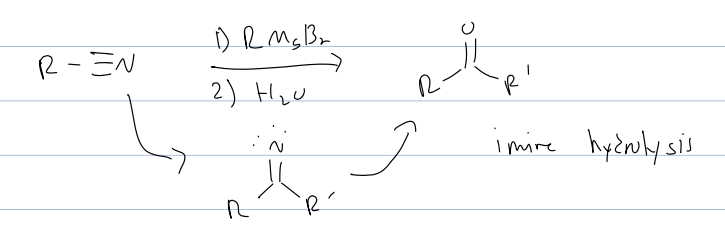carboxylic acid derivatives
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
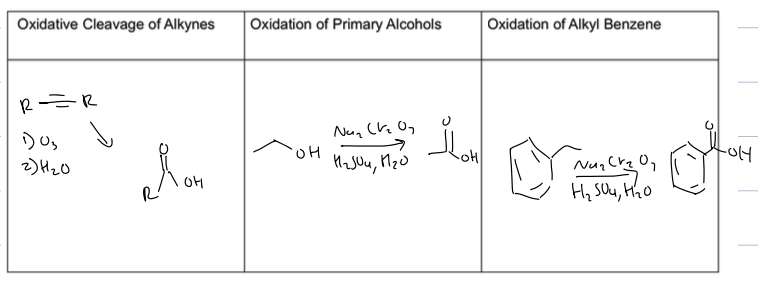
what are the 4 ways we already know how to make carboxylic acid
oxidative cleavage of alkynes, oxidation fo primary alcohols, oxidation of alkyl benzene, and grignard of CO2
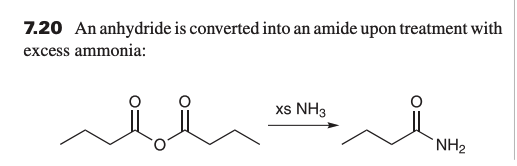
what is product when reacting anhydride with xs NH3
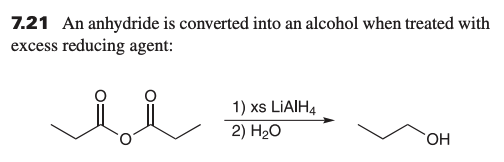
what is product when reacting anhydride with LAH
what is product when reacting anhydride with H3O
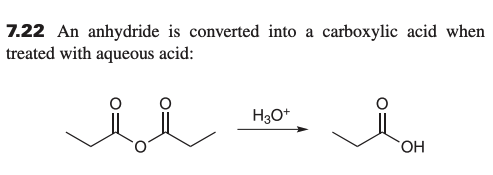
what is the reaction to take an ester to a carboxlic acid
what is nucleophilic acyl substitution rxn
carbox acid deriv, with a good leaving group is replaces by nuc
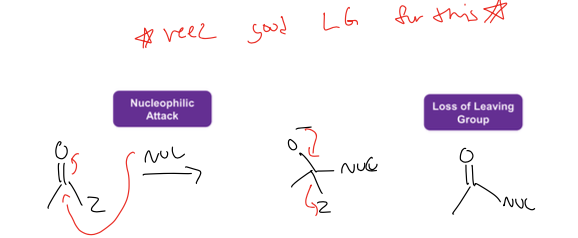
must have a good LG for this
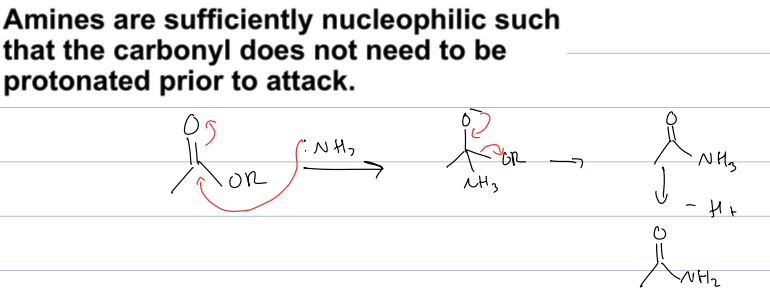
what is rxn with carbox acid deriv, and an amine
created an amide
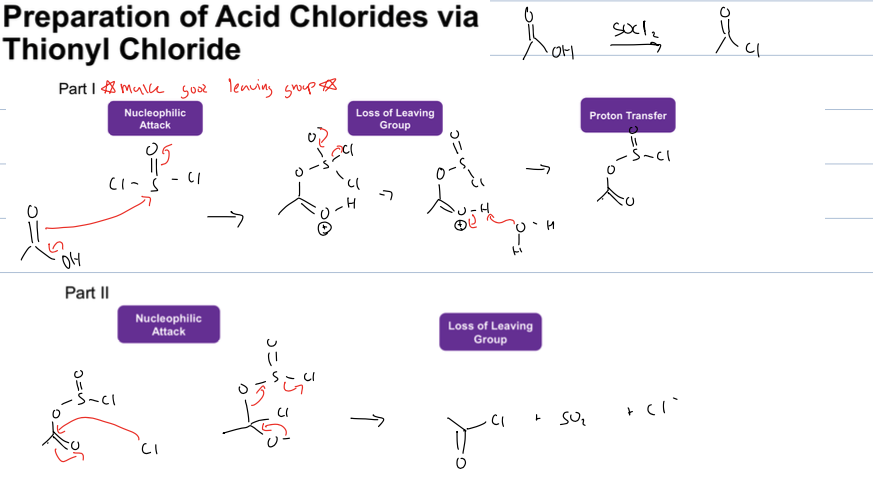
how to make an acid chloride with a carbox acid
use SOCL2 and products are acid chloride, SO2, and CL-
what is the hydrolysis of acid chloride
acid chloride to carbox acid
reagents: H2O and Pyr
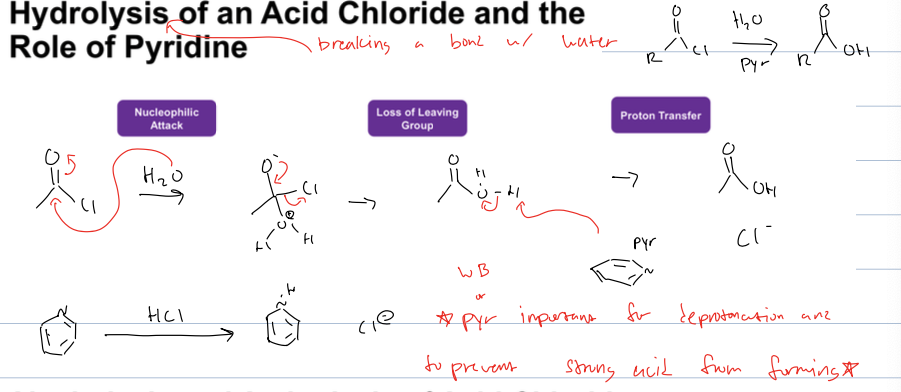
what is the role of pyr in the hydrolysis of an acid chloride
it deprotonates the H2O as well as binds with chloride ion in order to prevent strong acid from forming

what rxn with acid chloride and an alcohol and pyr
produces an ester
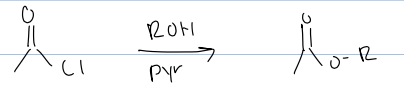
mech is nuc attacks and kicks bond up then deprotonates with pyr
what rxb with acid chloride and 2eq of NH3
amide
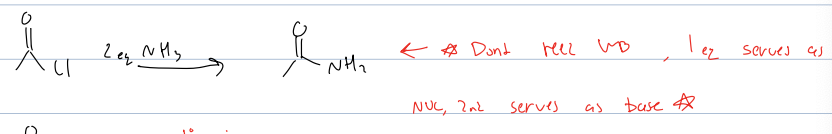
dont need WB bc NH3 acts as one
mech is nuc attack and then kicks bond up then deprotonate with Nh3
what rxn with acid chloride and 2eq of primary amine
produces a secondary amide
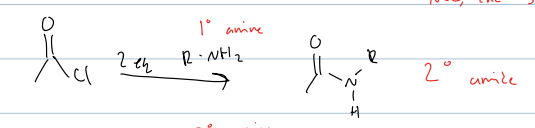
much is nuc attack and then kicks bond up and deprotonates with the primary amine.
what rxn with acid chloride and 2eq of secondary amine
produces a tertiary amide
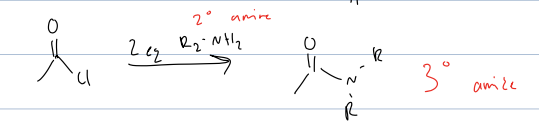
mech is nuc attack and then kicks bond up and then deprotonates with the secondary amine.
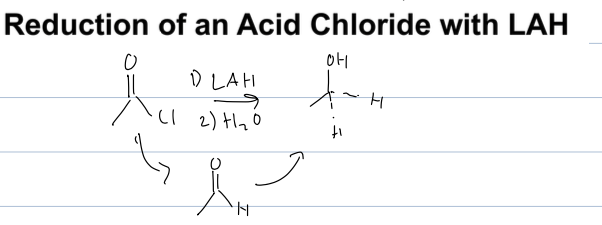
what is the rxn of a reduction of acid chloride
acid chloride to alcohol
reagent: LAH and H2O
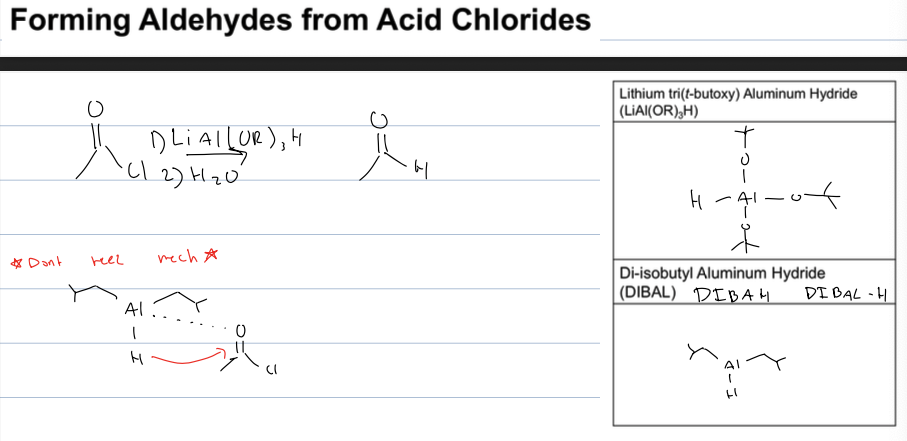
what rxn to go from acid chloride to aldehyde
use reagent LiAL(OR)3H with H2O or DIBAH with H2O
what is gillman reagent rxn
acid chloride to ketone
reagent: R2CuLI
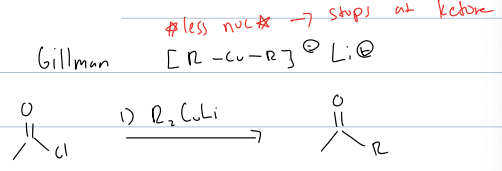
Also can add any carbon chain to an acid chloride
how to prepare anhydrides with acid chloride
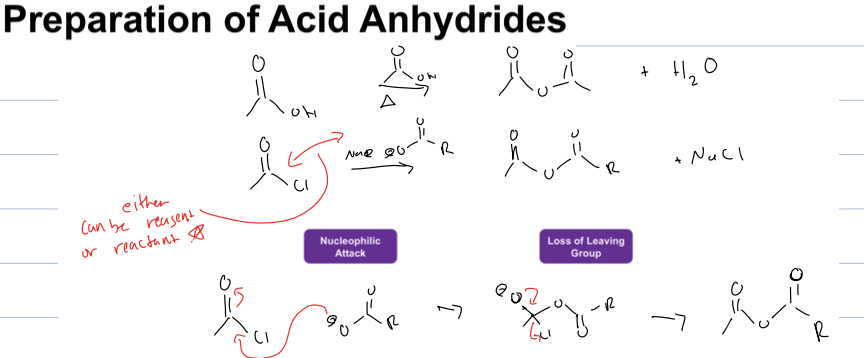
what is rxn with anahydride and nuc
adds nuc to the carbonyl atom
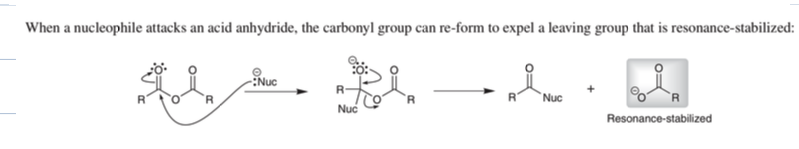
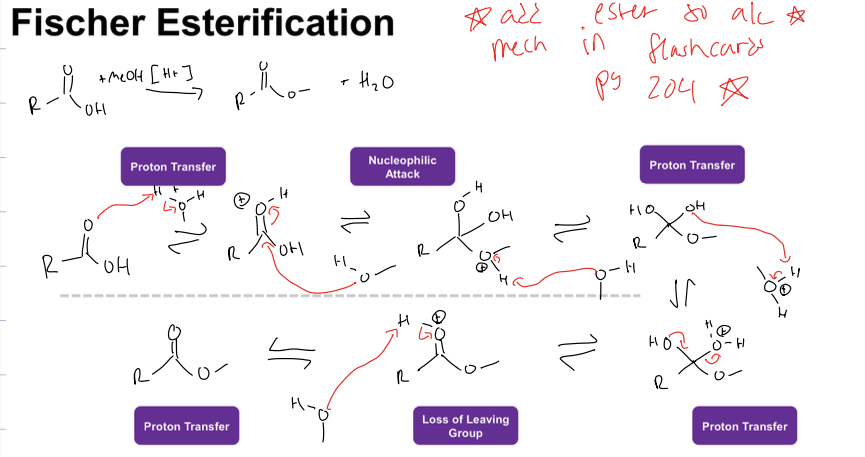
what is. fischer esterification rxn
add ester to carbox acid
reagent: alcohol,[H+]
what is saponification rxn (hint the carbox acid is an ester)
creating carboxylate and alcohol
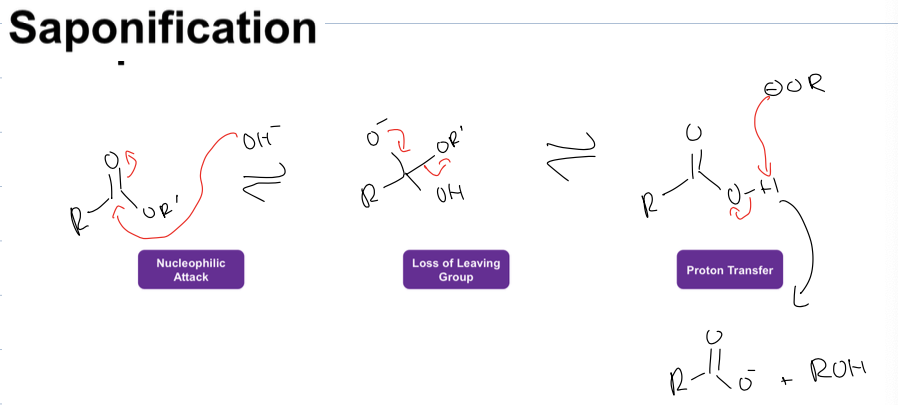
when you react it with H3O afterwards you protonate the carboxylate
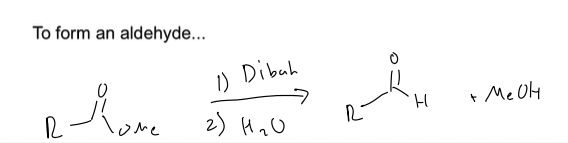
what are the two rxn to reduce esters
you can form 2 alcohols by using LAH an H2O
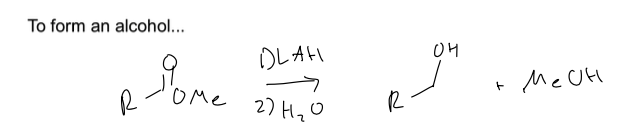
you can form an aldehyde and an alcohol with DIBAH and H2O
what is rxn is hydrolysis of amide in acidic condition
goes from amide to alcohol and NH3
reagent: [H+]

what rxn is hydrolysis of amide in basic conditions
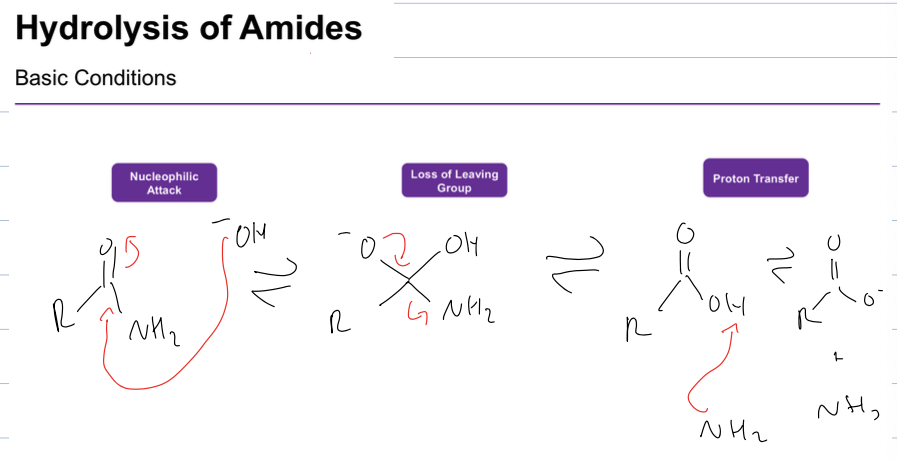
get NH3 and alcoxide
how to make amide from ester
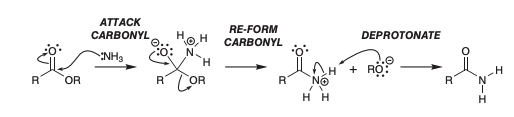
reagent: NH3
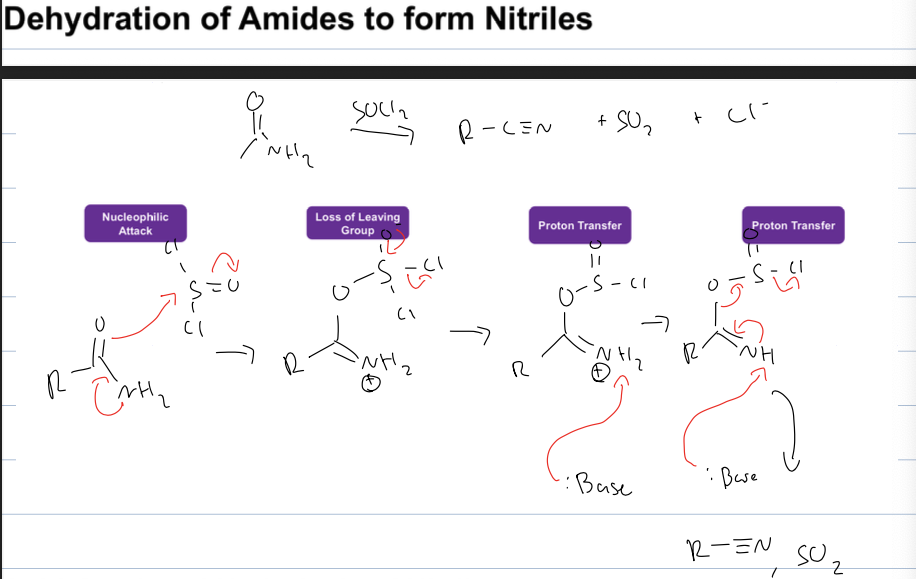
what is rxn to dehydrate amide to form a nitrile
amide to R-CN and SO2 and CL-
reagent: SOCl2and a strong base
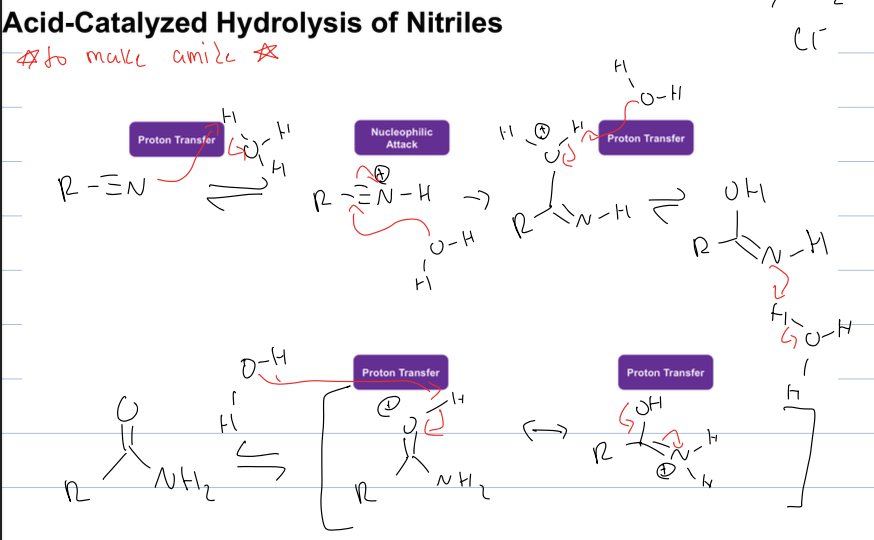
what is acid catalyzed hydrolysis of nitriles
makes amide from nitrile
reagent, H3O+
what is base catalyzed hydrolysis of nitriles
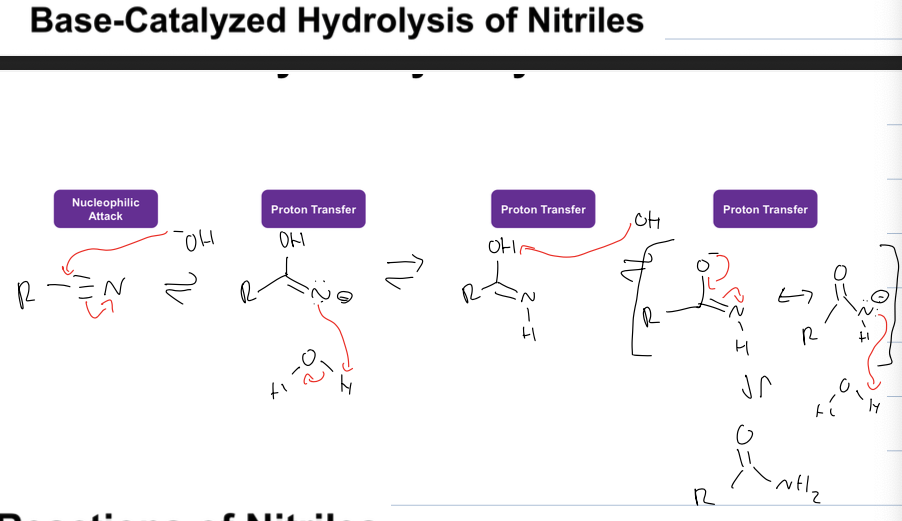
What is diff in base cat and acid cat hydrolysis of nitriles
In acid cat you don’t de protonate OH group until the end, but in basic cond you deprotonate to get neg charge on O so double bond can form and you do this after N protonates the first time
what reaction with LAH and h2o and nitriile
reduction to an amine

what rxn with grignard , H2O and R-CN
creates a ketone