Ecology
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is a 'habitat'?
- the environment in which an organism lives
What is a 'population'?
- the total number of organisms of the same species living in the same geographical area
What is a 'community'?
- the populations of all of the different species that live in the same habitat
What is an 'ecosystem'?
- the interaction of a community of biotic parts with the abiotic parts of their environment
What is the difference between 'biotic' and 'abiotic'?
biotic = living organisms
abiotic = non-living parts
What do organisms need to survive and reproduce?
- organisms require a supply of materials from their surroundings and from the other living organisms there
What 3 main factors do plants in a community or habitat often compete for?
- light
- space
- water
What 3 main factors do animals often compete with each other for?
- food
- mates
- territory
What is the term for how within a community, each species depends on other species for certain things; if one species is removed, it can affect the whole community?
interdependence
What makes a community be stable?
all the species and environmental factors are in balance => population sizes remain fairly constant
How does the level of competition affect organisms in a community?
- if a species is outcompeted, its population can fall => may even become extinct if numbers are insufficient to breed
How do moisture levels affect organisms in a community?
- both plants and animals need water to survive => if there are low levels of moisture, plants that are not adapted may die
How does wind intensity and direction affect plants?
- stronger winds may cause plants to lose water via transpiration
How do the carbon dioxide levels affect plants?
- a higher carbon dioxide concentration means plants can photosynthesise more
How do the oxygen levels in water affect aquatic animals?
- aquatic animals need dissolved oxygen from the water for respiration
3 types of adaptations?
structural
functional
behavioural
How are camels STRUCTURALLY adapted to the hot and dry conditions of a desert?
hump on their back which is a store of fat, metabolic reactions can be used to produce water from the fat
mouth is leathery => allows camel to chew cacti
long eyelashes → keep dust out of their eyes
- camels can close their nostrils → keep dust out of their nosewide feet →prevents the camel from sinking into the sand
How are camels FUNCTIONALLY adapted to the hot and dry conditions of a desert?
- camels produce CONCENTRATED URINE and DRY FAECES => reduce water loss
- camels can tolerate very large changes in their body temperature => helps them to cope with the intense heat of the desert
What are different ways that some animals BEHAVIOURALLY adapted to survive in both hot and cool conditions?
some animals are NOCTURNAL => avoid the heat of the daytime + these animals may also live in burrows underground during the day → keep cool and protects them from predators
animals, eg. polar bears, hibernate during the winter to avoid the cold (the animal becomes inactive and all the body processes slow down)
animals, eg. some birds, migrate south to warmer climates
How are some animals STRUCTURALLY adapted to survive the cold climate?
- very thick fur => provides insulation and reduces heat loss to the air
- fur on the soles of their feet, eg. the Arctic fox => reduces heat loss to the ice and the snow
- very small ears => reduces the overall surface area of the animal, eg. the Arctic fox => reducing heat loss
- white coat => effective camouflage (helps the animal to hunt its prey)
How are cacti adapted to live in the dry desert?
very small leaves => reduce surface area for water loss, spines deter herbivores
sunken stomata reduces transpiration
extensive and shallow roots => absorb maximum water after rainfall
cacti can store water in their stems (thick stems) => survive many months without rain
What are 'extremophiles'?
- organisms that live in environments with extreme conditions, eg. bacteria that live in deep sea vents

Give 3 examples of extreme conditions that an extremophile may be able to survive in?
- high temperature
- high pressure
- high salt concentration
What do feeding relationships show?
- flow of energy in a community
What do all food chains begin with?
all food chains begin with a PRODUCER which synthesise glucose from sun energy
plant or algae
(trophic level 1)
What is the general food chain?
producer => primary consumer (prey) => secondary consumer => tertiarry consumer => apex predator
Explain this predator-prey cycle graph.
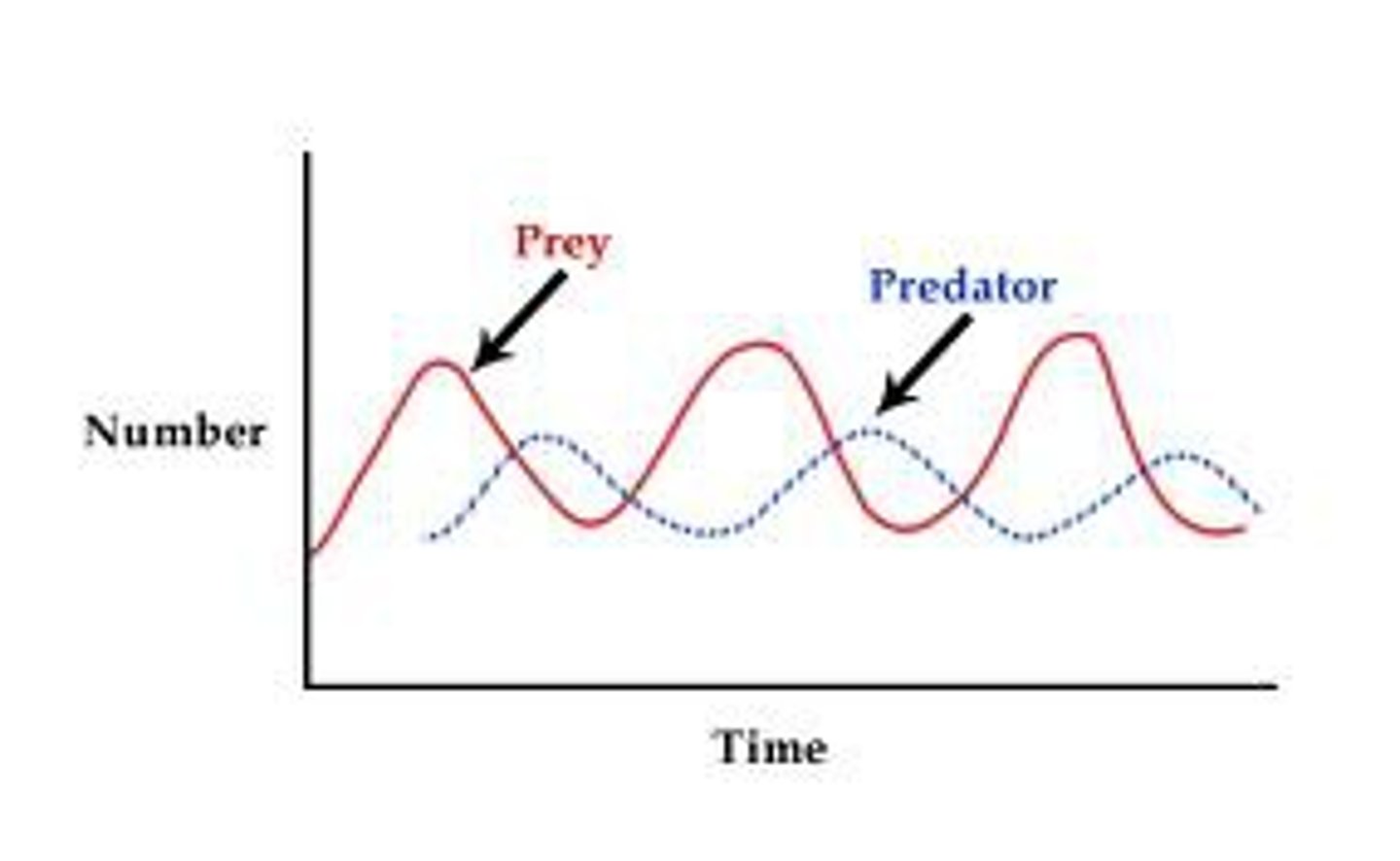
- prey population increases => more food for predators => predator population increases => more of the prey are eaten => prey population falls => less food for predators => predator population decreases => prey population increases
- only true in a stable community

What are transects and quadrats used for?
used by ecologists to determine the distribution and abundance of species in an ecosystem
How can we increase the accuracy of random sampling?
- using smaller divisions on quadrat
setting rule e.g only count squares with over 50% coverage
What is sampling along a transect used for?
What is a transect? How is sampling along a transect done?
to investigate how the numbers of species change as we move across a habitat
a transect is a line (tape measure)
use a quadrat to count the organisms at intervals on the transect
How can we increase the validity of sampling along a transect?
- move the tape measure of rope further along in the horizontal direction => repeat the whole process
What is the importance of the carbon and water cycles?
- all materials in the living world are recycled to provide the building blocks for future organisms
How is carbon cycled?
photosynthesis by plants/algae remove co2 from atm
carbon used to make glucose, protein and lipids
respiration by all organisms releases co2 into atm
carbon passed through animals through ingestion/feeding/digestion
when plants, animals and algae die, decomposeres secrete enzymes to break them down (decomposers respire)
combustion/burning fossil fuels releases co2 into atm
What do decomposers do + what are they?
reutrn mineral ions to soil
return carbon to atmosphere as co2 when they respire, which is used by plants
clean up environment by removing dead organisms and waste
fungi and bacteria
How is water cycled?
evaporation of water from the earth’s surface which falls as rain and snow (precipitation)
absorbtion of plants via osmosis into roots
transpiration - evaporation of water from leaves of plants out of stomata
producition of urine, faeces and sweat by animals
respiration by animals and plants produces water
water is continuously evaporated and precipitated
optimum conditions for decay
warm
high oxygen availability
high moisture levels
What is the slurry used for from biogas generators
- used as a natural fertiliser for growing garden plants or crops
- compost is very rich in the minerals that plants need to grow (the decomposers return the mineral ions back to the soil)
molecules before and after decomposition
large, insoluble
small, solluble (can diffuse)
Why is it important to control the temperature of a compost heap? (stop it from getting too hot)
- if the temperature gets too high, the enzymes in the decomposers can denature
what gas is produced in biogas generator
methane
What is the method to investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of decay of fresh milk by measuring pH change?
1. label test tube milk and add 5ml + one drop phenolthalene
2. measuere 2ml of microbe solution and add to different test tub
add to waterbath, leave to equilibriate
after 5min, combine test tubes
time how long it takes to fo from bright pink to cream
repeat at different temps
i.v. =effect of temp temperature
d.v. = decay of milk
c.v.. = volume of each component, type of milk
How can we increase the accuracy of the decompostion required practical?
- using several people to stop the timer when they believe that phenolthalene is gone colour => calculating a mean
What is the impact of a change in temperature on the distribution of species in an ecosystem?
- species that live in hot conditions, eg. a desert, will be more suited to the environment
- eg. the Desert fox lives in Africa and it has large ears which increase the fox's surface area, allowing it to lose heat more easily => the Desert fox would not be found in cooler places => as we move further north, the conditions get colder and we find the Arctic fox, with very small ears
- temperature shows geographic variation
What is the impact of a change in availability of water on the distribution of species in an ecosystem?
in the dry desert, we find plants that are adapted to live here where the water is scarce
=> cacti are not found in regions where water is more plentiful,
eg. a tropical rainforest (we instead find plants that are adapted to live in wetter conditions, such as ferns)
A large amount of untreated sewage entered the river. Many fish died. Untreated sewage contains organic matter and bacteria.
Explain why many fish died. (Exam Q)
- bacteria decay organic matter
- by digestion
- bacteria respire aerobically using oxygen
- which lowers the oxygen concentration in the water, leaving less oxygen for the fish
- so the reduced energy supply causes death of fish
What is 'biodiversity'?
- the variety of all the different species of organisms on earth, or within an ecosystem
Why is a higher level of biodiversity beneficial and important?
- a great biodiversity ensures the stability of ecosystems by reducing the dependence off one species on another for food, shelter and the maintenance of the physical environment, eg. decomposers break down the remains of dead organisms
- if the population of a species falls, it is less likely to affect the whole ecosystem
How is deforestation having a negative effect on biodiversity?
- tropical rainforests contain a very high level of biodiversity
- large areas of these forests are being destroyed to provide land, removing habitats at the same time
How do trophic levels represent the feeding relationships in an ecosystem?
Level 1: Plants and algae make their own food and are called producers.
Level 2: Herbivores eat plants/algae and are called primary consumers.
Level 3: Carnivores that eat herbivores are called secondary consumers.
Level 4: Carnivores that eat other carnivores are called tertiary consumers
- apex predators are carnivores with no predators
What is the role of decomposers?
- decomposers break down dead plant and animal matter by secreting enzymes into the environment
- small soluble food molecules then diffuse into the microorganism
What do pyramids of biomass represent?
- the relative amount of biomass (the living tissue of an organism, including proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates) in each level of food chain
- trophic level 1 is at the bottom of the pyramid
Why is biomass lost between the different trophic levels?
not all ingested material absorbed, some egested as faeces
some absorbed material is lost as waste, e.g co2
water in respiration and urine
lots of glucose used in respiration
How can we calculate the efficiency of biomass transfer as a decimal or percentage?
(gain in biomass / total intake) x 100 for a %
7 abiotic factors
temp
water/moisture levels
light intensity
wind speed/direction
soil ph + mineral ion conc
oxygen availability (aquatic)
CO2 conc (plants)
4 biotic factors
new pathogens
more competition between species
new predators arriving
availability of food
intraspecific competition
competition within a species
interspecific competition
competition within different species
reproducible
if someone else does sample + gets similar results
repeatable
you repeat and get similar estimate
valid
able to answer the question being asked accurately
how to do random quadrat sampling
split study area into grid with coordinates using two tape measures
randomly choose which coordinates to sample using random number generator
place quadrat at the coordinates and count the number of indivicuals
repeat at least 20 times
from this data, calculate the mean
mean number of individuals in quadrat X area of field = estimate of populatoin
what to do before random quadrat sampling
establish inclusion criteria e.g count half or not?
3 environmental changes effecting distribution of species in ecosystem, 3 causes
temp
water availability
composition of atmospheric gas
seasonal
geographic
human intercation