(DONE) Agents - Soft Tissue Mobilization
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
mechanical manipulation of soft tissue by the hands; specialized manual therapy technique widely utilized in PT to enhance recovery and improve function of mm, tendons, ligaments, and fascia
soft tissue mobilization (STM)
does soft tissue mobilization need to be therapeutically necessary?
yes
is soft tissue mobilization useful as the primary intervention or more so as a adjunct to other interventions as part of a comprehensive tx plan
the latter
what comprises soft tissue
mm, fascia, tendons, and ligaments
____ can assist in restoration of structures, function, and activity performance
soft tissue massage
how can soft tissue massage assist in restoration of structures, function, and activity performance
breaks down adhesions
relaxes muscle tension
reduces edema
decreases pain
restores functionality
“Manipulations of the soft tissues of the body . . . for the purpose of producing effects on the nervous, muscular, and respiratory systems and the local and general circulation of the blood and lymph.”
massage
“A specific assessment, evaluation, & treatment of soft tissues for the purpose of creating beneficial effects on the nervous, MSK, lymph, & circulatory systems.”
soft tissue mobilization
the goal of ______ is relaxation and temporary relief of muscle tension
massage
the goal of ______ is to restore normal function to affected areas
soft-tissue mobilization
clinical indications for STM
decreased muscle and/or connective extensibility
intermittent MSK pain
pain that is altered by postural changes
pain relieved/provoked by particular motions or positions
muscle spasm
edema
pathologies commonly addressed by STM
muscle spasms
muscle tightness
myofascial restrictions
scar mobility
trigger points
pain modulation
tension headaches
stress/tendon in mm
tendonitis
edema
the 3 therapeutic effects/ purposes of STM
mechanical
physiological
psychological
the following describe the (psychological//mechanical//physiological) purpose of STM:
increases viscoelastic properties (ie extensibility)
improves pliability of connective tissue
transforms scar tissue
increases venous/lymph flow
mechanical
the following describe the (psychological//mechanical//physiological) purpose of STM:
relaxation (via slow, superficial stroking of skin)
decreased alpha motor neuron excitability
decreased BP/HR
improved circulation
stimulation (via quick, brisk action)
physiological
the following describe the (psychological//mechanical//physiological) purpose of STM:
mental relaxation, stress reduction
stimulation of endogenous opioids + endorphins ?
helps create bond b/w pt and therapist
simple caring touch may promote feelings of general wellbeing
the following are key effects of ____:
modulate pain
improve rom
muscle relaxation
stretching/loosening of adhesions
improve muscle activation
increased venous + lymphatic flow
edema control
therapeutic alliance
STM
contraindications of STM
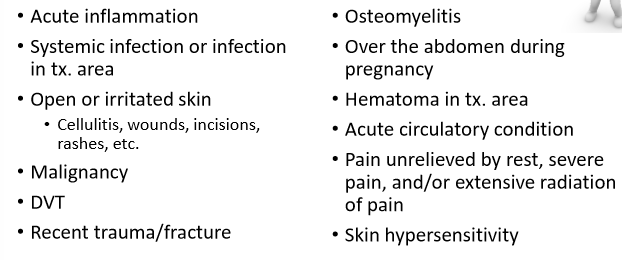
STM precautions

rhythmic, long strokes with constant contact
effleurage
why use effleurage
relaxation/warm-up
pain, muscle tension
stimulates sensory nerves, prepares for deeper work
can ID tissue restriction
T/F: effleurage should always be completed first and last
true
effleurage strokes should be along the direction of ______ and toward ____
muscle fibers; heart
should you use lotion for effleurage
yes
for effleurage, use 2 hands or hand-over-hand; can also use _____
other body parts
“kneading,” lifting of skin/tissues is called what
petrissage
_____ can be used to…
free adhesions b/w muscle and fascia
assist venous/lymph return
assist removal of waste products
petrissage
petrissage involves ___ reps in one area before moving on
3-4
(more//less) lotion is required for petrissage
less
T/F: petrissage may be with or against direction of fibers
true
4 common strokes of petrissage
kneading, wringing, picking up, skin rolling
“small, slow, specific, circular” describes which of the 4 common petrissage strokes
kneading
“lift and release tissue with opposing forces of the hands” describes which of the 4 common petrissage strokes
wringing
“grasp muscle and lift away, work toward heart where possible” describes which of the 4 common petrissage strokes
picking up
“picking up the skin and rolling it, generally less lotion” describes which of the 4 common petrissage strokes
skin rolling
______ used to be called “transverse friction” but isn’t referred to that way much anymore since it doesn’t have to be transverse
cross-friction
cross-friction is used for ____ alignment
collagen
what 3 reasons would cross-friction be used for
adhesions (tendons, scar tissue)
muscle spasms (stretch tissue, increase circulation)
trigger points
T/F: cross-friction movement can be transverse, parallel, or circular
true
how many areas should you target at a time with cross-friction
1 small area at a time
use cross-friction for acute, subacute, or chronic conditions
subacute/chronic conditions in remodeling phase
cross-friction is fairly (gentle//aggressive)
aggressive
cross-friction usually has (lubricant//no lubricant)
no lubricant or very little, b/c we want lots of friction for therapeutic effect
documentation as ___ for muscle, TFM/CFM for tendon
STM (soft tissue mobilization)
myofascial release (MFR) is (high//low) load, (short//long) duration stretch to restore fascia length
low; long
myofascial release (MFR) involves (gentle//firm), (brief//sustained) pressure to fascia at ____ range
gentle; sustained; end
MFR is (gentle//firm)
gentle
MFR involves (brief//sustained) pressure
sustained
MFR is done at ____ range
end
what 3 reasons do we do MFR for
release fascial restrictions
decrease pain
restore movement
examples of myofascial release (MFR)

does the type of foam roller used make a difference?
no
(any should decrease pain and increase rom the same)
ischemic compression for trigger points involves compression applied to a trigger point to create (local//systemic) ischemia
local
once ischemic compression trigger point is released, theory is that _____ is induced and pain receptors are modulated
hyperemia
(higher blood flow than normal)
what are 3 goals of ischemic compression for trigger points
relieve muscle tension + pain
increase pressure pain threshold (PPT)
improve muscle elasticity
should soft tissue mobilization (STM) for pressure point be excessively painful? why?
no, b/c this will cause muscle to cease up, which stops you from gaining a therapeutic effect
procedure for ischemic compression for trigger points using pressure-pain threshold
apply pressure until pt says it just starts to hurt, hold constant compression here until pain subsides (no more than 3’)
maintain pressure and push in more, until pt says it just starts to hurt again, hold constant compression here until pain subsides
once more push in to pain threshold, maintain compression until the pain diminishes (3x total)
with ischemic compression for trigger points, how many sessions does it take to see big results?
a single session showed significantly improved results in the literature
STM positioning
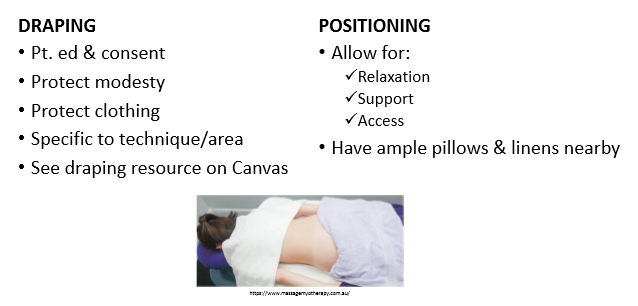
basic procedural guidelines for STM part 1

basic procedural guidelines for STM part 2

use your ___ to assess tissue quality, edema, scar tissue, and restrictions during STM
hands
key points of STM

note: multiple videos linked at the end of the PPT