Thalamus
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Diencephalon has 4 major parts
epithalamus, subthalamus, hypothalamus, thalamus
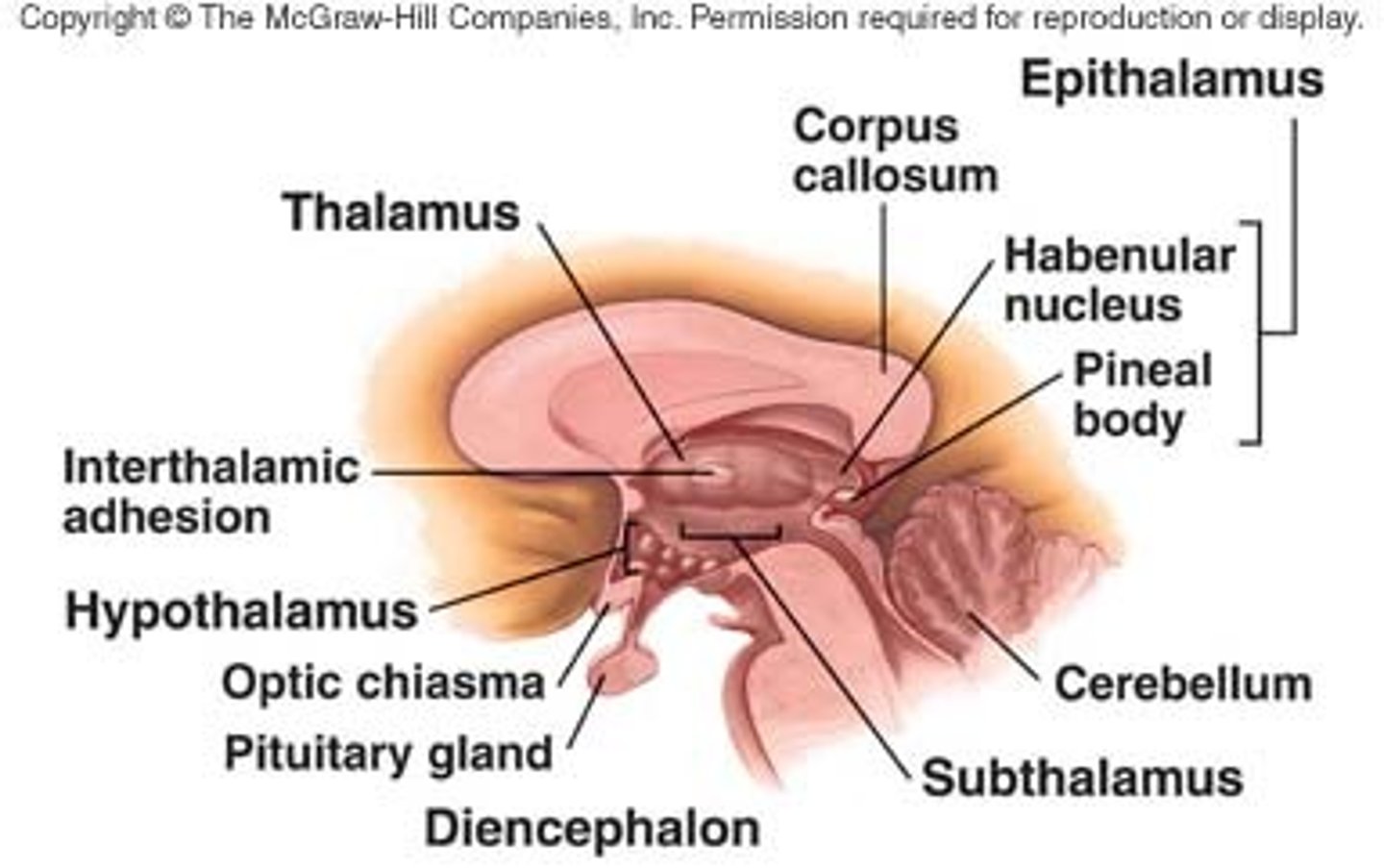
Epithalamus
contains habenula and pineal gland
Habenula (epithalamus)
pathway for limbic system to influence brainstem reticular formation;
emotions to influence autonomic functions
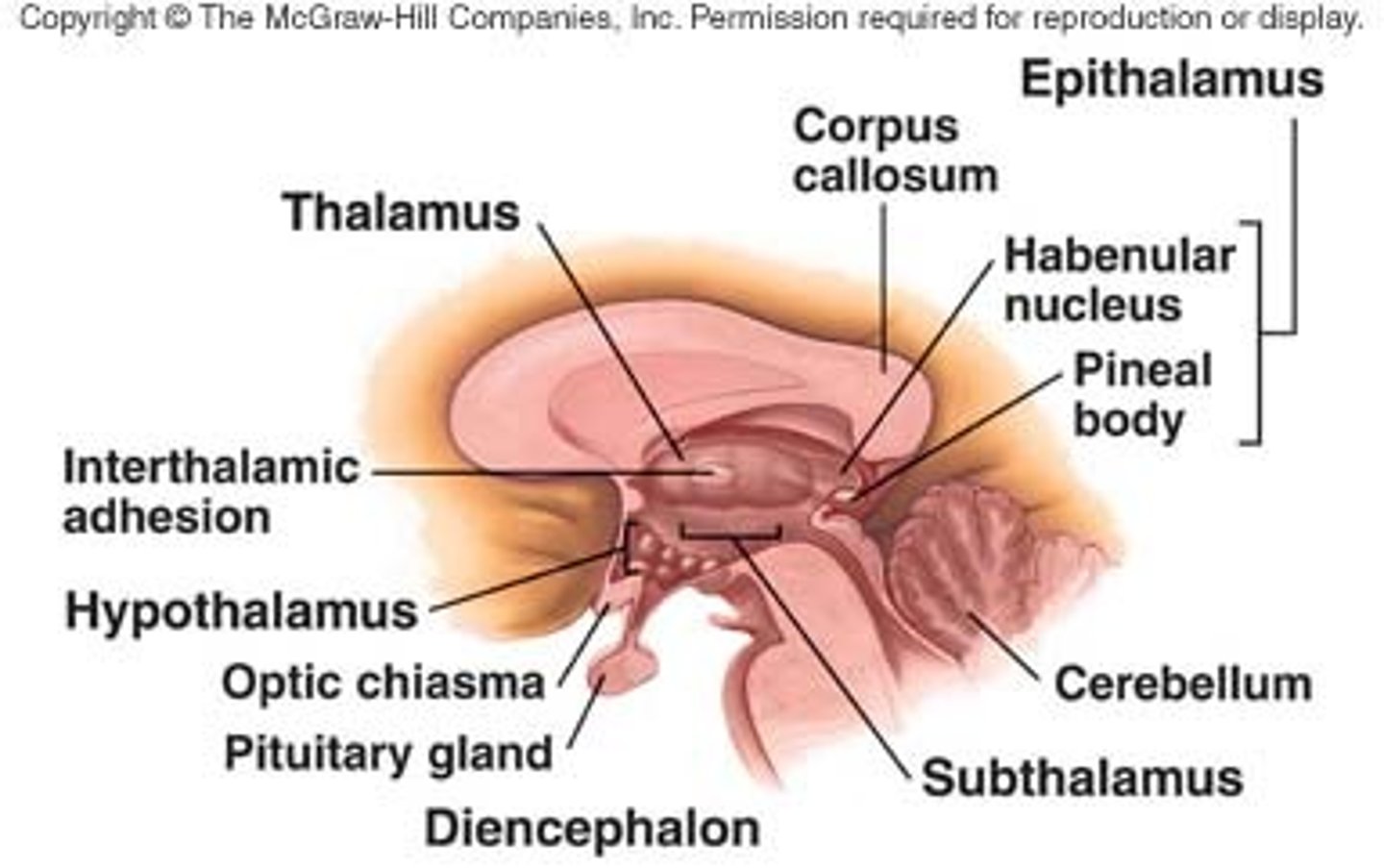
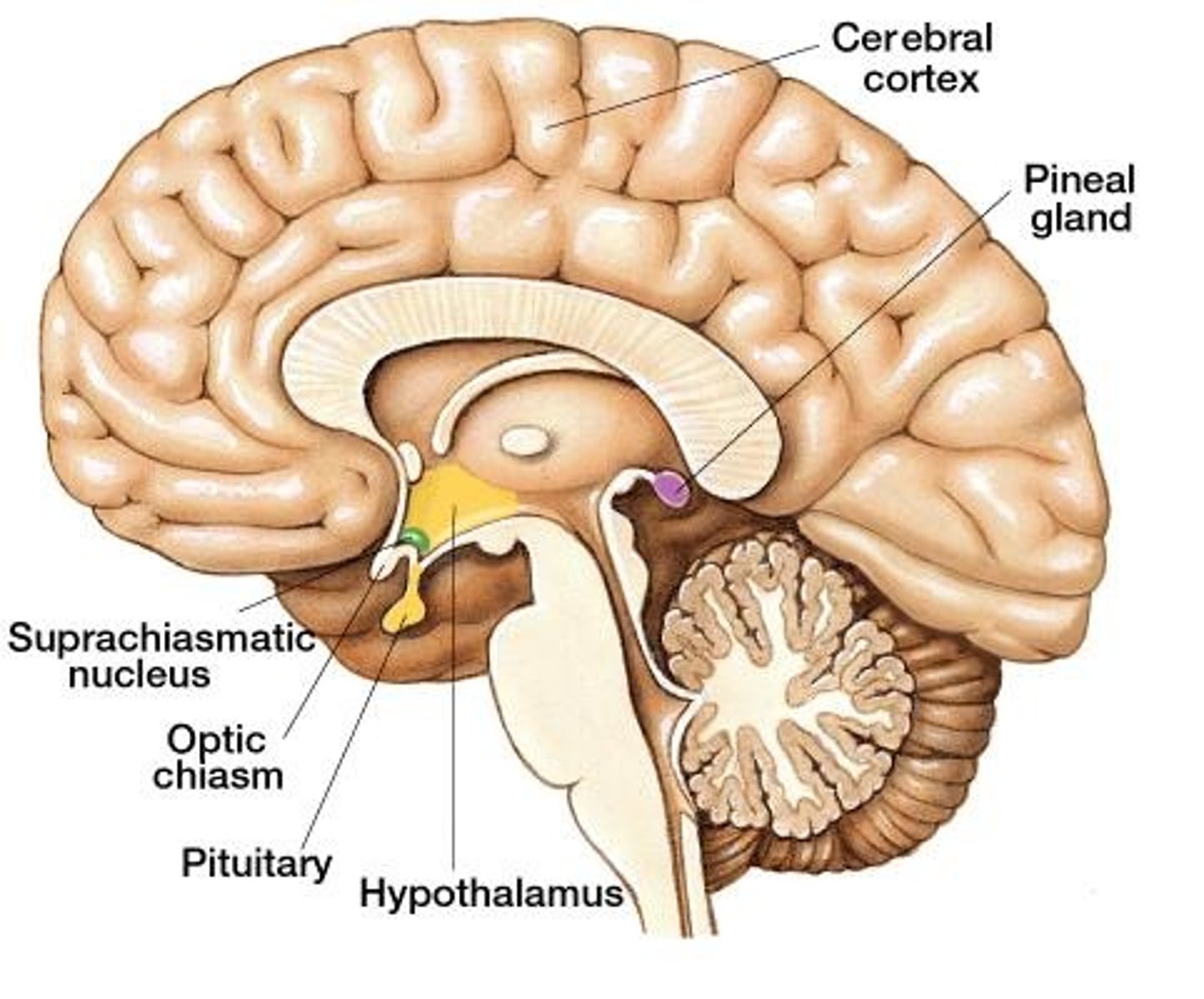
pineal gland (epithalamus)
endocrine organ that releases melatonin. Codes photoperiodism; inhibited by light
tumors associated w/ early puberty
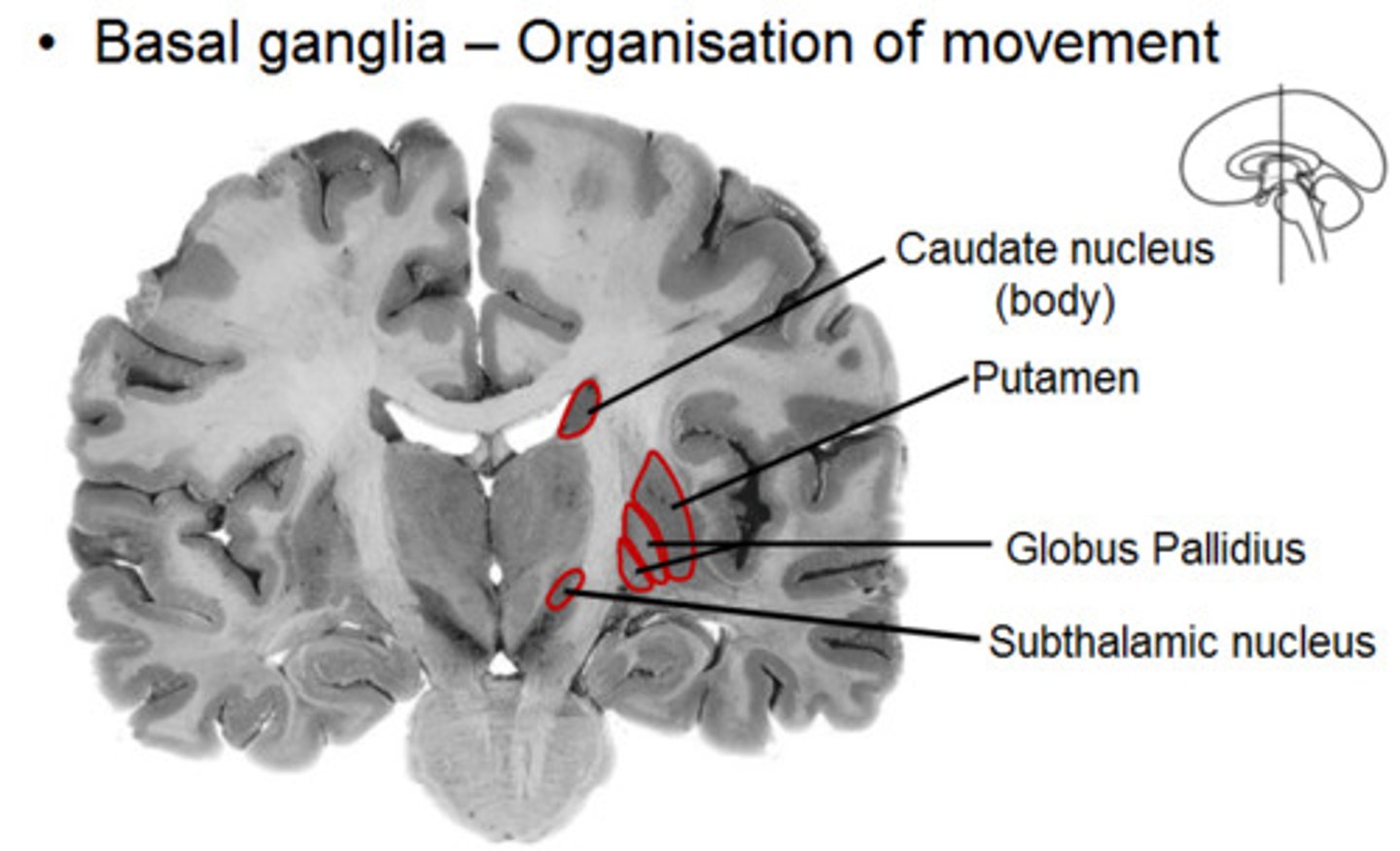
Subthalamic nucleus (subthalamus)
major role in indirect pathway of basal h=ganglia cortex modulation;
inhibiting movements
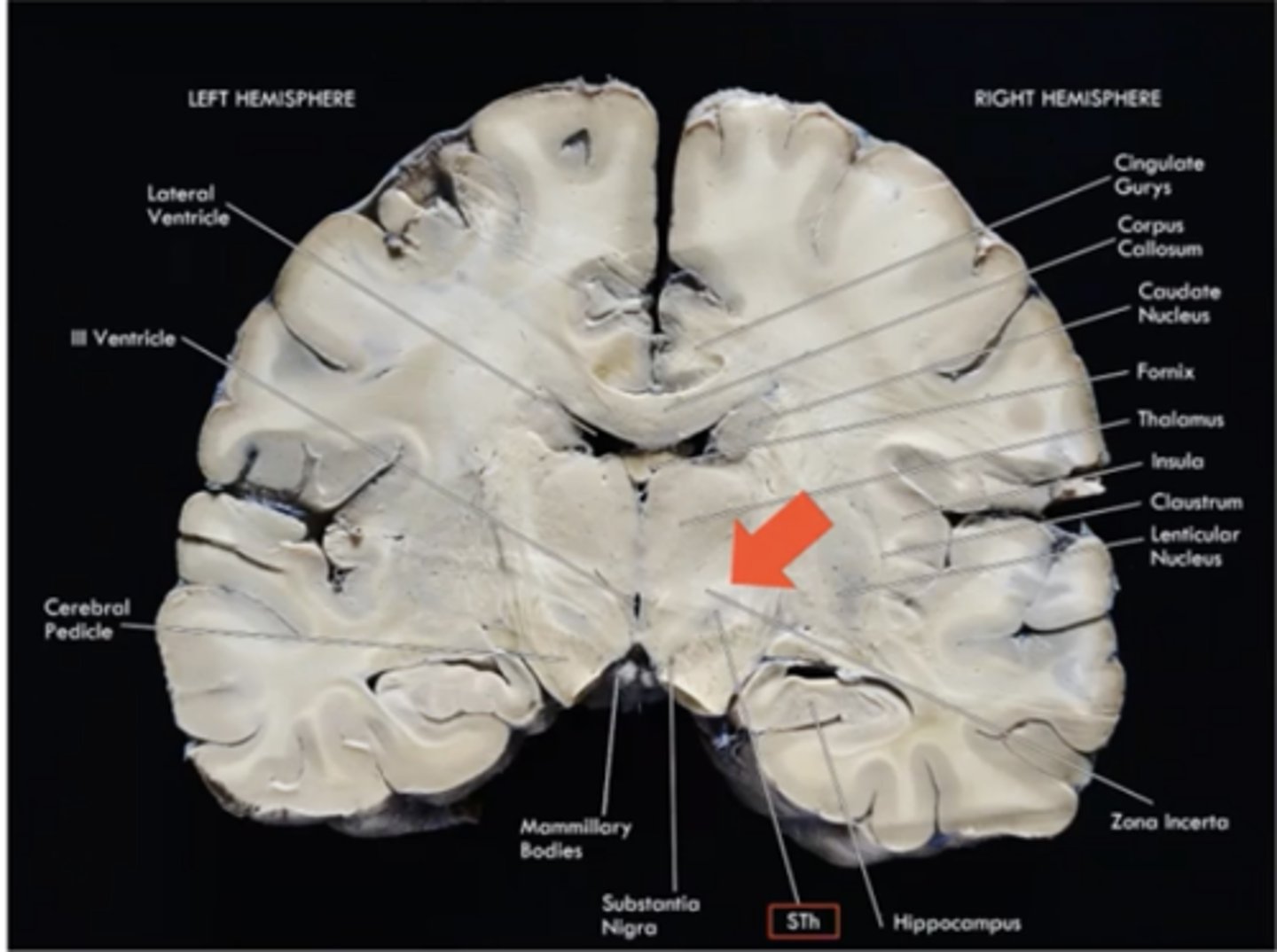
zona incerta (subthalamus)
rostral continuation of the midbrain reticular formation;
regulate consciousness, arousal, and attention
Thalamus
-all sensory pathways relay in the thalamus except smell
-31 nuclei separated by internal medullary lamina
- divided into anterior, medial, lateral ( dorsal, ventral)
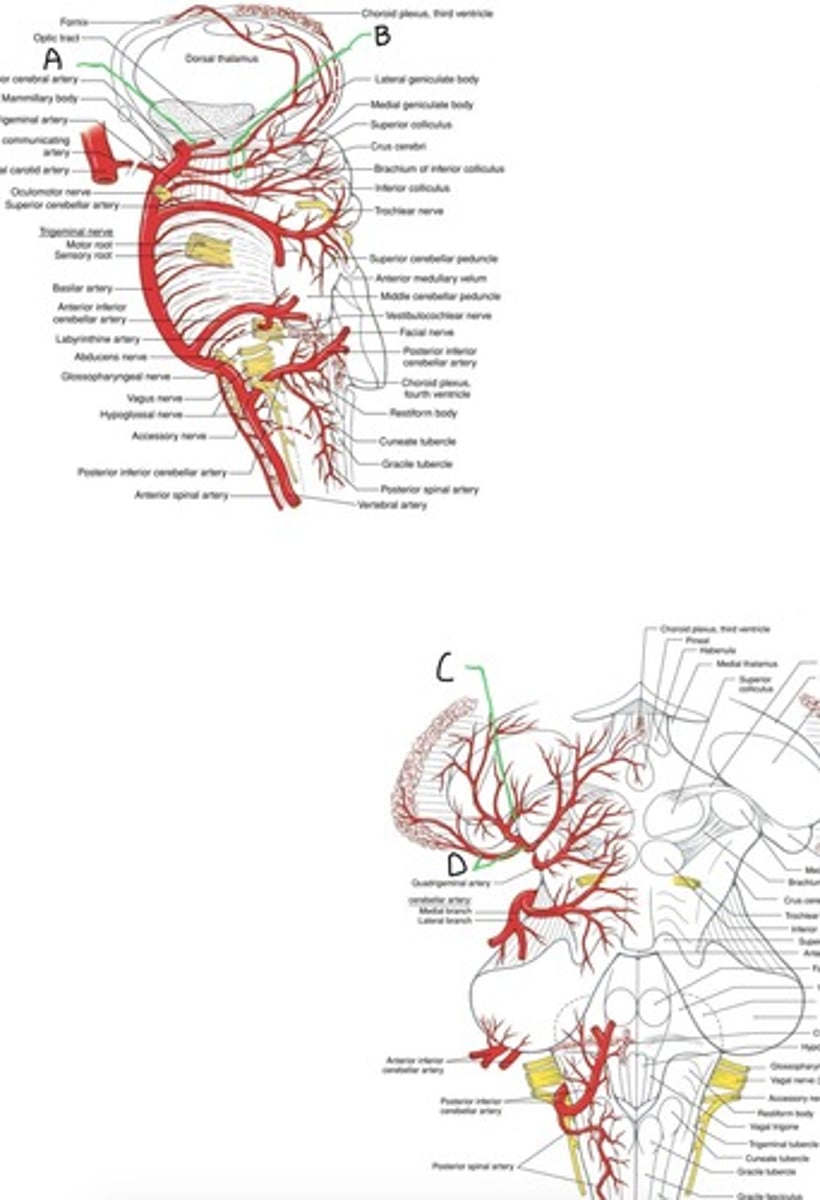
Blood supply of the thalamus
supplied by the tuberothalamic branch of posterior communicating artery and brs of the posterior cerebral artery; thalamogeniculate arteries
Thalamocortical relays
sending ahead to cortex
ex: spinothalamic
thalamic reticular nuclei
regulates if information leaves thalamus
like attention, consciousness
Anterior nucleus
-sensory from mammillothalamic tract
-motor info to cingulate gyrus
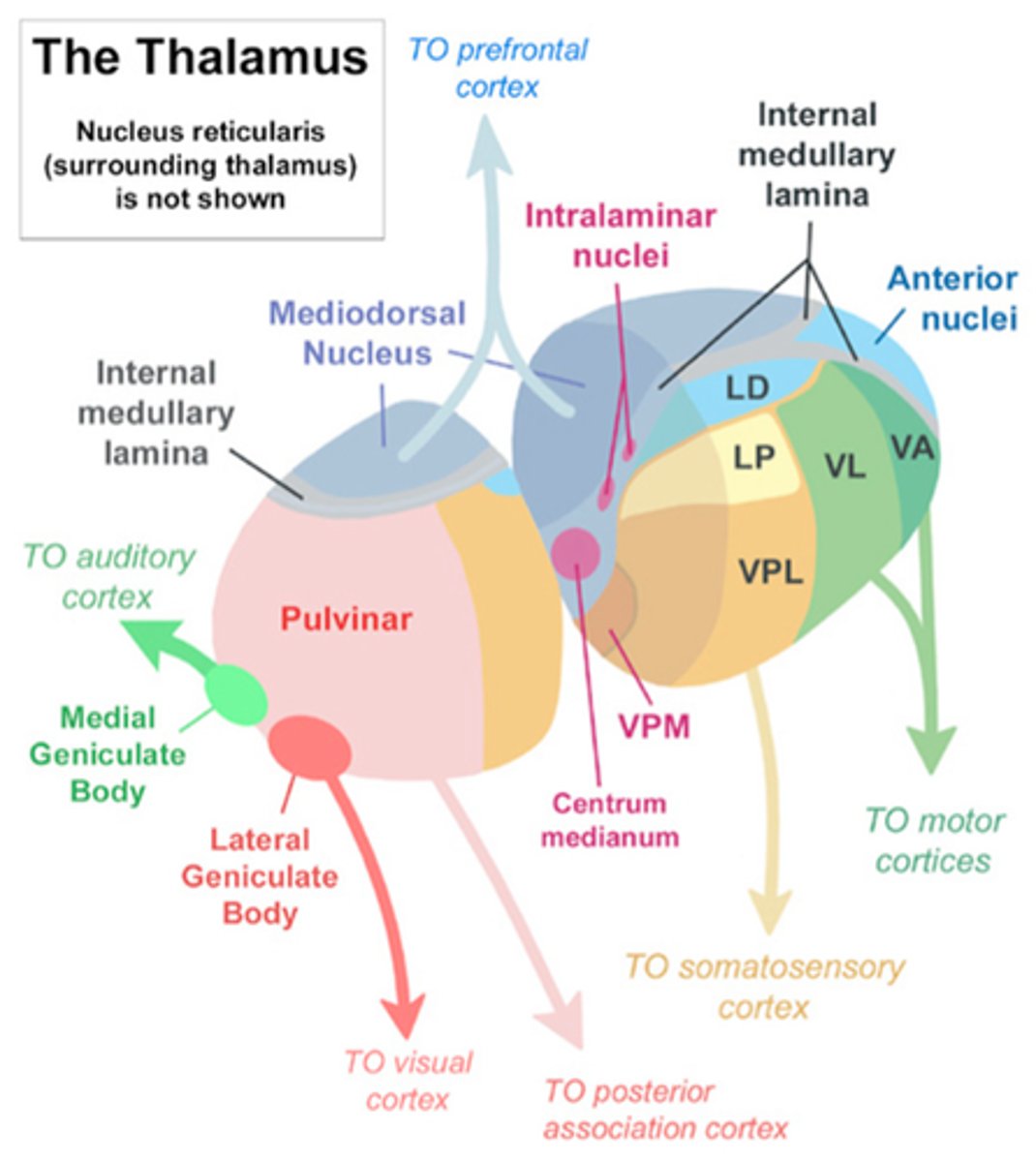
Dorsomedial nucleus DM
sensory: prefrontal cortex, olfactory, and limbic
Motor: prefrontal cortex
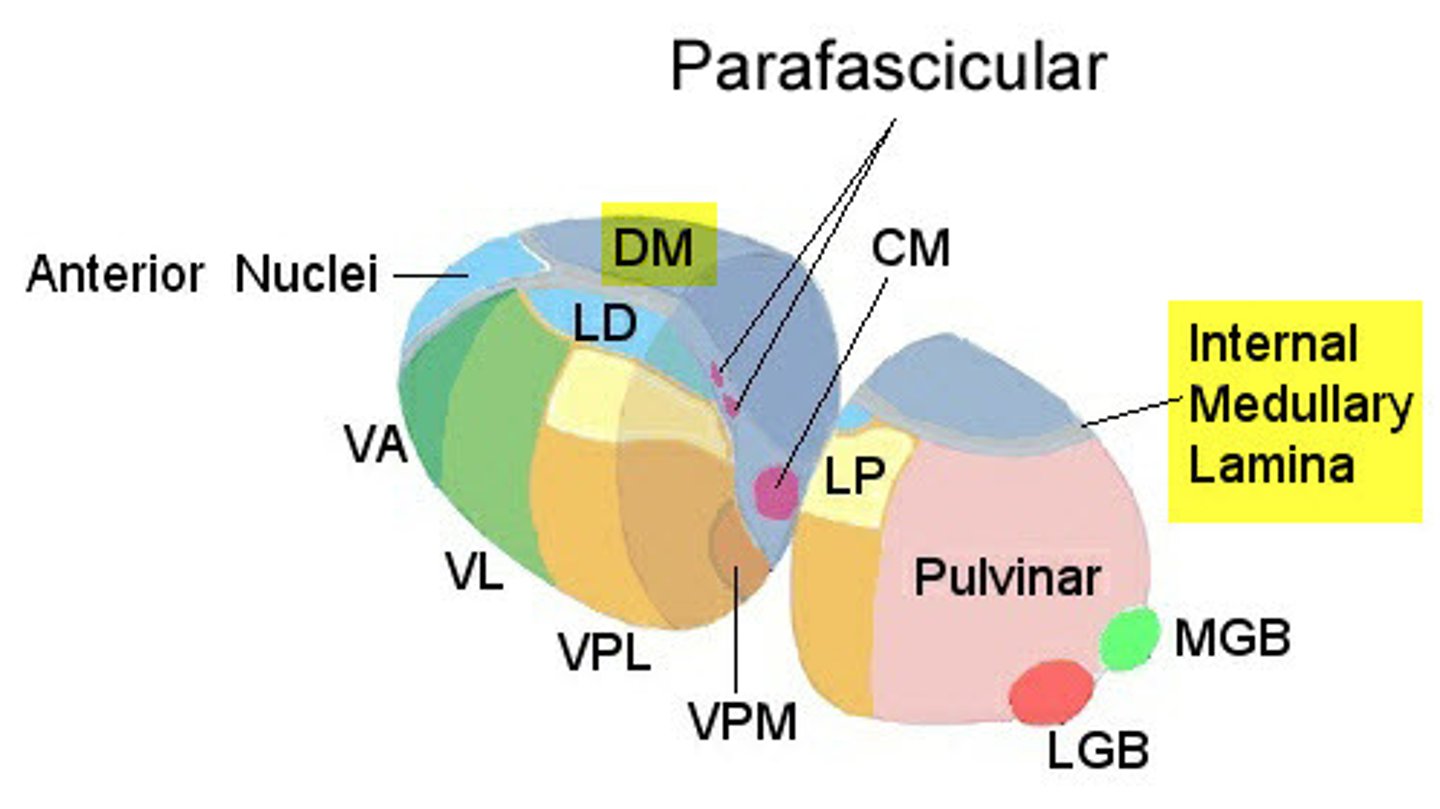
Laterodorsal nucleus LD
sensory: hippocampus
motor: cingulate gyrus
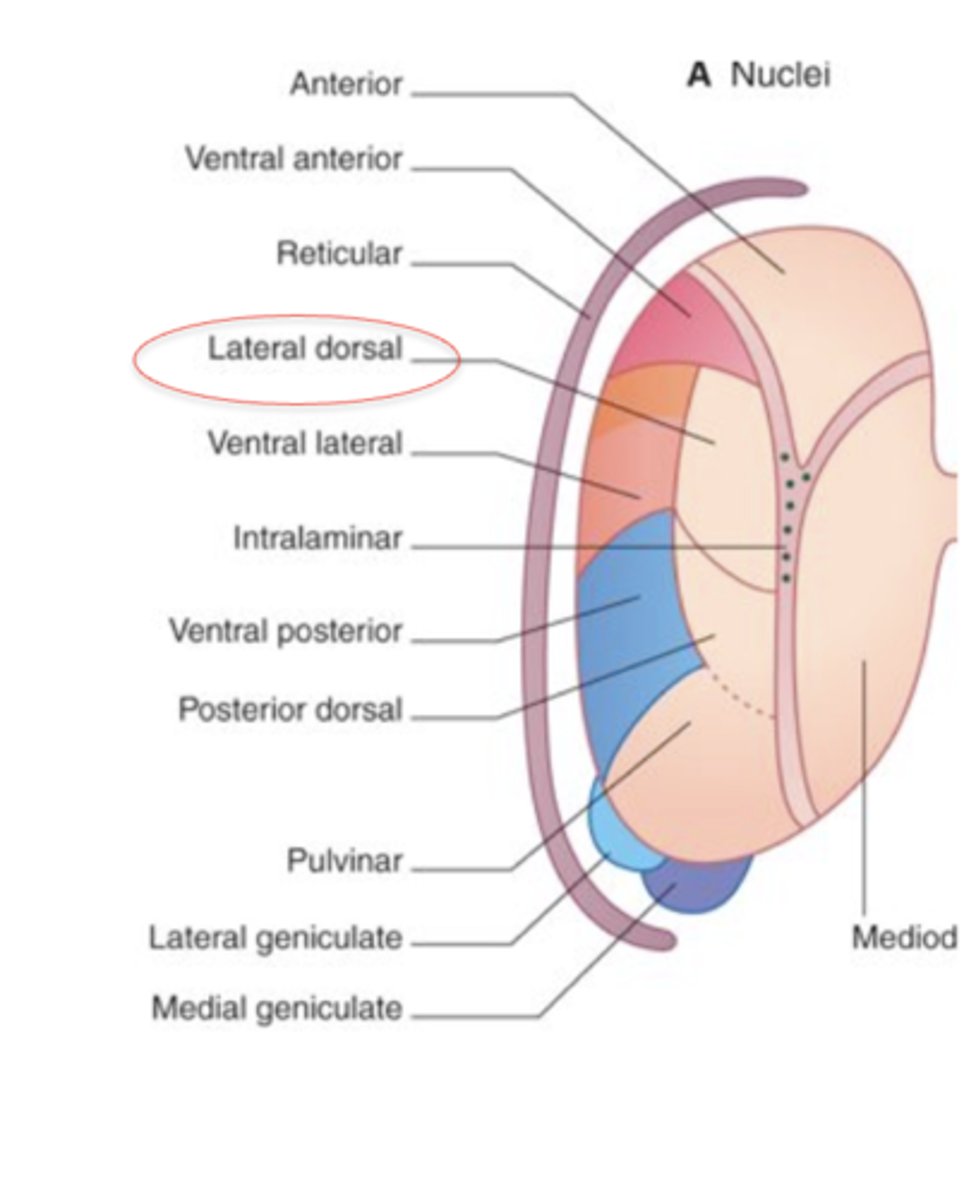
Lateral posterior LP/ pulvinar
Connected reciprocally w/ parieto-occipital-temporal association cortex; vision
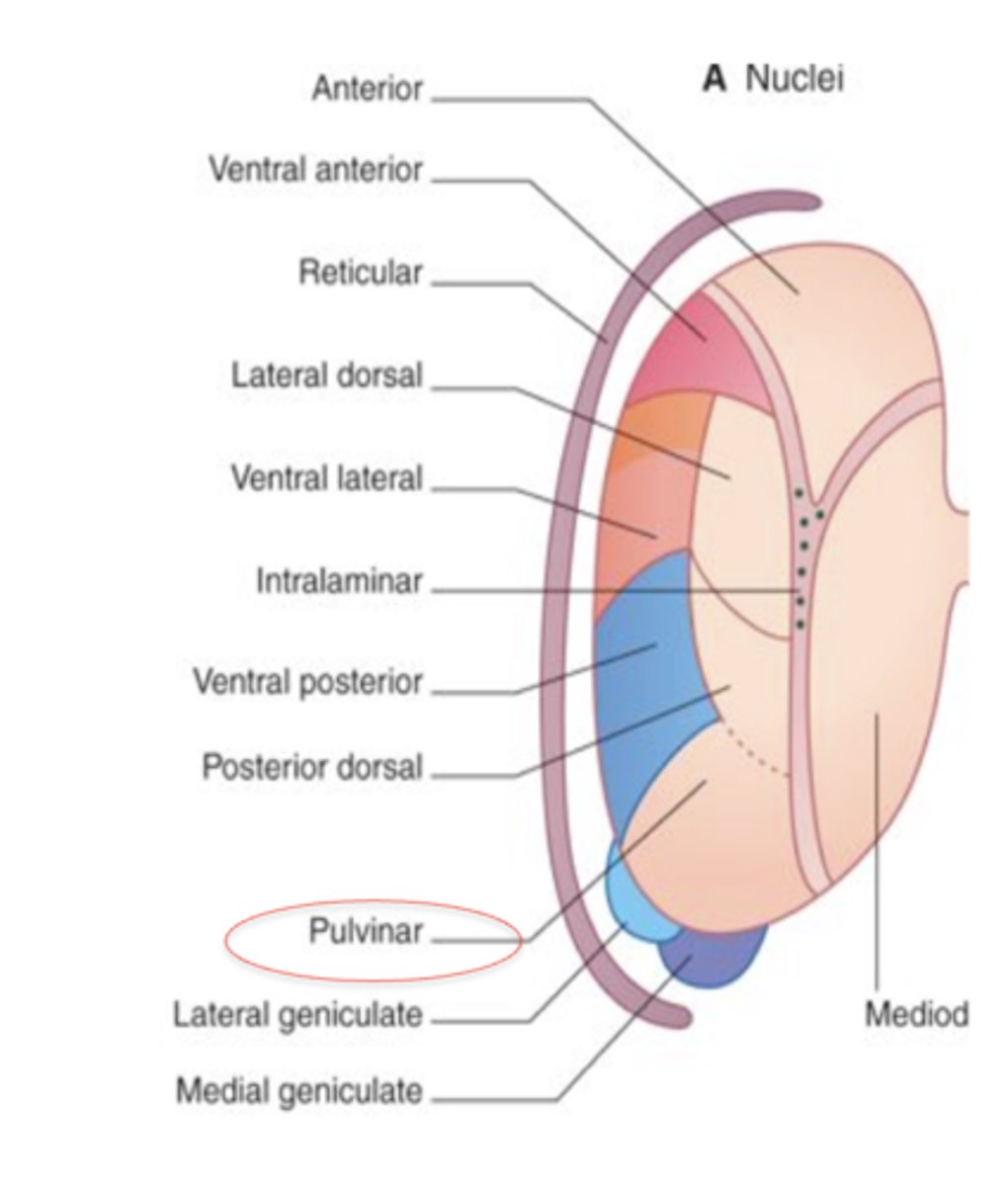
Ventral anterior, ventral lateral (VA, VL)
motor control
VA: basal ganglia
VL: cerebellum
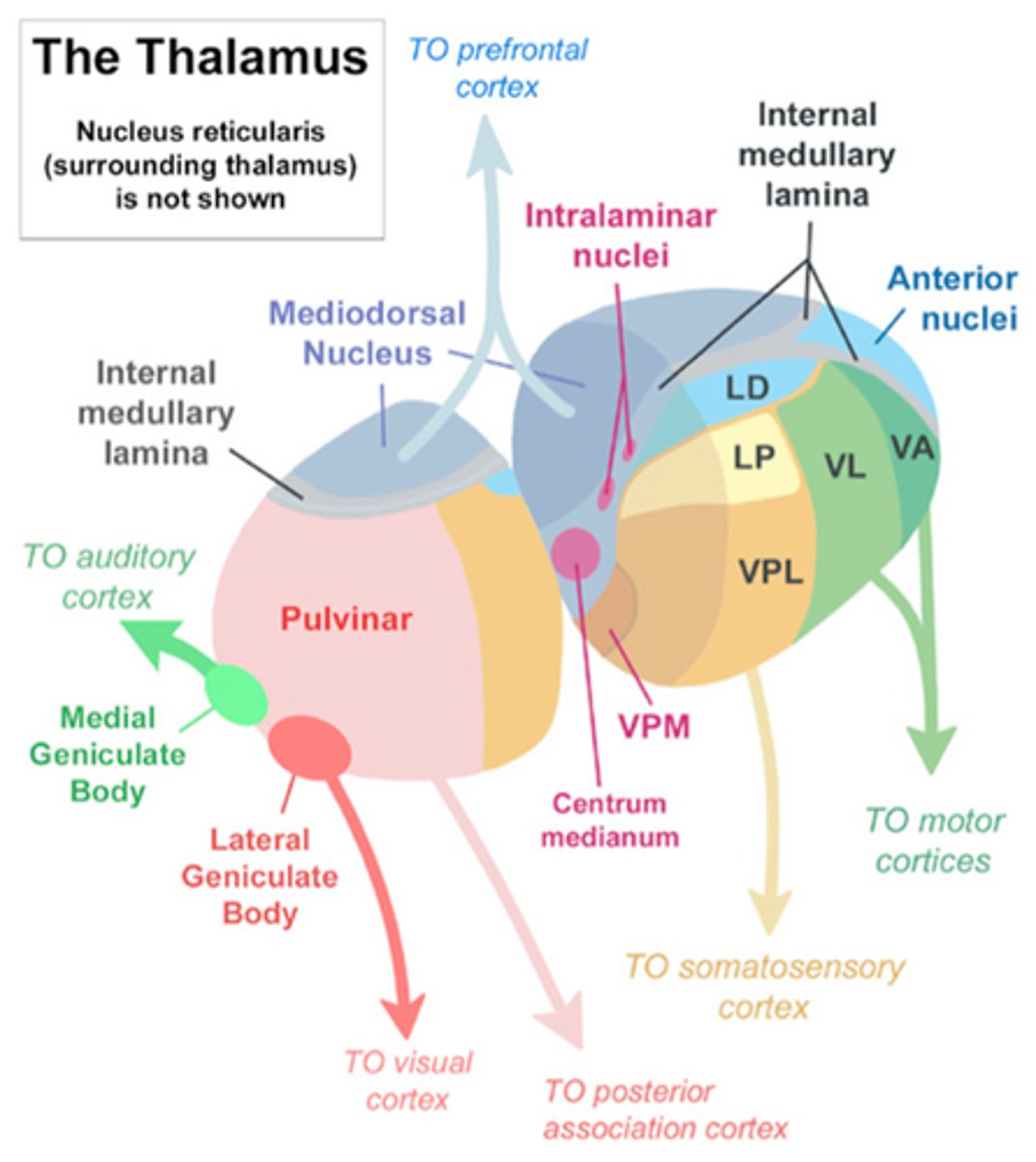
Ventral posterior lateral VPL
Sensory: medial lemniscus, spinothalamic (trunk and extremities)
Motor: somatosensory cortex
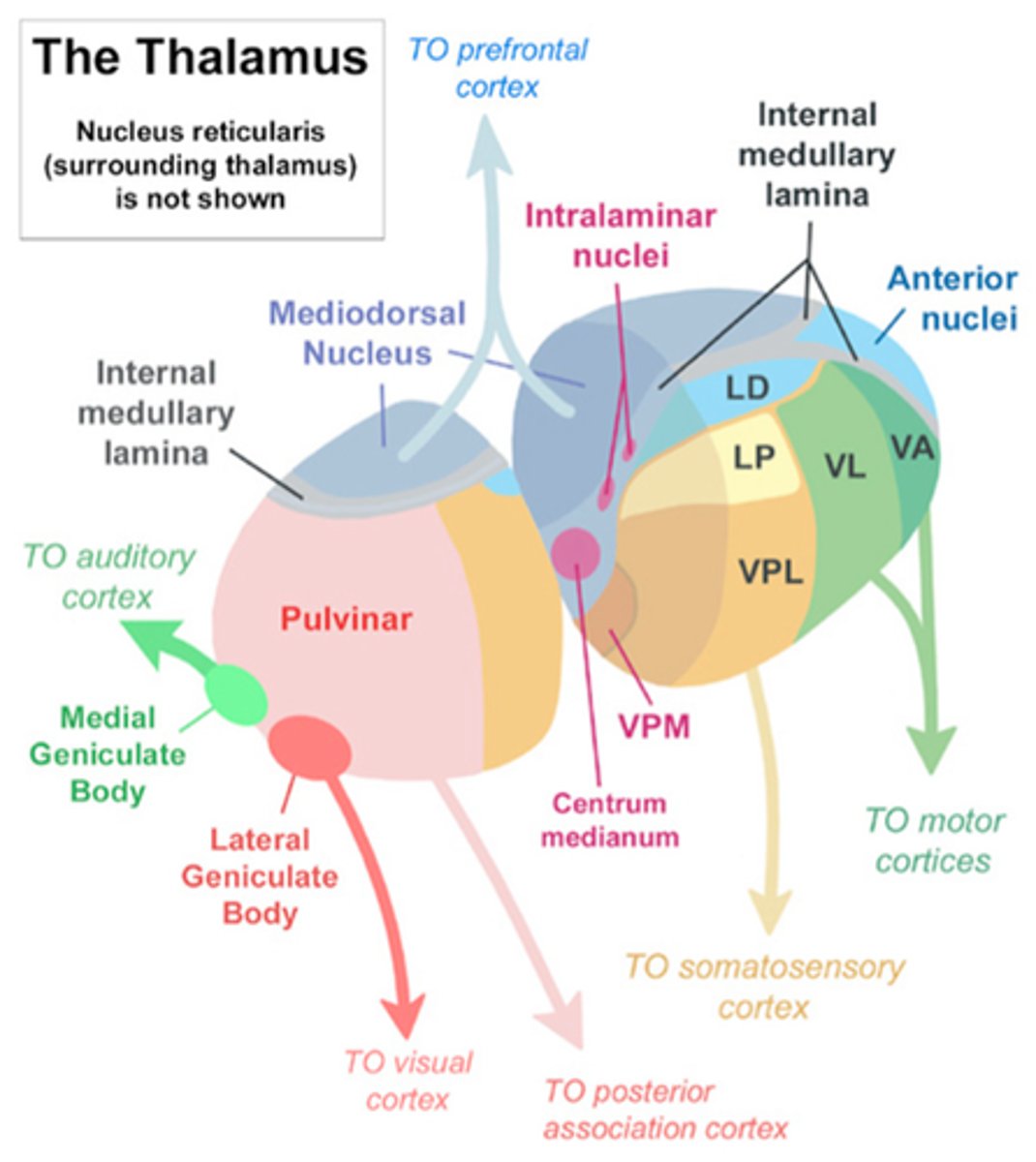
Ventral posterior medial VPM
Sensory: trigeminothalamic (head)
Motor: somatosensory cortex
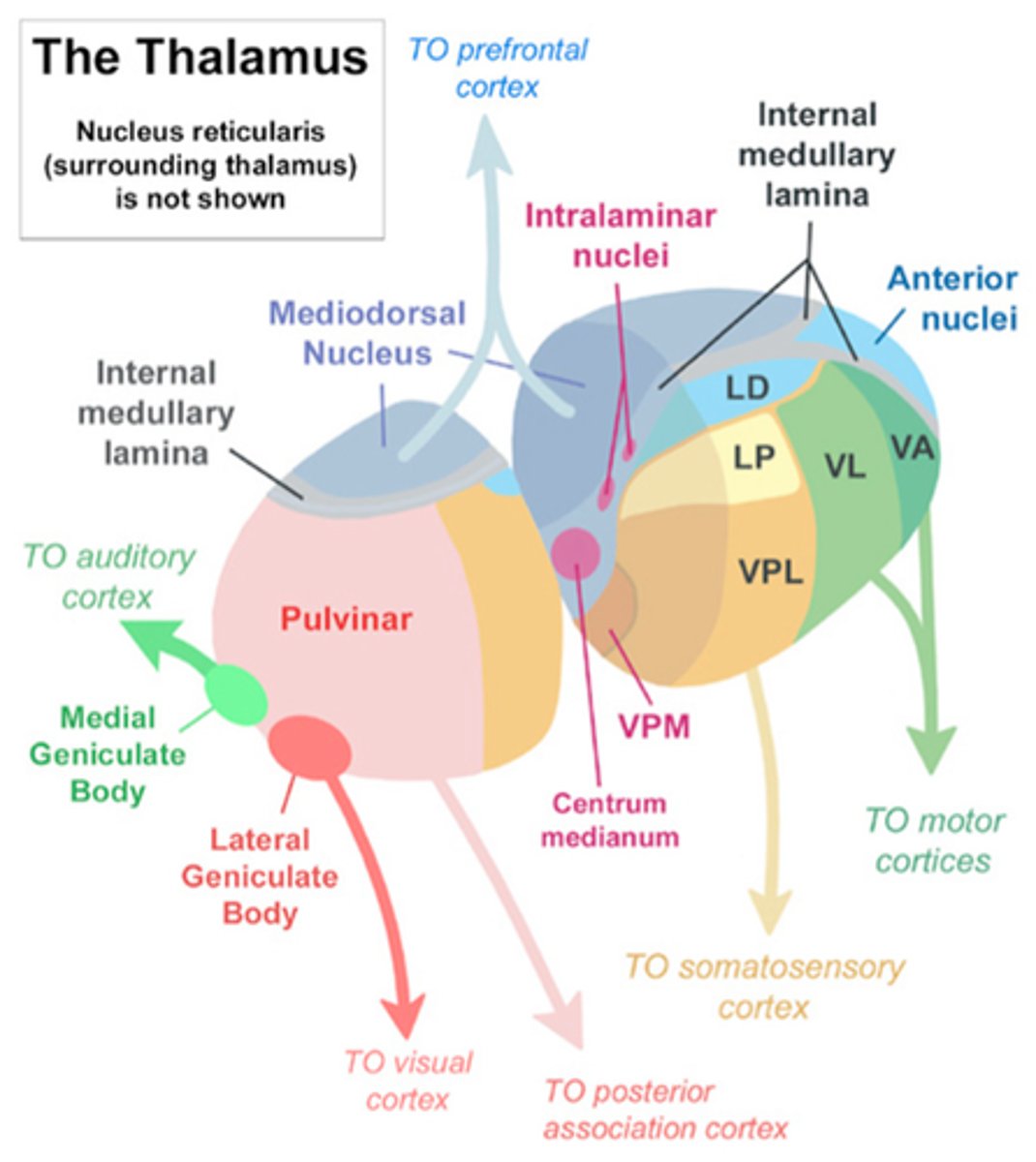
Vascular damage in the thalamogeniculate arteries
cause major damage to VPL/VPM, thalamic pain
Thalamic syndrome
extensive damage can cause ataxia and tactile insensitivity+ thalamic pain
OCCURS CONTRALATERAL TO LESION
Medial geniculate nucleus
major auditory relay
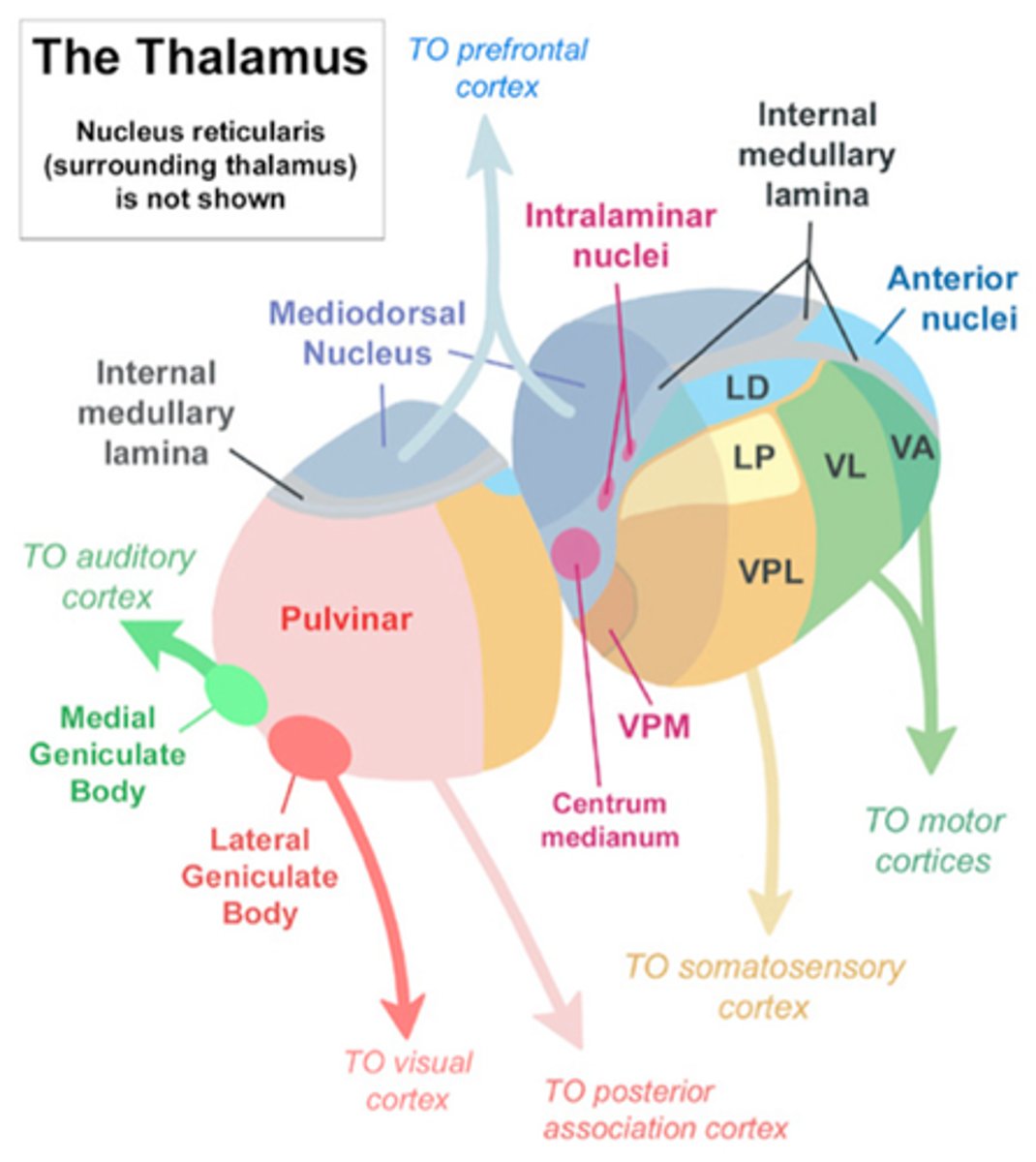
Lateral geniculate nucleus
major visual relay
optic n-LGN-primary visual cortex
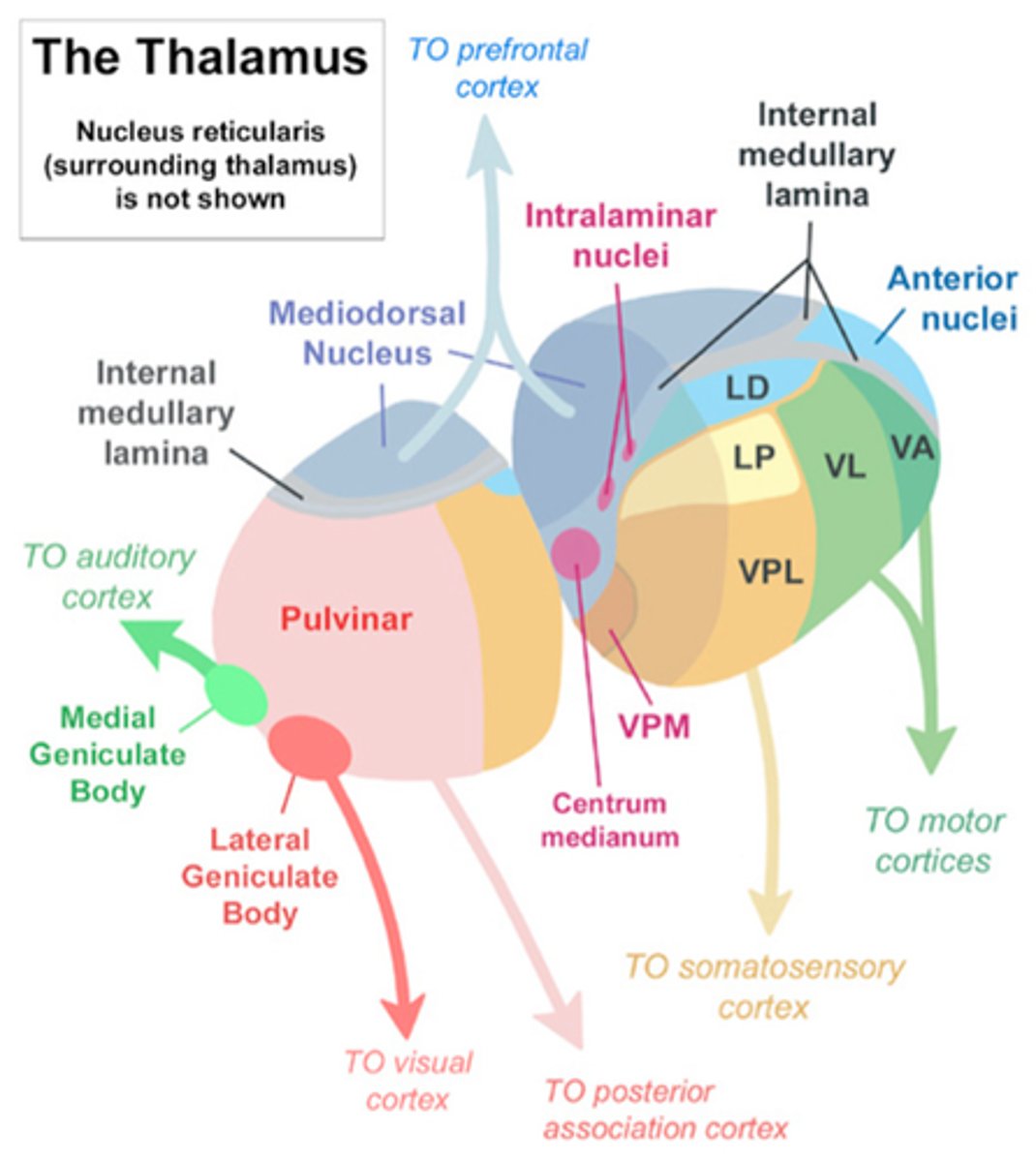
Intralaminar nuclei
Centromedian: motor to putamen and motor cortex
Parafascicular: motor to caudate and prefrontal cortex
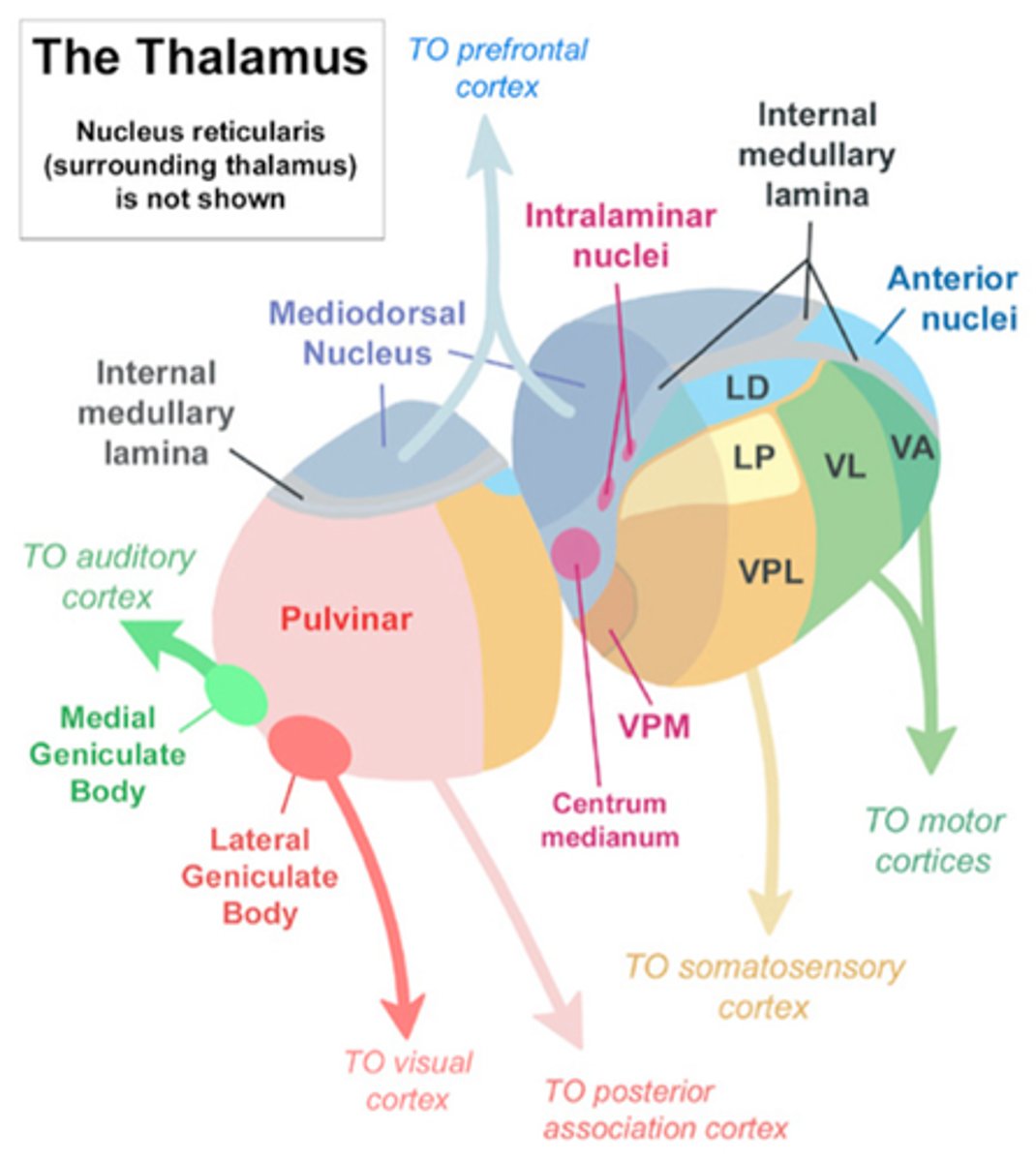
external medullary lamina
this sheet covering surface of thalamus
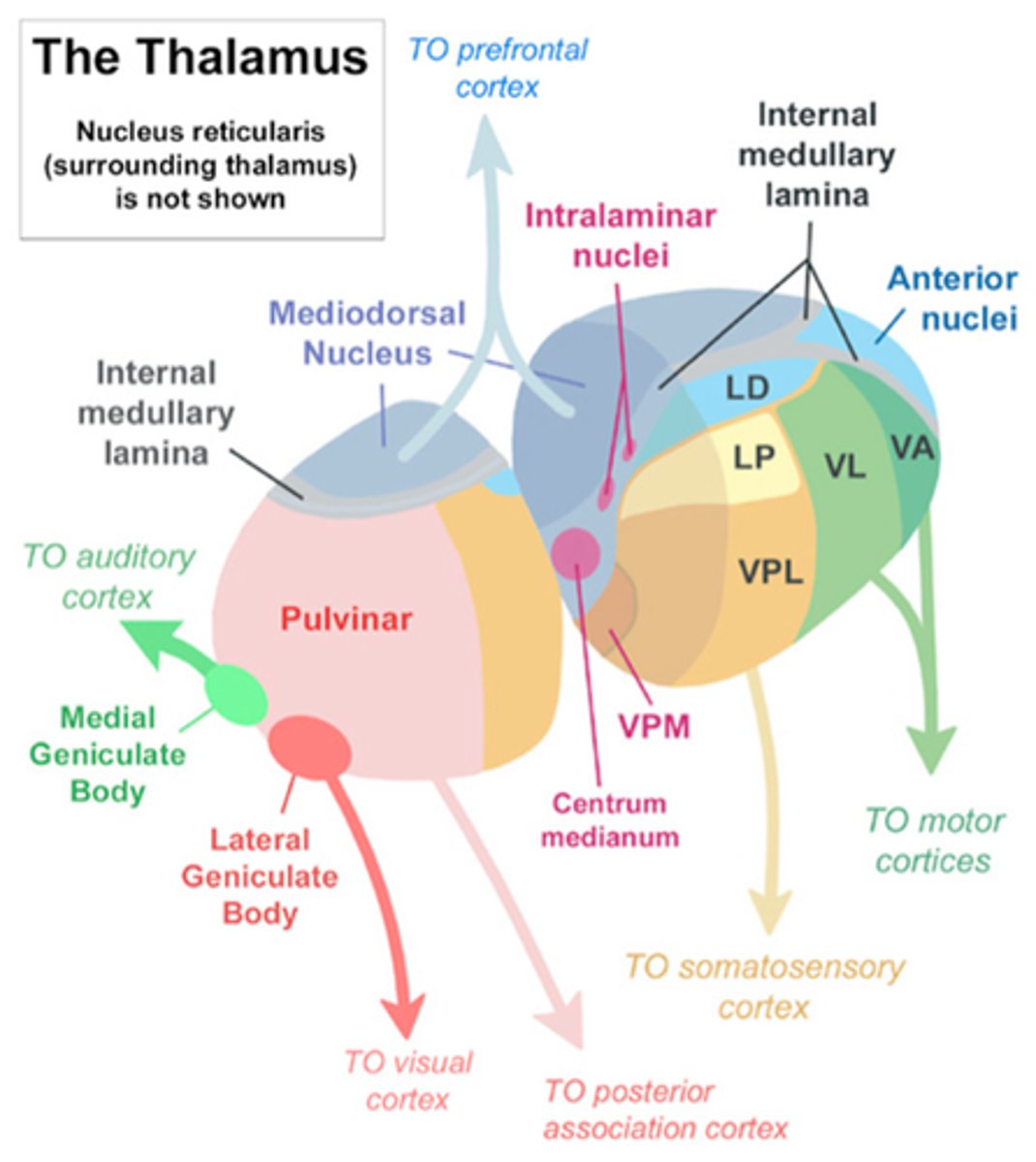
tonic state of thalamic neurons
normal depolarization of thalamic neuron
burst state of thalamic neurons
thalamic neuron is hyperpolarized, sensory info blocked
TRN neurons control tonic and burst states
Attention: No TRN inhibition, high thalamocortical activity
Sleep: high TRN inhibition, low thalamocortical activity