Anatomy Lab Practical #1
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
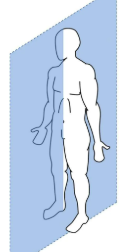
Sagittal Plane
left and right
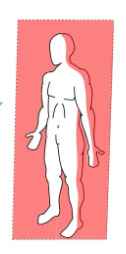
Coronal Plane
front and back
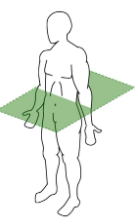
Transverse Plane
above and below
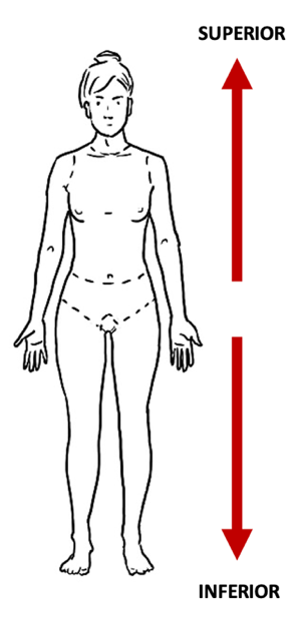
Superior and Inferior
closer to head vs closer to feet
Anterior and Posterior
closer to the front (ventral) vs closer to the back (dorsal)
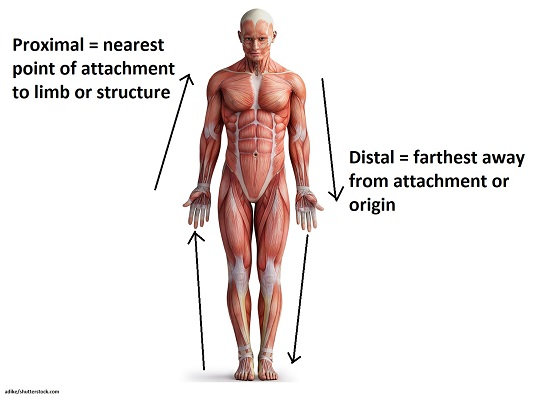
Proximal and Distal
closer to the point of attachment vs farther from the point of attachment
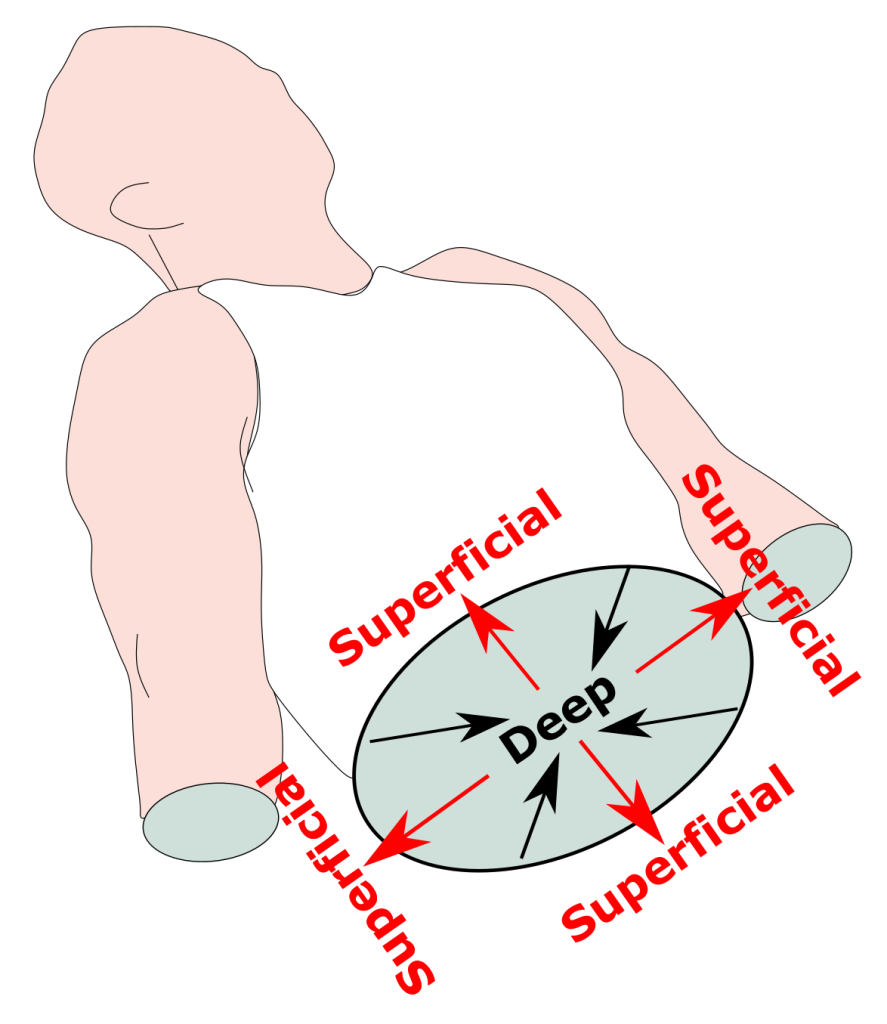
Superficial and Deep
closer to the surface vs further from the surface
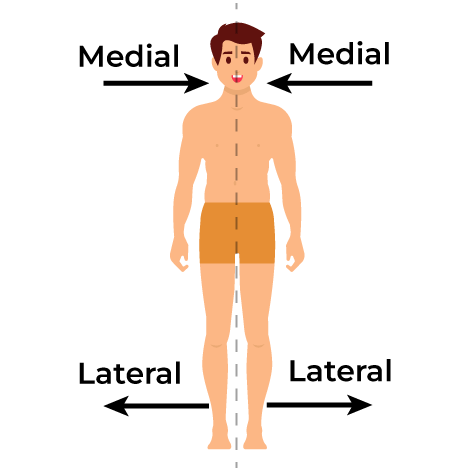
Medial and Lateral
closer to the midline vs farther from the midline
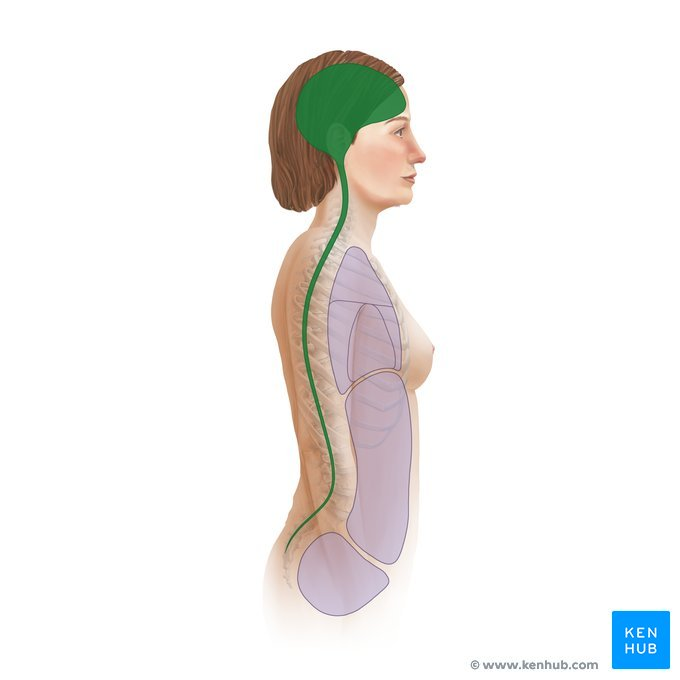
Cranial Cavity (brain) and Vertebral Cavity (spinal cord) surrounded by Meninges (membranes)
Dorsal Body Cavity
Thoracic Cavity (heart and lungs) and Abdominopelvic Cavities (digestive organs, urinary system, and reproductive organs) seperated by the Diaphragm and surrounded by Serous Membranes
Ventral Body Cavity
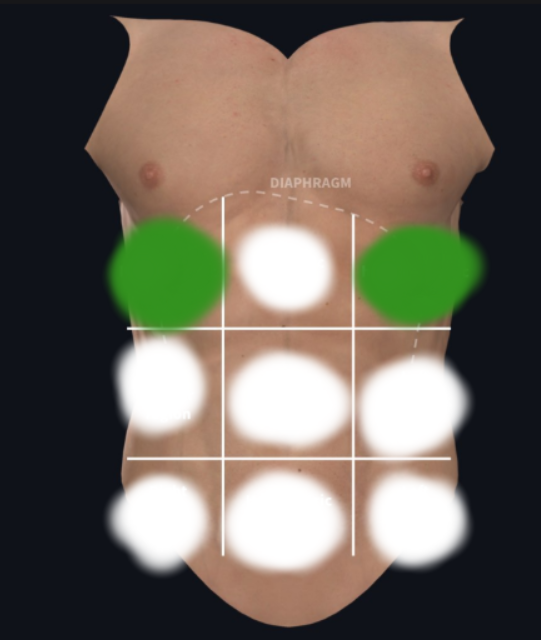
Right and Left Hypochondriac Region
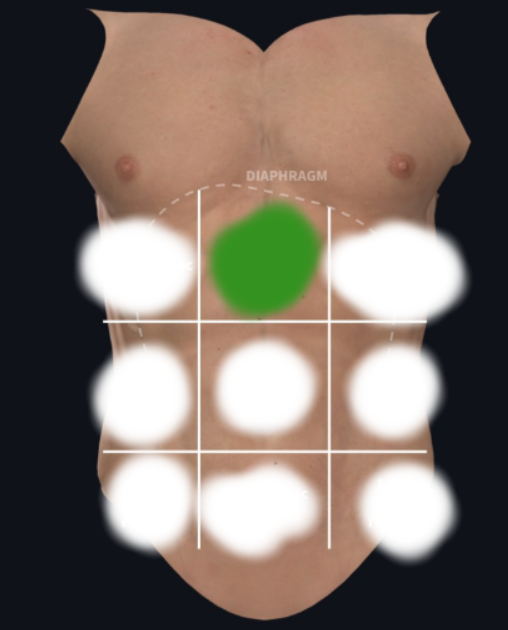
Epigastric Region
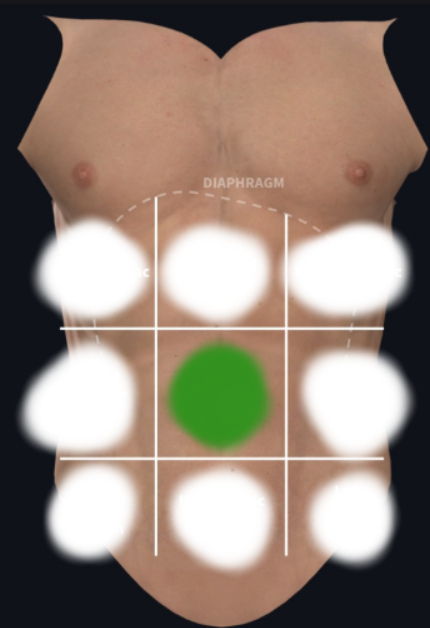
Umbilical Region
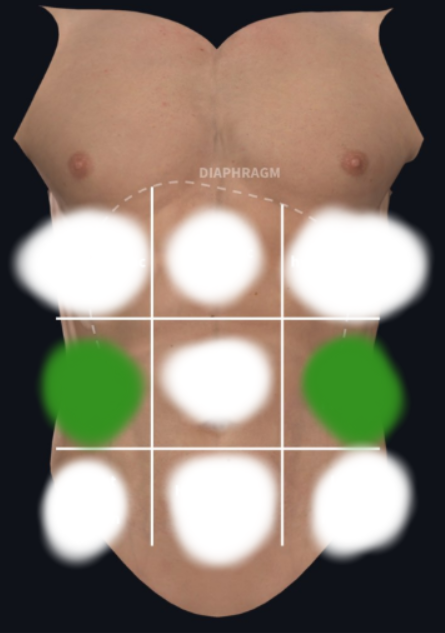
Right and Left Lateral (Lumbar) Region
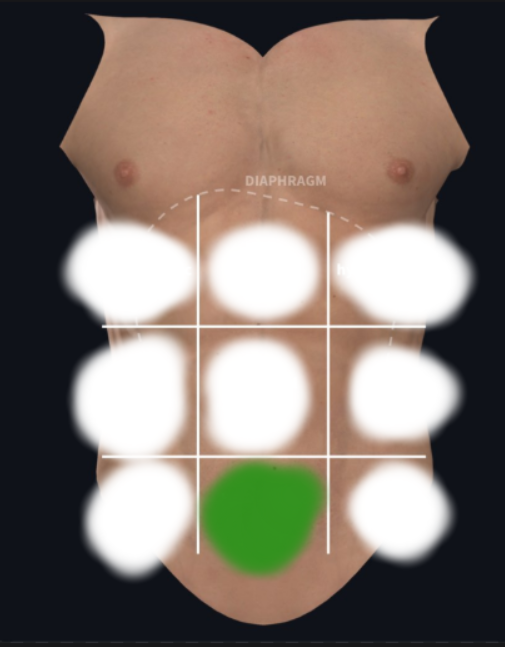
Pubic (Hypogastric) Region
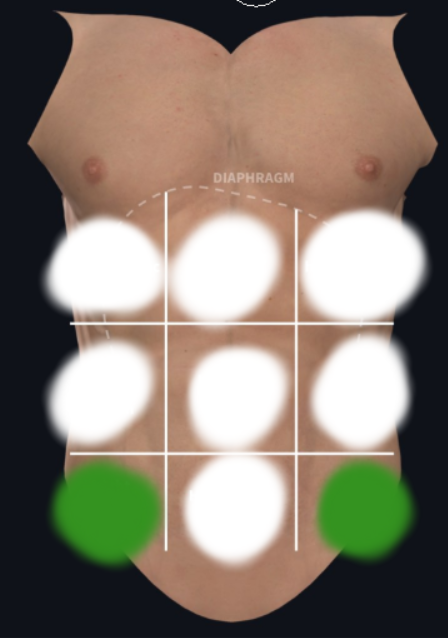
Right and Left Inguinal (Iliac) Region
4 Primary Tissue Types
Epithelial (cover), Connecting (support), Muscle (movement), Nervous (control)
Epithelial Subtypes

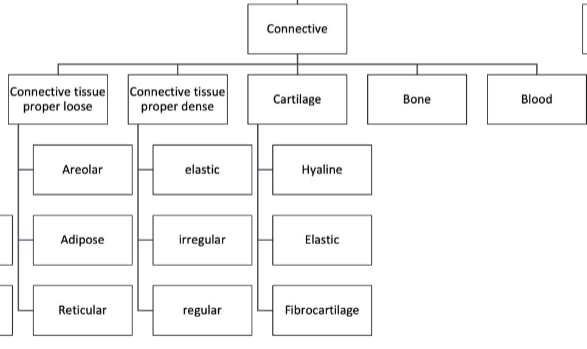
Connective Subtypes
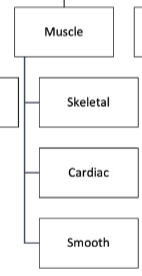
Muscle Subtypes
Characteristics of Epithelial Membranes
Polarity— having one free surface (apical) and one surface in contact with the basement membrane (basal)
Specialized Junctions— cells are fitted together closely, limited extracellular matrix
Supported— Highly vasculized connective tissue underlies the basement membrane
Avascular but Innervated— no blood vessels but have nerves
Regeneration— cell division can replenish epithelia if well nourished
Where is Epithelial tissues found?
Covering the external body surfaces and lining cavities and tubules
What are the functions of Epithelial Tissues?
Protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion, and sensory reception
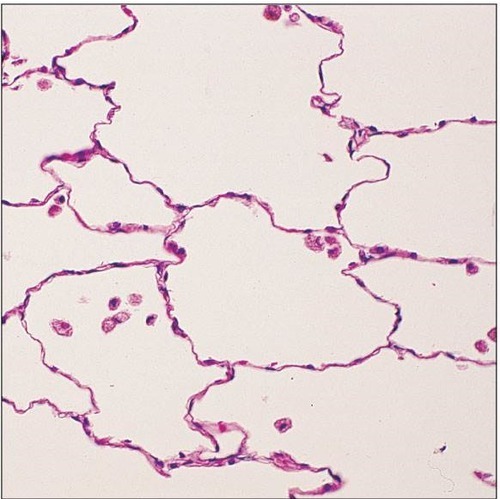
Simple Squamous Epithelium
What are the functions of Simple Squamous Epithelium?
Allows rapid passage of chemical compounds (filtration or diffusion)
Secrete lubricating substances
Example Locations of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs
Blood vessel, heart lining
Lymphatic vessels (—>Endothelium)
Lining of ventral body cavity (—>Mesothelium)
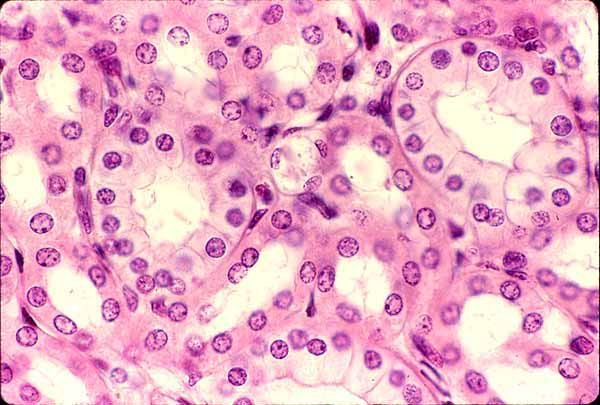
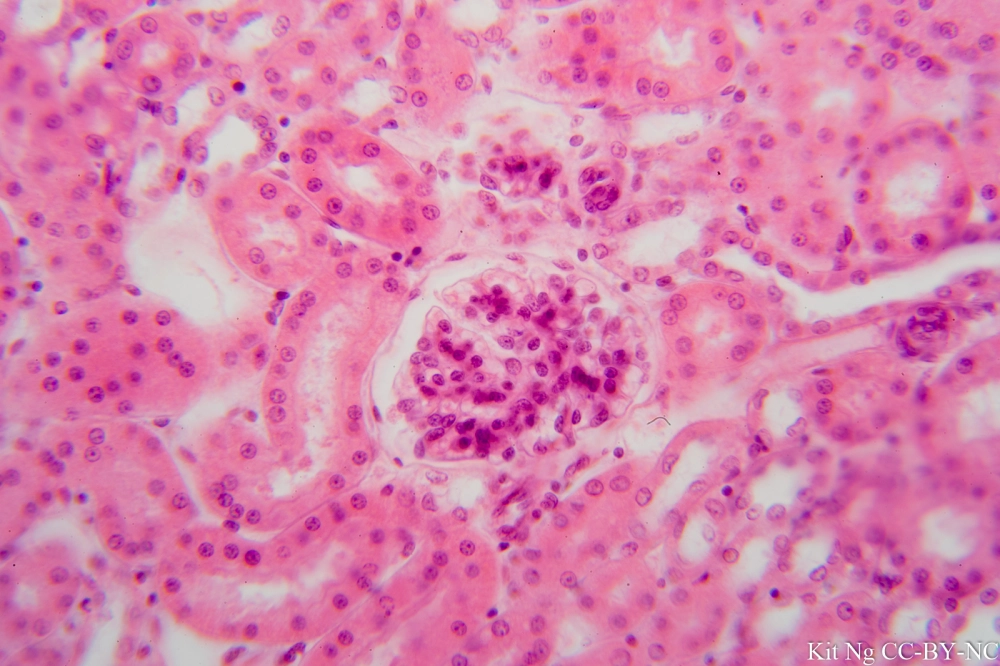
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
What are the functions of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium?
Secretion
Absorption
Example Locations of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Kidney tubules
Ducts of secretory glands
Ovary surfaces (—>Germinal Epithelium)
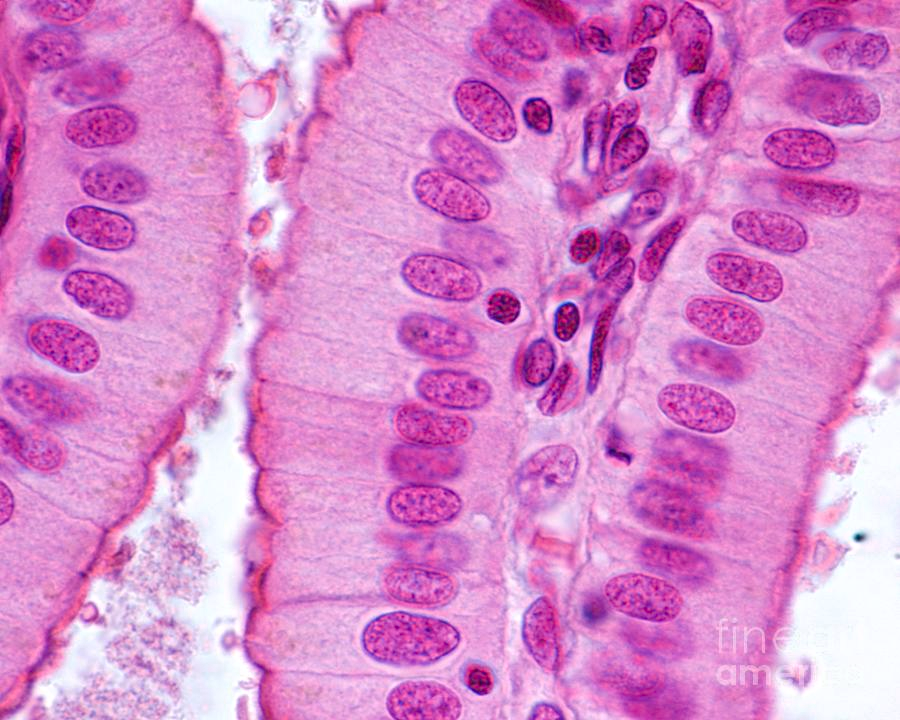
Simple Columnar Epithelium
What are the functions of Simple Columnar Epithelium?
Absorption
Secretion of mucus, enzymes, and etc.
Example Locations of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Non-cilliated— most digestive tract (stomach to rectum), gallbladder, excretory glands of some ducts
Ciliated— small bronchi, uterine tubes, some regions of the uterus
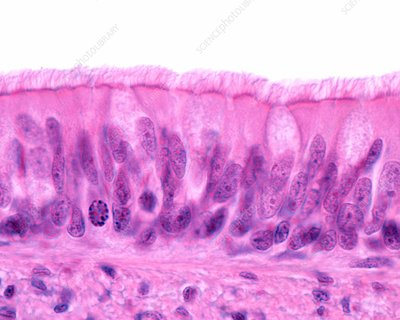
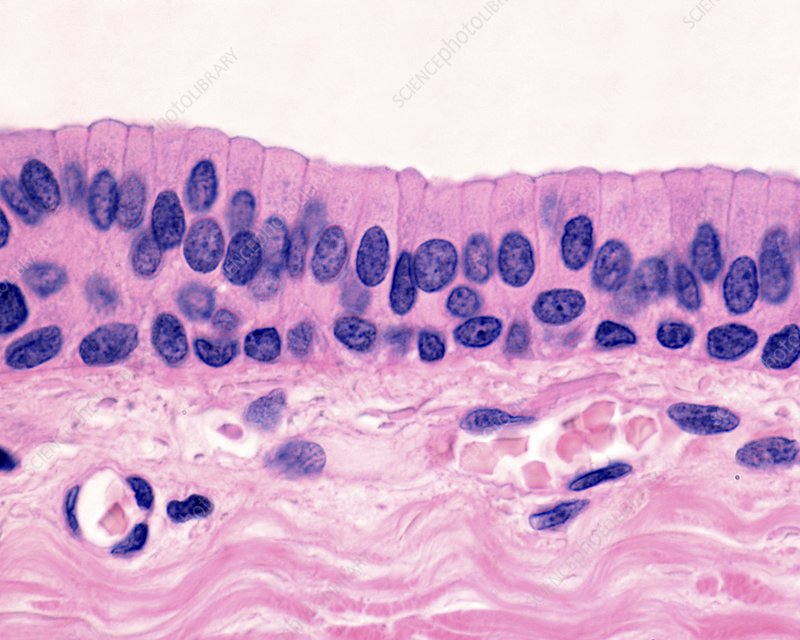
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
What are the functions of Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium?
Secrete substances, especially mucus
Example Locations of Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Non-ciliated— male’s sperm-carrying and large glands ducts
Ciliated + Mucus-secreting goblet cells— lines the trachea, most of the upper respiratory tract (—> Respiratory Epithelium)
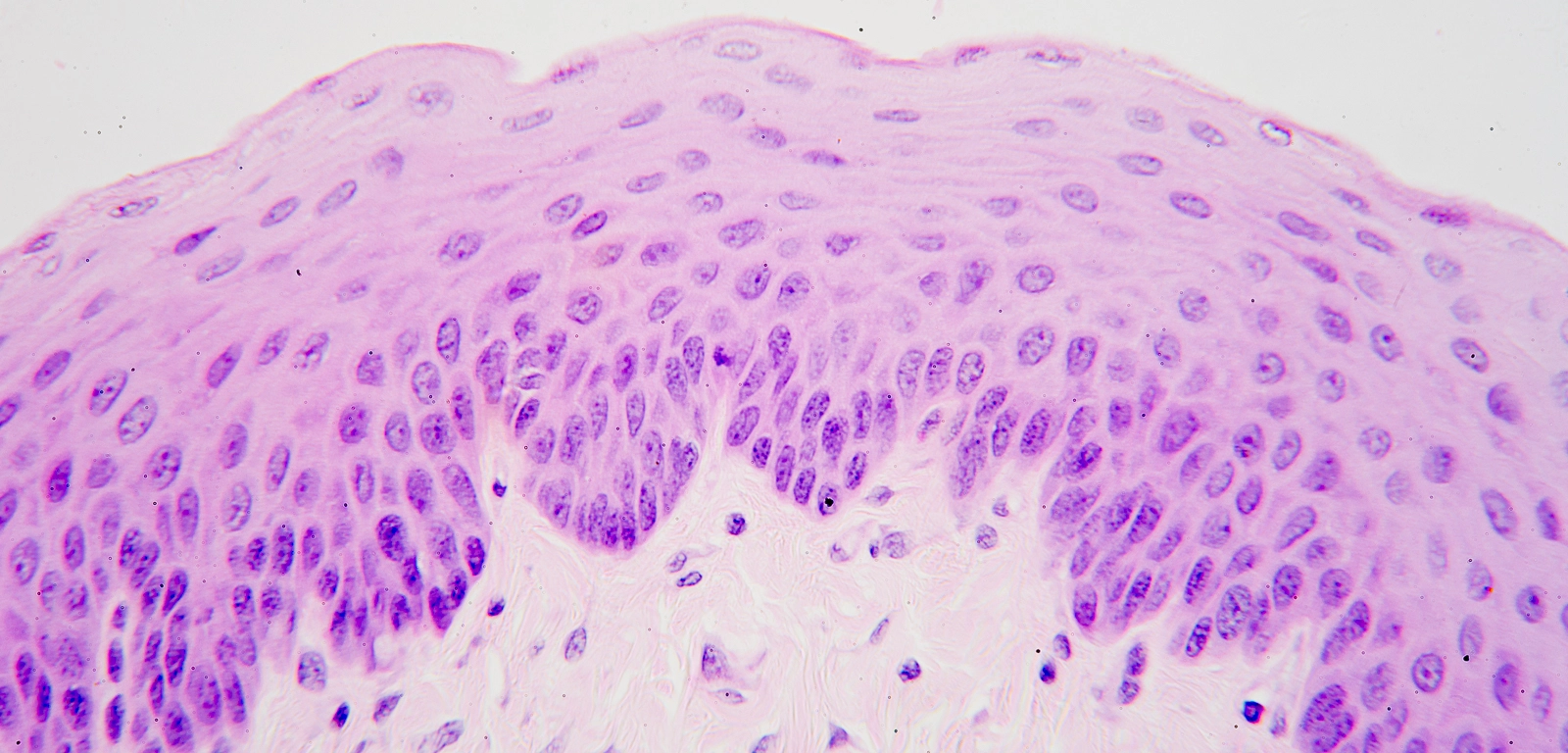
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
What are the functions of Stratified Squamous Epithelium?
Can be keratinized
Protects underlying tissues from abrasion
Examples Locations of Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Non-Keratinized— line the mouth, esophagus, and vagina
Keratinized— makes up the epidermis
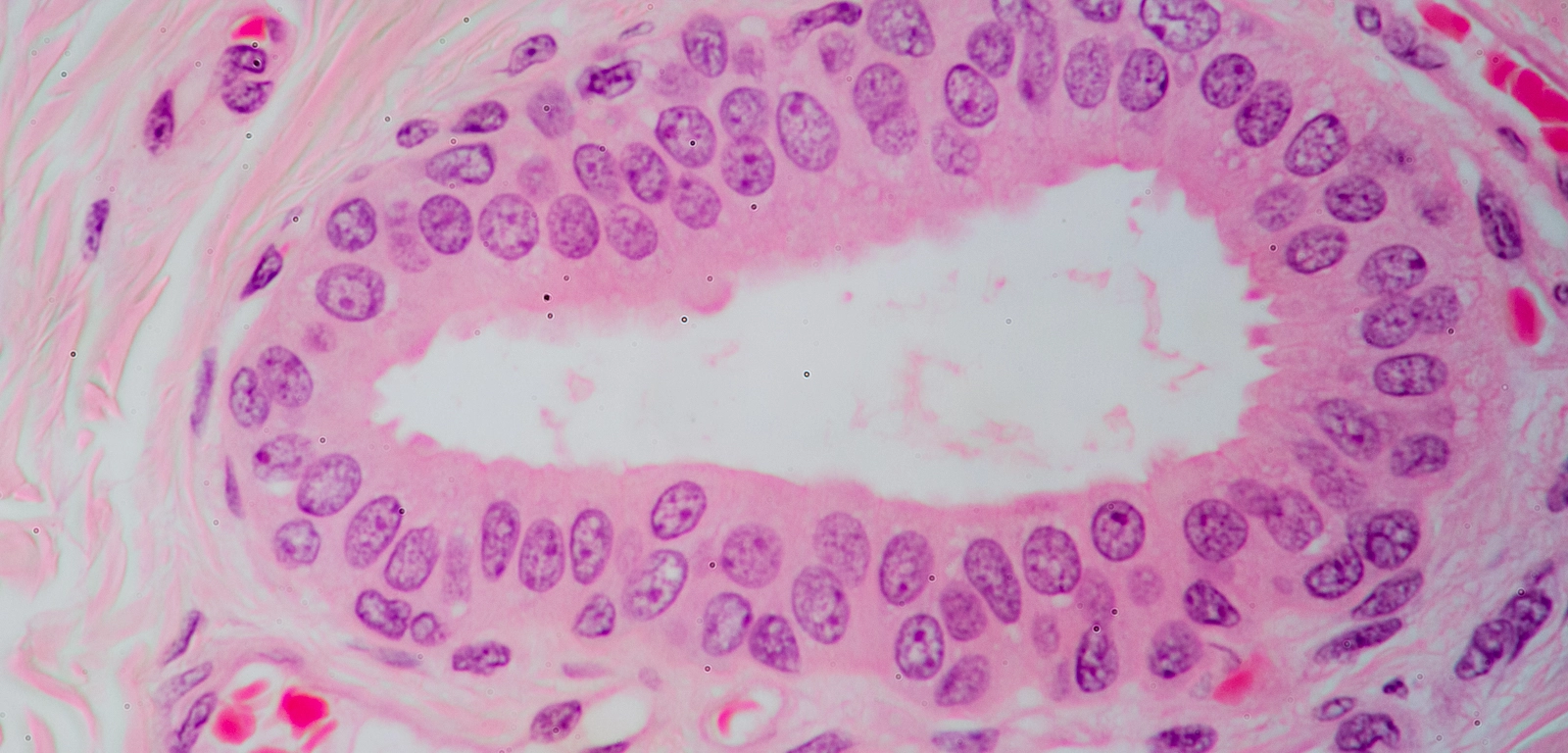
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
What are the functions of Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium?
Protection
Example Locations of Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Ducts of excretory glands (salivary, sweat, mammary)
very rare
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
What are the Functions of Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Occurs in the transition areas or junctions between two other types of epithelia
Never ciliated
Protection
Secretion
Example Locations of Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Male Urethra
Ducts of some glands
Pharynx
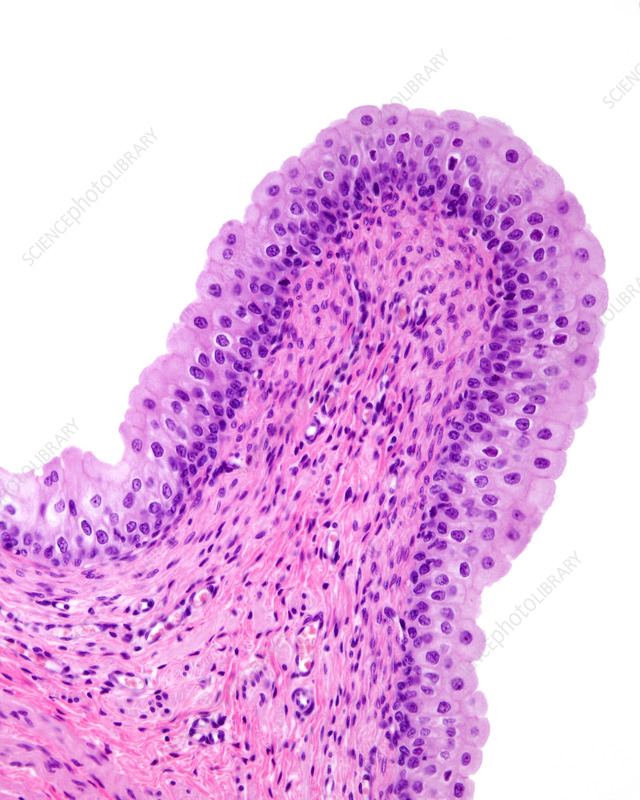
Transitional Epithelium
What are the Functions of Transitional Epithelium?
allow urinary organs to expand and stretch as they fill/ empty urine
when empty they become 6 layers of stratified cuboidal epithelium
when filled they become 3 layers of stratified squamous epithelium
Example Locations of Transitional Epithelium
Exclusively found in the urinary system
Characteristics of Connective Tissues
Non-living portion— extracellular matrix made of fibers and ground substances; fiber content of Collagen, Elastic, and or Reticular
Living portion— cells that produce the contents of the nonliving portion; originated from mesenchyme, Fibroblasts, Chondroblasts, Osteoblasts, Hematopoietic stem cells
Exhibit different degree of vascularity
Connective Tissue Proper Loose
Higher proportion of ground substance and fewer loosely organized fibers, leaving large spaces in between
Areolar
Adipose
Reticular
Connective Tissue Proper Dense
Reinforced by tight bundles of fibers that provide tensile strength, elasticity, and protection
Elastic
Irregular
Regular
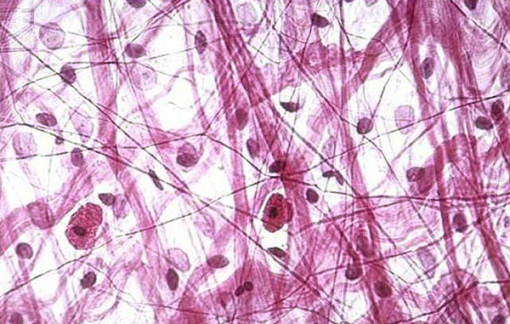
Areolar CT Proper Loose
What are the Functions of Areolar CT Proper Loose?
The main tissue all other connective tissues are variated from
Consists of collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers
Mainly consists of Fibroblasts
Cushions organs
Example Location of Areolar CT Proper Loose
Widely distributed under many epithelia of organ systems and capillaries
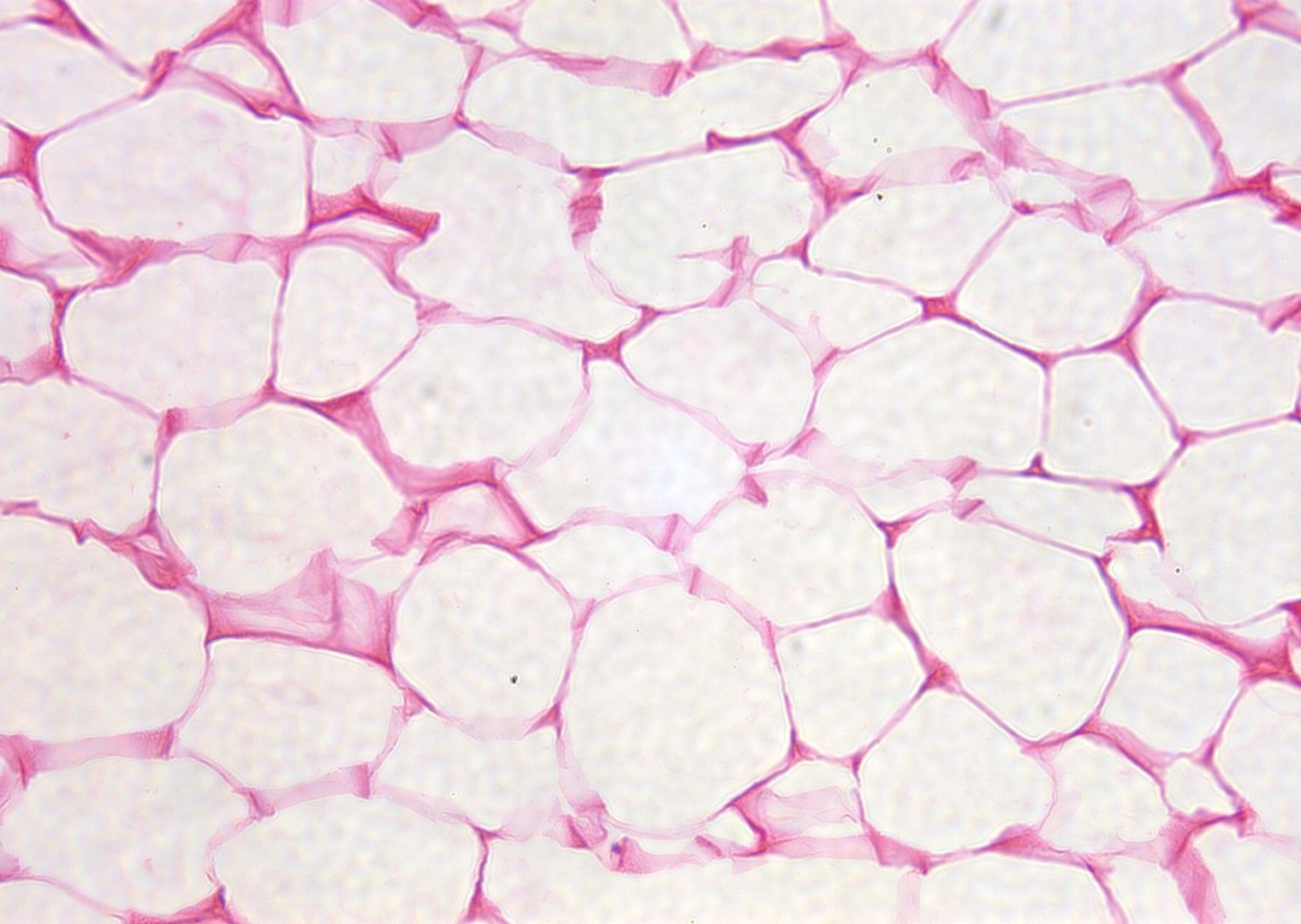
Adipose CT Proper Loose
What is the Functions of Adipose CT Proper Tissue?
Mainly consists of Adipocytes
Fuel Reserve
Insulation against heat loss
Supports and protects organs
Example Locations of Adipose CT Proper Loose
Under skin dermis
Around the Kidneys
Breasts
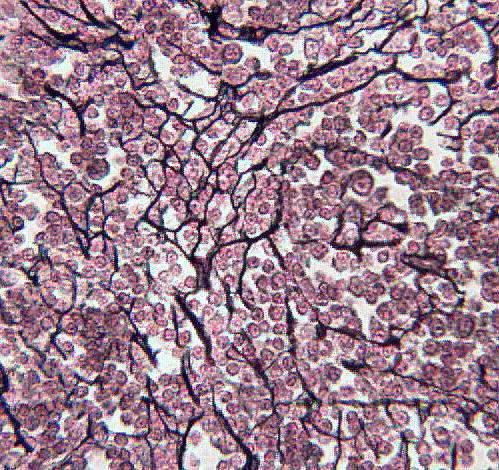
Reticular CT Proper Loose
What are the Functions of Reticular CT Proper Loose?
Contains high proportion of reticular fibers and various types of blood cells
Forms a soft internal skeleton that supports embedded cells
Example Locations of Reticular CT Proper Loose
Lymphoid organs
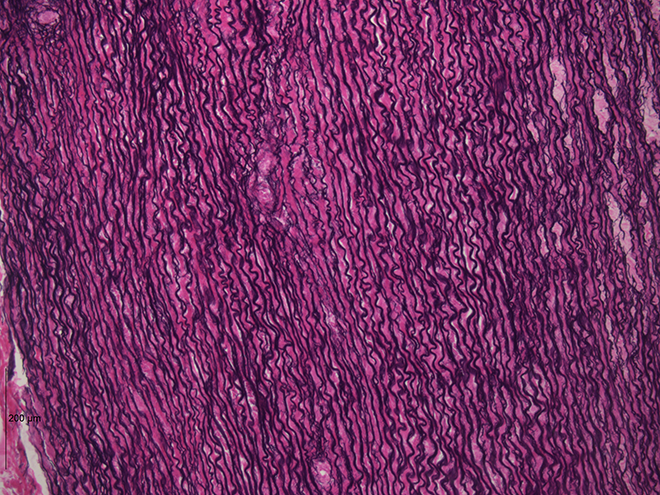
Elastic CT Proper Dense
What are the Functions of Elastic CT Proper Dense?
Higher proportions of elastic fibers
Allows a recoil of tissue following stretching
Example Locations of Elastic CT Proper Dense
Walls of large arteries
Within ligaments
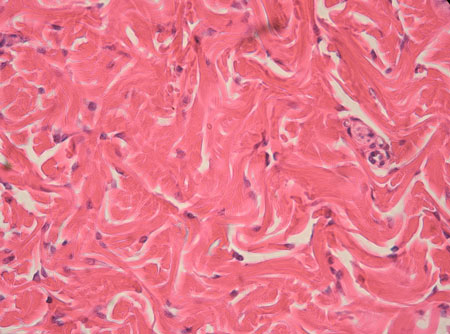
Irregular CT Proper Dense
What are the Functions of Irregular CT Proper Dense?
Primarily consists of irregularly arranged collagen fibers and some elastic fibers
Primary cell type is Fibroblasts
Withstand tension from multiple directions
Example Locations of Irregular CT Proper Dense
Dermis of the skin
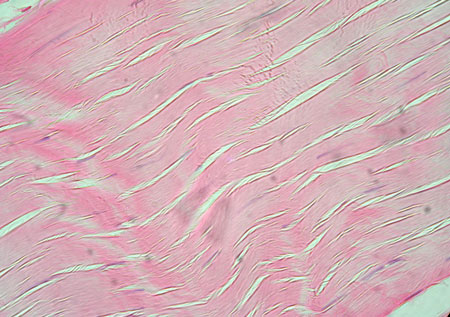
Regular CT Proper Dense
What are the Functions of Regular CT Proper Dense?
Primarily composed of parallel collagen fibers and some elastic fibers
Primary cell type is Fibroblasts
Attach muscles to bones or other muscles
Attach bones to bones
Withstand tensile stress when pulled in one direction
Example Locations of Regular CT Proper Dense
Ligaments
Tendons
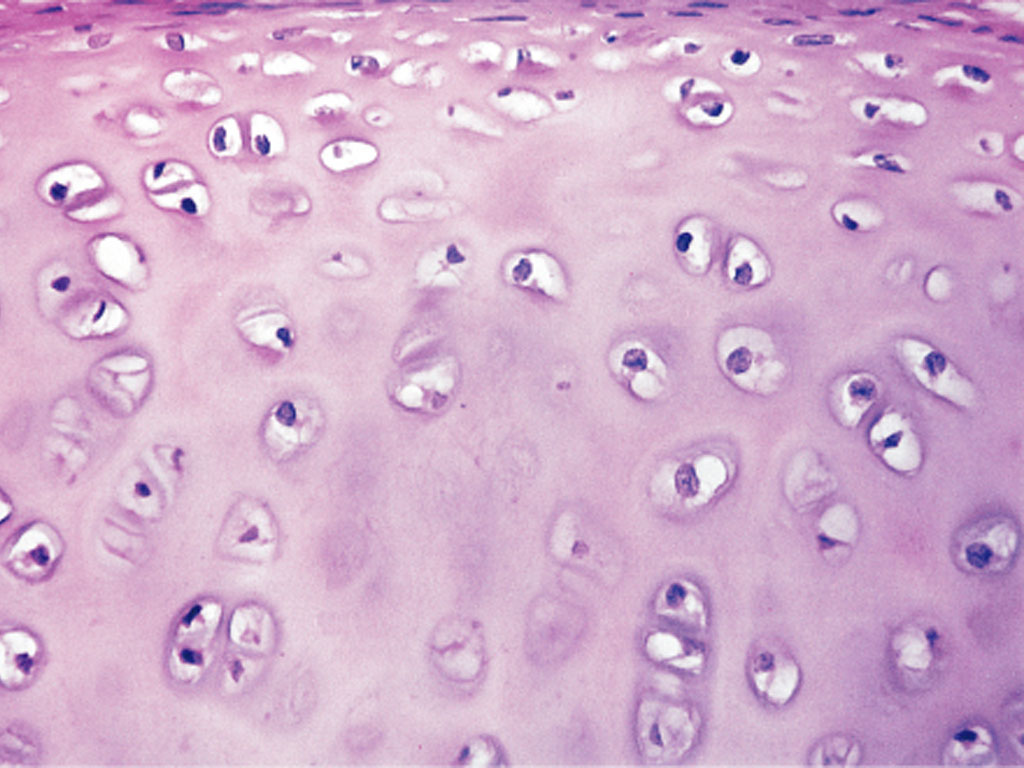
Hyaline Cartilage CT
What are the Functions of Hyaline Cartilage CT?
Amorphous but firm matrix with collagen fibers and chondrocytes
Supports and reinforces structures
Resists compressive stress
Resilient Cushion
Example Locations of Hyaline Cartilage CT
Most of embryonic skeleton
Nose
Trachea
Larynx Cartilage
Ends of long bones at joints
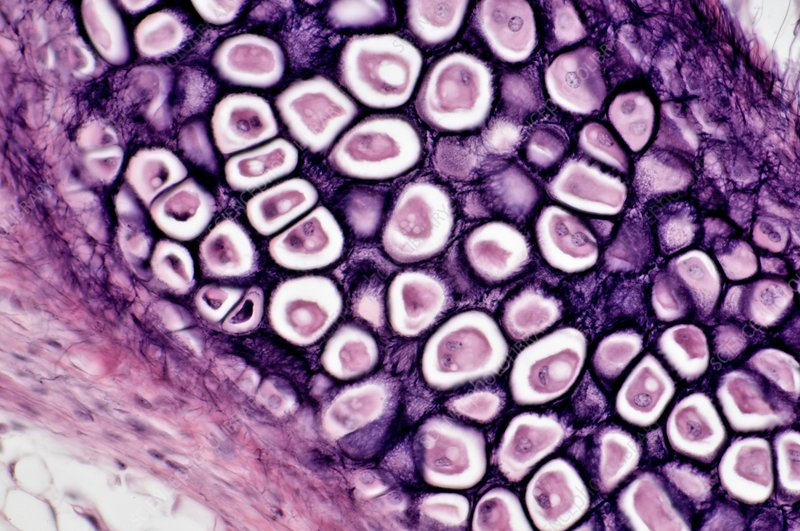
Elastic Cartilage CT
What are the Functions of Elastic Cartilage CT?
Primarily elastic fibers
Rare in body
Maintain the shape of structure while allowing flexibility
Example Locations of Elastic Cartilage CT
External ear
Epiglottis

Fibrocartilage CT
What are the Functions of Fibrocartilage CT?
Less firm extracellular matrix
Primarily made of collagen fibers
Compressive shock absorption
Example Locations of Fibrocartilage CT
Intervertebral discs
Pubic symphysis
Discs of knee joints
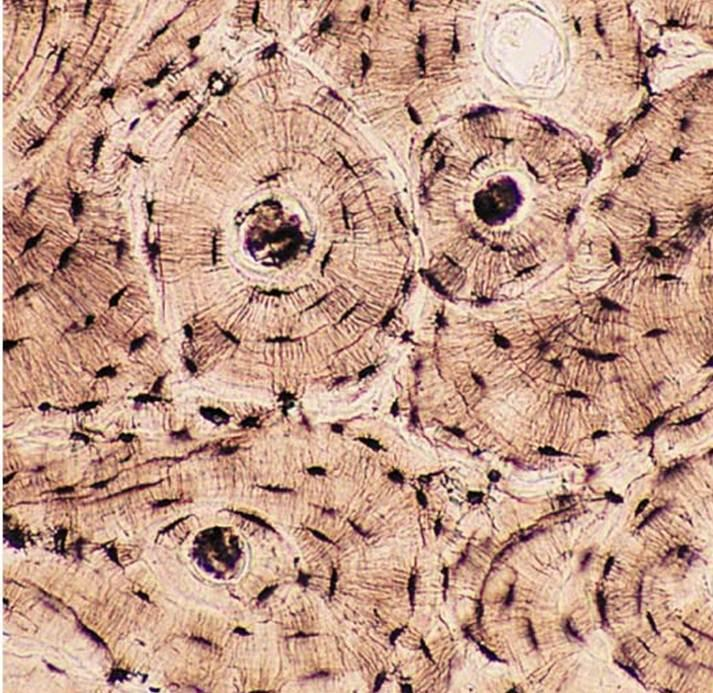
Bone CT
What are the Functions of Bone CT
Hard calcified matrix containing collage fibers
Primarily cell type is osteocytes
Highly vascularized
Support and protect soft organs by encasing them in bone
Calcium Storage
Hematopoiesis in bone marrow
Example Locations of Bone CT
Bones
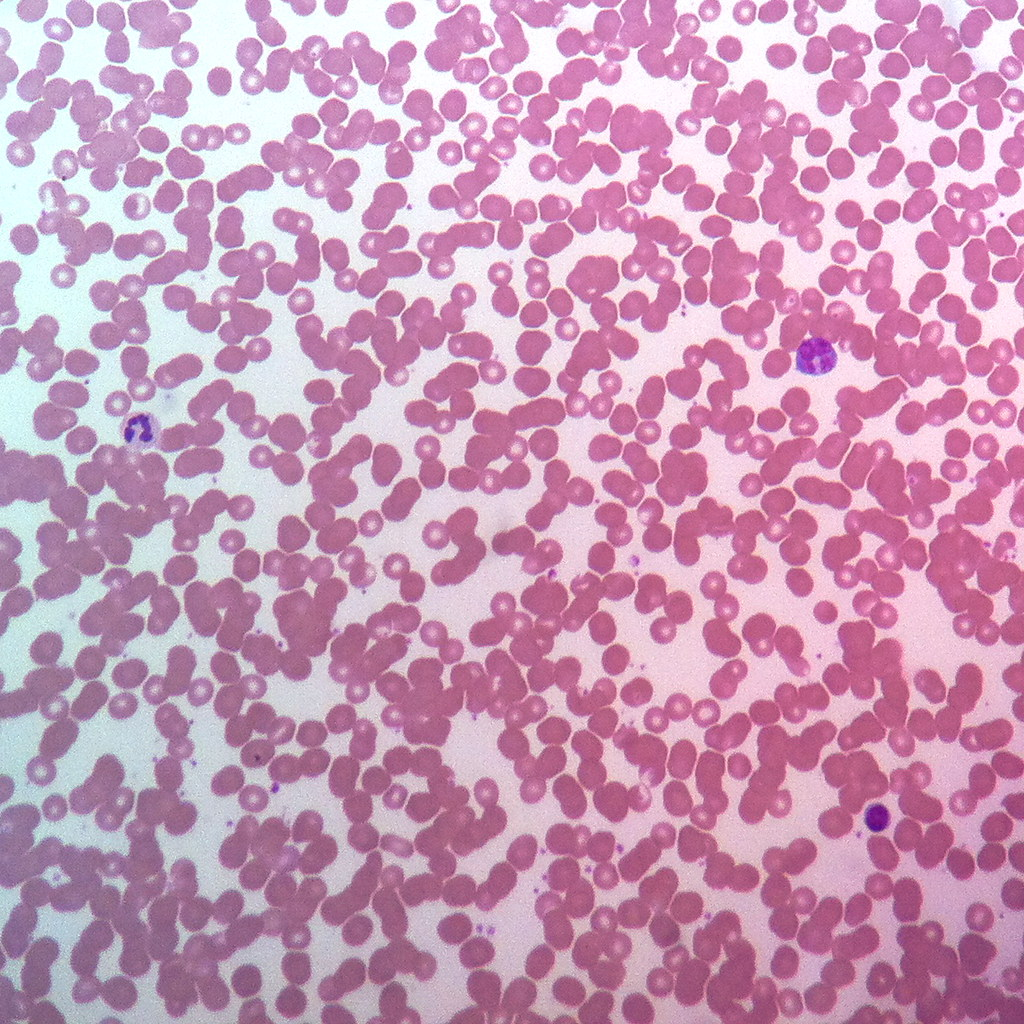
Blood CT
What are the Functions of Blood CT?
Completely fluid matrix (blood plasma)
Transport of respiratory gasses, nutrients, wastes, and other substances
Example Locations of Blood CT
Within the circulatory system
Characteristics of Muscle Tissue
Contractility—The ability to shorten and generate force in response to a stimulus
Excitability—The capacity to respond to electrical or chemical signals
Extensibility—The ability to be stretched without tearing
Elasticity—The tendency to return to its original length after being stretched
Atrophy and Hypertrophy— change in size, either decreasing (atrophy) or increasing (hypertrophy), often in response to activity levels or lack thereof
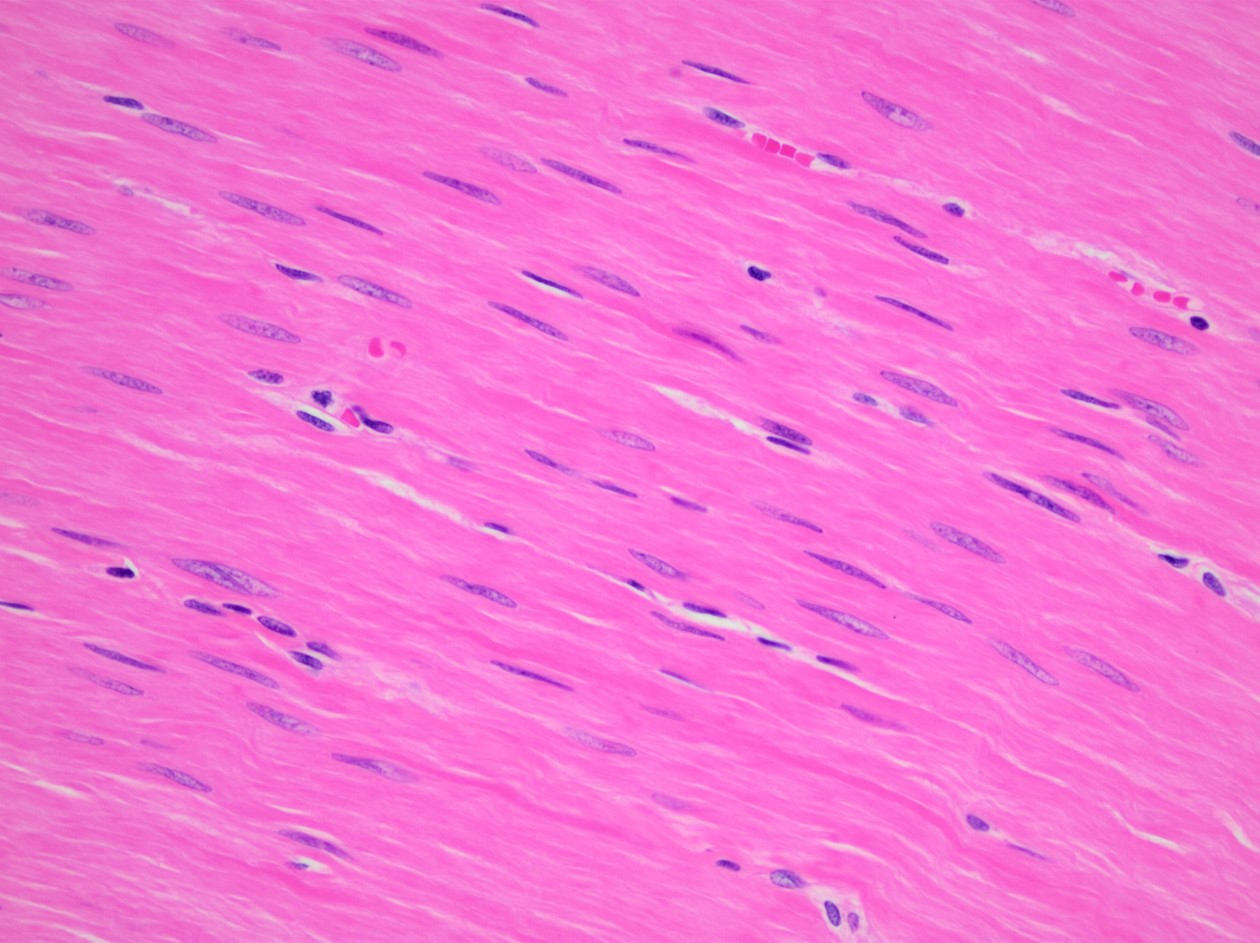
Smooth Muscle Tissue
What are the Functions of Smooth Muscle Tissue?
Uninucleated
No visible striations
Involuntary
Propel foodstuffs along GI tract, urine through urinary tract, baby through birth canal
Example Locations of Smooth Muscle Tissue
Walls of hollow organs
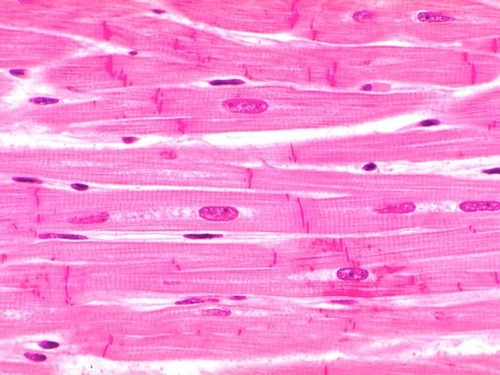
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
What are the Functions of Cardiac Muscle Tissue?
Uninucleated
Involuntary
Make contact with each other at intercalated discs
Propels blood out of the heart and into arteries
Example Locations of Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Walls of the heart
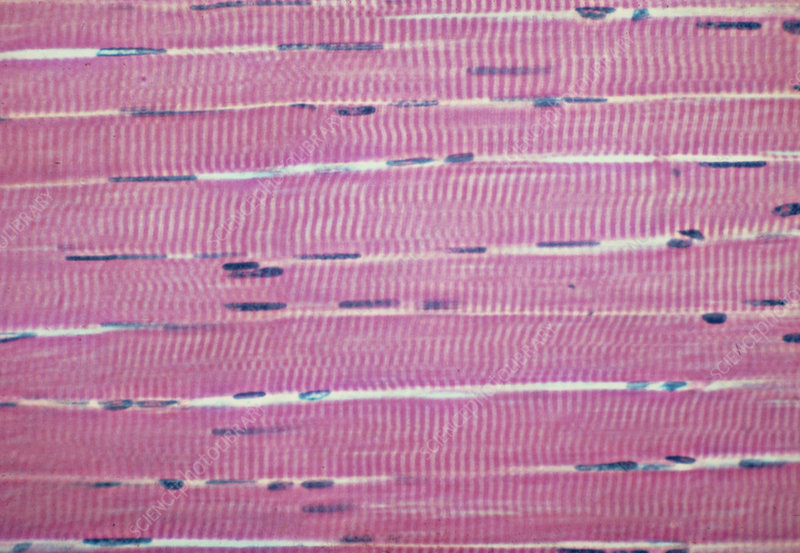
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
What are the Functions of Skeletal Muscle Tissue?
Multinucleated
Voluntary
Locomotion
Facial Expressions
Example Locations of Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Skeletal muscles attached to bones, other skeletal muscles, or skin
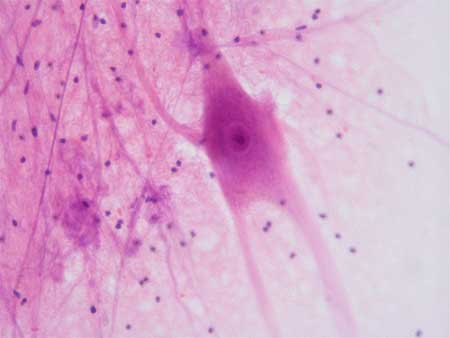
Nervous Tissue
What are the Functions of Nervous Tissue
Neurons— transmit messages through out the body (excitability and conductivity)
Glial Cells— support, protect, and insulate neurons
Regulate involuntary processes such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion
Initiate motor commands to muscles
Example Locations of Nervous Tissue
Brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system
Nerves of the peripheral nervous system
What are the two divisions of the Integumentary System?
Skin— tough outer protective layer, composed of superficial epidermis layer and deeper dermis layer
Accessory skin structures— all derived from epidermis residing in the dermis, sweat (sudoriferous) glands, oil (sebaceous) glands, nails, hair and follicles
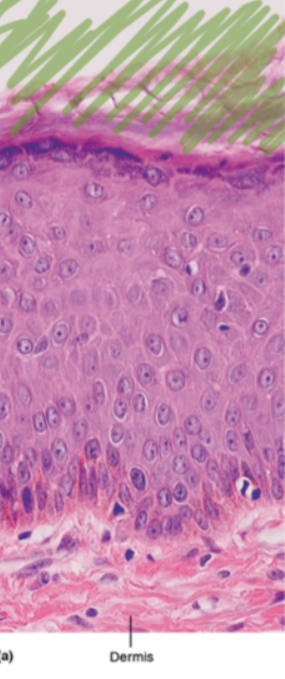
Stratum Coreum
Characteristics of the Stratum Corneum
Superficial stratum
Contains many layers of dead keratinocytes
Glycolipids in extracellular space
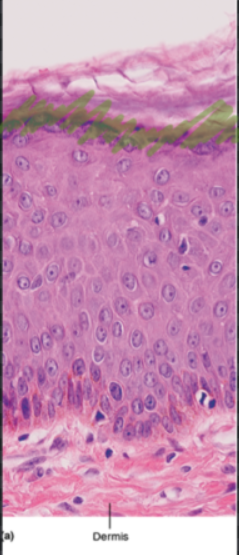
Stratum Granulosum