affordable care act
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pubhlth
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Which of the four main problems of the health care system does the ACA cover?
Main four problems:
cost of care
access to coverage and care
quality and accountability
racial and economic disparities
Answer: Access to coverage and care
However, the ACA addresses the other problems in small or indirect ways
total and per capita spending on health is unsustainable
Large numbers of Americans are uninsured
nonelderly unisured = 25.6 million in 2022 = 9.6% of US population
What was the ACA designed to expand?
insurance access
Groups that faced barriers to insurance coverage before the ACA:
young adults
excluded from parents insurance after 19 years old (22 if student)
people with pre-existing conditions
could be denied insurance if they had a health condition prior to the start of a new insurance plan
childless adults
not eligible for medicaid, no matter the income level
very sick individuals
could face limits on coverage → limits on annual or lifetime coverage
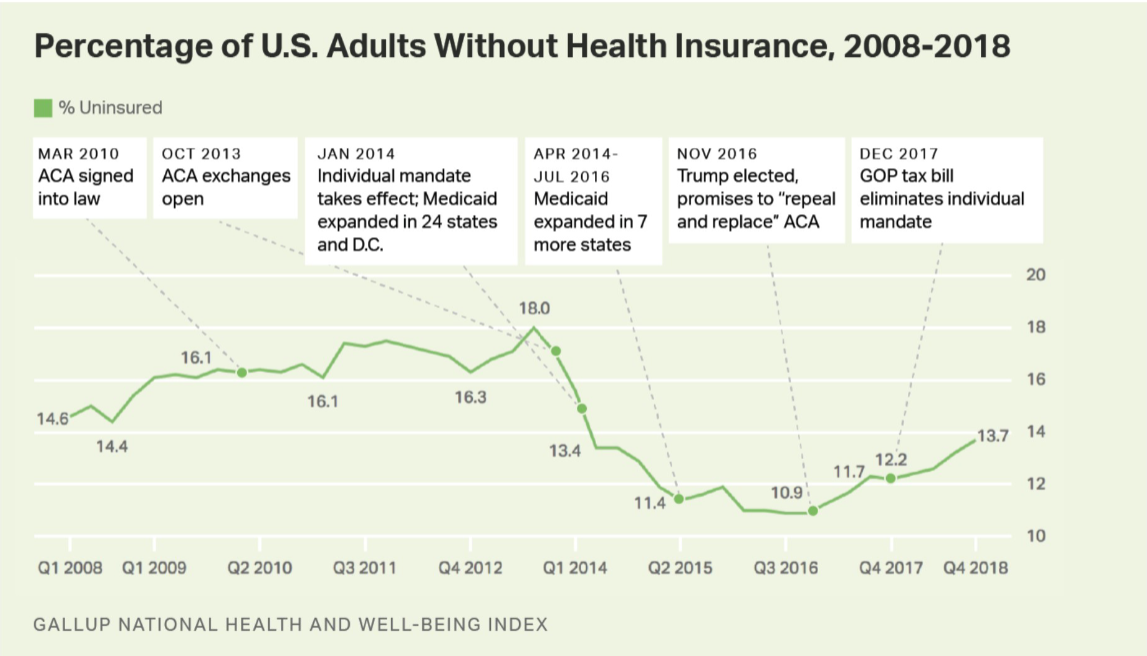
ACA successfully decreased the uninsured rate
affording care is challenging, esp for working class and historically disenfranchised individuals
ex. americans putting off medical treatment in 2019 because of costs
Why was the ACA an unfulfilled promise?
political and legal challenges have diminished the ACA, especially its ability to provide access to coverage for low-income individuals
components of the ACA
built on the existing models of coverage (ex romneycare in massachusetts and obamacare)
ACA reformed health insurance industry but left fundamental structure in place
ACA does not (and never meant to)… (3 items)
create single payer or government sponsored care
eliminate health insurance companies
make people change doctors or other health care providers
the ACA created hundreds of regulations and administrative rules by various agencies within the department of health and human services
ex. center for consumer information and insurance oversight
centers for medicare and medicaid services
health services resources administration
food and drug administration
centers for disease control and prevention
ACA TITLES
quality, affordable health care for all americans (most controversial)
the role of public programs (most controversial)
improving the quality and efficiency of health care (component of PH importance)
prevention of chronic disease and improving public health (component of PH importance)
health care workforce
transparency and program integrity
improving access to innovative medical therapies
community living assistance services and supports
revenue provisions
strengthening quality affordable care
ACA TITLE 1: quality, affordable health care for all americans
employer mandates
most americans insurance via employer-sponsored plans (50%)
dependents can stay on parents’ insurance until 26 years old
penalties for companies with 50+ employees who don’t provide insurance
tax credits for companies with less than 50 employees who provide insurance
insurance industry reforms (designed to end insurance company efforts to avoid adverse selection)
guaranteed issue (cannot exclude people with pre-existing conditions
no rescission (cannot kick sick people off of their plans)
no annual or lifetime caps to care
adverse selection: insurance companies acceptance of applicants who are at greater risk of poor health
individuals have an ‘adverse’ effect on insurance companies b/c insurance premiums are calculated on the basis of policy holders being in average (good) health
individual mandate
everyone must have health insurance or pay a penalty
exceptions: financial hardship, those who don’t pay SS for religious reasons, indigenous tribes, undocumented immigrants, uninsured for period of less than 3 months
requiring everyone to have health insurance offsets the additional costs health insurance companies feared incurring due to mandated health insurance reforms (recission, etc.)
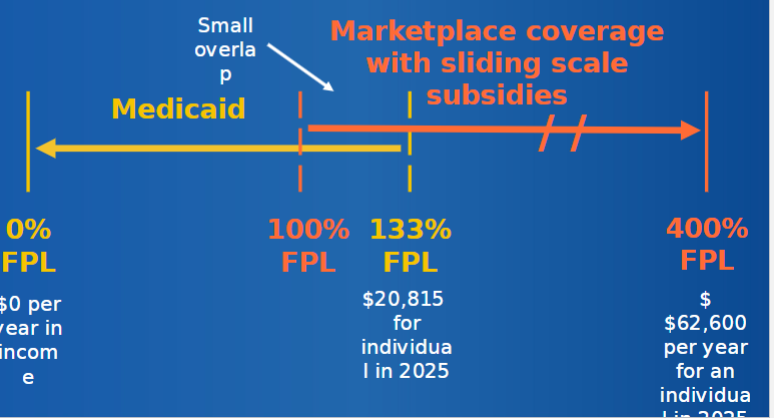
gov assistance in affording health insurance through new “marketplace” for purchasing publicly subsidized private insurance and expansion of public programs
insurance marketplaces (exchanges) are for people to purchase insurance; individuals and small employee groups can purchase private insurance plans through insurance exchanges
three types of marketplaces (exchanges):
state, federal, state/fed partnership
subsidies and tax credits available to offset costs
for individuals making up to 400% of federal poverty level (62,000/year for an individual in 2025)
insurance subsidies for low-income persons through exchanges
subsidies and tax credits available to offset costs
for individuals making up to 400% of federal poverty level (62,000/year for an individual in 2025)
ACA TITLE 2: role of public programs
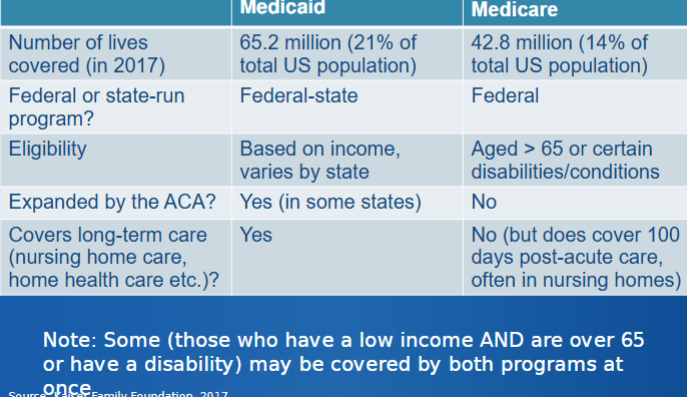
medicaid
expansion of medicaid is central component of ACA
pre-ACA: childless adults not eligible for medicaid despite income level; and amount of coverage based on “category”
post-ACA: medicaid will cover everyone under the 133% of FPL ($20815 for individual; $42760 for family of 4 in 2025)
indian health service
community health centers
Other MAJOR FEATURES of ACA
essential health benefits package
set of 10 categories of services health insurance plans must cover
includes: outpatient care, hospitalization, emergency services, maternity and newborn care, pediatric care, mental health and addiction treatment, prescription drugs, rehab services and devices, laboratory services, clinical preventive services (ex vaccinations)
limit on annual out-of-pocket spending
caps on the amount people pay in deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance annually
in 2024: individual plan = 9450; family plan = 18900
What did the ACA address in regards to public health?
insurance plans must cover evidence-based preventive services
ex. immunizations, smoking cessation counseling, cancer screening
creation of prevention and public health fund
nation’s first dedicated federal funding for prevention
created national prevention, health promotion, and public health council
promote healthy policies and establish a national prevention and health promotion strategy
challenges to ACA
controversial and politically divisive
national federation of independent business v. sebelius (2012)
penalties imposed enforcing individual mandate are a tax and are allowable under government’s authority
ruled that medicaid expansion provision as unconstitutional
threatened states with the loss of their ecisting medicaid funding if they declined to comply with the expansion
allowed states to choose whether or not to expand medicaid
king v. burwell (2015)
scotus ruled that people were eligible for subsidies and tax credits whether they bought their insurance via a state or federal insurance exchange
dozens of votes to repeal
ACA today
successful in reducing the number of uninsured americans
~30 million individuals gained insurance following implementation of ACA because..
medicaid expansion
private insurance market subsidies
stay on parents’ plan till 26
majority of states expanded medicaid coverage
41 states adopted medicaid expansion (including dc)
10 states have not adopted expansion
millions more could be covered if more state expanded medicaid coverage
uninsured individuals include…
low-income on medicaid non-expansion states
those unable to afford marketplace coverage
undocumented immigrants
documented, low-income immigrants in the US less than 5 years
How Trump weakened the ACA…
eliminated individual mandate
no federal penalty for not having health insurance
supported work requirements for medicaid beneficiaries
ended subsidies to insurers participating in exchanges
payments meant to motivate insurance companies to be in exchanges and keep premiums down
assistance to navigate exchanges cut
cut federal funding for navigators
no advertising for open enrollment
most americans support ACA provisions, regardless of political affiliation
tax credits supported by both parties
marketplace coverage meant to insure those with incomes just above those on medicaid
differences between medicaid and medicare
ACA expanding healthcare coverage (shortened ver)
