involved root
- muscle spasms or fasciculations
- weakness
- lack of coordination
- changes in handwriting
- diminished grip strength
- dropping objects from hand
- difficulty w/ manipulative tasks
- occipital HAs & pain radiating into the paraspinal & scapular regions
- pain may be relieved by placing hands on top of head (decreases tension on the involved nerve root)
abnormal response when testing the biceps reflex could indicate pathology in which disk spaces?
C4-C6
3 multiple choice options
abnormal response when testing the brachioradialis reflex could indicate pathology in which disk spaces?
C5-C6
3 multiple choice options
abnormal response when testing the triceps reflex could indicate pathology in which disk spaces?
C6-C7
3 multiple choice options
what diagnostic studies can help to differentiate hand paresthesia caused by cervical pathology vs peripheral neuropathy?
electromyography (EMG) & nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies
although cervical radiculopathy usually resolves spontaneously within 2 - 8 weeks,
what 2 treatments are usually beneficial?
1. short course of anti-inflammatory medication coupled w/ cervical traction in a head halter
2. referral to PT/rehab specialist
what is the appropriate treatment for an uncomplicated whiplash injury &
how long might it take for symptoms to resolve?
- provide reassurance about natural hx of these disorders
- acute care (1 to 2 wks): pain meds &/or short-term NSAIDs, & possible use of a soft cervical collar, muscle relaxants, &/or cervical pillows
- appropriately applied rehab, esp. in 1st 4 wks
- mild narcotic meds initially, but should be restricted to the 1st wk or 2
- dexepine or amitriptyline for sleep
- aerobic activities (walking) ASAP; add isometric exercises as pt's comfort improves (preferably 1st 2 wks)
- encourage an early return to normal activities & work
cervical strains that are not a result of trauma, but from gradual tightening of muscles (includes spasmodic torticollis), respond best to stretching and strengthening exercises.
what are the two home exercises the text recommends for this type of cervical strain?
1. head rolls
2. cat back stretch
what is the distribution of numbness w/ cauda equina syndrome?
"saddle" distribution
- both legs, but may be more severe in 1 extremity; perineal numbness
what are the 3 ways that leg weakness may present w/ cauda equina syndrome?
1. stumbling gait
2. difficulty rising from a chair
3. foot drop (often symmetric)
what are the possible urinary & anal complaints w/ cauda equina syndrome?
difficulty voiding or loss of urinary sphincter control