Lesson 5.5: Inflation and Deflation
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards made from a presentation segment created as a lesson on inflation and deflation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Inflation
The rate at which the value of a currency is falling and, consequently, the general level of prices for goods and services is rising
Leads to a decline of the purchasing power of a given currency over time
Deflation
The general decline of the price level of goods and services
Associated with a contraction in the supply of money and credit, but prices can also fall due to increased productivity and technological improvements

Aggregate price level
A measure of the overall level of prices in an economy

Consumption bundle
A typical group of goods and services purchased by customers
Market basket
A hypothetical consumption bundle used to measure changes in the overall price level
Revised approximately every decade to reflect shifts in consumer purchasing behavior
Price index
A way of measuring how the average price of a standard group of goods changes over time
Helps consumers and businesses make economic decisions
Aids governments in making policy decisions, such as in setting interest rates to ease inflation
Base year
A year arbitrarily chosen for comparison when calculating a price index, which compares the price of the market basket of goods in a given year to its price in this
Inflation rate
Calculated as the annual percentage change in an official price index
Can lead to workers or pensioners losing money if income does not keep up with this

Consumer price index (CPI)
Measures the cost of a market basket of a typical urban American family
Calculated by the Bureau of Labor Statistics by surveying 23,000 retail outlets in 87 cities, tabulating over 80,000 prices per month for an overall weighted average
Used to evaluate changes in the cost of living as well as the rate of inflation or deflation; is thus used to index the price of certain goods or payments like Social Security
However, it can ignore technological improvements or households moving away from a good due to price increases
Producer price index (PPI)
Measures the cost of a typical basket of goods and services purchased by producers
Usually moves in tandem with other measures of inflation
Money supply
One of the factors of inflation describing a rise in the supply of a currency without a matching rise in the production of goods and services
Prices thus rise due to heightened demand for a limited supply of products, reducing purchasing power
Quantity theory of money
Believes that the value of money and resulting inflation are caused by the supply and demand of the currency
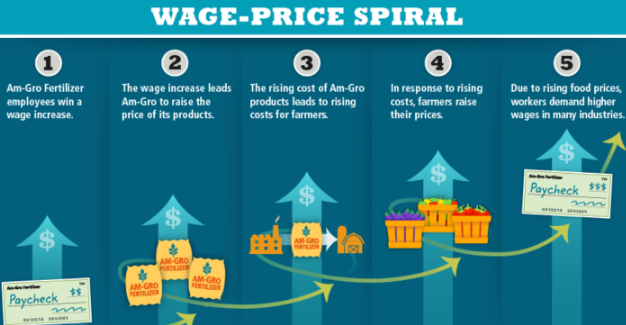
Wage-price spiral
Phenomenon that states that employers providing higher wages lead to higher costs, leading to higher overall prices and thus a need for even higher wages