Models of Memory
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Model
A visual representation of a theory designed to explain it
Memory
The faculty of encoding, storing, and retrieving information
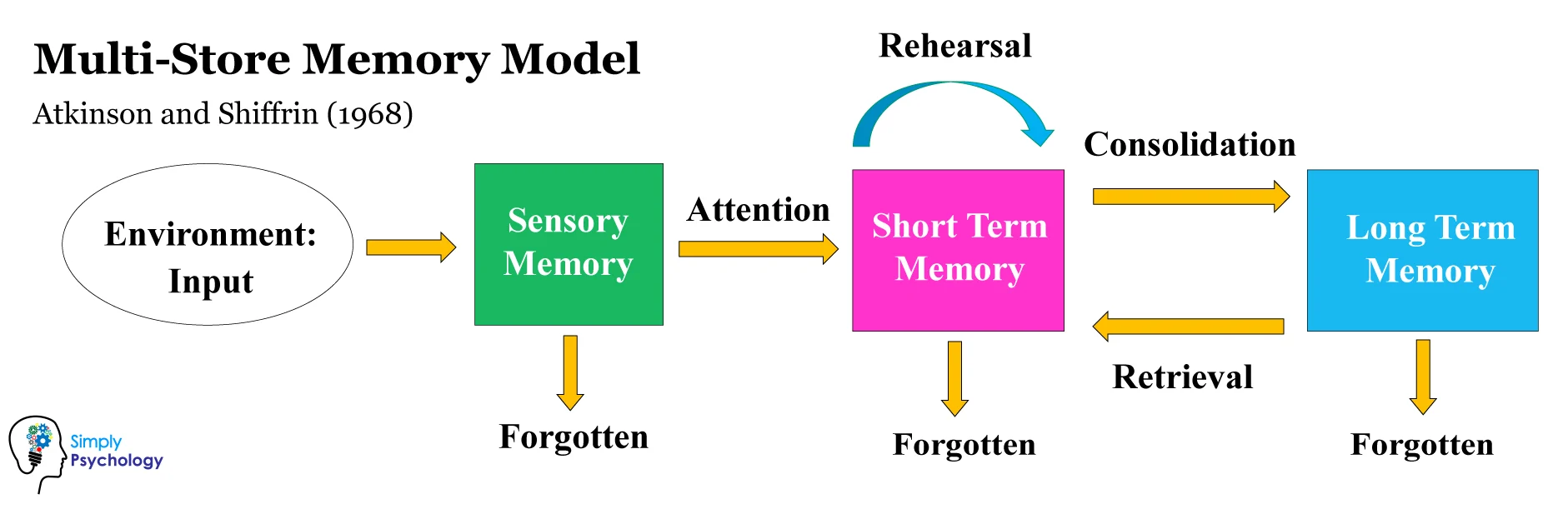
Multistore Memory Model
The mind is divided into 3 stores for memory: sensory, short-term, and long-term
Information passes through the stores in a linear fashion
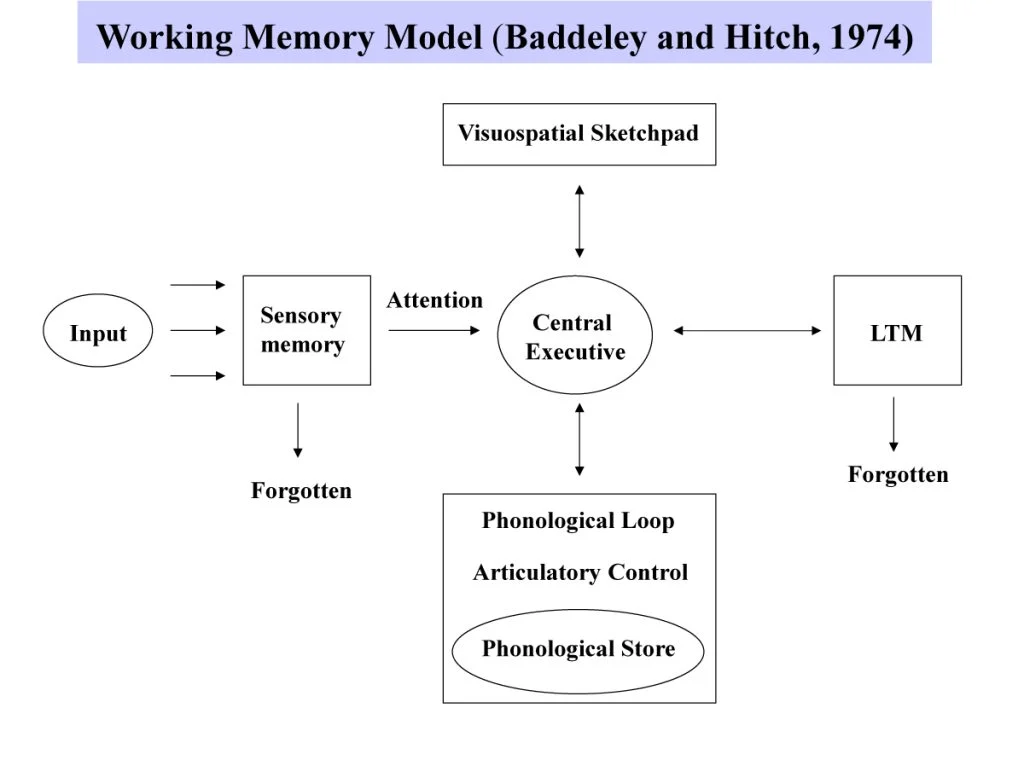
Working Memory Model
Sensory Memory
Duration: ¼ to ½ seconds
Capacity: all sensory experience (large)
Encoding: Sensory
Short-Term Memory
Duration: ~15-30 seconds
Capacity: 7±2 chunks
Encoding: Acoustic
Long-Term Memory
Duration: unlimited
Capacity: unlimited
Encoding: Semantic
Rehearsal
A type of repetition where the user repeats information and learns through it in order to be stored in memory
Encoding
the way information is transformed into a format that can be stored and retrieved from memory
Maintenance Rehearsal
Repeating information temporarily long enough to retain it in the short-term memory but unable to transfer to long-term memory
Elaborative Rehearsal
The act of connecting new knowledge to pre-existing knowledge meaningfully in order to transfer to long-term memory
Phonological Loop
Handles the auditory and spoken short-term memory, comprises of 2 components
Phonological Store - verbal information can be stored for brief periods (approximately 2 seconds)
Articulatory Control System - serves to refresh the verbal and auditory content through rehearsal
Central Executive
Responsible for controlled processing in working memory, including (but not limited to):
directing attention
maintaining task goals
decision making
memory retrieval
Visuo-spatial Sketchpad
Visualises objects and spatial layouts in the brain.
Episodic Buffer
a temporary store that integrates information from the other components and ensures it’s ordered chronologically, allowing events to unfold in a coherent and continuous sequence
Similarities of Models
Both contain biological evidence - case studies KF and HM
Both contain the act of rehearsal in order to retain information in the process
Differences of Models
Multi-store Memory
Presents memory as a passive system with fixed stores
Primarily describes the flow of information through different memory stores
Working Memory
Focuses more on the processes within short-term memory
Emphasizes the active processing of information and how it is manipulated
Focuses on the processing of information, decision-making, and problem-solving in real-time
Strengths of MSM
Empirical evidence supported the concept of separate memory stores + model itself
MSM was a pioneering model of memory that inspired further research and, consequently, other influential models (e.g.: WMM)
Weaknesses of MSM
Oversimplifies the complexity of memory processes by presenting memory as a linear system
Lacks an explanation for how memory stores interact and how information is transferred between them
Strengths of WMM
Explains parallel processing (i.e. where processes involved in a cognitive task occur at once)
The model was developed based on evidence from laboratory experiments so confounding variables could be carefully controlled to produce reliable results
Weaknesses of WMM
WMM has been criticized for being too simplistic and vague (e.g.: it is unclear what the central executive is or its exact role in attention)
Results from laboratory experiments researching the WMM will often have low ecological validity
Decay
When information exceeds duration (forgotten)
Displacement
When information exceed capacity (forgotten)