Necropsy Technique (Cram)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Decomposition is more rapid in _____ and ________ animals, due to heat retention and the fermentation process
obese, ruminants
True or false: If a necropsy cannot be done immeadiately after death, it is often better to freeze the specimen than just refrigerate it
False. Freezing creates artefactual changes
What are the two diseases that if you suspect, you should NOT cut into the carcass?
Rabies
Anthrax
What is the agency that should be notified if a veterinarian suspects an animal is affected with rabies?
CFIA (Canadian Food Inspection Agency)
What is the best method of carcass disposal? It is not always practical for large animals
Incineration
What are some other ways of disposing a carcass?
Deep burial, natural disposal, rendering, composting
What is the most important necropsy record to have?
Signed consent form from the client
How should you position a ruminant for a necropsy, why?
Left side down, keeps rumen out of the way
How do you place a small laboratory animal, fur–bearing animal, or cat for necropsy?
Pinned on its back, on a special board
What are the lungs, heart, mediastinum, trachea, esophagus, and tongue called as a unit?
Pluck
In large animals, what is the structure that indicates where you should tie off so that the forestomachs and abomasum should be removed as a unit?
Ampulla of Vater (aka: Hematopancreatic ampulla, union of pancreatic duct and common bile duct)
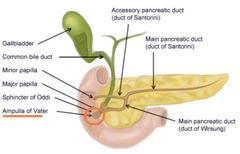
Which bones do you cut through to release the larynx, trachea, and esophagus from the skull?
Hyoid bones
What joint do you cut through to remove the skull from the cervical spine?
Atlantooccipital joint (specifically from the ventral side)
How do you ensure that a joint is free of hair or surface micro–organisms before taking a synovial fluid or membrane sample?
Skinning first
What solution is used to fix eyes and the pituitary gland?
Bouin's solution
True or false: Samples for culture are fixed in formalin
False. Samples for culture shoudln't even be put NEAR formalin. This will kill microbes
Large tissue samples don't fix well. What is the maximum size of sample in thickness you should cut?
1cm in thickness
What is the ratio of fixative to tissue in a specimen jar?
10:1 (ie. 10L formalin to 1L tissue)
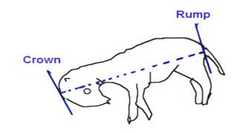
What is the meaurement used to determine gestational age on an aborted fetus?
Crown to rump length
What is the most important tissue sample to collect from an aborted fetus?
Placenta with caruncles
What is the fluid sample that is important to collect from fetuses, where can you take it from?
Amniotic fluid from stomach or abomasum
What is the zoonotic risk that makes it so psittacine (parrot–type) birds are soaked in disinfectant (genus species)?
Chlamydia psittaci
What does Chlamydia psittaci cause in humans?
Parrot fever (aka psittacosis or ornithosis)
What is a consideration you should make when sending an entire bird carcass to the lab?
Proper cooling and expedite shipping
What are the three basic principles of specimen submission?
Preservation of specimens
Safety of handler and other
Compliance w/ legal requirements
Submissions for _____________ should be routinely fixed
Submissions for histopathology should be routinely fixed
What is the range of pH of 10% buffered formalin?
6.8–7
What is the solution used to to preserve retiuclo–endothelial tissue (lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, bone marrow)?
Zenker's fixative
What are the the other two tissue types zenker's fixative is used on?
Congested tissue
Nerve tissue
What solution do you put zenkerized tissues into after 6–8 hours to prevent them from excessive hardening?
70% alcohol (needs to be done for bouin's fixative too)
What is the safer alternative to formalin, it is not a dangerous good (WHMIS)?
Mirsky's fixative
True or false: Sections of intestine should not be tied off to be placed in fixative for histopathology samples
True. They need to be cut open, otherwise they'll float
Can you pool histopathology samples?
Yes
Can you pool microbiology samples?
No
What is the amount (grams) to collect for a microbiology sample?
100–400g
True or false: Like for histopathology, GIT samples should not be tied off
False. They can be tied off at both end because they are not being fixed
What is a common situation in microbiological samples that will yeild false results?
Animal was treated with antibiotics
What are the two organs always taken for toxicology?
Liver
Kidneys
True or false: You should never request "routine" testing for toxicology. There are thousands of toxins to potentially test for
True. Make specific requests
What solution should you fix ectoparasites in?
70% ethyl alcohol
What solution should you preserve fecal samples for parasite examination in?
2.5% potassium dichromate
Should you fix your blood smears before sending them to the lab?
No
What are the two phases of a disease that you should collect a paired serum sample from?
Acute phase
Convalescent phase
What can be learned from sending in just one serum sample?
The animal was vaccinated or previously infected. Not very helpful information!
What should you NOT pack blood or cytology slides with?
Formalin containers, will affect the stain rendering it useless
What are the three containers used for packing specimens?
Primary container
Secondary container
Tertiary container
What kind of writting device is used to label specimens?
Permanent marker

What happens to whole blood during transportation?
Hemolysis. Blood slides, serum, or plasma can be sent
What is the medium used for virology samples?
Viral transport medium
What is the term that means "in its original place", used to refer to the examination of a structure without removing it from the animal
In–situ