APHG Unit 4 - Political Geography
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
physical geographic boundaries
natural barriers between areas such as oceans, deserts, and mountains
cultural boundaries
boundary that divide people according to some cultural division, such as language, religion, or ethnicity
antecedent boundary
a boundary that existed before the cultural landscape emerged and stayed in place while people moved in to occupy the surrounding area
physical
Antecedent boundaries are typically based on ___________ features
subsequent/ethnographic boundary
boundary that is typically created while the cultural landscape is evolving and is subject to change over time
ethnocentric
Subsequent boundaries are characteristically _______________ in nature, meaning they are usually related to cultural phenomena
ethnocentric
believing in the superiority of one's own ethnic and cultural group, and having a corresponding disdain for all other groups
subsequent/ethnographic boundary
may be drawn to accommodate ethnic, religious, linguistic, or economic differences among groups; often altered as a result of non-cultural developments such as governmental negotiations or war
superimposed boundary
boundary that is drawn by outside powers and may have ignored existing cultural patterns; often LACKS conformity to natural features
landlocked states
states without territory connected to an ocean
relic boundary
boundary that no longer exists, but is still evident on the landscape (ex: Berlin Wall)
geometric boundary
boundary that is a straight line or arc drawn by people that does NOT closely follow any physical feature
consequent boundary
A type of subsequent boundary that takes into account existing cultural or physical landscapes
cultural consequent boundary
border that is drawn taking into account language, ethnicity, religion, or other cultural traits
cultural
Consequent boundaries are created with the _____________ landscape as a PRIMARY consideration
physical consequent boundary
a division that uses already-existing natural features that divide a territory such as rivers, deserts, or mountains
open boundary
boundary that is unguarded and people can cross it easily, with little or no political intervention
militarized boundary
boundary that is heavily guarded and discourages crossing
begins, ends
Boundaries signal where one political entity __________ and another _________.
Uncertain
Throughout history, ___________ boundaries have been a frequent cause of bloodshed and war.
defined boundary
A boundary that is established by a legal document, such as a treaty, that divides one entity from another (invisible line)
delimited boundary
a boundary that is drawn on a map by a cartographer to show the LIMITS of a space
demarcated boundary
boundary that is identified by physical objects placed on the landscape (ex: a sign, set of fences and walls)
definitional boundary dispute
boundary dispute that occurs when 2 or more parties disagree over how to interpret the legal documents or maps that identify the boundary
antecedent
Definitional boundary disputes often occur with _____________ boundaries.
locational/territorial boundary disputes
boundary disputes that center on where a boundary should be, how it is delimited (mapped), or demarcated
irredentism
type of expansionism when one country seeks to annex territory where it has cultural ties to apart of the population or historical claims to the land
operational/functional boundary dispute
boundary dispute that centers NOT on where a boundary is BUT how it functions
state
the largest political unit, the formal term for a country; has a DEFINED boundary, contains a PERMANENT population, maintains SOVEREIGNTY over its domestic and international affairs, recognized by other states
sovereignty
the power of a political unit or gov't to rule over its own affairs
nation
group of people who have certain things in common such as a common CULTURAL heritage, a set of BELIEFS and values that unify them, a traditional CLAIM to a particular space as their HOMELAND a desire to est their own state/express self-rule in another way
nation state
a nation of people who fulfill the qualifications of a state
multinational state
country that contains more than one nation (ex: Canada)
autonomous region
a defined are within a state that has a high degree of self-government and freedom from its parent state
semiautonomous region
A state that has a degree of, but not complete self-rule
stateless nation
A cultural group that has no independent political entity
allocational/resource boundary dispute
a boundary separates natural resources that may be used by both countries
demarcation
How a border is labeled on the physical landscape such as with a fence, wall, stones or signs; can indicate the type of relationship that exists b/w countries and be a clue to how the border functions
administered boundary
how a boundary will be maintained, how it will function, and what goods and people will be allowed to cross
controlled boundary
boundaries that have checkpoints where a passport or visa are required to enter the country; these boundaries ALLOW some people and goods to cross the border while DENYING entry to others
exclaves
Territories that are part of a state, yet geographically separated from the main state by one or more countries (ex: Alaska)
political enclaves
states, territories, or parts of a state or territory that are completely surrounded by the territory of another state (ex: Lesotho)
shatterbelt
a place located between two very different and contentious regions; under consistent STRESS and may suffer INSTABILITY or FRAGMENTATION due to external aggression
internal boundaries
used at the subnational scale to divide countries into smaller units (states, counties, cities, etc.)
electoral geography
using spatial thinking techniques and tools to analyze elections and voting patterns
voting districts
internal boundaries that divide a country's electorate into subnational regions
electorate
people of a country who are eligible to vote; vote for leaders in each district to govern on their behalf
census
a count of the population, ever 10 years
reapportionment
changing the number of representatives granted to each state so it reflects the state's population
redistricting
the redrawing of district boundaries so that each distract contains roughly the SAME number of people
gerrymandering
the drawing of boundaries for political districts by the party in power to protect or increase its power
cracking
type of gerrymandering where you are dispersing a group into several distracts to prevent a majority
packing
type of gerrymandering where you are combining like-minded voters into one district to prevent them from affecting elections in other districts
stacking
type of gerrymandering where you are diluting a minority-populated district with majority populations
hijacking
type of gerrymandering where you are redrawing 2 districts in order to force 2 elected representatives of the same party to run against each other
kidnapping
type of gerrymandering where you are moving an area where an elected representative has support to an area where he or she does NOT have support
centripetal force
force that helps unify people within a country
centrifugal force
force that tends to divide people, break states apart, or even prevent state from forming
nationalism
a nation's desire to create and maintain a state of its own; unifies people
satellite state
independent nation under the control of a more powerful nation
devolution
the transfer of some powers and responsibilities from the federal government to the states; one or more regions are given INCREASED AUTONOMY by the central political unit
self-determination
the right of people to choose their own sovereign government WITHOUT external influences
geopolitics
the study of the effects of geography on politics and relations among states
territoriatlity
a willingness by a person or a group of people to defend space they claim; key concept in geopolitics
neocolonialism
economic, political, or even cultural control that is indirectly exerted over developing countries
choke point
place of physical congestion between wider regions of movement and interaction
federal state
state that unites separate political entities into an overarching system that allows each entity to maintain some degree of sovereignty
unitary state
state where most or all of the governing power is held by the NATIONAL government
large, US, Canada, Russia
__________ landmass countries - such as _________, ____________, & __________ - tend to be federal states
smaller, Japan, Egypt, Spain
__________ landmass countries - such as _________, ____________, & __________ - tend to be unitary states
annexation
the process of legally adding territory to a city
European Union (EU)
a political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe; trading partners
subnationalism
describes people who have a primary allegiance to a traditional group or ethnicity
ethnic separatism
the advocacy of full political separation (or secession) from the larger group along cultural, ethnic, tribal, or governmental lines
ethnic cleansing
Process in which more powerful ethnic group forcibly removes a less powerful one in order to create an ethnically homogeneous region
autonomous regions
regions that have their own local and legislative bodies to govern a region w/ a population that is an ethnic minority within the entire country; they handle their own DAY-TO-DAY GOVERNANCE BUT are NOT fully independent from the state in which they are located
Balkanization
the fragmentation of a state or region into smaller, often hostile, units along ethno-linguistic lines
supranationalism
the practice of multiple countries forming an organization for the benefit of all members
democratization
the transition from autocratic to more representative forms of politics
time-space compression
the social and psychological effects of faster movement of information over space in a shorter period of time
regionalism
when loyalty to a distinct portion of a country is more important than loyalty to the entire country
ethnonationalism
support for the political interests of a particular ethnic group within a state, especially its national independence or self-determination
Organic Theory
theory that argues that states are born and that they need nourishment and living space to survive; lebensraum; Friedrich Ratzel
Heartland Theory
theory that argued LAND-based power was essential in achieving global domination; Sir Halford Mackinder
Rimland Theory
theory that argued power is derived from controlling strategic MARITIME areas of the world (SEA POWER WAS KEY [the RIMLAND comprises densely populated coastal areas that reside outside the heartland; they have more varied resources than the heartland & access to the sea])
compact
state shape in which the distance from the center to any boundary does not vary significantly.
elongated
state shape that has a long sliver of land that extends far in one direction; can be challenging for communication
fragmented
state shape whose territory is disconnected and divided into segments; looks broken; usually separated by water
enclave
a distinct region or community enclosed within a larger territory
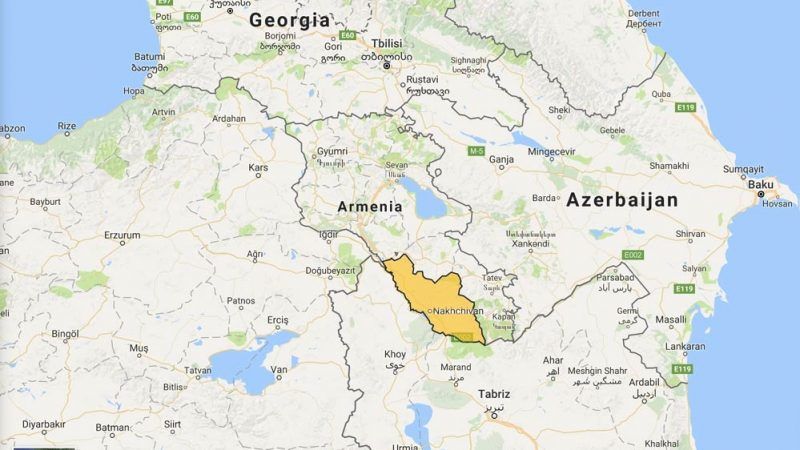
perforated
a state that completely surrounds another state
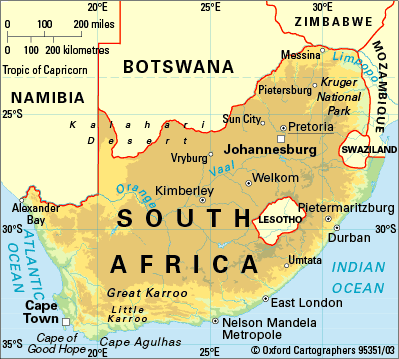
prorupted
a compact state with a large projecting extension