Skeletal System Bones
1/99
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
sutural bones/wormian bones
Which type of bones are…
small, flat, oddly shaped
ranges in size from a grain of sand to a quarter with borders similar to pieces of a jigsaw puzzle
found between the flat bones of the skull
irregular bones
Which type of bones…
have a complex shape with short, flat, notched or ridged surfaces
form the vertebrae of the spinal column, bones of the pelvis, and several bones in the skull
short bones
Which type of bones…
are cube-like in shape and approximately equal in length, width and thickness
only exist in the carpals of the wrists and tarsals of the ankles
provide stability and support as well as some limited motion?
flat bones
Which type of bones…
provide protection for underlying soft tissues
offer an extensive surface area for the attachment of skeletal muscles
form the cranial bones, the scapulae (shoulder blades), the sternum (breastbone) and the ribs
long bones
Which type of bones…
are cylindrical in shape and longer than they are wide
form the humerus, ulna, radius, femur, tibia, fibula metacarpals, phalanges metatarsals, and phalanges?
sesamoid bone
Which type of bones…
are usually small, round, and flat
are found near the joints of the knees, hands, and feet and embedded inside tendon
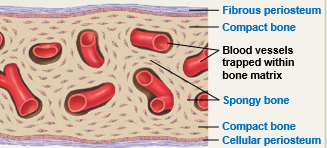
compact bone
Which of the two types of bone…
is the cortex (outer parts) in a flat bone
contains a hard bony matrix
is heavy
spongy bone
Which of the two types of bone contains…
red and yellow marrow cavity
network of struts, honeycomb-like, diploe
metaphysis
In a femur (long bone), the epiphysis and diaphysis (shaft) meet at the (?)?
medullary cavity
In a femur (long bone), the central space of the diaphysis contains yellow marrow and is called the what?
diaphysis (shaft)
Which part of the femur (long bone) has a wall of solid, dense compact bone and a central space called a medullary cavity?
epiphysis
Which part of the femur (long bone) is mostly spongy bone and contains red marrow?
lacunae
What are the pockets that contain a single osteocyte called?
canaliculi
What are the narrow passageways that join the central canal with lacunae to exchange nutrients, waste, and gasses with osteocytes?
bone matrix
Dense, solid tissue composed of collagen fibers and minerals are part of the what?
calcium phosphate (Ca3(PO4)2
Which component makes up almost 2/3 of the bone matrix?
1/3
Collagen fibers make up about (?) of the bone matrix?
decalcified
A (?) bone would only contain collagen fibers
collagen fibers
Which component of the bone matrix reinforces bone strength?
calcium hydroxide
In the bone matrix, calcium phosphate interacts with what to form crystals of hydroxyapatite?
osteogenic cell
What do you call an osteoprogenitor cell that produces daughter cells that differentiate osteoblasts?
epiphyses of long bones
In long bones, spongy bone is found predominantly in what?
circumferential lamellae
Concentric layers (lamellae) of bone containing osteocytes that are organized around a central canal are called
osteoclasts
Cells that secrete enzymes and acids to dissolve the bony matrix
periosteum
Osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts are all found in the what?
diaphyses of long bones
What are the sites within bone containing large amounts of compact bone called?
epiphyses of long bones
Which part of long bones are the sites of bone marrow and blood cell production?
calcium salts
Deposits of what make the matrix of compact bone dense?
osteon
A functional unit of compact bone is called (?)?
central canal
In compact bone, what contains a blood vessel(s) and run parallel to the bone?
lamellae
In compact bone, what do you call the ring-like layers of bone matrix?
concentric lamellae
In compact bone, what surrounds the central canal and resembles a "bulls eye"?
circumferential lamellae
In compact bone, what are at outer and inner bone surfaces called?
interstitial lamellae
In compact bone, what fills spaces between osteons?
dense irregular connective tissue
What kind of tissue does the periosteum consist of?
perpendicular
Collagen fibers run (?) to the surface of bone
parallel
Osteons run (?) to axis
canaliculi
What contains processes of osteocytes which is important for the communication between cells?
fibrous, cellular
The periosteum contains outer (?) and inner (?) layers
periosteum
The (?) covers outer surfaces of bones with the exception of joints
dense irregular connective tissue
The outer fibrous layer of the periosteum contains (?)
osteogenic cells, osteoblast, osteoclast (NO osteocyte)
The inner cellular layer of the periosteum contains (?), (?), and (?).
periosteum
The (?) helps with growth repair, contains a network of lymphatic vessels, blood vessels, and sensory nerves.
perforating fibers
What are tendons that have been trapped inside the compact bone by layers of bone deposit called?
perforating fibers
What makes muscle to bone connection very strong?
endosteum
The (?) is an incomplete cellular layer containing exposed osteoblasts, osteogenic cells, and osteoclasts.
spongy
The endosteum wraps around marrow by covering trabeculae in a (compact/spongy) bone
spongy
(Compact/spongy) bone lacks osteons
trabeculae
The matrix of spongy bone forms an open network of (?)
red
In spongy bone, (red/yellow) bone marrow fills spaces between trabeculae
yellow
Although uncommon, spongy bone may contain (red/yellow) bone marrow
trabeculae
During compression on weight-bearing bones, (?) in epiphysis of the femur transfer forces from pelvis to compact bone of temporal shaft across knee joint
pelvis
During compression on weight-bearing bones, trabeculae in epiphysis of the femur transfer forces from (?) to compact bone of temporal shaft across knee joint
temporal shaft
During compression on weight-bearing bones, trabeculae in epiphysis of the femur transfer forces from pelvis to compact bone of (?) across knee joint
lateral side
During tension on weight-bearing bones, the weight can force the (?) to bow and bend. The tension in this area resists the tendency of the femur to bend.
nutrient artery and vein
Which type of major blood vessel supplies diaphysis?
nutrient artery and vein
Which type of major blood vessel pass through nutrient foramina in diaphysis?
metaphyseal vessels
Which type of major blood vessel supplies blood to epiphyseal cartilages?
metaphyseal vessels
Which type of major blood vessel is where bone growth occurs
periosteal vessels
Which type of major blood vessel is found on periosteum?
periosteal vessels
Which type of major blood vessel supplies blood to superficial osteons?
ossification/osteogenesis
Bone formation is called (?)
calcification
Deposition of calcium salts is known as (?)
ossification
Calcification occurs during (?)
intramembranous ossification
In which of the two forms of ossification does bone develop directly from mesenchyme and occurs mostly in flat bones?
Endochondral ossification
In which of the two forms of ossification does bone replace existing cartilage?
long
Endochondral ossification occurs mostly in (?) bones?
8
Intramembranous ossification starts at about the (?)th week of embryonic development
mesenchyme
In intramembranous ossification, (?) is responsible for bone formation
5
Intramembranous ossification occurs in (?) main steps
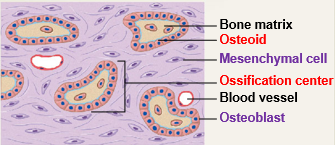
1
The following occurs during the (?) stage of intramembranous ossification.
Mesenchymal cells cluster together and differentiate into osteoblasts
Osteoblasts cluster to form ossification center
In ossification centers, osteoblasts secrete osteoid
Osteoid becomes mineralized with calcium salts forming bone matrix
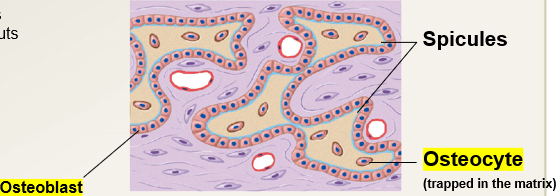
2
The following occurs during the (?) stage of intramembranous ossification.
the developing bone grows outward from the ossification center.
ossification center joins to form spicules
some osteoblasts are trapped inside ossification center pockets where they differentiate into osteocytes
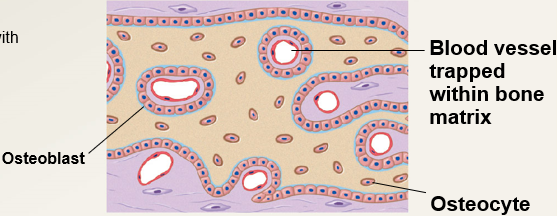
3
The following occurs during the (?) stage of intramembranous ossification.
blood vessels branch and grow between spicules
spicules interconnect, trapping blood vessels within bone
the rate of nutrient growth accelerated with oxygen and a reliable supply of nutrients
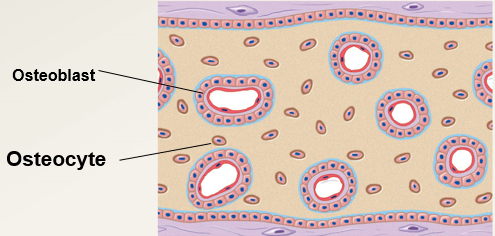
4
The following occurs during the (?) stage of intramembranous ossification.
all spicules disappear
a "filled" plate of spongy bone with full matrix and blood vessels appears
5
The following occurs during the (?) stage of intramembranous ossification.
osteons begin to develop due to remodeling around blood vessels
the matrix has appearance of spongy bone. Compact bone appears on superficial surface
periosteum develops (fibrous and cellular)
hyaline cartilage
The process by which (?) is gradually replaced by bone; also the process by which most bones form
primary, secondary
(?) ossification center and (?) ossification center develop inside hyaline cartilage
6
Endochondral ossification begins at week (?) of embryo when most limbs are made of hyaline cartilage
7
Endochondral ossification occurs in (?) steps
chondrocytes
During endochondral ossification, (?) produce and maintain the hyaline cartilage matrix
1, 4
During endochondral ossification, primary ossification center (diaphysis) occurs during steps (?) - (?)
5, 7
During endochondral ossification, secondary ossification center (epiphysis) occurs during steps (?) - (?)
primary
In endochondral ossification, during which ossification center does the following occur?
Hyaline cartilage is growing in embryo
Chondrocytes in the center of cartilage growing big in size
Hyaline cartilage matrix calcifies
Chondrocytes starve due to lack of nutrients.
Chondrocytes die and surrounding cartilage is disintegrated.
Blood vessels invade the resulting spaces carrying osteogenic cells
Primary ossification center forms.
Enlarged spaces combine to become the medullary cavity.
appositional growth
In endochondral ossification, growth in width/diameter is called (?)
interstitial growth
In endochondral ossification, lengthening of bone through primary and secondary ossification centers is called (?)
secondary
In endochondral ossification, during which ossification center does the following occur?
Hyaline cartilage matrix at two epiphysis calcifies; Chondrocytes die; blood vessels invade the resulting spaces carrying osteogenic cells. Matrix forms.
Blood brings osteogenic cells to synthesize bone in the epiphyseal regions
When last of the chondrocytes are replaced with bone matrix, epiphysial line can be seen
epiphyseal closure
completion of epiphyseal growth is called (?)
2
secondary ossification centers lead to development of (?) epiphyses
primary ossification
primary ossification center leads to development of the diaphysis shaft
epiphyseal
width of (?) cartilages reveals timing of endochondral ossification
epiphyseal line
Former location of epiphyseal cartilage is visible on x-rays as an (?)
weaken
The process of bone remodeling must be balanced. if removal is faster than replacement, bones will (?).
osteoblasts
exercise, particularly weight-bearing exercise, stimulates (?)
a lack of activity
bone degenerates quickly when there is (?)
elongate
Growth hormone and thyroxine maintain epiphysial cartilage so bones can (?).
epiphyseal line closure
sex hormones lead to (?) by increasing osteoblast activity more than epiphysial cartilage expansion. Estrogen causes this faster, so females “tend” to be shorter.
parathyroid hormone
The hormone(s) that helps increase blood Ca2+ is (?)
sex hormones, growth hormones
hormone(s) that stimulate osteoblast activity
osteoporosis
decrease in bone matrix to the point where bone cannot function normally
cartilage and spongy bone
during repair of bone fractures the external callus is initially made of (?)