Med Surg Exam 3
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
dysphagia, odynophagia, xerostomia
complications of stomatitis
stretta procedure
Radiofrequency energy to produce small burns that tighten the muscular wall to reduce reflux
-used in GEJ through needles positioned near it for treatment of GERD
hernia
protrusion of abdominal contents through area of weekended muscle in the abdominal cavity
-may occur anywhere in the body, frequently occurs in abdominal cavity with intestines protruding through abnormal opening
-reducible or irreducible (want it to be reducible)
-indirect or direct inguinal, femoral, umbilical, ventral or incisional
-could cause strangulation of the intestine, obstruction, or necrosis of bowel
Hemorrhoids
swollen, twisted, varicose veins in the rectal region
-could be internal or external, may become thrombosed or clotted
-cold packs and sitz baths 3-4 x's/day
-can be caused by constipation, high portal vein pressure, pregnancy, prolonged sitting, lack of fiber
femoral hernia
A type of hernia that causes a bulge in the upper part of the thigh near the groin.
-more common in women
-fat in canal enlarges and pulls contents down into sac
inguinal hernia
the protrusion of a small loop of bowel through a weak place in the lower abdominal wall or groin
-more common in men
-direct is due to connective tissue being weakened or strained
-indirect is congenital and formed in utero
IBS (irritable bowel syndrome)
An intestinal disorder causing pain in the belly, gas, diarrhea, and constipation.
-3 types: C, D, and M
possible causes:
-GI motility, visceral hypersensitivity, intestinal inflammation, postinfectious bacterial overgrowth, food sensitivity, carb malabsorption,, gluten sensitivity, genetics
peppermint, fennel, herbal teas, and ginger
herbal medications that can be used for IBS
umbilical hernia
protrusion of the intestine through a weakness in the abdominal wall around the umbilicus (navel)
-more common in women, especially with pregnancy
ventral hernia
A weakness in the abdominal wall, usually resulting in protrusion of abdominal viscera against the peritoneum and abdominal fascia.
-usually from abdominal incision
-spontaneously sometimes more in men than women
Grade 2 hemorrhoid
prolapse out of the anal canal with defecation or with straining but reduce spontaneously
grade 3 hemorrhoids
protrude into the anal canal on defecation but can be returned to their original position manually
grade 4 hemorrhoids
chronically protrudes and cannot be manually reduced
-type Tx with surgical excision
inflammatory bowel disease
umbrella term for 2 similar chronic GI tract diseases: Crohn's and ulcerative colitis
-cause unknown but linked to genetic predisposition, environmental conditions, and defects in immune regulation
-sometimes foods exacerbate it
-carbohydrate malabsorption, increased gas and bloating
Crohn's disease
affects GI tract, more commonly in the terminal ileum and colon
-not uniform in appearance and noted for having skip lesions and normal appearing bowel between lesions
-strictures and adhesions are common
-diarrhea is less severe than in ulcerative colitis
-pain worse in right lower quadrant
-could cause fistula
-surgery if failed medical management or experience complications
-high risk for cancer
tenesmus
The feeling that you need to pass stools, even though your bowels are already empty.
-It may involve straining, pain, and cramping.
ulcerative colitis
affects large intestine and involves only mucosa and submucosa
-diarrhea is common with blood, mucus, or pus
-abdominal pain and tenderness worse in left lower quadrant
-tenesmus
-higher risk of colon cancer
-may need colectomy
-pseudopolyps
diverticulitis
small pouchlike protrusion or herniation, often in the GI tract, particularly the colon
-more common in western societies and in older people
-extraluminal and referred to as outpouching
-treat with broad spectrum antibiotics
-can lead to perforation, abscess and fistula formation, bowel obstruction, and bleeding
appendicitis
inflammation of the vermiform appendix that commonly occurs in 10-19 year olds
-affects more males than females
-fecalith or foreign body blocking the opening that leads to inflammation and infection
-surgical management
-laxatives and enemas should be avoided
colorectal cancer
3rd most common forma of cancer and 2nd leading cause of death in the US
-most are adenocarcinomas and metastasis
-unexplained weight loss and fatigue may be 1st sign
-colonoscopy first at 45/50
-treatable if caught early
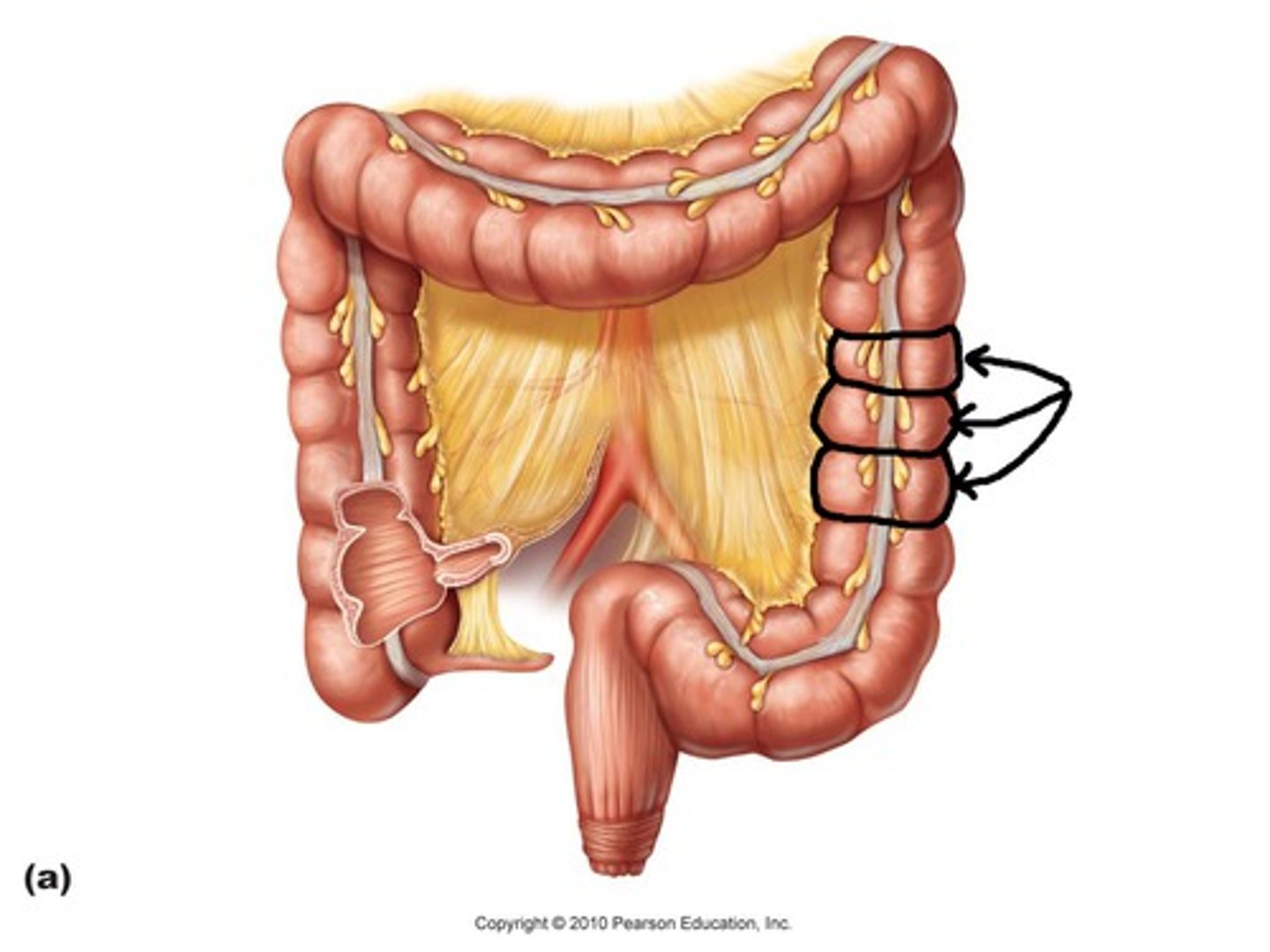
taenia coli
The longitude muscle of the colon arranged into three distinct bands.
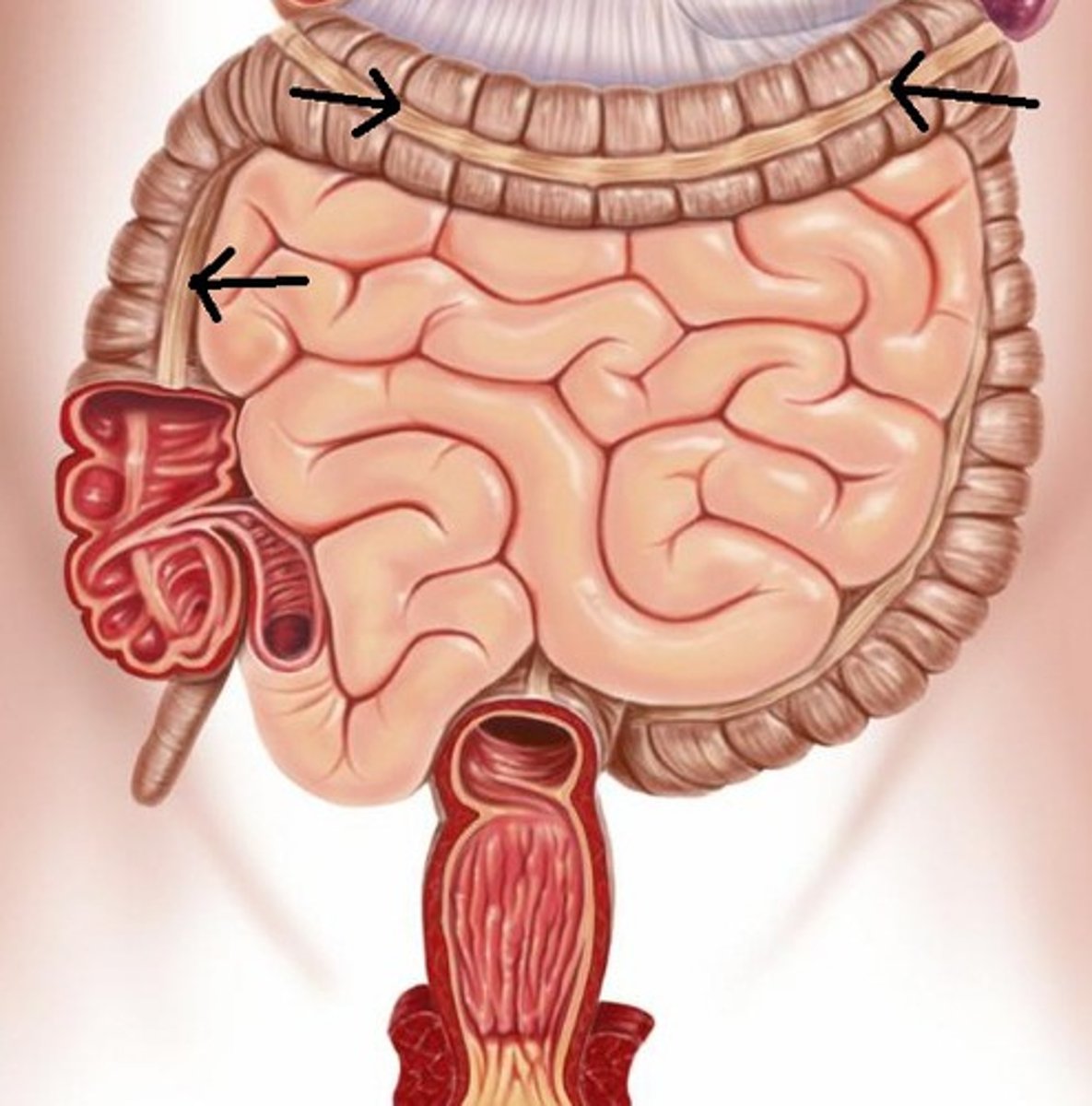
haustra
pouches that form in the large intestine when the longitudinal muscles are shorter than the colon
-circular muscle layer
mucosa, submucosa, circular muscle, longitudinal muscle, outer
five layers of the GI wall
-beings below the upper 1/3 of the esophagus
inner layer
portion of the GI wall consisting of the mucosa, columnar epithelium and goblet cells
middle layer
portion of the GI wall consisting of the submucosa, connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, cellular containment of digestive enzymes
circular and longitudinal layer
portion of the GI wall that is muscular and has haustrations and propulsions
large bowel
surface is smooth, one of the main functions is the absorption of water and electrolytes (mainly sodium and chloride)
-normal flora bacteria break down proteins that were not digested or absorbed in the small intestine, which leaves ammonia
-convert unabsorbed carbs into absorbable organic acids
-metabolize bile salts and facilitate absorption of bile
constipation
common problem, especially in the elderly
-can cause fecal impaction and obstipation
fecal impaction
occurs when hard stool that cannot be passed is lodged in the sigmoid colon and rectum
-can develop liquid stools that pass around fecal impaction
obstipation
sensation to defecate with no passage of stool, liquid, or gas from the colon
benzos, chemo, diuretics, lithium salts, opiates, TCAs
medications that can decrease intestinal motility and constipation
cathartic colon
the anatomical and physiological change in the colon that occurs with chronic use of stimulant laxatives
-more than 3 time per week for at least a year is excessive
-bloating, feeling of fullness, abdominal pain, incomplete fecal evacuation
-atonic and redundant colon
acute abdomen
tender and showing signs of inflammation of the peritoneal membrane
-waves of sharp constricting pain that is worsened by movement
-muscles contract with palpation (guarding)
-abdomen is rigid and could have rebound tenderness
-opiates usually withheld until Dx is made
tympany
high-pitched, musical, drumlike percussion note heard when percussing over the stomach and intestine
-gas filled
Murphy's sign
Pain with palpation of gall bladder (seen with cholecystitis)
incarcerated hernia
is an irreducible hernia in which the contents of the hernial sac are entrapped or stuck in the groin
-commonly a missed cause of bowel obstruction
perforation of bowel
hole/tear in the bowel that can be seen in x-ray with air under the diaphragm
-can cause referred shoulder pain
ileostomy/colostomy
surgical procedure in which the healthy end of the intestine is brought out og the abdomen though an incision in the anterior abdominal wall
-opening called a stoma allows for excretion of intestinal contents into an attached collection appliance
skip lesions
seen in Crohn's disease where there are areas of disease separated by healthy areas
cobblestoning
a lumpy appearance of the muscosa that occurs in Crohn's disease
-bowel mucosa develops granulomas
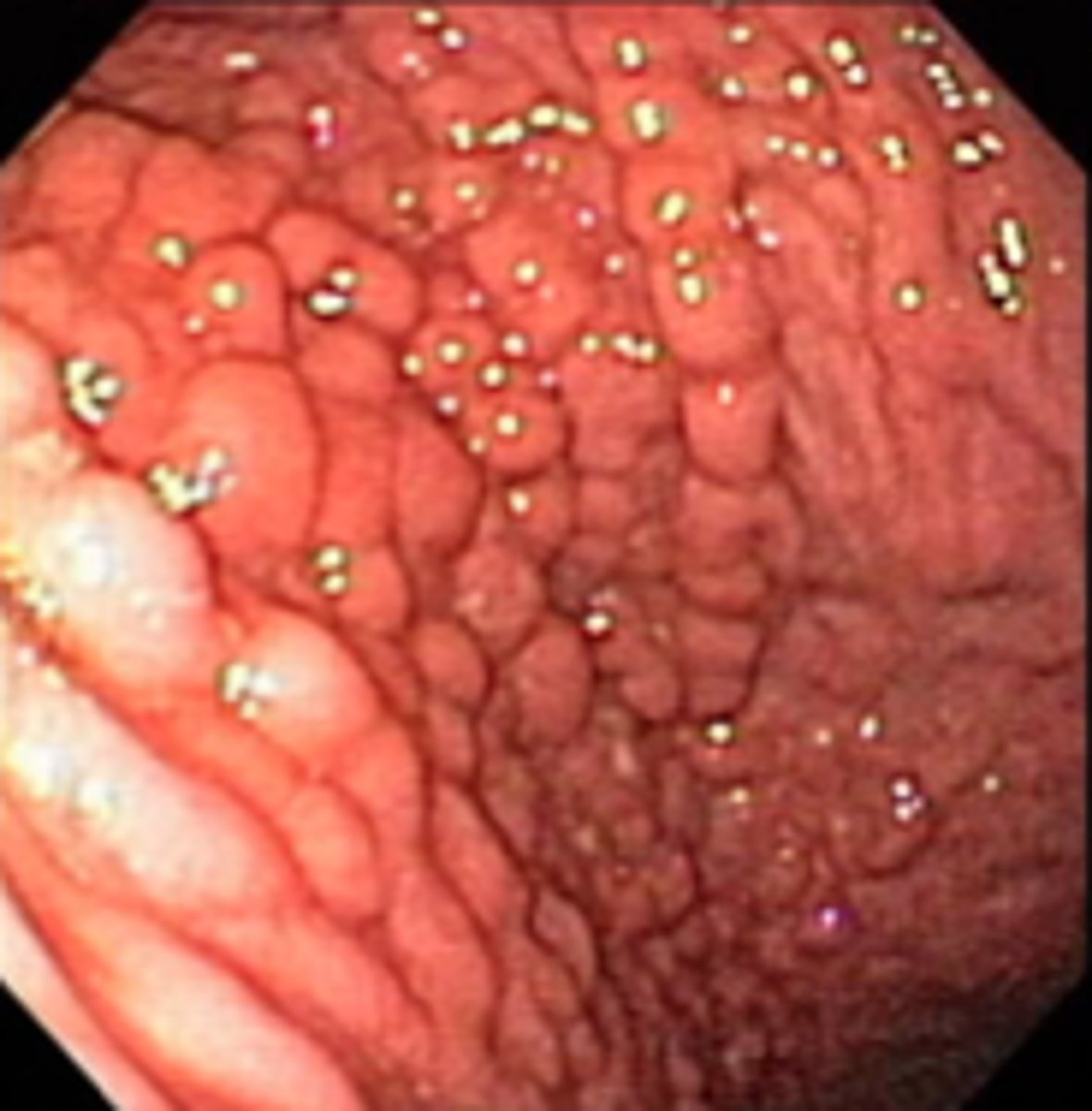
toxic megacolon
extreme dilation of a segment of the diseased colon, commonly the transverse
-complete obstruction and impaired absorption of fluids and electrolytes
-life-threatening perforation and peritonitis can result
-complication of Crohn's
uveitis
vascular layer of the eye that becomes inflamed and can cause renal detachment
-complication of Crohn's
chelitis
Cracking, inflammation, or splitting of the corners of the mouth
-common complication of Crohn's
erythema nodosum
inflammation of subcutaneous tissues resulting in tender, nodules
-complication of Crohn's
stomatitis
inflammatory condition affecting the oral mucosa, dentition, and periosteum
-occurs in 40% of patients receiving chemo
-ulceration in the lining
-can result from vitamin deficiency, mouth washes, allergic reactions, alcohol, CKD, inflammatory bowel
primary stomatitis
chancre sores, herpes simplex, traumatic ulcers
secondary stomatitis
usually results as a result of bacterial or fungal infection in pt with suppressed immune system
-can be caused by chemo or radiation
hiatal hernia
portion of the stomach protrudes upward through the LES and into the esophagus because sphincter doesn't close as its supposed to
-sliding vs rolling
-increases with age as supportive structures weaken over time (60% are over 50)
-diagnosed by endoscopy
Type 1 hiatal hernia
Sliding
-Most common
-Slides through opening of diaphragm d/t coughing, bending, tight clothes, ascites, obese, pregnant
-dysfunction of GEj
type 2 hiatal hernia
paraoesophageal or rolling
-5 % of patients
-anatomic effect that causes improper anchoring of the stomach to the diaphragm
Barrot's esophagus
from GERD or hernias, leads to columnar epithelium development in the esophagus that can lead to carcinomas
-treat with nitro to relax and dilate
-diagnosed by endoscopy
GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
digestive disease in which stomach acid or bile irritates the food pipe lining leading to inflammation
-highly prevalent disorder in western countries
-H. pylori has been found to decrease gastric acid secretion
-need pH monitoring and recording, esophageal manometry or motility itesting
-antihistamine, antacids, PPIs, prokinetics
acute gastritis
inflammatory process that can be accompanied by a hemorrhage to the mucosa
-from chronic ingestion of irritating foods and alcohol
-could be from acute illnesses such as traumatic injuries, burns, severe infections, hepatic renal or respiratory failure, or major surgery
-spicy food an increase pain
-synthetic marijuana leading to cyclic vomiting
chronic gastritis
Appears as a patchy, diffuse inflammation of the mucosal lining of the stomach
-most common cause is H. Pylori
-alcohol, NSAIDs, Crohn's, TB
-associated with presence of antibodies to parietal cells and intrinsic factor
atrophic gastritis
chronic inflammation of the stomach accompanied by a diminished size and functioning of the mucous membrane and glands
-usually seen in older population; may be autoimmune process
parietal cells
secrete HCl and intrinsic factor
-affected in gastritis, leading to pernicious anemia
Gastritis treatment
-supportive care for relieving symptoms or removing reducing cause of discomfort
-healing is spontaneous (high turnover rate)
-meds for discomfort
-H. pylori depends on type and duration of therapy with patient compliance
vagotomy
cutting of certain branches of the vagus nerve, performed with gastric surgery to reduce the amount of gastric acid produced and thus reduce the recurrence of ulcers
gastrectomy
surgical removal of part or all of the stomach
-sometimes done with gastritis (very rare though)
pyloroplasty
surgical repair of the pyloric sphincter
-enlarging the sphincter opening
-sometimes used with gastritits
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
-duodenal (80%) or gastric
-ulcerations and erosion of the upper GI; gastroduodenal mucosa cannot withstand digestive action of gastric acid and pepsin
-from H. pylori, chronic NSAID, increased acid production, stress
-pain
-Dx with upper endoscopy, and lab test
duodenal ulcers
Ulcers of the small intestine caused by an excessive secretion of hydrochloric acid and Helicobacter pylori infection.
-exacerbated by fasting with little to no relief with antiacids
gastric ulcers
erosion of the gastric mucosa
-can be triggered by eating
Mallory-Weiss syndrome
tear of the mucosa at the GEJ; type of complication from PUD
-traumatic vomiting and seizures can cause
gastric cancer
diet is a significant factor (rich in smoked foods, pickled vegetable, salted foods, meat)
-low gastric acidity (achlorhydria) exacerbated risks
-starts with chronic gastritis, progressing and causing atrophy, leading to abnormal cells and adenocarcinoma
-most frequently found in distal portion
-affects males 2xs more than females
-often asymptomatic until late in their course
-indigestion, anorexia, weight loss, etc.
dumping syndrome
Rapid emptying of gastric contents into small intestines.
-Client experience ab pain, nausea, vomiting, explosive diarrhea, weakness, dizziness, palpitations & tachycardia.
-complication of gastric cancer
oral cancer
malignancy of the lip or muscosa
-risks: smoking
-men are affected 2-4xs more than women
-squamous cell or basal cell
-early symptoms affect the floor of the mouth or tongue; usually asymptomatic in early stages; can infiltrate and metastasis to lungs, liver, bone
-oral bleeding, raised areas, ulcers, white and red patches, increased pain radiating to ear or neck, difficulty speaking, dysphagia, lymph node involvement, weight loss
basal cell carcinoma
lips typically; raised scabs that turn into a scabby ulcer with pearly borders
-tend to grow slowly and become invasive over time
squamous cell carcinoma
malignant tumor of the squamous epithelium
-tend to grow rapidly an metastasize
leukoplakia
thickened, white, leathery-looking spots on the inside of the mouth that can develop into oral cancer
-premalignant lesions on lips often found incidentally
erythroplakia
Less common but more worrisome than leukoplakia
-red plaque usually occurs with leukoplakia and found on mucosal surface
oral trauma
injury to specific bone of the face, including nasal, mandibular, and maxillary fractures
-increase in elderly due to fall risk and most are on blood thinners
-direct damage to oral cavity that can lead to partial or complete airway occlusion
-increased respiratory rate, stridor, SOB, hypoxia
Le Fort I
Floating palate. Horizontal fracture through maxillary sinuses, nasal septum, and inferior ptyergoid plates.
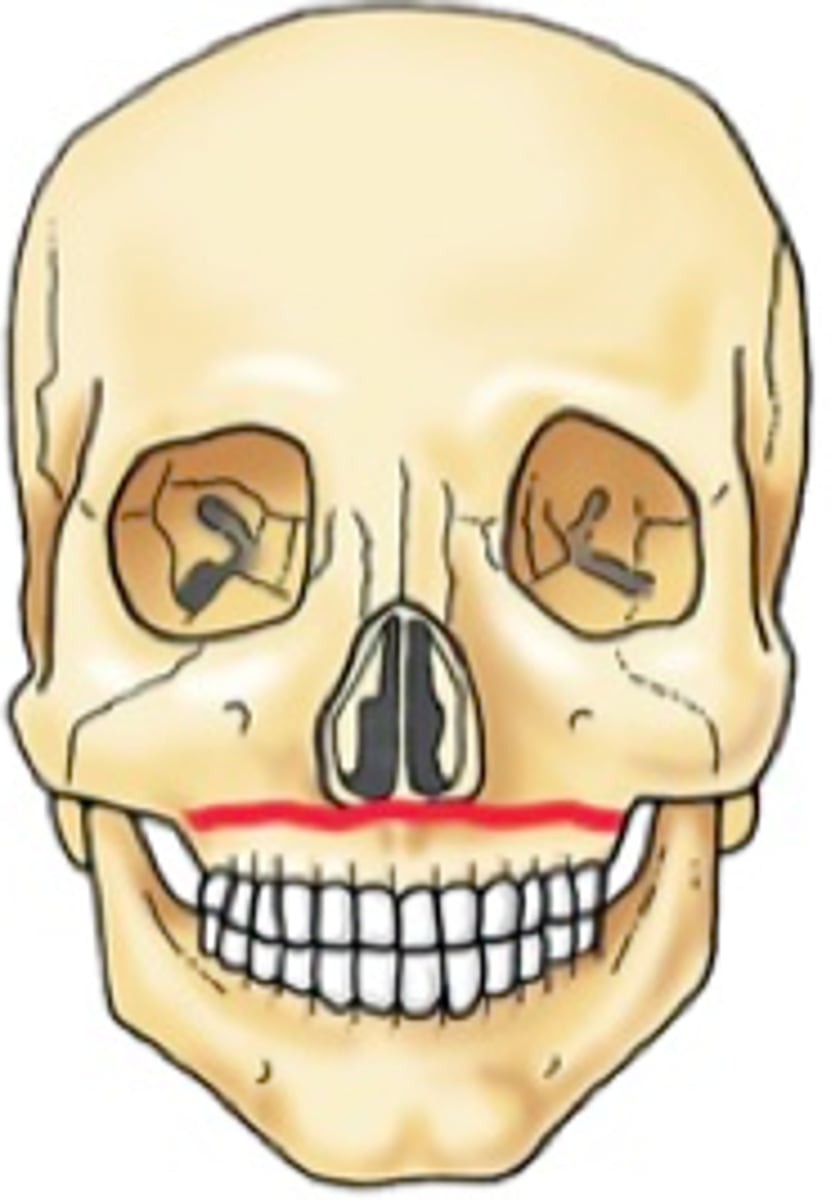
Le Fort II
Pyramidal fracture through bridge of nose, medial orbits, lateral and posterior maxillary walls, nasal septum, inferior orbital rim (infraorbital nerve injury), and midportion of ptyergoid plates.
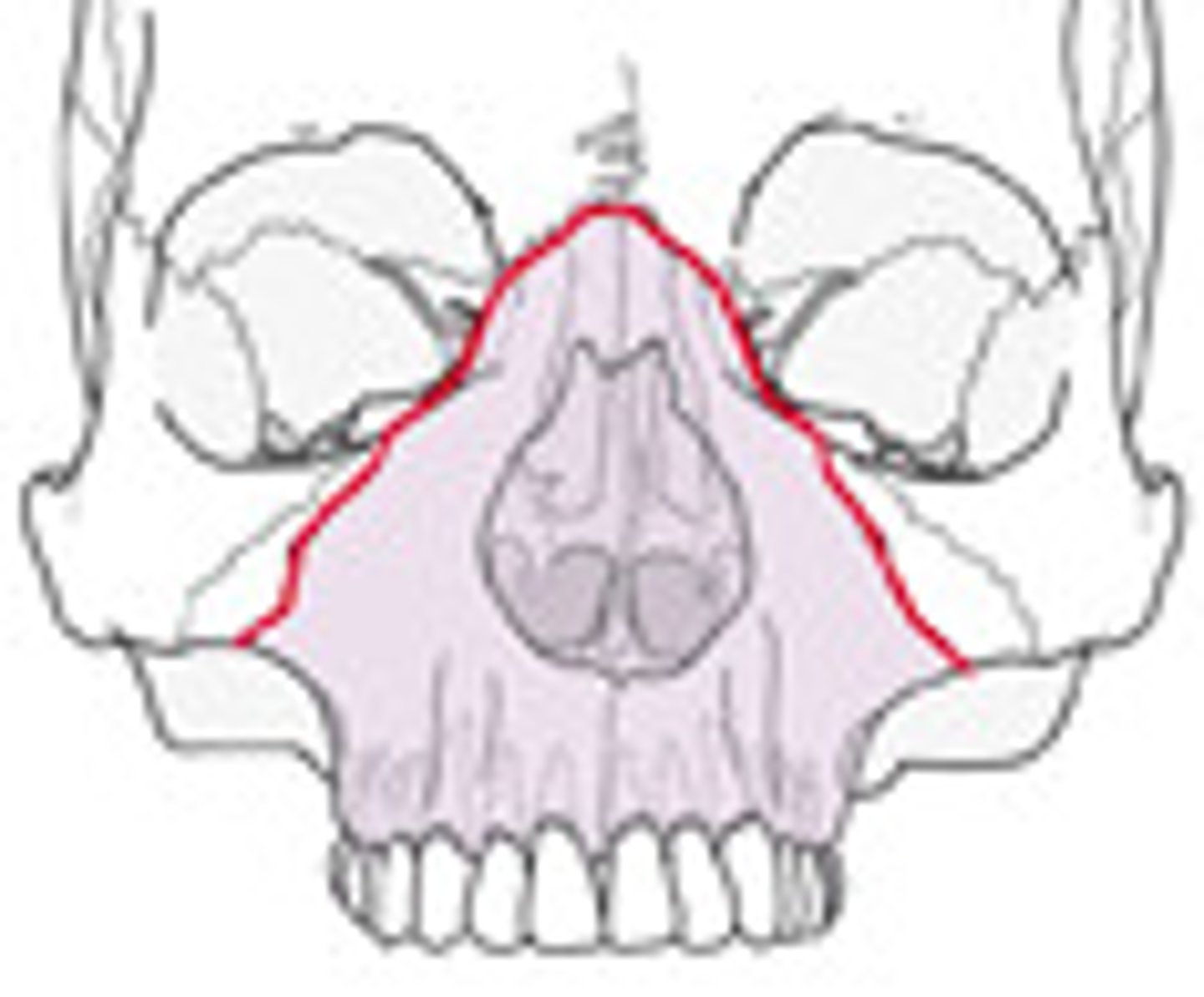
Le Fort III
Located high in the midface and extends transversely from the zygomatic arches through the orbits and to the base of the nose
digestion, absorption, and elimination of waste products
major functions of the intestinal system
-small is nutrient absorption
-large is water absorption; sodium absorption with potassium excretion
duodenum
first part of the small intestine that is approximately 10 in long
jejunum
second part of the small intestine, about 8 ft long
ileum
third part of the small intestine that is approximately 12 ft long
cecum
a pouch connected to the junction of the small and large intestines.
-approximately 2-3 inches
colon
consists of the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid
-there is a lot of resections of this from diverticulitis, Crohns, etc.
rectum
A short tube at the end of the large intestine where waste material is compressed into a solid form before being eliminated
-7-8 inches long
pseudopolyps
found in ulcerative colitis
-inflammatory areas of protruding growths
UC symptoms
-Colicky/cramping abdominal pain
-Diarrhea > pus, blood, mucous
Malabsorption and weight loss
-Fever
-Uveitis
-Dermatological disorders pyoderma gangrenosum and
erythema nodosum
-Arthritis
-Dehydration, poor appetite
LBO (large bowel obstruction)
the inability of the intestinal contents to move through the large intestine
-may be partial or complete, acute or chronic reversible or irreversible
-large about occur in sigmoid section
-high mortality rate after first 24 hours
mechanical obstruction
physically blocks the movement of material through the intestines
-may be caused by scar tissue (adhesions), tumors, bolus of undigested food, volvulus, stricture, diverticula
nonmechanical obstruction
stem from disruption of peristalsis because of weakness of muscles of the intestinal wall (dysmotility syndrome) or paralysis of the bowel wall
-can cause air and secretions to collect in the bowel in the elderly, leading to dilation of the bowel not an obstruction (Ogilvie syndrome)
partial obstruction
LBO sign with high-pitched bowel sounds
complete obstruction
LBO with no bowel sounds and no feces in rectum
intestinal decompression
a nasogastric tube is inserted into the stomach or a colorectal tube through the rectum to relieve pressure from the obstruction
anastomosis
surgical procedures that remove the dysfunctional area of the large intestine then reattach the healthy ends together
McBurney's point
abdominal pain that originates in the umbilical region and radiates to the right lower quadrant
-sign of appendicitis
Psoas sign
place hand just above right knee, ask pt to raise thigh, increased abdominal pain, suggesting irritation of this muscle by an inflamed appendix
Rovsing's sign
palpation of the left lower quadrant causes right lower quadrant pain that may indicate appendicitis
Obturator sign
Pain in the RLQ when hip and knee are flexed and leg is rotated internally and externally
-may indicate appendicitis
Mesenteric adenitis
swollen mesenteric lymph nodes present with signs and symptoms exactly like appendicitis
-undergo negative appendectomies
volvulus
a twisting of the large intestine around a point of attachment in the abdomen
-sigmoid is the most common type in adults
-results in bowel obstruction and ischemia of the bowel
hematochezia
passage of fresh, bright red blood from the rectum
-sign of hemorrhoids
rubber band ligation
Most widely used technique for hemorrhoid removal
-hemorrhoid is identified and a band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid, restricting circulation
-leads to sloughing off in 2-4 days
bipolar/infrared/laser coagulation
this technique uses bipolar current or infrared or laser light, which causes coagulation and necrosis of the hemorrhoid, leaving fibrosis in the submucosal layer.