Glycogen Synthesis and Breakdown
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
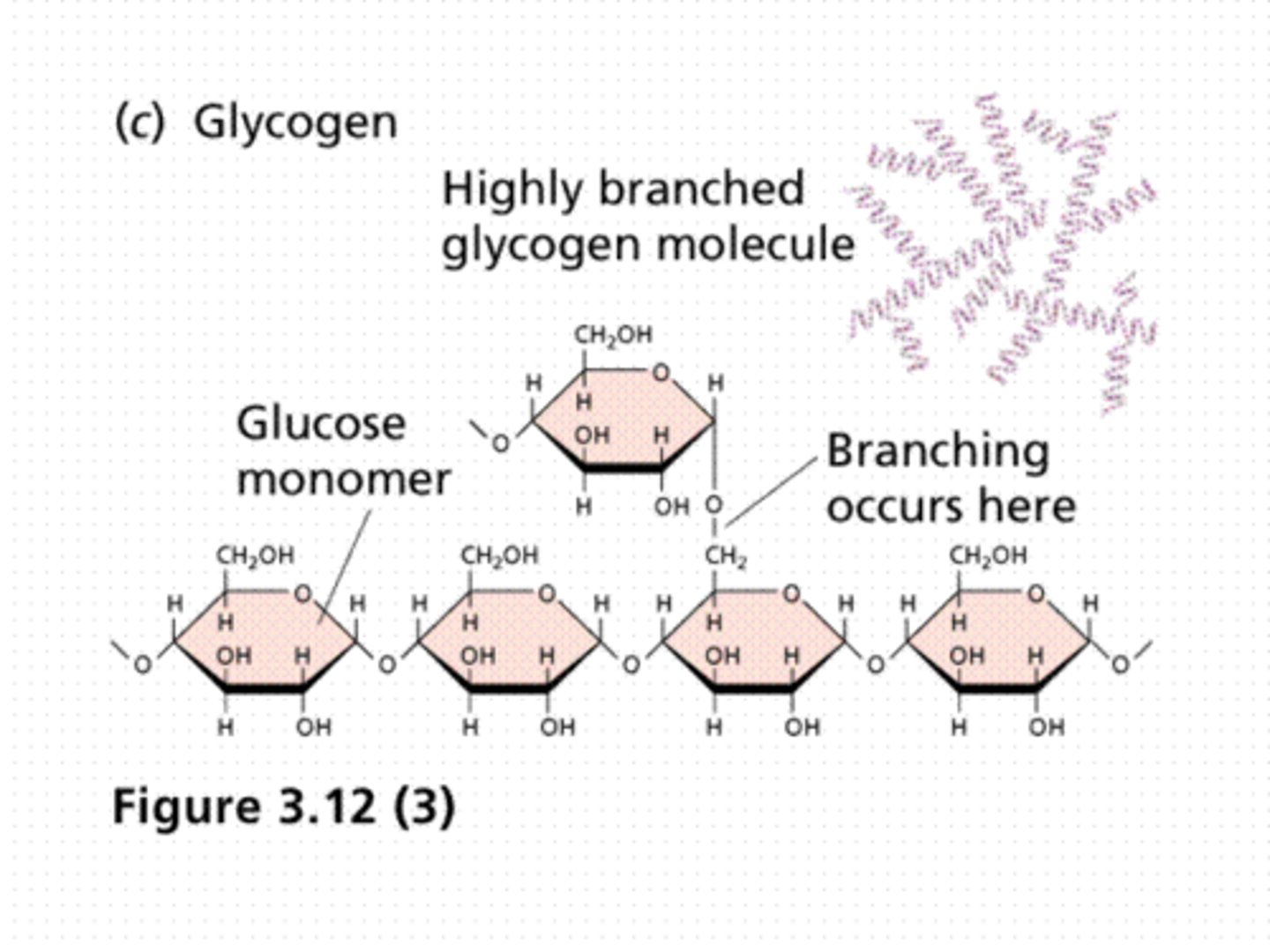
Glycogen Structure
-Many non-reducing ends
-The only reducing end is attached to glycogenin "primer"
Glycogenolysis
-Glucose removed from multiple non-reducing ends simultaneously
-Allows rapid mobilization of glucose
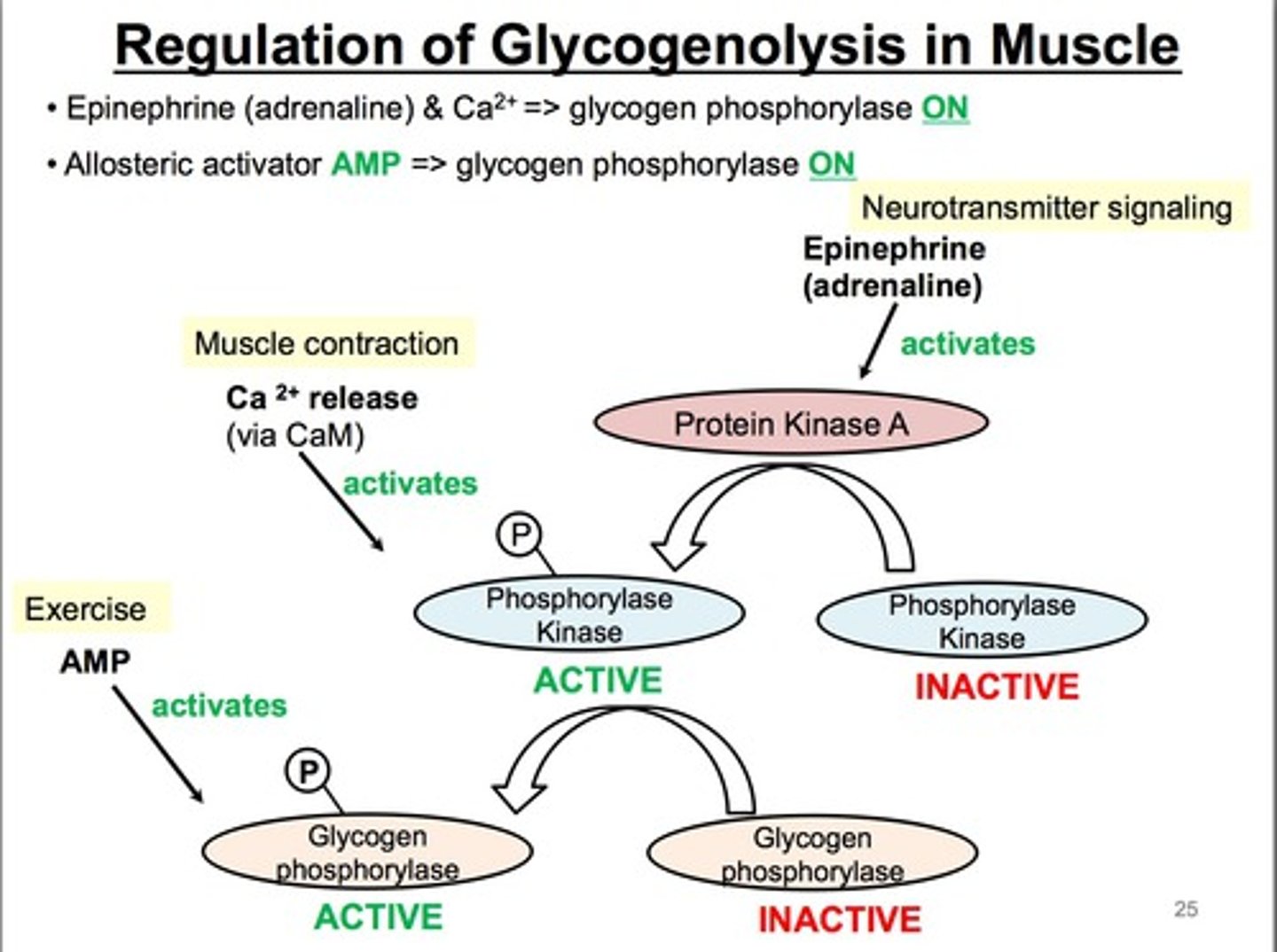
Glycogenolysis in Muscle
-Provides glucose 1P
-Converted to Glc 6P for glycolysis
-ATP responds to exercise, epinephrine
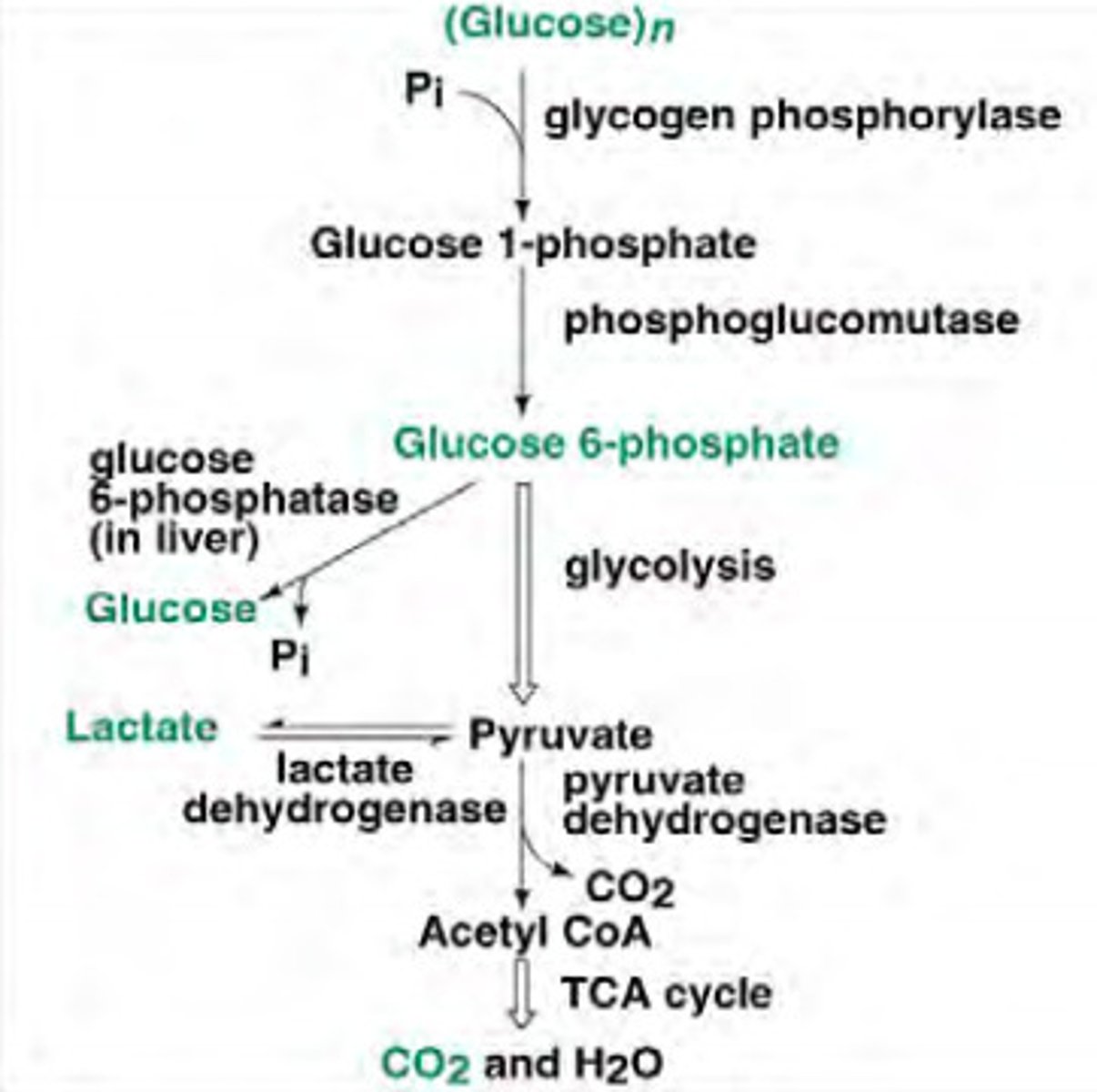
Glycogenolysis in liver
-Provides glucose 1P
-Converted to Glc 6P
-Phosphatases hydrolyses it to glucose
-Secreted into blood for other organs
-Responds to low blood glucose, glucagon
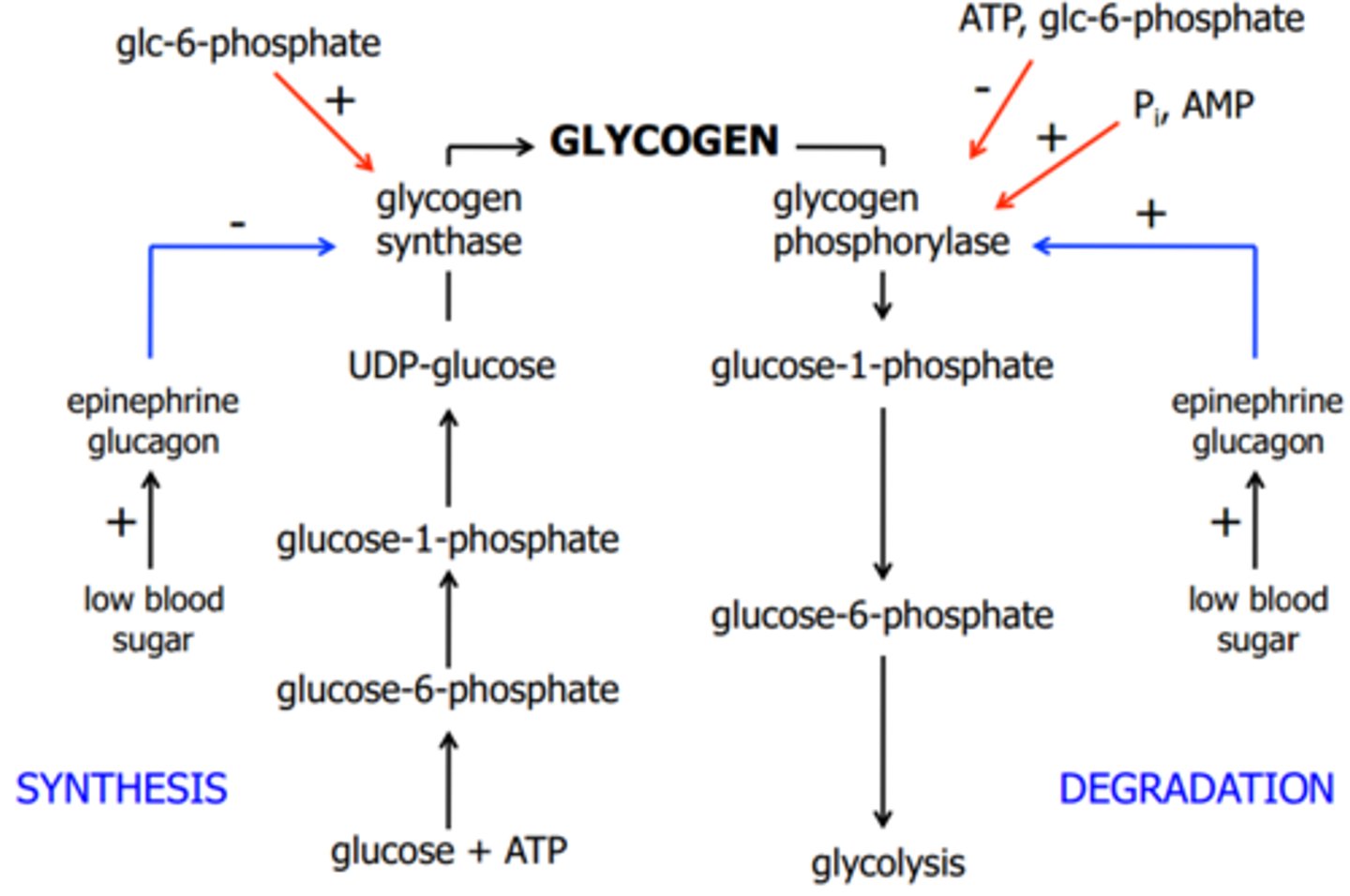
Degradation of Glycogen
Does not require energy
D1
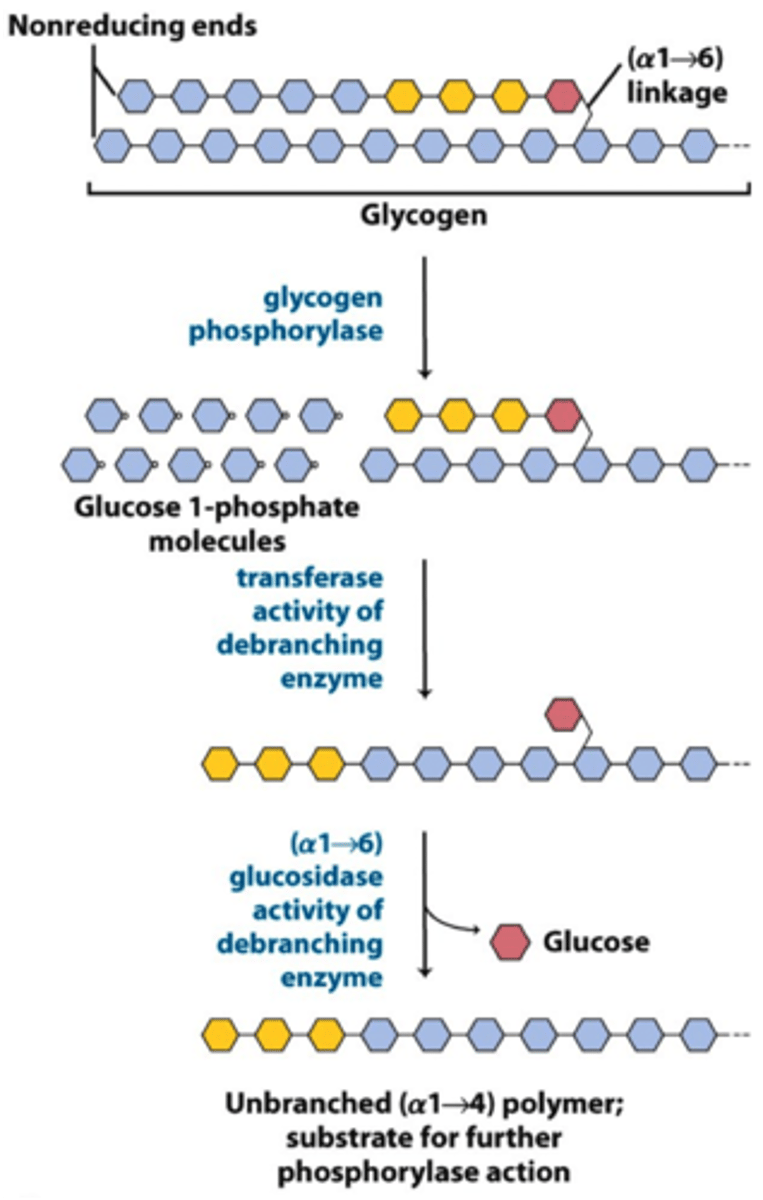
Debrancher glycogen phosphorylase hydrolyses a-1,4
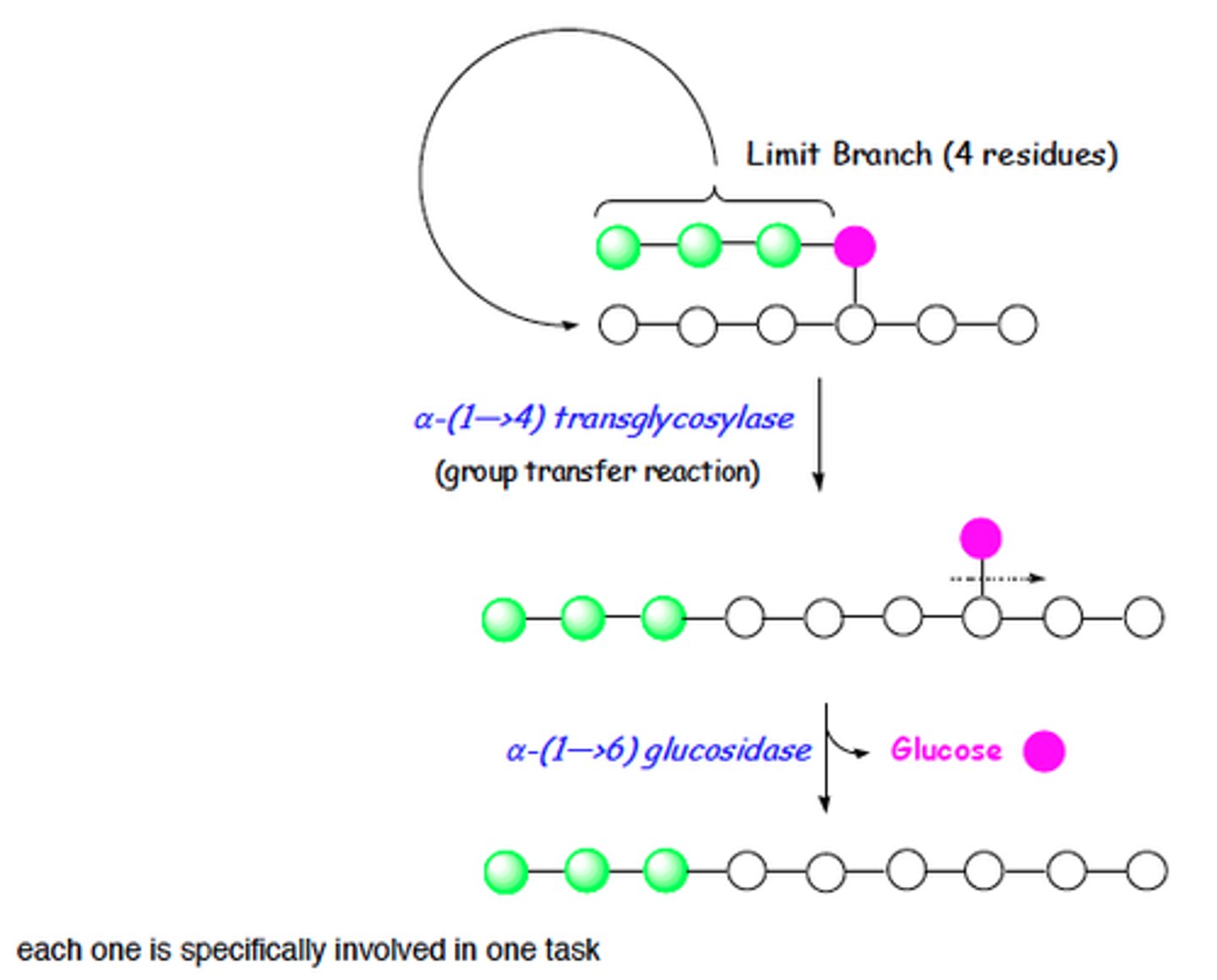
D2
Glucose 6 phosphatase removes phosphate for glucose transport
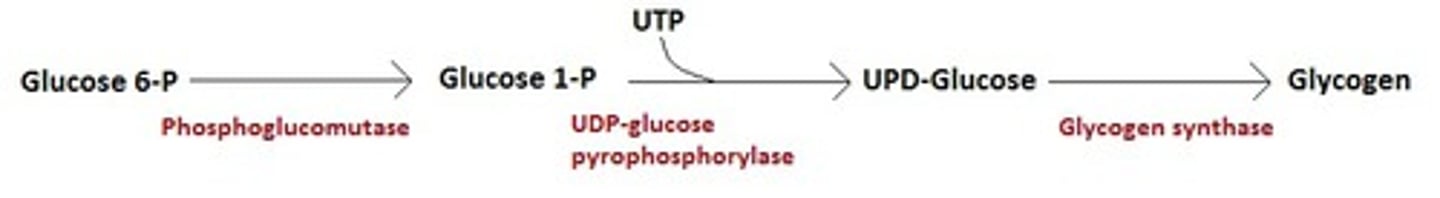
S1
-Glucose phosphorylated by hexokinase (glucokinase)
-Glucose converted to Glucose 1P by phosphoglucomutase
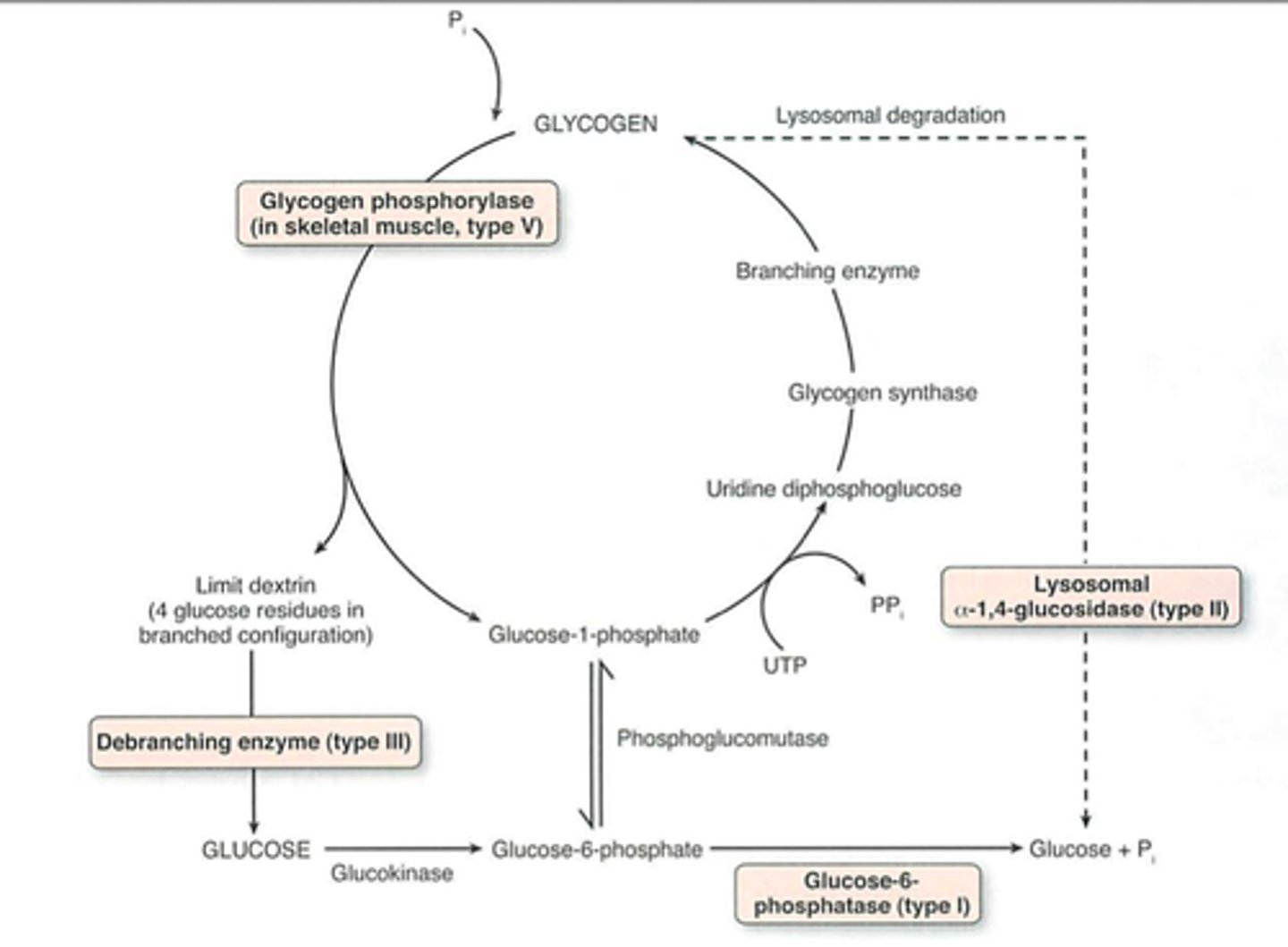
S2
UDP glucose synthesized uses UTP
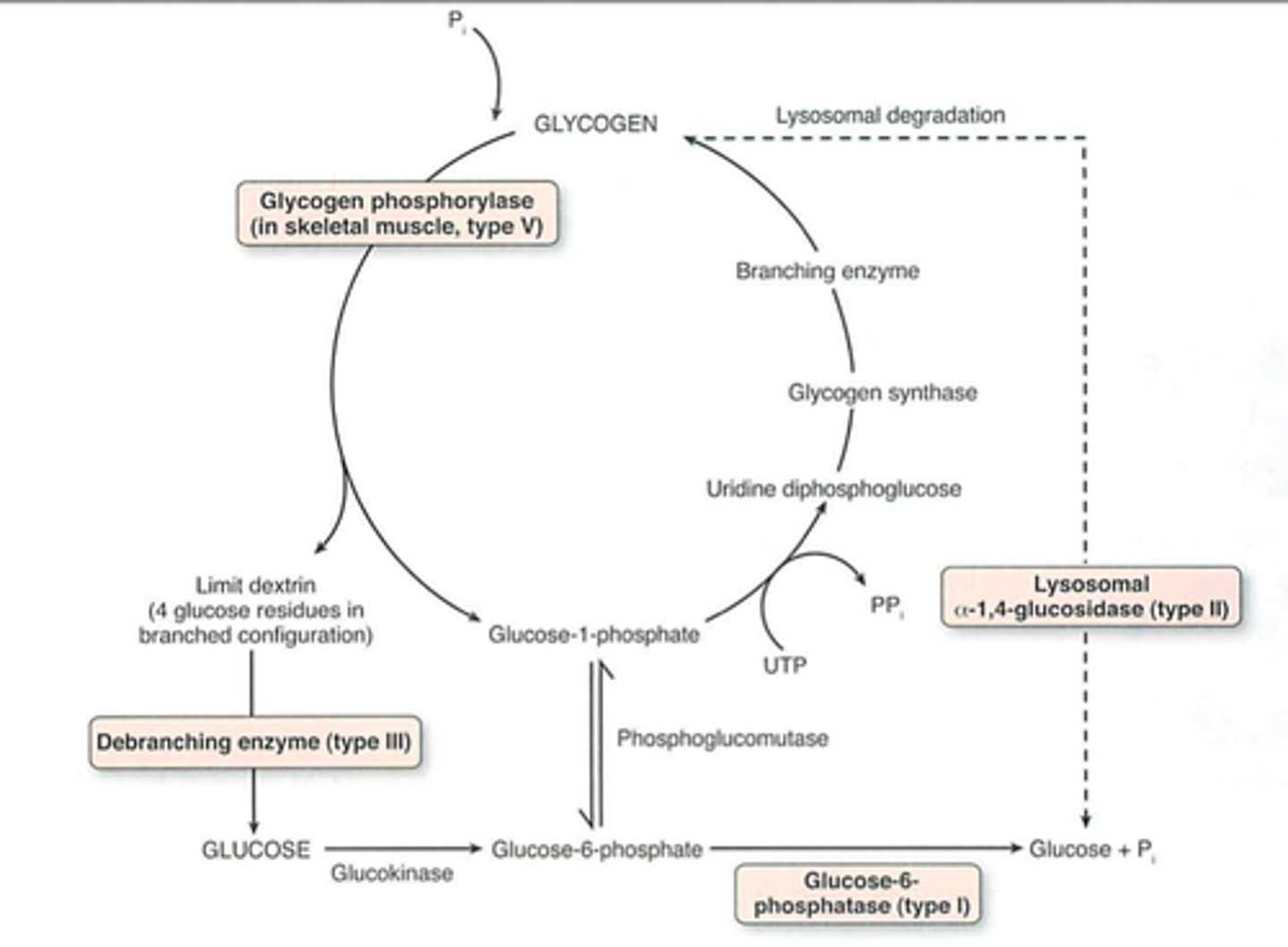
S3
Glucose added to primer or to non-reducing end of a glycogen molecule branching enzyme
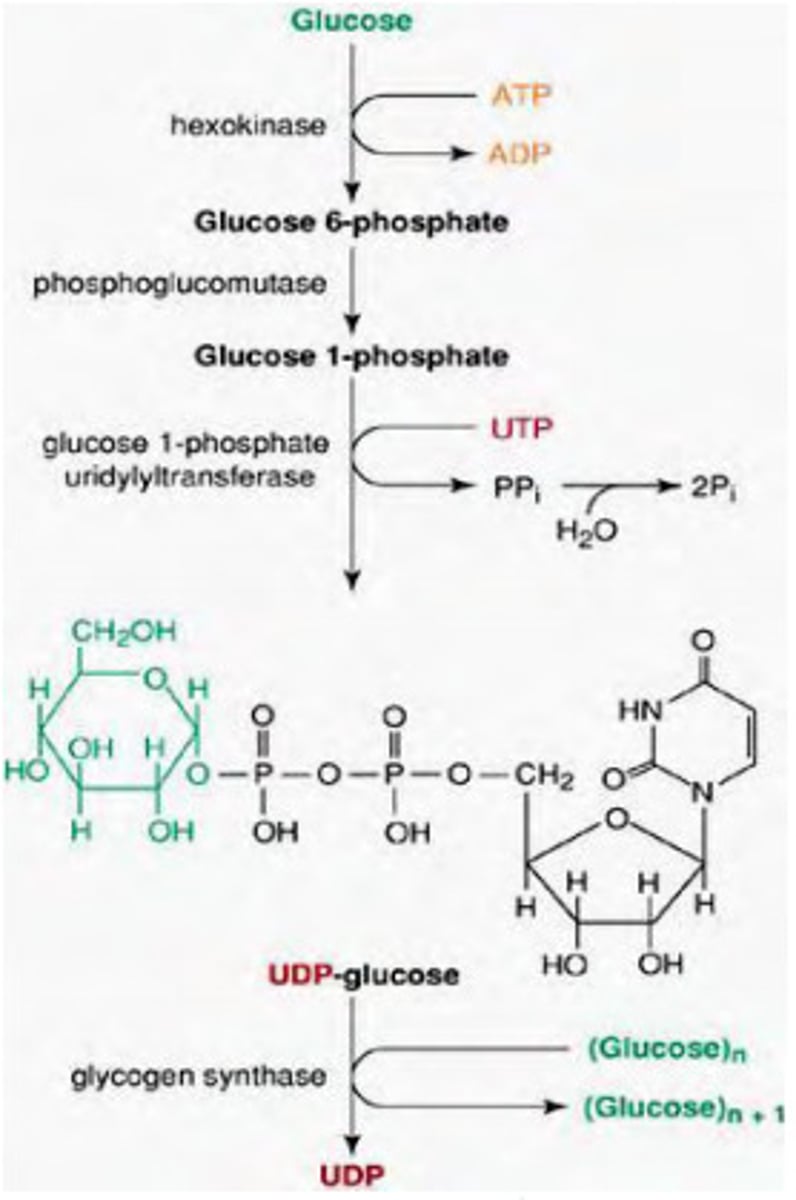
Glycogen Synthesis
-UDP Glucose pyrophosphorylase uses Glucose 1P and UTP to generate UDP-glucose, a high energy intermediate pyrophosphate
-Glucose is then added to non-reducing end of glycogen in an a-1,4 linkage by glycogen synthase
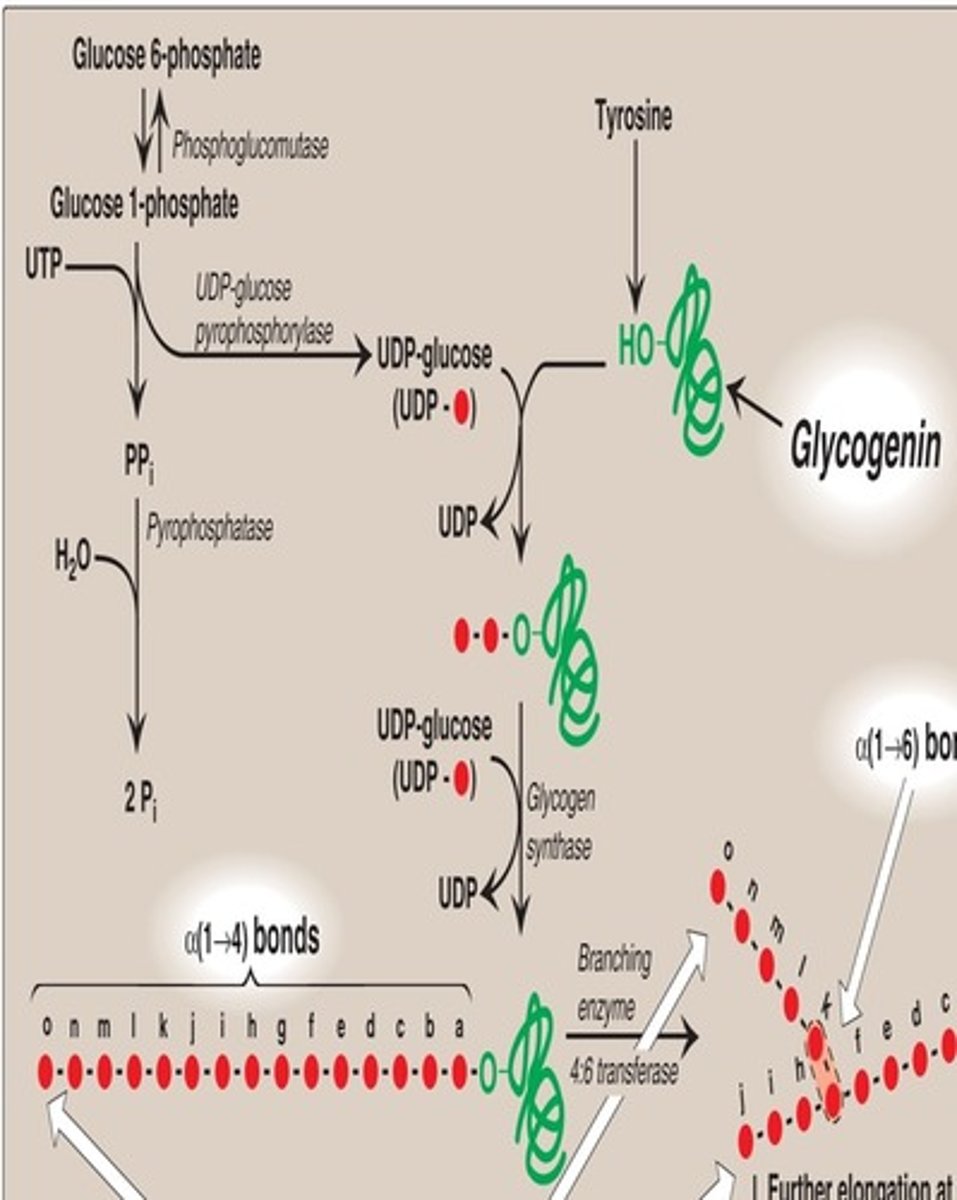
Glycogen Synthesis Steps
1) Glycogen synthase adds straight chains (regulated step)
2) When chains have about 10-12 residues per chain, a 6-8 residue piece is cleaved and reattached to a different glucose unit via an a(1->6) bond
3) Branching enzymeL Amylo 4,6 Transferase removes and relocates 6-8 glucose residues, glycogen primers are also synthesized
Glycogenin protein
Uses UDP glucose to autoglycosylate itself on a serine hydroxyl, extending a glycosyl chain long enough for glycogen synthase to use it as a substrate
Branching
Increases:
-Sites for synthesis and degradation
-Site of solubility
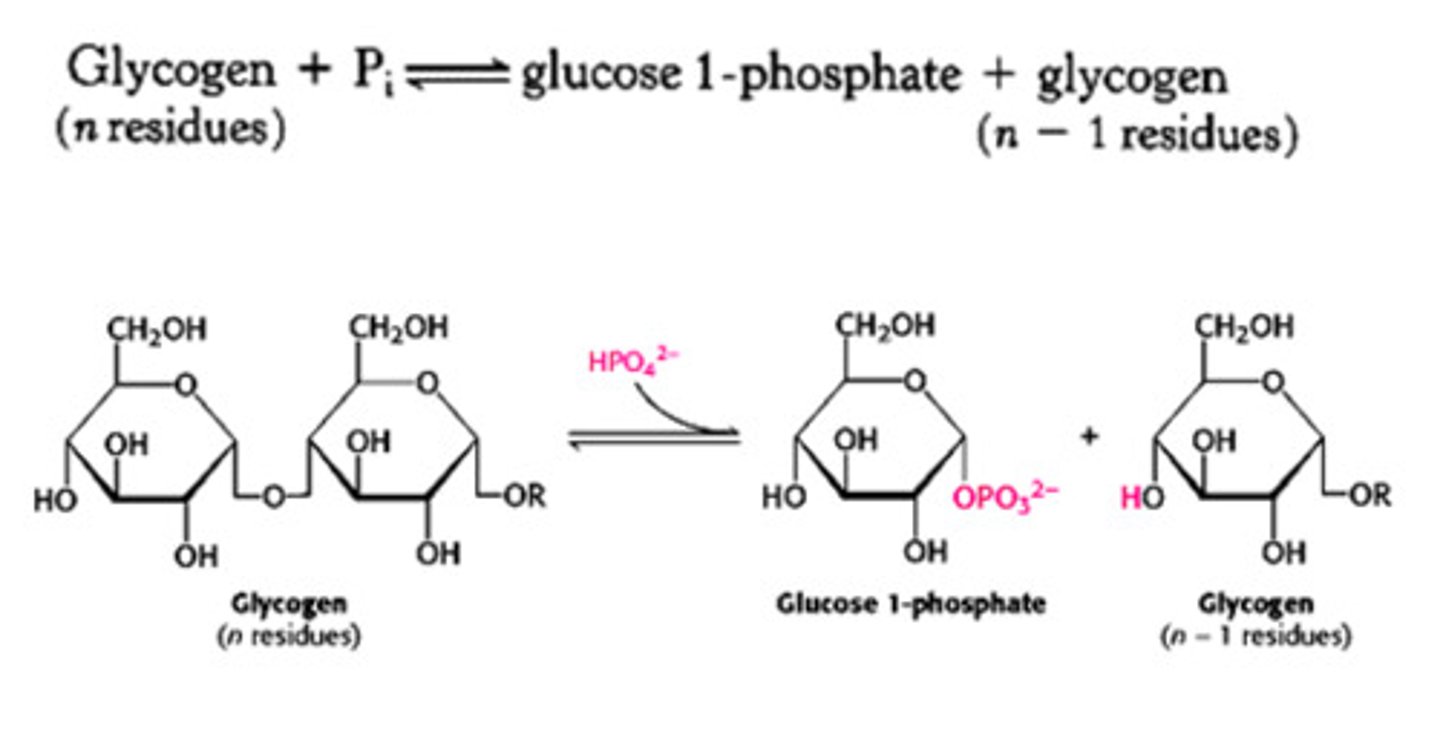
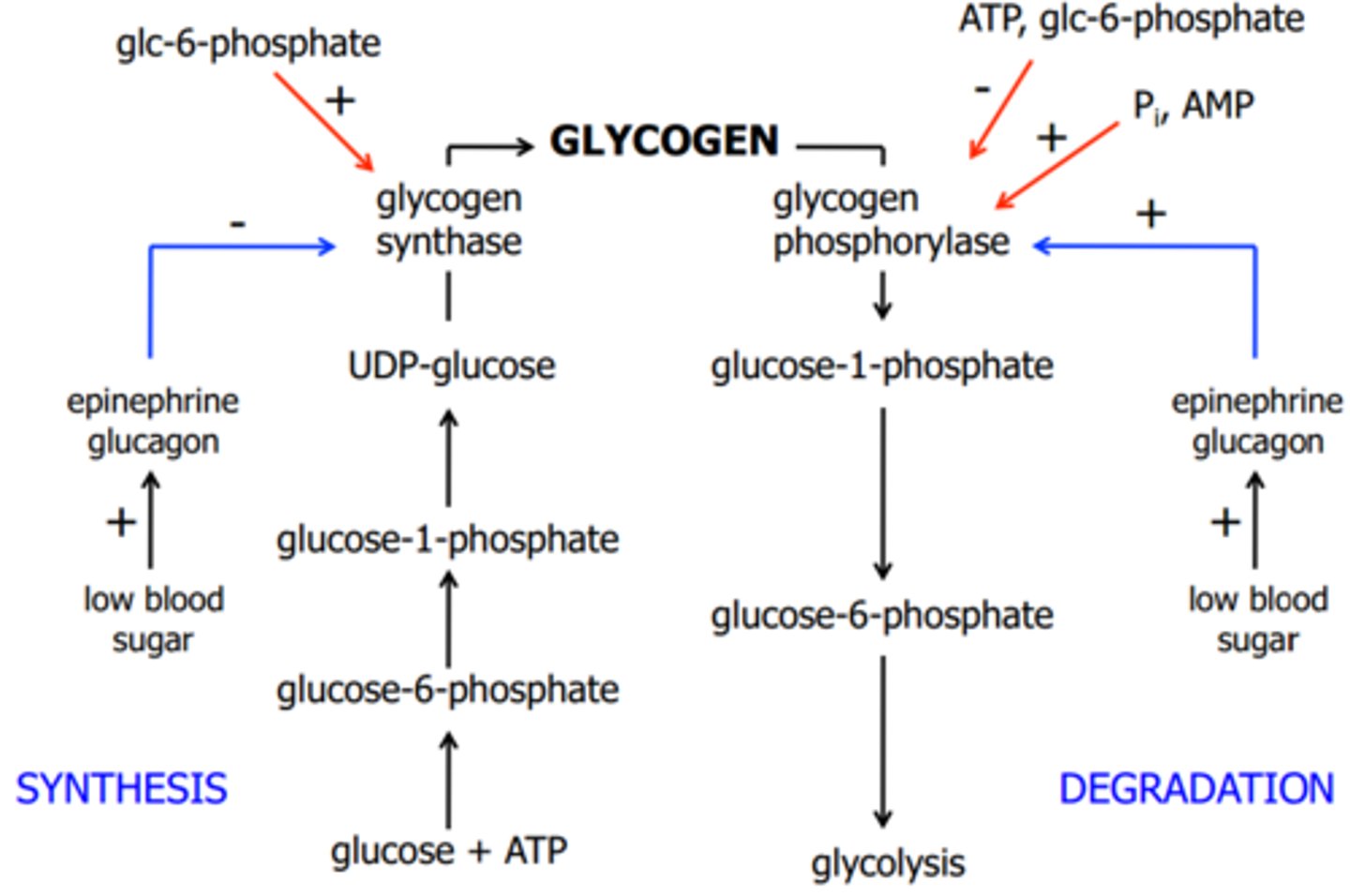
Glycogen phosphorylase
-Cleaves a(1->4) glycosidic bonds between glucose residues at non-reducing ends using phosphate ion as a nucleophile
-Adds phosphate to anomeric carbon of the terminal glycosidic bond
-Releases glucose 1-phosphate
*Cannot act on bonds of the 4 glucose residues closest to the branch point (steric hindrance)*
Release of glucose 1-P
- Muscle: Converted back to glucose 6-phosphate
- Liver: Glucose 1-P is converted to free glucose
Debranching enzyme
1) 4:4 Translocase breaks a 1,4 bond and moves 3 glucosyl residues to main chain
2) a 1,6 glucosidase removes branchpoint residue as free glucose
Pompe Disease, Type II
-Lysosomal a-glucosidase
-All organs with lysosomes
-Infantile form, early-onset progressive muscle hypotonia, cardiac failure, death before 2
-Only lysosomal storage disease
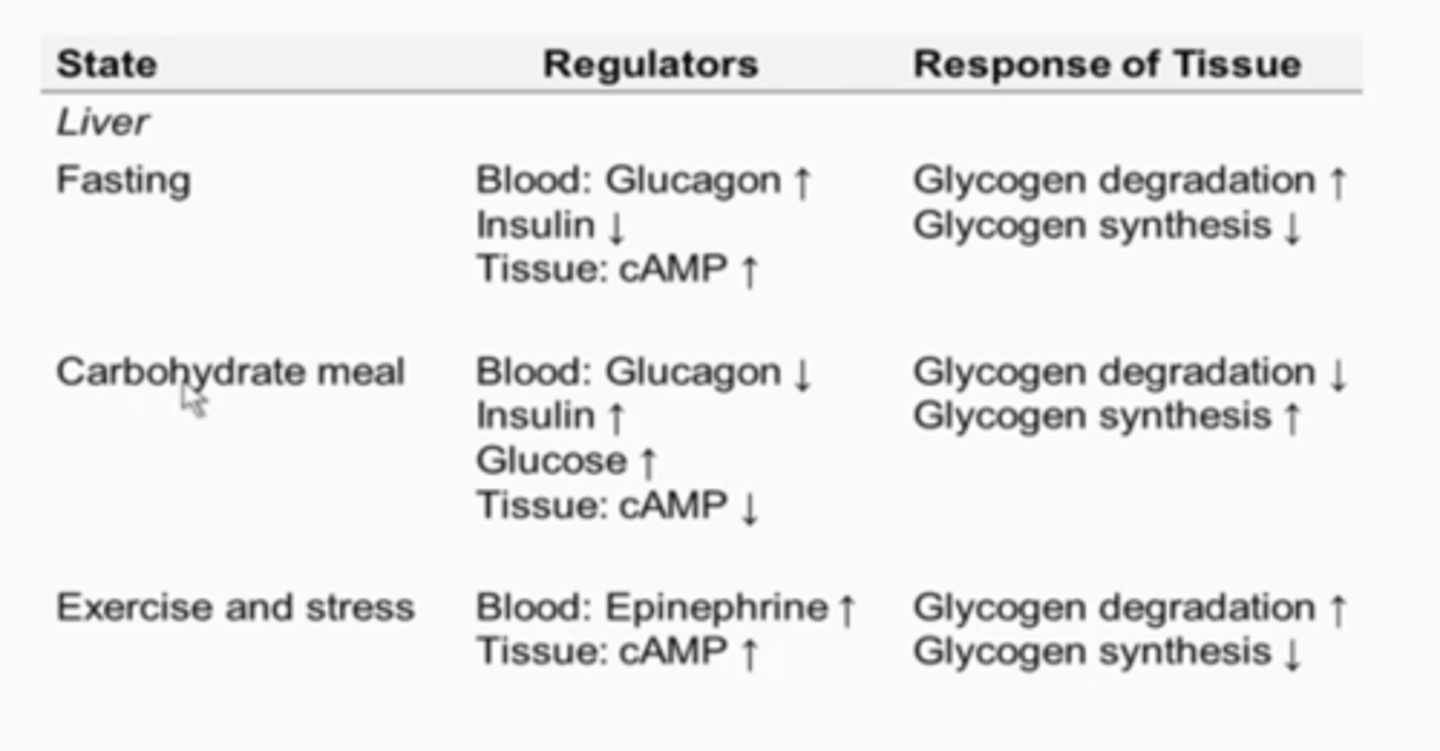
Regulation of Glycogen Stores: Liver
-Glucose to blood
-Insulin
-Glucagon (cAMP)
-Epinephrine (cAMP)
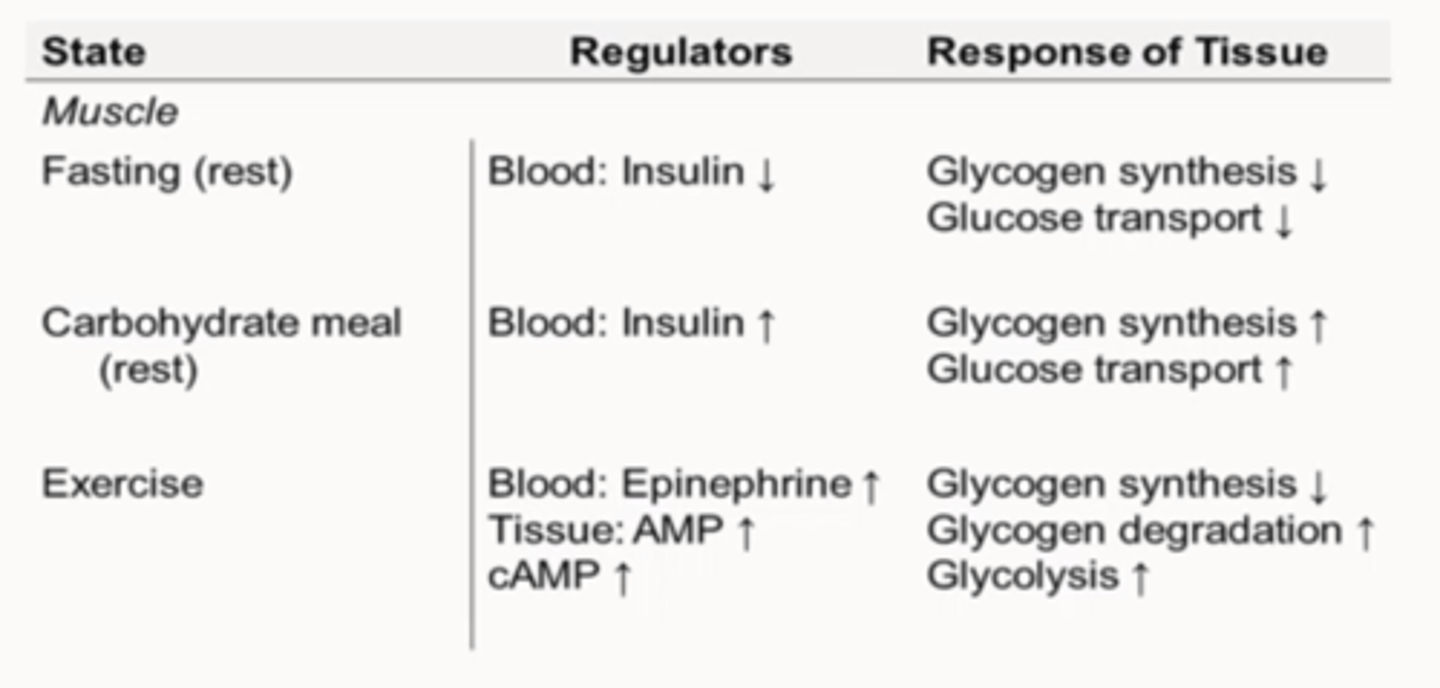
Regulation of Glycogen Stores: Muscle
-Glucose to ATP
-Insulin
-Epinephrine (cAMP)
-AMP
Liver Glycogen
-Glucose is mobilized first from glycogen
-Substantial amount of glycogen is mobilized within first few hours of fast
-First 22 hours of fast: glycogenolysis is fairly constant
-Gluconeogenesis is later
Degradation of Glycogen
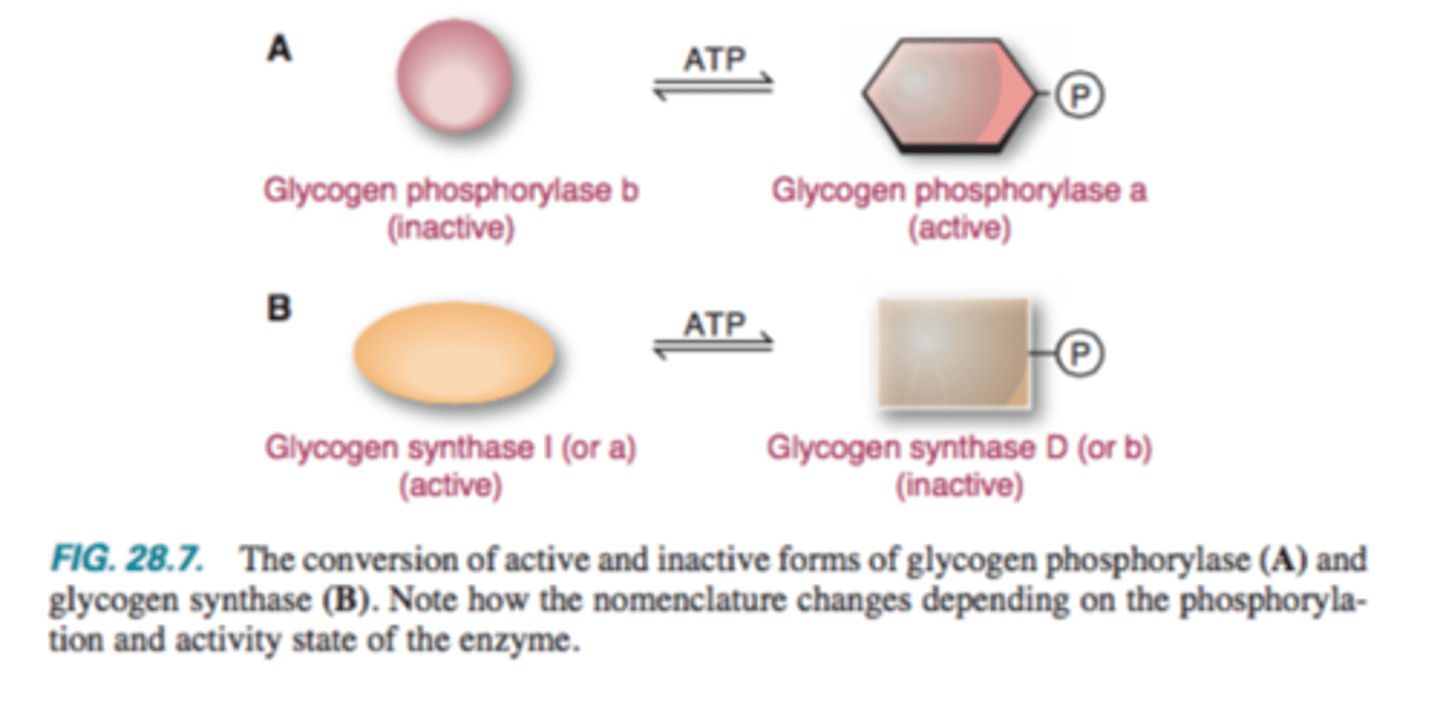
a: Phosphorylated form is ACTIVE
b: dephosphorylated is inactive
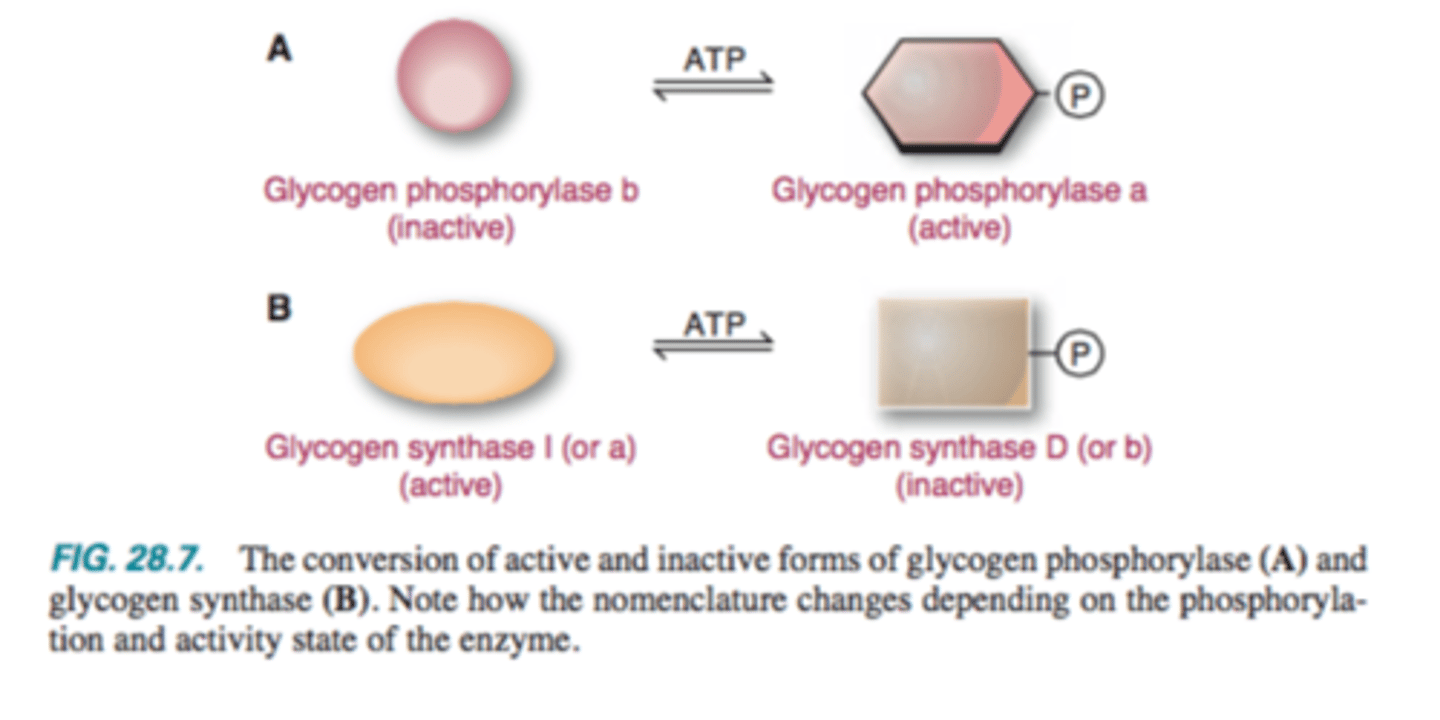
Synthesis: Glycogen Synthase
D: Phosphorylated form is INACTIVE (b)
I: Dephosphorylated form is active (a)
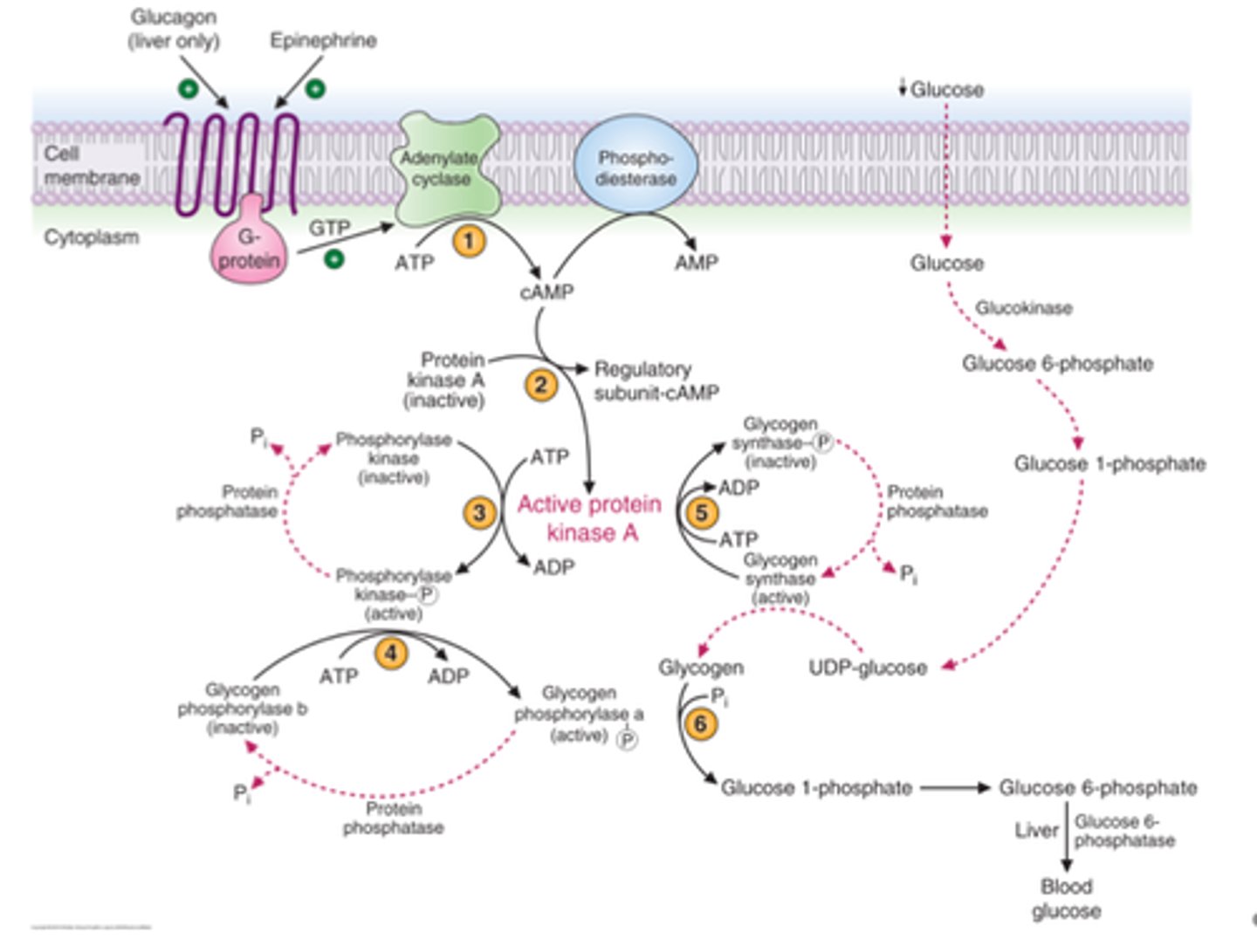
Glucagon activates glycogen degradation and inhibits synthesis in the liver
1) Glucagon receptor associated G protein activate AC to make cAMP
2) cAMP activates protein kinase A
3) PKA phosphorylates & activates phosphorylase kinase
4) Phosphorylase kinase phosphorylates and activates glycogen phosphorylase
5) PKA phosphorylates and inactivates glycogen synthase
6) Glucose 1-P released from glycogen
**Epinephrine (but not glucagon) acts on muscle through B-receptors in a similar way**
Epinephrine action at a receptors in the hepatocyte
1) G proteins activate Phospholipase C: Cleaves phosphatidyl inositol 2P (PIP2) to DAG and IP3
2) IP3 stimulates Ca release from endoplasmic reticulum (Ca and DAG activate Protein Kinase C (plasma membrane))
3) Ca binds calmodulin to activate phosphorylase kinase
4) Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, which phosphorylates and inactivates glycogen synthase (PKC and Phosphorylase Kinase do too)
5) Phosphorylase kinase phosphorylates and activates glycogen phosphoryase