Chapter 39 (PART 1) : Pancreatic hormones and antidiabetic drugs
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is being described:
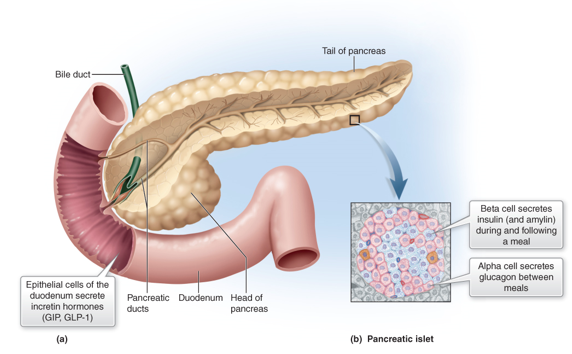
a triangular gland, which has both exocrine and endocrine cells, located behind the stomach
pancreas
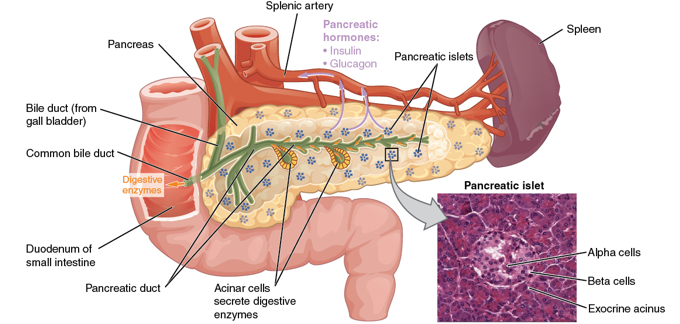
What kind of cells in the pancreas produce an enzyme-rich juice used for digestion (exocrine)?
acinar cells
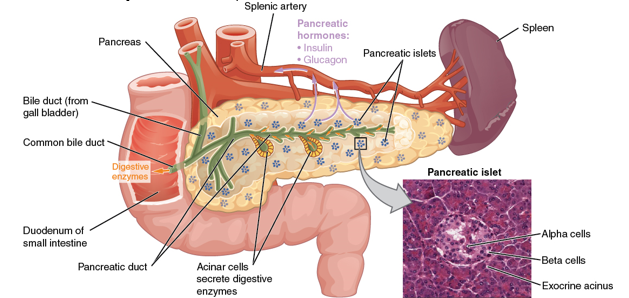
What kind of cells in the pancreas produce hormones (endocrine)?
pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans)
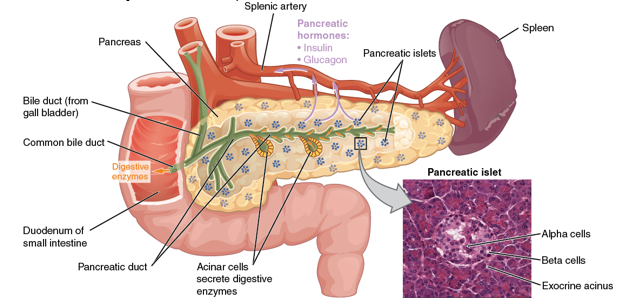
What 2 major cell types do the islets contain?
Alpha cells
Beta cells
What do alpha cells produce?
glucagon
What do beta cells produce?
insulin and amylin together
True or False:
Insulin and glucagon are antagonists to each other:
Increase glucose = increase glucagon ; Decreased glucose = Increase insulin
False, yes antagonists but its flipped.
Increase glucose = increase insulin ; Decreased glucose = Increase glucagon
What is amylin and what does it do?
peptide secreted from B cells with insulin
works to help lower blood sugar
slows rate of appearance of glucose in blood after eating
slows gastric emptying, inhibits digestive secretion, provides feeling of satiety → reducing food intake
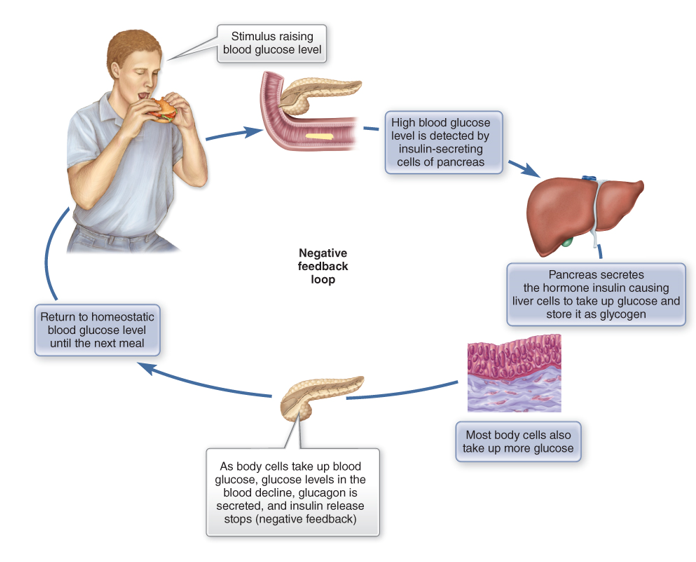
In what 3 ways does insulin lower blood glucose levels?
promote cell use of glucose and carb storage
stimulates glycogen synthesis in the liver
facilitates entry of AA/glucose into the cell
Fill in the blank:
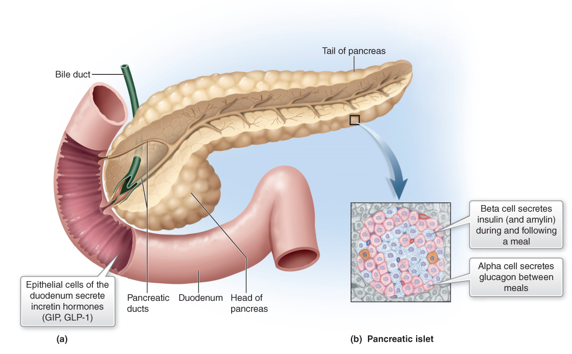
______________ also stimulate insulin secretion and are made by enterocytes
Incretins
hormones released from epithelial cells of the duodenum that stimulate insulin secretion in response to meals
What are the precursor peptides to pancreas that tell them to get ready for glucose intake to release insulin via B cells?
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide/gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)
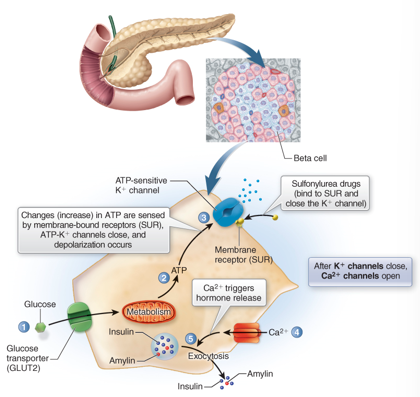
How is insulin secreted? (the process)
Increase glucose after meal → stimulates GLUT 2 transporter of B cells → increase ATP inside cell → closes ATP sensitive K+ channels → more K+ in cell → depolarization → influx of EC Ca2+ → Ca2+ influx = Exocytosis of insulin and amylin
True or False:
Insulin also binds to receptors on adipose, skeletal, and heart muscle cells causing the translocation of the GLUT4 receptor from the cytoplasm to the cell membrane when it acts as a glucose channel, decreasing blood glucose levels
True
True or False:
Cell types like brain, RBCs, and kidneys do not require insulin for glucose uptake but have special glucose transport proteins (GLUT1, GLUT3)
True
True or False:
The insulin receptor is a GPCR.
False, a tyrosine kinase enzyme.
What 3 enzymatic activity does insulin binding trigger after glucose enters a cell?
catalyzes the oxidation of glucose for ATP production
polymerizes glucose to form glycogen (gluconeogenesis) in liver
converts glucose to fat (particularly in adipose tissue)
What does glucagon do?
Increase blood glucose, like during fasting
stimulates glycogenolysis (glycogen breakdown) in liver, making glucose
helps convert AA to glucose and triglycerides to fatty acids
Glucagon receptor = GPCR
What is diabetes mellitus?
Disorder of pancreatic endocrine function resulting in:
Deficient secretion of insulin
Insulin resistance (can be related to receptor-binding)
Combination of both
What are the cardinal signs of DM?
Glycosuria – increased urine glucose (glucose not being absorbed)
Polyuria – huge urine output
Polydipsia – excessive thirst
Polyphagia – excessive hunger and food consumption (cells aren’t getting any energy)
Which type of diabetes is being described?
Autoimmune disorder
destruction of beta cells
cessation of insulin production
not symptomatic until only 10% B cells left
10% of DM in people
Type 1

Which type of diabetes is being described?
insulin resistance
obesity
genetic link
90% of DM in people
Type 2
What is type 1 DM?
Autoimmune disorder where autoantibodies are produced against the beta cells of the pancreas, results in destruction of cells that make insulin → increase glucose in blood
because glucose cannot enter the cell, glycogenolysis occurs ( breakdown fat to glucose)
What is type 2 DM?
Failure of target tissue to respond to insulin (insulin resistance)
Typically the insulin receptors of the skeletal muscle and liver have a decreased sensitivity to insulin, thus insulin cannot bind effectively
initiates a feedback cycle for beta cells to produce even more insulin to transport glucose into the cells = hyperinsulinemia
What is a healthy and diabetic fasting blood glucose level?
Healthy: 70 and 110 mg/dL
Diabetic level: >126 after fasting, >200 2 hrs after meal
What is normal insulin levels and insulin resistance levels?
Normal: <10
Insulin Resistance: >10
What is glycolated hemoglobin?
glucose levels taken up by RBCs that bind to hgb
used to evaluate 3 months of glucose levels
what is the immediate therapy of DM?
correcting metabolic imbalance
What is the maintenance therapy of DM?
regulating blood glucose levels:
diet control
exercise
medication
True or False:
Insulin available today comes in different onsets and durations of actions, as well as slightly modified aa sequences
True
True or False:
Changes in insulin requirements are NOT dependent on physiological changes.
False, they are.

Insulin adverse effects (think about too much insulin and what it does to the body)

True or False:
Without enough amylin, glucose from food enters bloodstream too quickly → blood glucose rise
True
How do amylin analogs (Pramlintide aka Symlin) work?
mimics amylin to control glucose levels
usually combined with insulin and given before meals
What are incretins?
hormones (GLP-1, GIP) secreted from the duodenum, increase insulin secretion (inhibit glucagon secretion and delays stomach emptying so absorption is distributed)
(Act on G-protein receptors located on the beta cells, as well as those located on the brain, duodenum, kidneys, liver, lungs, and stomach)
How do incretin mimetics (Exenatide aka Byetta) work?
acts like incretin (Sub-Q)
ex. ozempic → GLP 1 agonist , Manjiro → GLP 1 and GIP agonist