World War I and Effects
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Powers Form
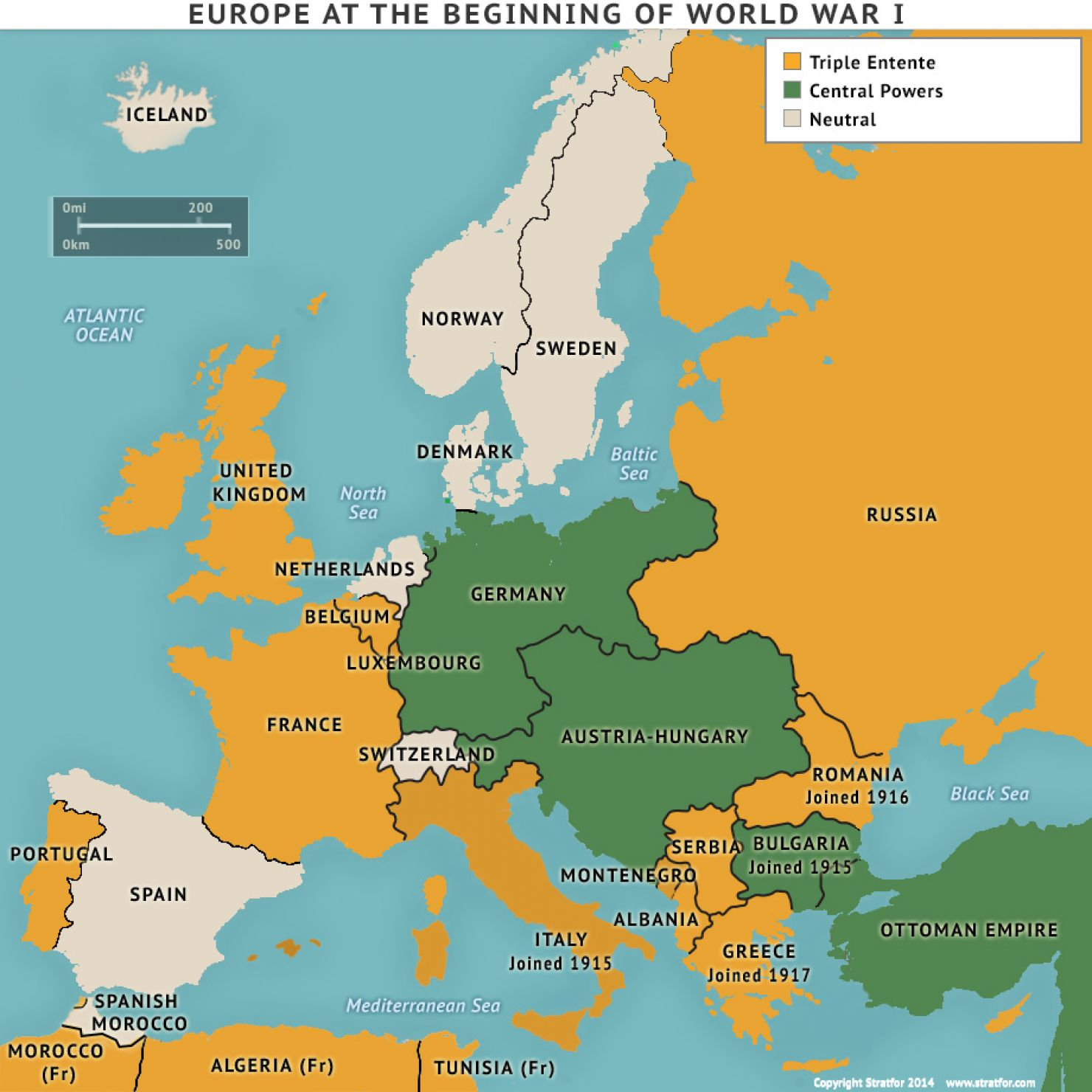
Allied powers:
Great Britain, France, Russia, Serbia, Italy, Greece, Czekoslovakia, Poland, Belgium, Japan, US, Romania
Italy joined for the A-H territory
US joins after Russia leaves
Central Powers:
Austria-Hungary, Germany, Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria
The Fronts:
Western: France/GB/US vs. Germany
Eastern: Russia/Serbia/Romania vs. Germany/A-H/Bulgaria
Middle East: GB vs. Ottoman Empire
Southern: Italy vs. A-H
Early Battles (1914-1915)
Western:
The Marne: GB/F stop Germany’s advance to Paris.
Germany fails at preventing a two front war, leading to 500k casualties
Ypres: Germay began chemical warfare. Results in 1,000,000 casualties.
Eastern:
Tannenberg: Germany stops Russia’s advance, leading to 150k deaths.
Masurian Lakes: Germany advances East, crushes 250k Russians.
South:
Serbian Campaign: A-H/Bulg decimate Serbia with 300k casualties.
Asiago: Ita/A-H stalemate, 250k casualties
Gallipoli (OE): France/GB fail at capturing Istanbul from OE, 500k casualties
Bloody Year of 1916
West:
Verdun: France wins 11 month definite battle versus Germany, 300k dead.
Jutland: Largest naval fight ever, 150 GB ships vs 100 G ships
Somme: 150k killed on each side. GB lost 20k soldiers in one hour.
GB’s worst lost in military history. First time tanks are used.
East:
Brusilov offesnive: Russia decimates 700,000 A-H, but with the cost of 1.4 million Russian calsulaties.
Ottoman Empire:
Armenian Genocide: 1.5 Christians systematically killed
Ottoman Empire never punished
Palestine Campaign: OE tried to get Suez Canal, fails, and GB retaliates and eventually controls all of ME, killing 700k inhabitants.
Bolshevik Revolution
After 1.7 million casualties, the Russians revolt. → Tsar Nicholas II and all family are executed.
Red October 1917: Soviet Union born under Vladimir Lenin.
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk: Russia ended participation in WWI & gave lang/money to central powers.
Russia’s Civil War (1917-1923): Communist Reds under Trotsky vs White Tsarists, independence movements, foreign intervention.
Reds win but there are 3,000,000 casualties.
USA Factors
Between 1914-1917, the US was isolationist but:
Loaned GB/F $500 million each
In 1915, RMS Lusitania sunk by Germany’s U-Boat, killing 1.2k (140 from USA)
Riled up people about joining the war.
Naval Blockade on Germany by GB had G desperate due to food scarcity.
Only port blocked
Malnutrition deaths.
→ Germany began unrestricted submarine warfare. 100 submarines destroyed 120+ US GB boundships per month bringing allies food/arms.
Pissed off the US.
Zimmerman Telegram: Message to Mexican Ambassador from G trading SW USA for Germany’s allegiance
GB spies intercepted and showed USA
US joins
Germany knew she had to strike quickly because US was sending 10k men per day.
Caporetto: Germany used chemical warfare, captured 250k Italians.
German spring offensive (1918): 50 new divisions free from eastern front, Germany’s last attempt to break wastern front.
Shelled Paris with railway guns.
Sent army to get France before US joins.
In 1914, there were 200k US soldiers. By 1918, there were 2 million soldiers in Europe.
100 day offensive: Germany could not sustain spring offesnive gains.
US joins war, Germany taken aback.
August 1918, Allies countered & met western front with:
400+ tanks
120k troops
Took 100k Germans prisoners
Final Days
09/26: Allies break Germany’s line
09/28: Germany’s own generals recommend that KWII surrendor
10/6: Yugoslavia declares independence from A-H
10/7: Poland declares independence from Germany
10/23: Italy captures 300k A-Hs, counters A-H
10/28: Czekoslovakia declares independence from G/A-H
10/30: Ottoman Empire agrees armistice.
11/1: Hungary declares independence from A-H
11/3: A-H agrees to armstice
11/9: KWII abdicates
11/11: 11/11 at 11:00 Germany signs armstice
Beginning of WWI
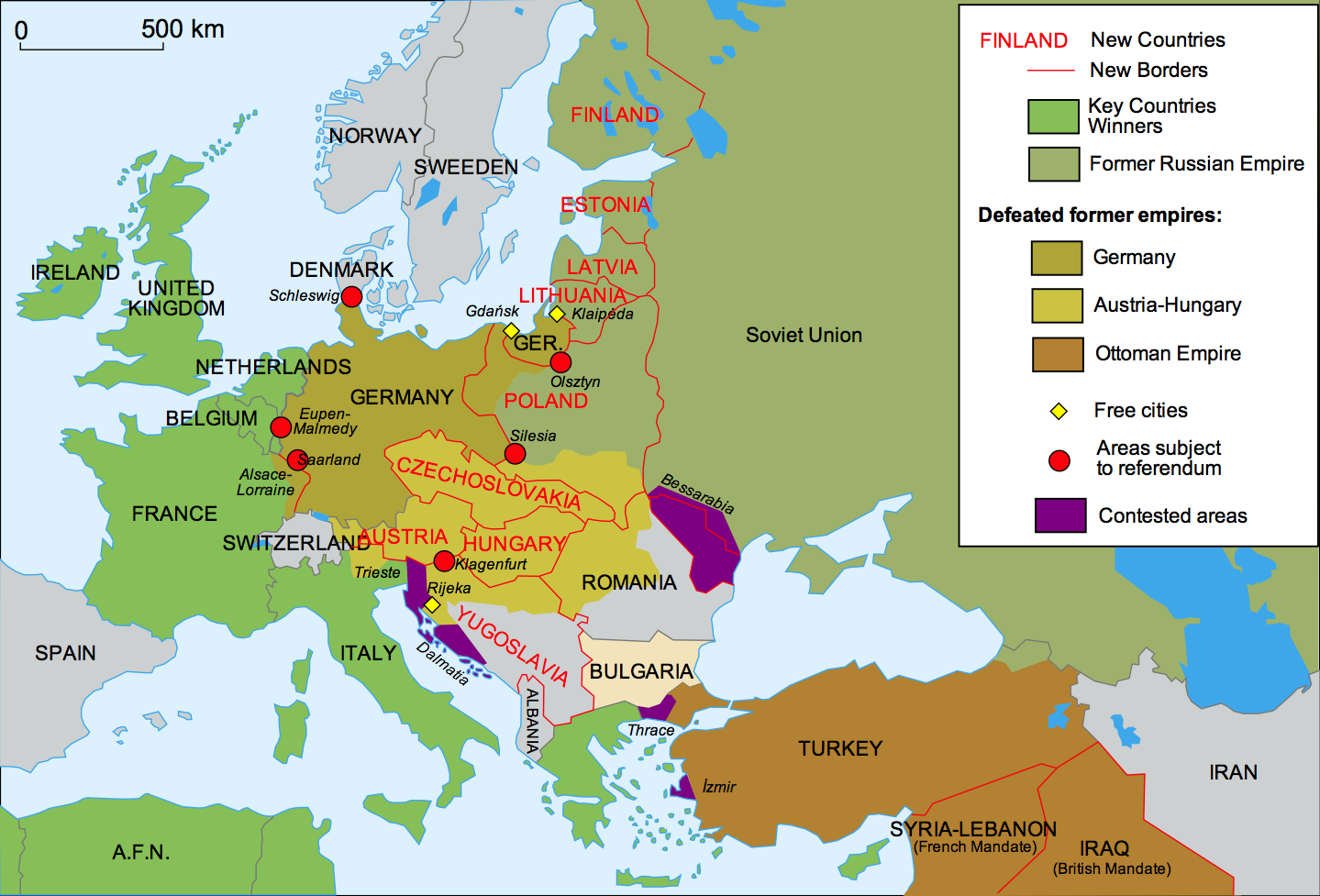
End of WWI
Effects of WWI:
Wilson’s 14 Points:
Wilson proposed change to the purpose of the war from vengeful disputes to moral aims. Notable points:
Reduce Arms
fix Belgium
Alsace-Lorraine to France
Sovereignty in Balkans
Existence of Poland
League of Nations
Non-US allies were skeptical of applicability
Political Results of the War:
Collapsed Empires:
Russia
Germany
Austria-Hungary
Ottoman Empire
11 new countries:
Austria
Hungary
Poland
Yugoslavia
Finland
Turkey
USSR
Lithuania
Estonia
Czechoslovakia
Latvia
Consequences
Balance of power gone. New states have ethnic rivalries within.
Republicanism is on the rise. Faith in monarchy is gone.
League of Nations set up in Geneva, Switzerland (1920) to resolve disputes but:
Nationalism is sitll radicalizing
France & GB kept their colonies
Economic Results
Allies’ Total Cost in Billions:
USA: 22
GB: 35
France: 24
Russia: 22
Italy: 12
Central Powers’ Total Cost in Billions:
Germany: 37
A-H: 20
OE: 1.5
All powers took out loans, especially from the US. This dept repayment creates tension in 1920s, especially for Germany.
Large amounts of land/indusry were destroyed where war was fought. Decline of Europe, rise of America.
Social Results:
Lost Generation:
10 milllion soldiers dead
7 million civilians dead
50-100 million killed by Spanish Flu
Consequences:
Dependents needed the gov’t. Scoial democracy born.
Improved waves, insurance, and conditions for workers.
Avoided strikes because gov’t dependent on industry for military.
Women operated male-dominated jobs.
19th amendment 1920.
More opportunity for women
Expectations of Treaty of Versailles
Treaty of Versailles: 01/1919: 27 nations met in france for settlement.
Expectations of Allies:
GB (Lloyd George):
Blame Germany, want KWII dead
Destroy G navy
Have G pay debts back
Divide G’s colonies amongst winners
France (Clemenceau):
Want revenge & balme Germany
Reclame Alsace-Lorraine
Divide Germany’s colonies amongst winners
Reparations to rebuilt France.
USA (Wilson):
Don’t blame G
Minimal reparations for G so that G didn’t seek revenge.
League of Nations
Dismantle all armies.
Reality of Treaty of Versailles
German colonial empire shared by allies
Alsace-Lorraine & Saar to France
Germany split
Germany has $33B debt
Navy/Air Force dismantled
Austria can’t unite with Germany
Rhineland dismantled
Germany blamed for war
League of Nations created to solve disputes
Results: Strengths and Weaknesses
→ Peace in European Union (League of Naitons as international court)
→ More sovereignty (less empires)
→ No immediate threat from Germany
Strengths:
Arguably just: Instead of giving France Rhineland, it was demilitarized.
Not as harsh as the ToB-L
First time something like League of Nations was attempted
Weaknesses:
LON had no army, therefore no authority for its decisions.
Ita & Japan resented ToV because expectations were unmet for joining allies.
US did not ratify because it preferred isolationism.
Germany too exposed, too helpless, would react badly
Allies thought Germany would abide the ToV
No one got their way, all left angrier