Topic 5: Parturition and Lactation
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Nutrition during pregnancy
balanced diet (protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, fiber)
important vitamins include vitamin D (support absorption of calcium at level of gut), folic acid (normal development of spine), vitamin K (clotting)
important minerals include iron (red blood cells), calcium (bones)
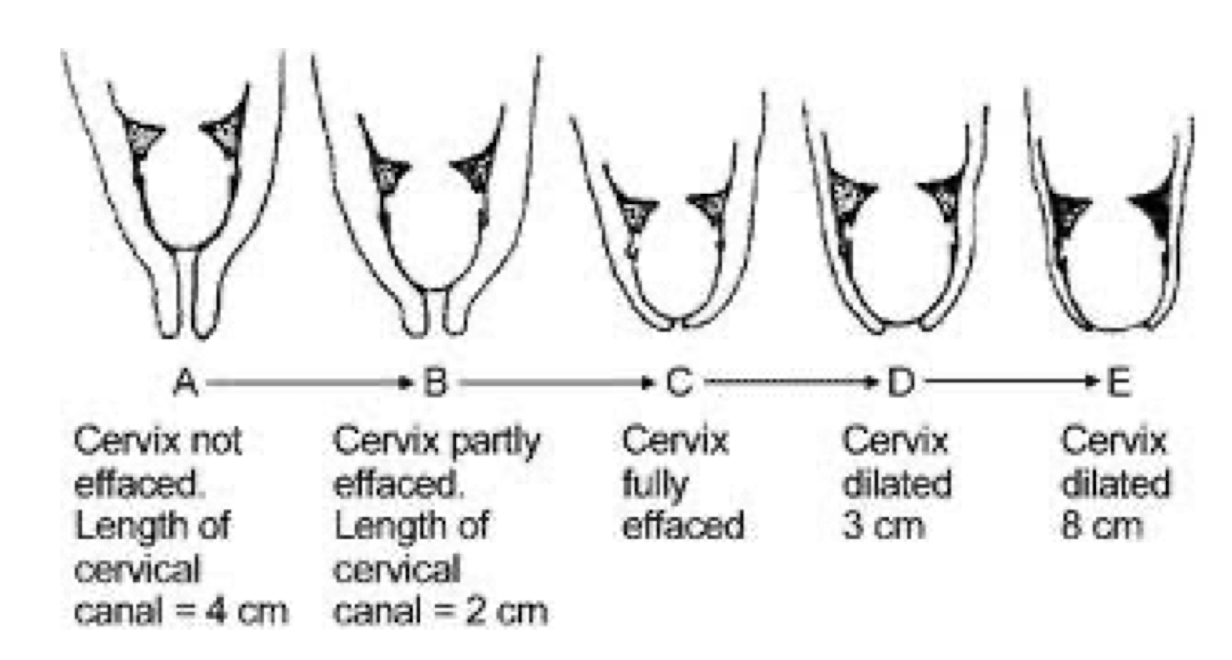
Effacement and dilation diagram
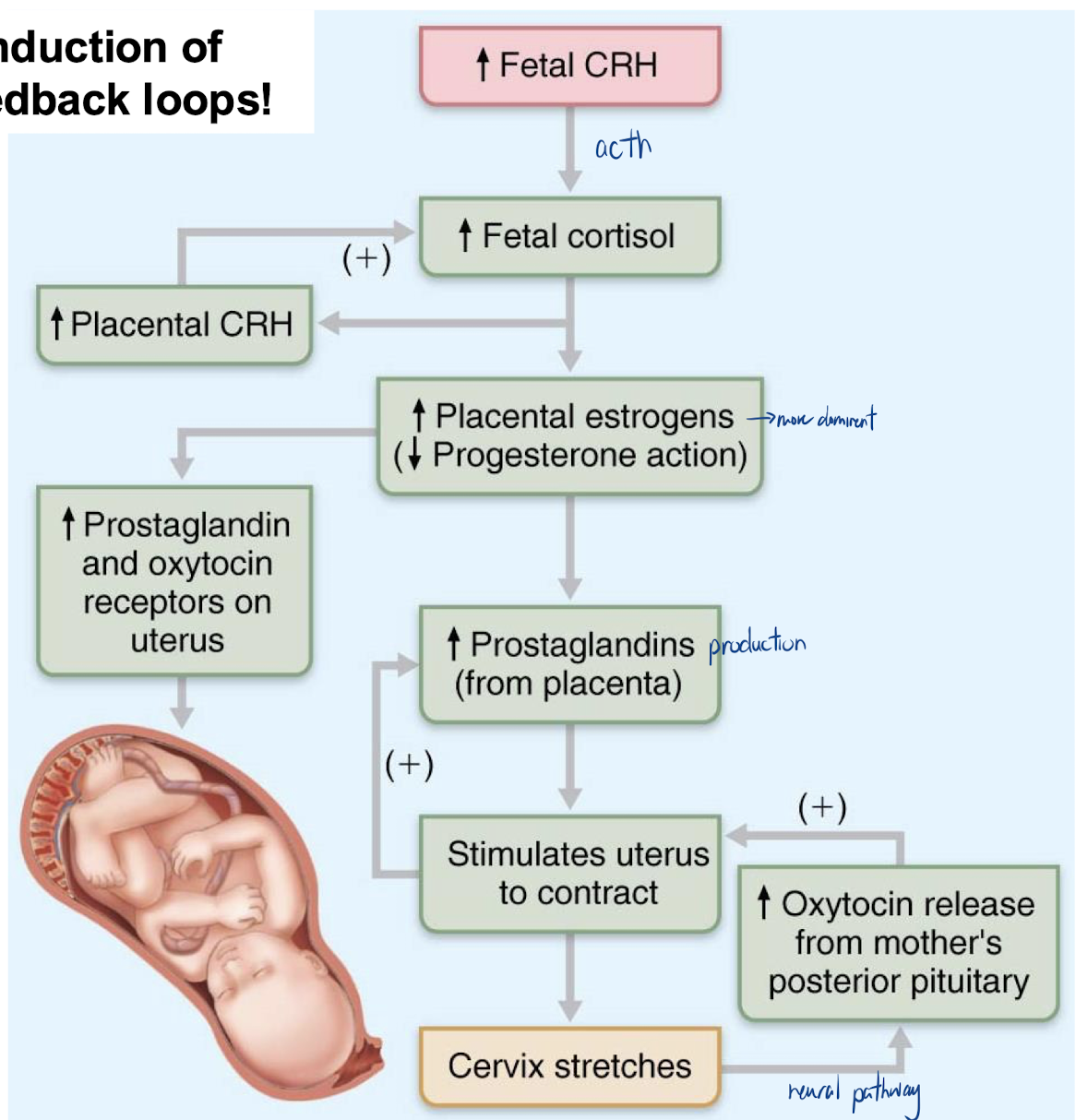
Hormonal feedback loops
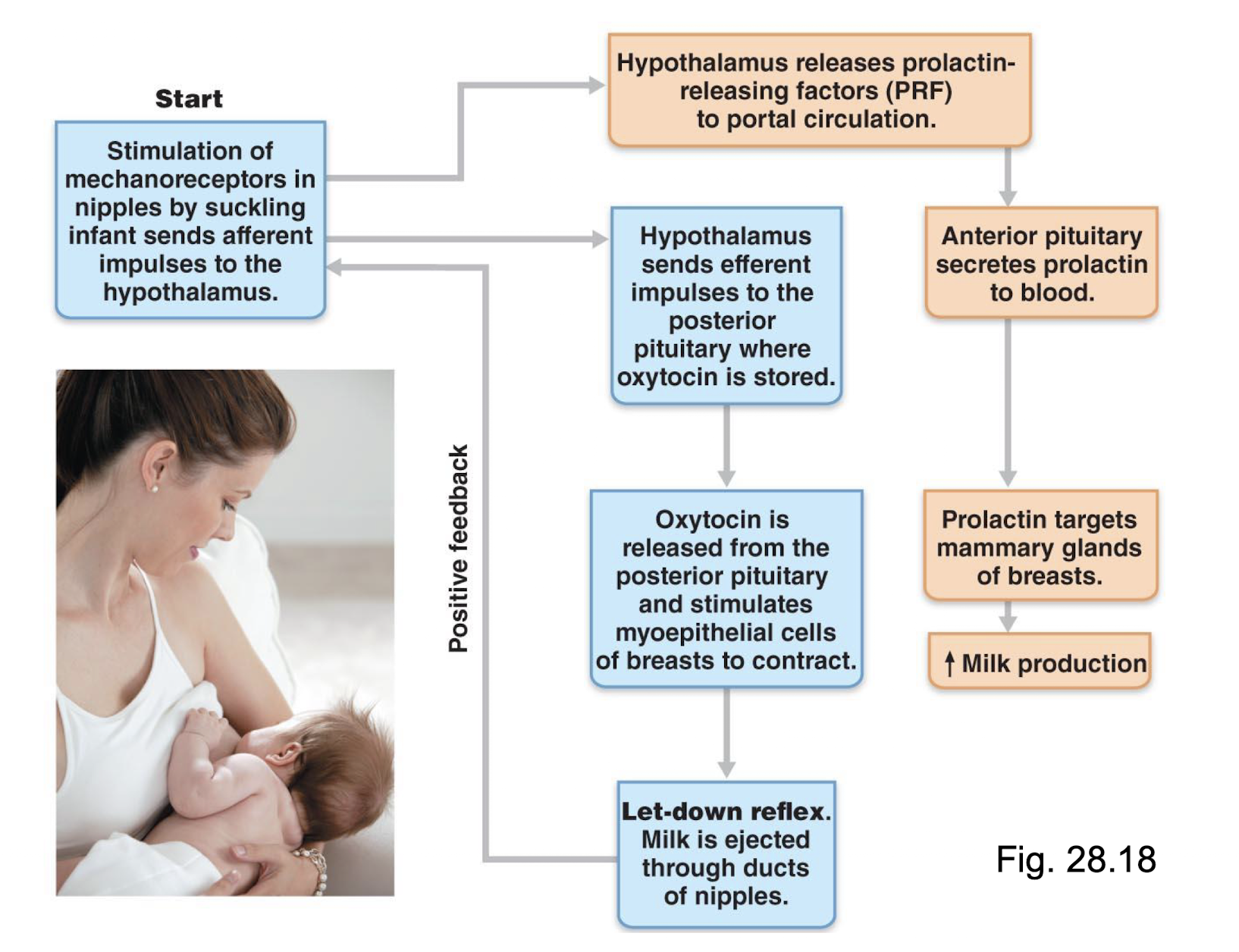
Stage of Labour- Early dilation
Baby's head engaged; widest dimension is along left-right axis.
Stage of Labour- Late dilation
Baby's head rotates so widest dimension is in anteroposterior axis (of pelvic outlet).
Dilation nearly complete.
Stage of Labour- Expulsion
Baby's head extends as it is delivered.
Stage of Labour- Placental stage
After baby is delivered, the placenta detaches and is removed.
Oxytocin
levels are high during latter part of pregnancy, but labour is not initiated because:
progesterone levels are also high (muscle relaxed)
myometrial cells have insufficient number of oxytocin receptors
Baby moves into birth canal; pressure of head on cervix neuroendocrine reflex – result??
stimulate uterine contraction, increase time and strength
Oxytocin stimulates placenta and uterus to synthesize prostaglandins → effects?
Regulation of Breast Development
each mammary gland divided into 15-20 lobes; subdivided into lobules; basic component of each lobule is the alveolus
Alveolus
glandular structure involved in milk production; lined by a single layer of milk-secreting epithelial cells
What hormones increase during pregnancy? what does that do?
estradiol and progesterone
stimulate further growth & development of alveoli & ducts also permissive actions of glucocorticoids, prolactin, human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS)
Prolactin
stimulates milk production; actual secretion during pregnancy inhibited by high levels of estrogen and progesterone
hCS
human chorionic somatomammotropin
Support growth and activation or epithelial cells for milk production
Postpartum estradiol and progesterone
decrease, allowing full expression of prolactin
now can have both production and secretion (move into lumen)
Classical Milk Let-down Reflex & Hormonal Maintenance of Lactation
2 important hormones:
prolactin → secretion of casein, lactose, fatty acids = production
oxytocin → contraction of myoepithelial cells = let-down
both of these hormones are required for continued lactation
Parturition
the action of giving birth to young; childbirth.
process not completely understood – esp. what is the signal to initiate parturition and how can we stop premature labour and delivery??
fetal cortisol seems to be an important trigger; it also stimulates production of surfactant in the lungs – why is this important?
cortisol triggers surfactant production (for lungs)
estrogen levels highest toward time of parturition:
ensures lots of oxytocin receptors on myometrium
antagonizes relaxing effect of progesterone
2 hormones important during labour and delivery:
oxytocin
prostaglandins – source?
Source of oxytocin
posterior pituitary, stimulates uterine contraction
Source of prostaglandins
uterus, stimulates uterine contraction
Effacement
the thinning and shortening of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus, in preparation for childbirth