Unit 8 Flashcards
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Algal bloom
occurs when toxin-producing algae grow excessively in a body of water.
Bioaccumulation
the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism, often at a rate faster than they can be eliminated. This can occur through ingestion, absorption, or inhalation of these substances.
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD)
the amount of oxygen a quantity of water uses over a period of time at a specific temperature. Lower BOD values indicate the water is less polluted and higher BOD values indicate it is more polluted by wastewater.
Biomagnification
the increasing concentration of toxic substances as they move up through different trophic levels in a food chain. Organisms at higher trophic levels accumulate greater amounts of these substances due to consuming prey with accumulated toxins.
Coral bleaching
occurs when a coral becomes stressed and expels most of its colorful algae. This occurs because of stresses such as increased water temperature and runoff of silt that covers the coral and prevents photosynthesis.
Dead zone
a location within a body of water that does not have enough dissolved oxygen to sustain life.
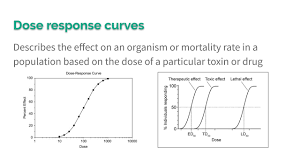
Dose Response Curve
Describes the effect on an organism or mortality rate in a population based on the dose of a particular toxin or drug
Endocrine disruptors
chemicals that can interfere with the endocrine system of animals. Endocrine disruptors can lead to birth defects, developmental disorders, and gender imbalances in fish and other species
Eutrophication
the process by which a body of water becomes enriched in excess dissolved nutrients, typically phosphates and nitrates , leading to an overgrowth of aquatic plants and algae
Great Pacific Garbage Patch
a collection of marine debris in the North Pacific Ocean. Ocean litter
Hypoxic
low concentrations of dissolved oxygen in bottom waters of a region.
LD50
LD stands for "Lethal Dose". LD50 is the amount of a material, given all at once, which causes the death of 50% (one half) of a group of test animals. The LD50 is one way to measure the short-term poisoning potential (acute toxicity) of a material.
Mangroves
tropical plants that are adapted to loose, wet soils, salt water and being periodically submerged by tides
Mesothelioma
a rare form of cancer that develops in the lining of certain organs, most commonly the lungs or abdomen
Methylmercury
a toxic form of mercury that forms when elemental mercury combines with carbon-containing compounds. It bioaccumulates in aquatic ecosystems and can have harmful effects on organisms higher up the food chain, including humans.
Oligotrophic
a body of water with a low level of productivity and low amount of nutrients
Oxygen sag curve
represents the decrease in dissolved oxygen levels downstream from a pollution source
Pathogen
disease causing organisms such as bacteria, viruses, protists or fung
Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
Things that don’t break down
Primary treatment
removes material that floats or will settle
Sanitary municipal landfill
An engineered method of disposing of solid waste on land in a manner that protects the environment, by spreading the waste in thin layers, compacting it to the smallest practical volume and covering it with compacted soil
Secondary treatment
The second stage of sewage treatment where microorganisms break down organic matter in the wastewater through biological processes
Septic system
a series of components that treat wastewater on site, most likely in a rural area that has no municipal sewer.
Tertiary treatment
the use of ecological or chemical processes to remove any pollutants left in the water after primary or secondary treatment
Wastewater
any water that has been adversely affected in quality by external influence. Wastewater can originate from a combination of domestic, industrial, commercial or agricultural activities, surface runoff and from sewer inflow or infiltration.
anoxic
greatly deficient in oxygen
LC50
Lethal CONCENTRATION—air quality.
Planned obsolescence
consumers update products necessarily to convince you to upgrade.
malaria
tropical disease spread by mosquitos
CERCLA - the Superfund Act
provides a Federal "Superfund" to clean up uncontrolled or abandoned hazardous-waste sites as well as accidents, spills, and other emergency releases of pollutants and contaminants into the environment
RCRA - Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
enacted in 76—principle law governing the disposal of solid/hazardous waste. this law based open dumping of waste (ocean/land)—just throwing it. governs landfill usage (manage leachate/landfill gas). “cradle to grave”, or corporate responsibility to track hazardous waste from its inception to death…every step of the game.
Safe Drinking Water Act
specifically sets drinking water standards
Clean Water Act
U.S gov’t passed to set standards that we put back water
MPRSA - Ocean Dumping Act
prohibited ocean dumping in the U.S
Brownfield
An urban area of abandoned, vacant factories, warehouses, and residential sites that may be contaminated from past uses