Chapter 20: Personal selling and sales management
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
The Scope and Nature of Personal Selling
-*Personal selling* is the two-way flow of communication between a buyer or buyers and a seller, designed to influence the buyer's purchase decision
-can happen face-to-face, videoconferencing, on the phone, on the internet
-B2C
-B2B= professional selling
Personal Selling as a Career
-people love the lifestyle
-there is a lot of flexibility
-there is a lot of variety in the job
-can be very lucrative
-very visible to management and good for promotions
The Value Added by Personal Selling
-salespeople are expensive, so they must do something good to make up for that...
-salespeople provide information and advice
-salespeople save time and simplify buying
-salespeople build relationships
Relationship selling
a sales philosophy and process that emphasizes a commitment to maintaining the relationship over the long term and investing in opportunities that are mutually beneficial to all parties
The Personal Selling Process
-may or may not use every step depending on the situation
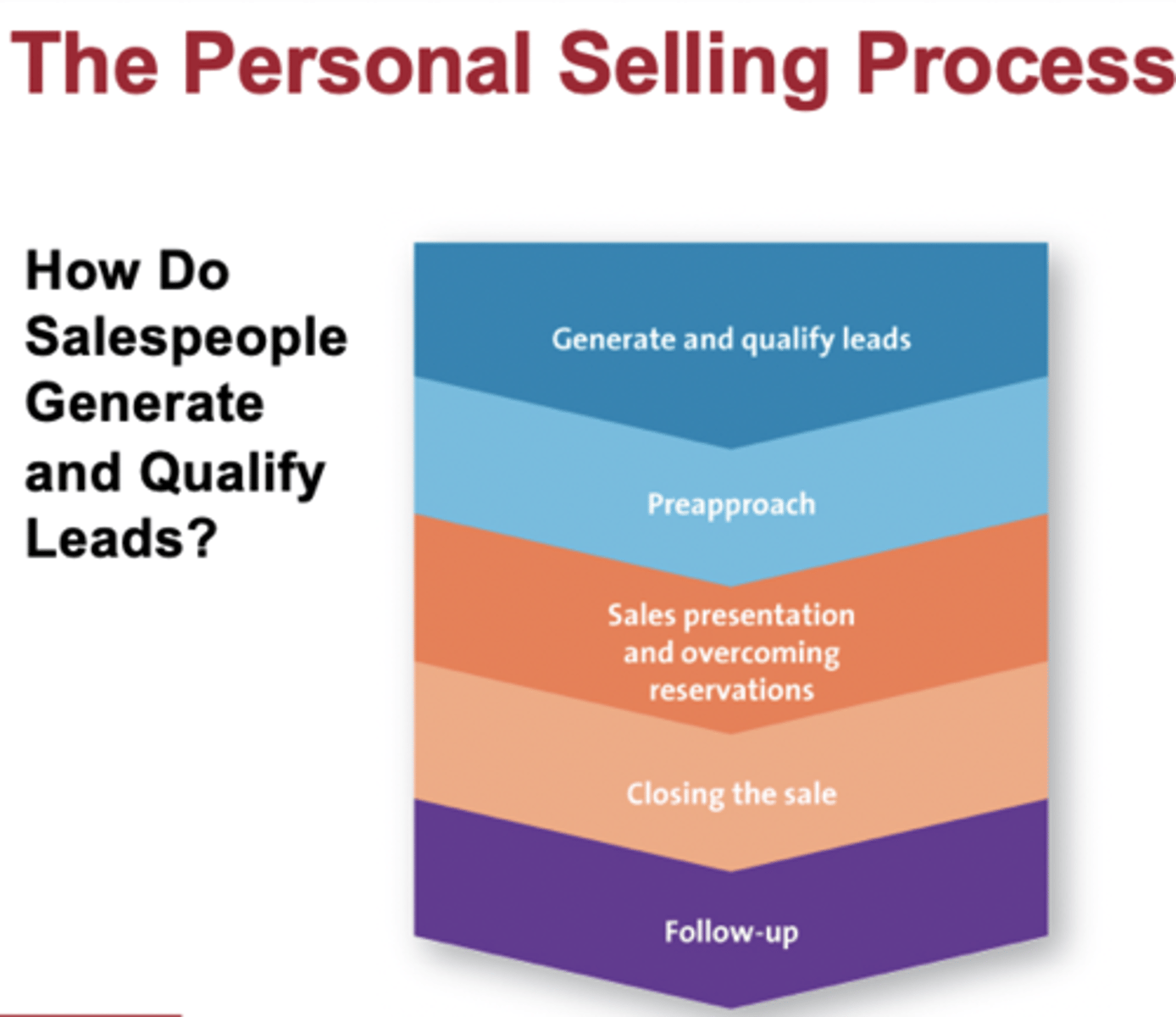
The Personal Selling Process: Step One->generate and qualify leads
-generate a list of potential customers (leads) and assess their potential (qualify)
-salespeople who already have a relationship skip this part and its not really used in retail, mostly B2B
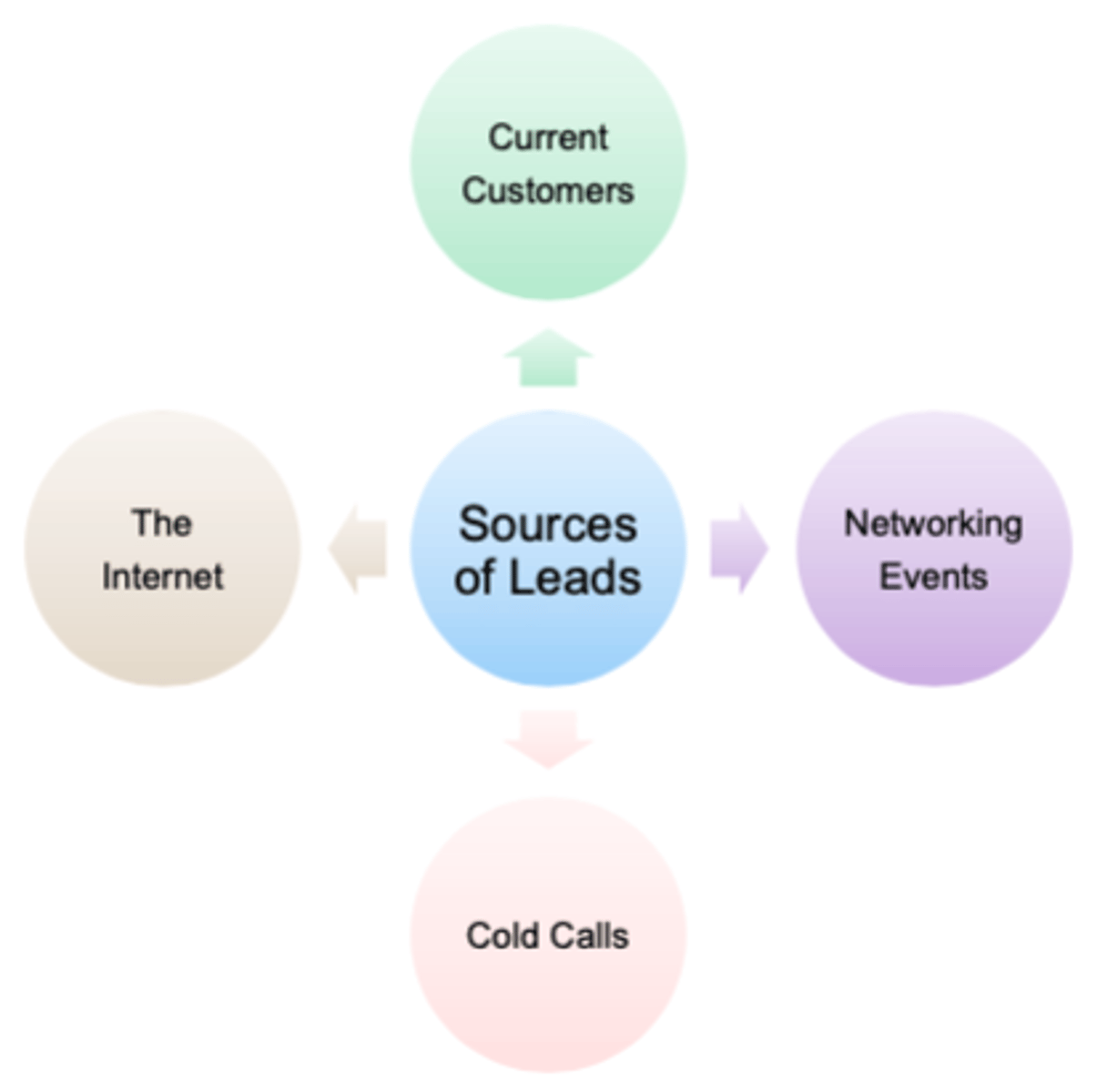
-discover potential leads by talking to current customers, doing research on the Internet, cold calls, telemarketing, inbound marketing, or networking at events such as trade shows, going on social media, industry conferences, or chamber of commerce meetings
-After salespeople generate leads, they must qualify those leads by determining whether it is worthwhile to pursue them and attempt to turn them into customers (Illegal for retail because you should never judge someone and say they aren't allowed to shop in your store)
Inbound marketing
-can be used to generate leads
-Marketing activities that draw the attention of customers through blogs, Twitter, LinkedIn, and other online sources, rather than using more traditional activities that require having to go out to get customers' attention, such as making a sales call.
Trade Shows
major events attended by buyers who choose to be exposed to products and services offered by potential suppliers in an industry
Cold calls
a method of prospecting in which salespeople telephone or go to see potential customers without appointments
-low success rate
Telemarketing
a method of prospecting in which salespeople telephone potential customers
-low success rate
The Personal Selling Process: Step Two->Preapproach and the Use of CRM Systems
In the personal selling process, *preapproach* occurs prior to meeting the customer for the first time and extends the qualification of leads procedure; in this step, the salesperson conducts additional research and develops plans for meeting with the customer.
-you can find customer info in the CRM system. which has several components including customer database or data warehouse
-when salesperson is meeting with a customer, they should have a goal on what they want to accomplish when meeting with them
-they can role play, so the sales person can act out what they want to say with a coworker and then get critiqued before doing it irl
The Personal Selling Process: Step Three->Sales Presentation and Overcoming Reservations
-sales presentation matches with the RFP from B2B buying process
-The presentation: At the beginning of the pres, get to know the customer, get their attention and create interest, and establish where the customer is in the buying process. Ask questions to the customer and listen intently to their answers. Apply this knowledge you learned to help the customer solve its problem or satisfy their need. You can use technology to talk to customers over zoom so customers can rewatch your presentation or you can have them try your product remotely.
- Handling Reservations: Customer might have reservations or objections abt your product during the sales presentation. Anticipate what these reservations might be so that you can handle them correctly. Relax, listen, and clarify any reservations.
The Personal Selling Process: Step Four->Closing the sale
-*closing the sale*= obtaining a commitment from the customer to make a purchase
-Without a successful close, the salesperson goes away empty-handed, so many salespeople find this part of the sales process very stressful.
-An unsuccessful close on one day may just be a means of laying the groundwork for a successful close during the next meeting.
-listen to customer and reading body language can help close a sale faster
The Personal Selling Process: Step Five->Follow-up
-With relationship selling, it is never really over, even after the sale is closed
-The attitudes customers develop after the sale become the basis for how they purchase in the future
-follow-up offers an opportunity to solidify customer relationship
-When customers' expectations are not met, they often complain. so learn how to handle complaints
- check in with customer right after they get their p/s
How do the five service quality dimensions apply to the follow-up?
-RATER (how well a service meets customer expectations)
-*Reliability*The salesperson and the supporting organization must deliver the right product or service on time.
-*Responsiveness* The salesperson and support group must be ready to deal quickly with any issue, question, or problem that may arise.
-*Assurance*. Customers must be assured through adequate guarantees that their purchase will perform as expected.
-*Empathy*. The salesperson and support group must have a good understanding of the problems and issues faced by their customers. Otherwise, they cannot give them what they want.
-*Tangibles*. Because tangibles reflect the physical characteristics of the seller's business, such as its website, marketing communications, and delivery materials, their influence is subtler than that of the other four service quality dimensions. That doesn't mean it is any less important. Retail customers are generally more pleased with a purchase if it is carefully wrapped in nice paper instead of being haphazardly thrown into a crumpled plastic bag. The tangibles offer a signal that the product is of high quality, even though the packaging has nothing to do with the product's actual performance.
The Digital Selling Process
-three essential components of digital selling: generate leads, acquire customers and close the sale using websites, and retain customers.
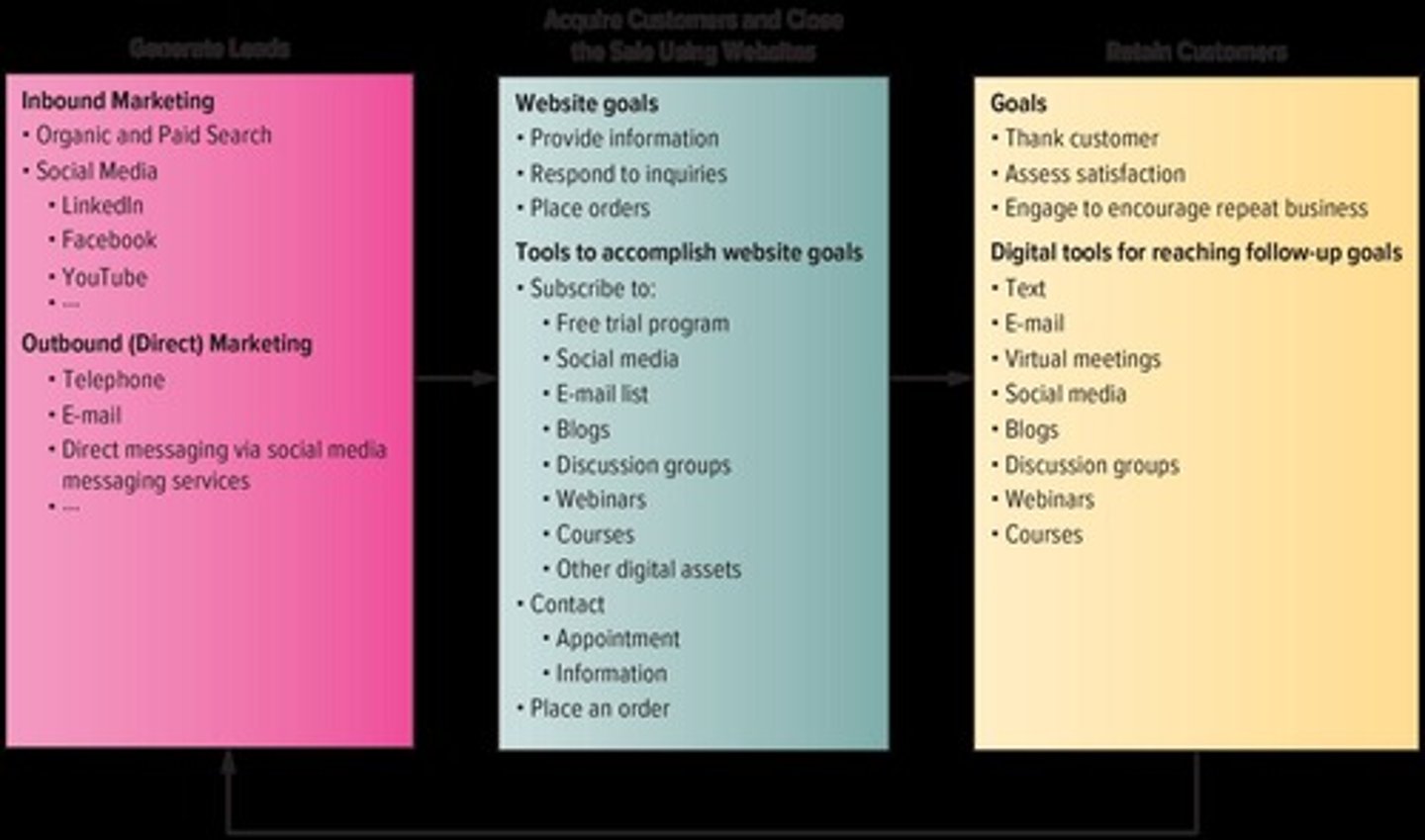
The Digital Selling Process: Generate Leads
-generate and qualify leads
-these leads are generated by either inbound or outbound marketing activities
-Inbound activities are initiated by customers, whereas outbound activities are initiated by the marketer
-Inbound marketing activities generate leads through organic and paid searches, as well as through social media like LinkedIn, Facebook, and YouTube, often without human interaction
-If sellers want to increase the probability that potential customers land on their digital platforms, they also can use search engine optimization (SEO) for paid searches so that you pop up first in searches
-Outbound marketing, also known as direct marketing, includes more traditional sales and promotional techniques that communicate directly with target customers to generate a response or transaction, such as telephone, e-mail, and direct-to-consumer messaging through social media platforms
The Digital Selling Process: Acquire Customers and Close the Sale
-not doing face-to-face interaction like in-person selling
-more cost effective to do it digitally though
-Traditional selling with salespeople is still the best, and often the only, way to close sales for expensive, complicated, and/or technical products in both B2C and B2B settings. But even these situations can benefit from a hybrid solution (mix of inperson and digital)
-a firm's website is the core vehicle for converting leads into paying customers by providing product or service information, responding to inquiries, and placing orders
-website should entice, offer lot of connection opportunity's and be interactive
The Digital Selling Process: Retain Customers
-keep in touch with customers
-make sure customers expectations have been exceeded
-immediately address any neg feedback
-keep the customer engaged with the firm and product and encourage them to buy again
-good retention=new leads
Managing the Sales Force
-Like any business activity involving people, the sales force requires management
-*Sales management* involves the planning, direction, and control of personal selling activities, including recruiting, selecting, training, motivating, compensating, and evaluating, as they apply to the sales force.
Managing the Sales Force: Sales force structure
Will you hire your own salespeople, or should they be manufacturer's representatives? What will each salesperson's primary duties be: order taker, order getter, sales support? Finally, will they work together in teams? In this section, we examine each of these issues.
Sales force structure: Company Sales Force or Manufacturer's Representative
-A *company sales force* comprises people who are employees of the selling company
-*Manufacturer's representatives, or reps, also known as independent agents*, are salespeople who sell a manufacturer's products on an extended contract basis but are not employees of the manufacturer. They are compensated by commissions and do not take ownership or physical possession of the merchandise. Useful for smaller firms or firms expanding into new markets because they can achieve instant and extensive sales coverage without having to pay full-time personnel and are more flexible
-An alternative approach, adopted by firms known as multilevel marketers, requires sales reps to take possession of the products that they sell, though this version often raises ethical concerns can achieve instant and extensive sales coverage without having to pay full-time personnel.
-Company sales forces are more typically used for established product lines. Because the salespeople are company employees, the manufacturer has more control over what they do
Sales force structure: Salesperson Duties
salespeople generally play three important roles: order getting, order taking, and sales support.
Salesperson duties: Oder getting
A salesperson whose primary responsibilities are identifying potential customers and engaging those customers in discussions to attempt to make a sale.
-also go and follow-up with people
-have extensive sales and product knowlege training
Salesperson duties: Order taking
-a salesperson whose primary responsibility is to process routine orders, reorders, or rebuys for products
-go into stores and distribution centers that already carry their products to check inventory, set up displays, write new orders, and make sure everything is going smoothly
Salesperson duties: Sales Support
-sales support personnel are employees who enhance and help with a firm's overall selling effort, such as by responding to the customer's technical questions or facilitating repairs.
Salesperson duties: Combination duties
-some salespeople have primary jobs while others do multiple
Managing the Sales Force: Recruiting and Selecting Salespeople
-When the firm has determined how the sales force will be structured, it must find and hire salespeople
-salespeople are expensive to train so don't select the wrong people
-The most important activity in the recruiting process is to determine exactly what the salesperson will be doing and what personal traits and abilities a person should have to do the job well
Generally accepted traits salespeople need
-Personality: Good salespeople are friendly, sociable, and, in general, like being around people. Customers won't buy from someone they don't like.
-Optimism: Good salespeople tend to look at the bright side of things. Optimism also may help them be resilient—the third trait.
-Resilience: Good salespeople don't easily take no for an answer. They keep coming back until they get a yes.
-Self-motivation: As we have already mentioned, salespeople have lots of freedom to spend their days the way they believe will be most productive. But if salespeople are not self-motivated to get the job done, it probably won't get done.
-Empathy: Good salespeople must care about their customers, their issues, and their problems.
Managing the Sales Force: Sales Training
-Even people who possess all these personal traits need training.
-various methods for training depending on the type of job
-using the internet for training is less expensive
What sales training entails
-selling and negotiation techniques
-product and service knowledge
-technologies used in selling processes
-time and territory management
-company policies and procedures
Managing the Sales Force: Motivating and Compensating Salespeople
-get to know salespeople and determine what motivates them to be effective
-do this for each individual person
Motivating and Compensating Salespeople: Financial Rewards
-salary: fixed sum of money paid at regular intervals
-commission: money paid as a percentage of the sales volume or profitability
-bonus: a payment made at management's discretion when the salesperson attains certain goals
-sales contest: a short term incentive designed to elicit a specific response from the sales force
Motivating and Compensating Salespeople: Nonfinancial Rewards
-good salespeople are self motivated
-but its good to let them know when they are doing good
-you can give them things like plaques or pens or rings or free trips or days off
-make sure you give it to them in a respectful way and in a way that other people see
Motivating and Compensating Salespeople: Evaluating salespeople by using marketing metrics
Salespeople's evaluation process must be tied to their reward structure. If salespeople do well, they should receive their rewards the way you do if you do well on your exams and assignments in a class: you earn good grades. However, salespeople should be evaluated and rewarded for only those activities and outcomes that fall under their control
-firms use ratios such as profit per customer, orders per call, sales per hour, or expenses compared to sales as their objective measures.
Ethical and legal issues in personal selling
1. sales manager and sales force
2. sales force and corporate policy
3. salesperson and customer
Ethical and legal issues in personal selling: Sales manager and the sales force
-sales manager must treat everyone equally
-With regard to the sales force, this fairness must apply to hiring, promotion, supervision, training, assignment of duties and quotas, compensation and incentives, and firing
Ethical and legal issues in personal selling: The sales force and Corporate policy
-Sometimes salespeople face a conflict between what they believe represents ethical selling and what their company asks them to do to make a sale
-Salespeople also can be held accountable for illegal actions sanctioned by the employer
Ethical and legal issues in personal selling: The salesperson and the customer
-As the frontline emissaries for a firm, salespeople have a duty to be ethically and legally correct in all their dealings with their customers. Not only is it the right thing to do, it simply means good business because you want long-term customers