ANSC 4410 Midterm
1/190
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TTU ANSC 4410 Clinical Vet Midterm
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
VCPR
Veterinary Client Patient Relationship
Triage
The assignment of degrees of urgency to wounds or illnesses to decide the order or treatment with large influx of patients
What is a signalment?
The patient chart that includes patient name, breed, sex, color, age and weight
SOAP
Subjective Objective Assessment Plan
Subjective
Chief complaint, history, impression/observations, clinical signs
Objective
Physical examination, vitals, and lab/imaging results
Assessment
Diagnosis and prognosis
Plan
Course of action recommended such as treatments or procedures, follow up recommendation
How often should an IMMATURE patient be seen and what for?
Every 3 weeks for vaccination, parasite control, feeding instructions
How often should an ADULT patient be seen and what for?
Annually; monitoring of health and early detection of potential problems
How often should an GERIATRIC patient be seen and what for?
Biannually; screening for any health problems that have developed
Physical Examination
Process of evaluating objective anatomic findings, observation, palpation
What should you go over/look at when performing a physical examination?
History, mentation (how the patient is acting mentally), appearance, symmetry, and posture
Body Condition Score (BCS)
Scale of 1-9 (1-3 = too thin, 4-6 = ideal, 7-9 = obese)
What is the normal color when looking at mucous membranes?
Pink
If the mucous membranes are either light pink, or blue, what does it probably indicated?
Either anemia or cyanotic; inadequate blood flow and or oxygenation
What does it mean if mucous membranes are bright red in color?
There is an increase in vasodilation which could indicate sepsis, fever, or an inflammatory response
What does it mean if mucous membranes are yellow in color?
Bilirubin (pigment from the breakdown of RBC) accumulation
What does it mean if mucous membranes are brown in color?
Methemoglobinemia; intravascular hemolysis
Capillary Refill Time (CRT)
Hydration assessment where you press on the gums and count the seconds it takes for normal color to return
Normal CRT
Less than 3 seconds
What is the desired range of hydration?
0-5%
What part of the body is a very important indicator of overall health in a patient?
The hair-coat
When looking at the NOSE, what should you look for?
It should be moist and clean with no dryness, cracking, discharge, or bleeding
Characteristics of a healthy hair-coat
It should be shiny, smooth, soft unbroken skin, with minimal odor
Characteristics of an UNHEALTHY hair-coat
Patchy hair, open sores, oily discharge, foul odors
How should a patient's eyes appear when giving a physical exam?
Bright, moist, clear, centered, and should react to the appropriate light setting
What are the indicators of abnormal eyes?
Dull, sunken, dry eyes thick from discharge. Unequal or unresponsive pupil characteristics
Feline heart rate
100 - 120 bpm
Canine heart rate
60 - 120 bpm, larger dog should have lower bpm
Normal characteristics of the cardiovascular system
Pulse is easily palpated, strong and regular. Normal resting rate is 15 - 60 breaths per minute
Normal characteristics of the musculoskeletal system
The animal should have normal symmetry and is non painful on palpation or manipulation
What should you observe when examining the neurological system?
You should check the cranial nerves, proprioception, withdrawals, and reflexes as well as the patient being symmetrical and stable
What should be observed when checking temperature?
Normal temperature should be between 101-102.5 F and the thermometer is clean when removed
Asepsis
The absence of pathogenic microbes in living tissue
Sterilization
Process of killing all microbes with the use of a physical or chemical agent
Antiseptic
A chemical agent that kills pathogenic microbes or inhibits their growth
Disinfectant
Germicidal that kill microbes on inanimate objects and cannot be exposed to heat
Antimicrobial Agents
Drugs used to alter the activity of microorganisms in the patient
Clean Operations
Non-traumatic wounds without inflammation or break in surgical technique
Clean-Contaminated Operations
The GI tract or respiratory tracts are entered without significant spillage or the oropharynx/genitourinary tracts are entered in the absence of infection
Contaminated Operations
Major break in sterile technique such as gross spillage from GIT or fresh traumatic wounds
Dirty Operations
Acute bacterial inflammation encountered such as a traumatic wound with necrotic tissue, fecal contamination, etc
-ECTOMY
Excision or surgical removal of tissue
-ORRHAPY
Surgical repair of/or by use of suture
-OSCOPY
Direct visual examination of a structure
-OSTOMY
Creation of a new permanent opening in a tissue
-OTOMY
Surgically incising tissue and closing of that tissue
-PEXY
Surgical fixation of a structure by use of suture
-PLASTY
Molding, shaping, or forming surgically (Plastic surgery)
Ablation
Removal by cutting, separation, detachment, or eradication
Brachycephalic Syndrome
Any upper airway disorder that leads to respiratory effort, noise, or distress
Cesarean Section
Delivery of a fetus by incision through abdominal wall and uterus
Debridement
Removal of all foreign material, or contaminated tissue until healthy tissue is exposed
Dehiscence
Splitting open (surgical wound)
Intussusception
Prolapse of one part of the intestines into the lumen of the adjacent part causing obstruction
Laparotomy
Incision though the body wall
Marsupialization
Conversion of a closed cavity into an open pouch
Mucocele
Dilation of a space/cavity with accumulated mucous secretion
Onychectomy
Excision of a portion of an organ or other structures
Resection
Excision of a portion of an organ or other structures
Torsion
State of being twisted
Volvulus
Rotation of a portion of the GIT on its mesenteric axis so as to occlude the lumen
Important aspects of canine castration
Identification of 2 testicles, dorsal recumbency, and removal of hair from incision site
Important aspects of feline castration
identification of 2 testicles, dorsal/lateral recumbency, pluck or clip hair from scrotum, incision remains UNSUTURED
What are some examples of ophthalmic surgeries
Entropion repair, eyelid tucking, neoplasm removal, marsupialization of eyelid, enucleation
Draping
Impermeable and secured sterile field that is performed by gowned surgeon and is secured with BACKHAUS TOWEL CLAMPS
Aspects of Post Operative Care
Hourly check of body temperature, checking of reflexes, and pain response
Pharmacology
The branch of medicine concerned with the uses, effects, and modes of action of drugs
Drug
Any chemical compound used on or administered to a patient as an aid in the diagnosis, treatment, or prevention of a disease
Poison
A substance that on ingestion, inhalation, absorption within the body may cause structural or functional disturbances
Any drug administered has the potential to become a poison (T/F)
True
Therapeutic Index (TI = LD50/ED50)
Comparison between a drug's ability to achieve the desired effect and its tendency to produce toxic effects
"Extra-Label Use"
Use of a drug in any way other than the approved way
Controlled Substances
Drugs that have potential to be abused (Scale of C1-C5)
Pharmacokinetics
Study of the processes of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of medicinal products
What are the 5 Rights?
Right DRUG, DOSE, ROUTE, TIME, PATIENT
Nutraceuticals
Non-drug substnace that is produced in a purified form and administered orally to provide agents required for normal body structure and function with the intent of improving overall health and well being
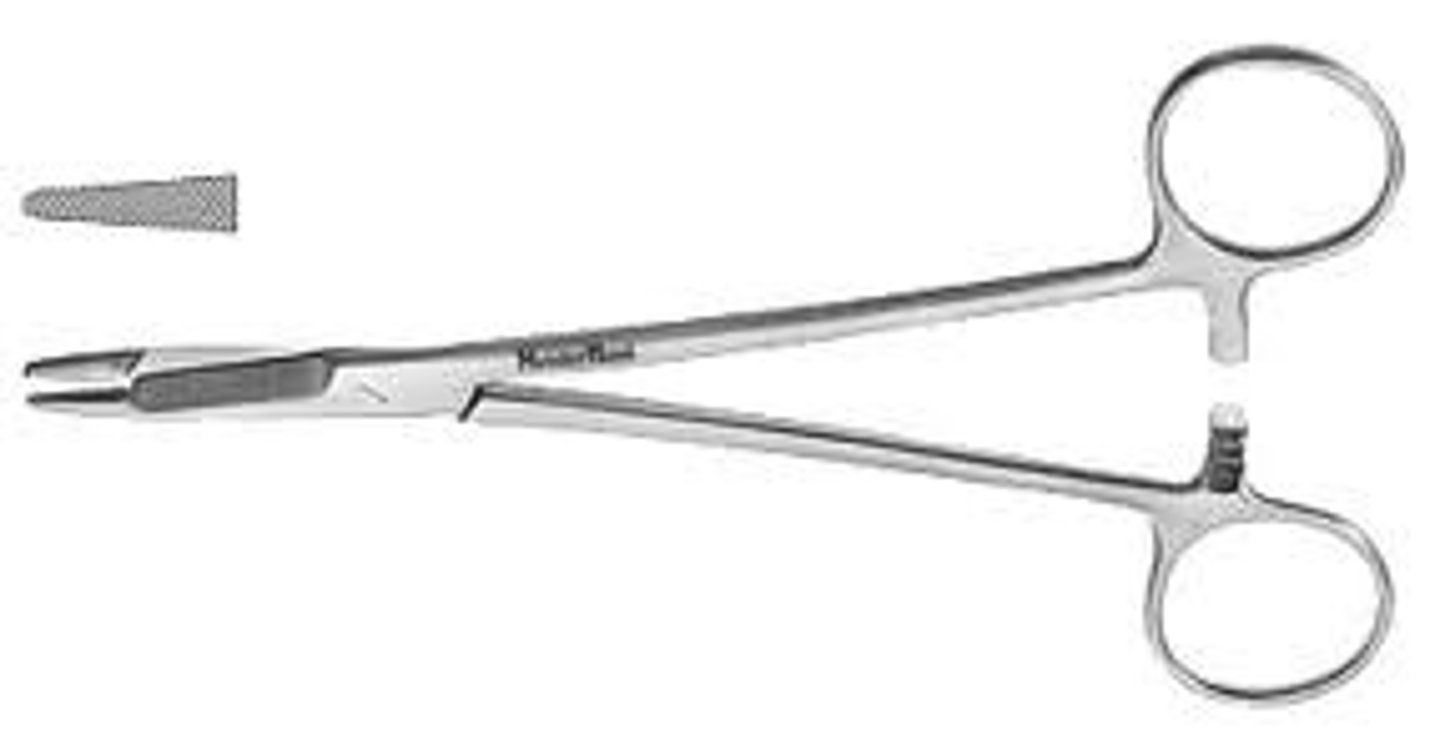
Mayo-Hegar
Needle drivers without cutting edge
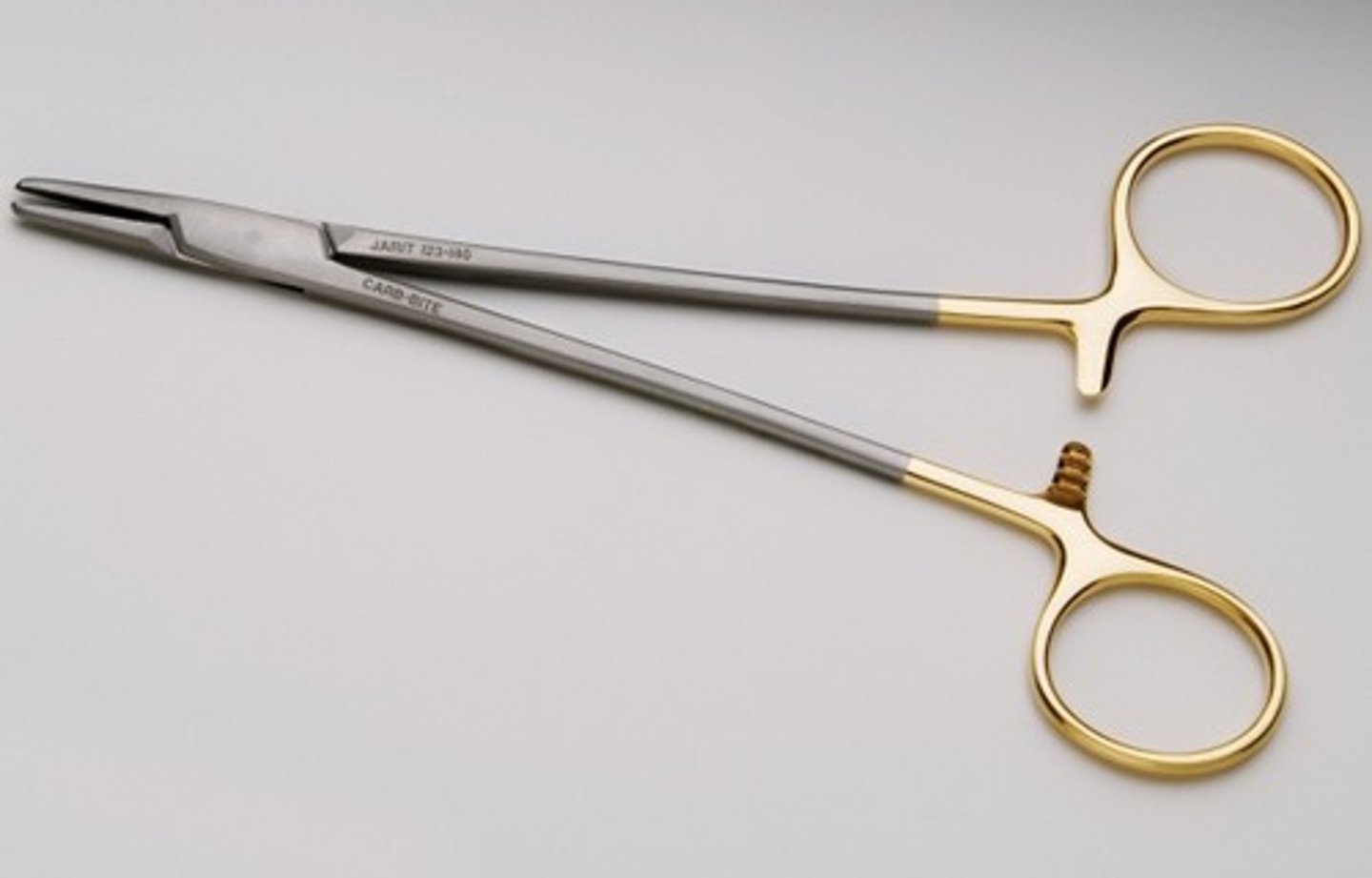
Olsen-Hegar
Needle drivers WITH cutting edge

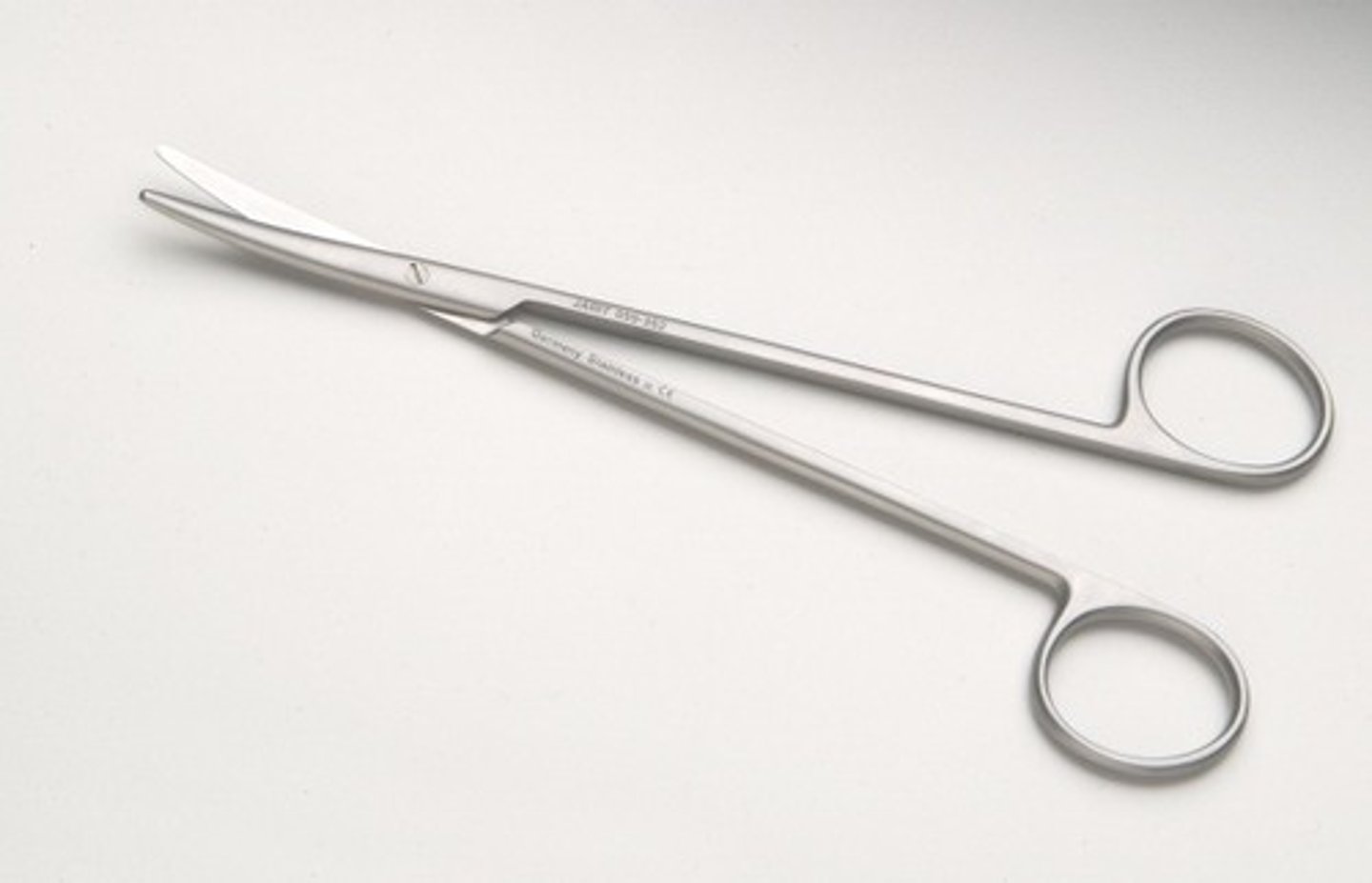
Mayo (Scissors)
Used for dissecting dense tissue, blunt on both points
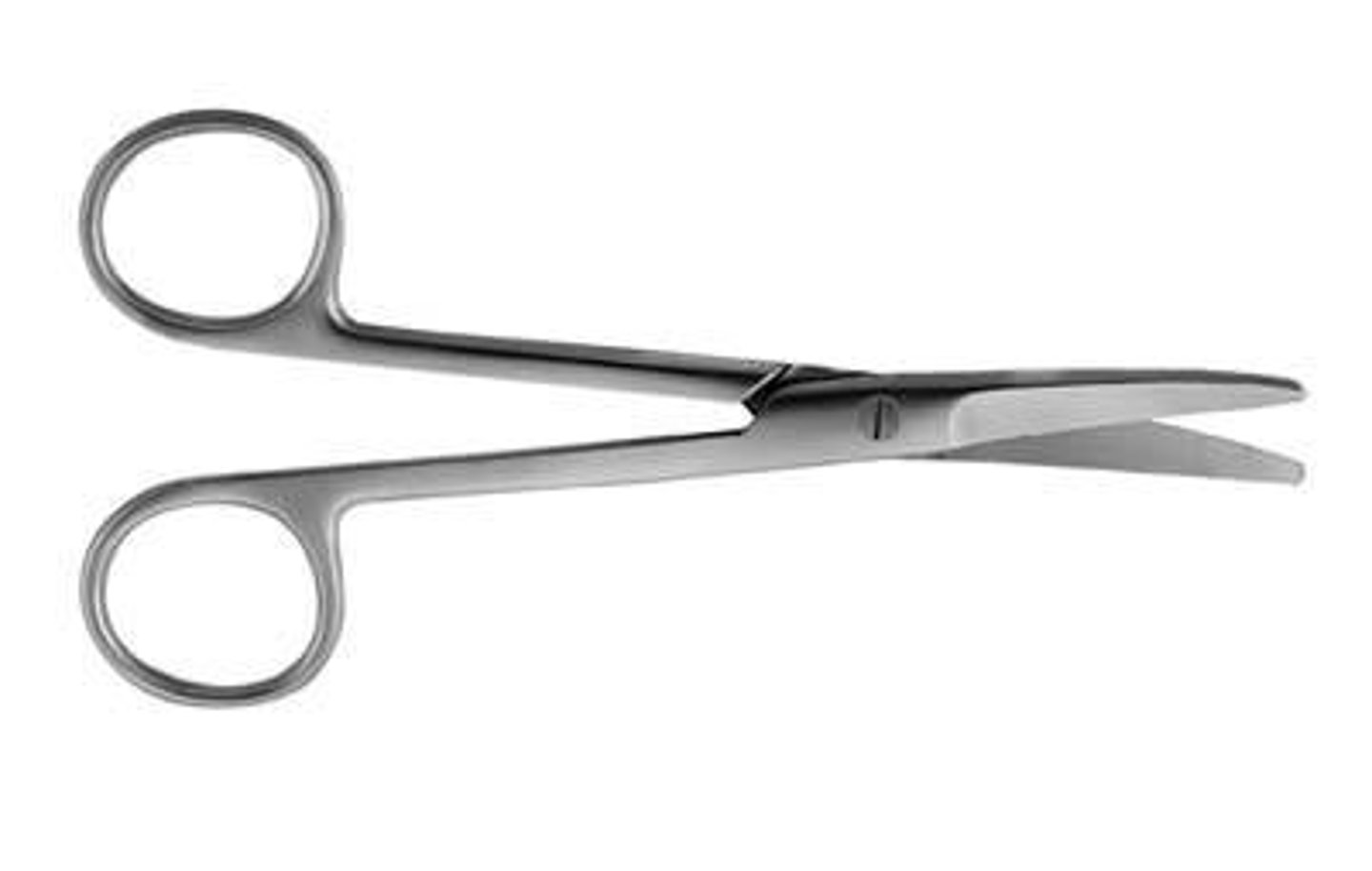
Metzenbaum (Scissors)
Used for dissecting delicate tissues, thinner and slightly curved at the point
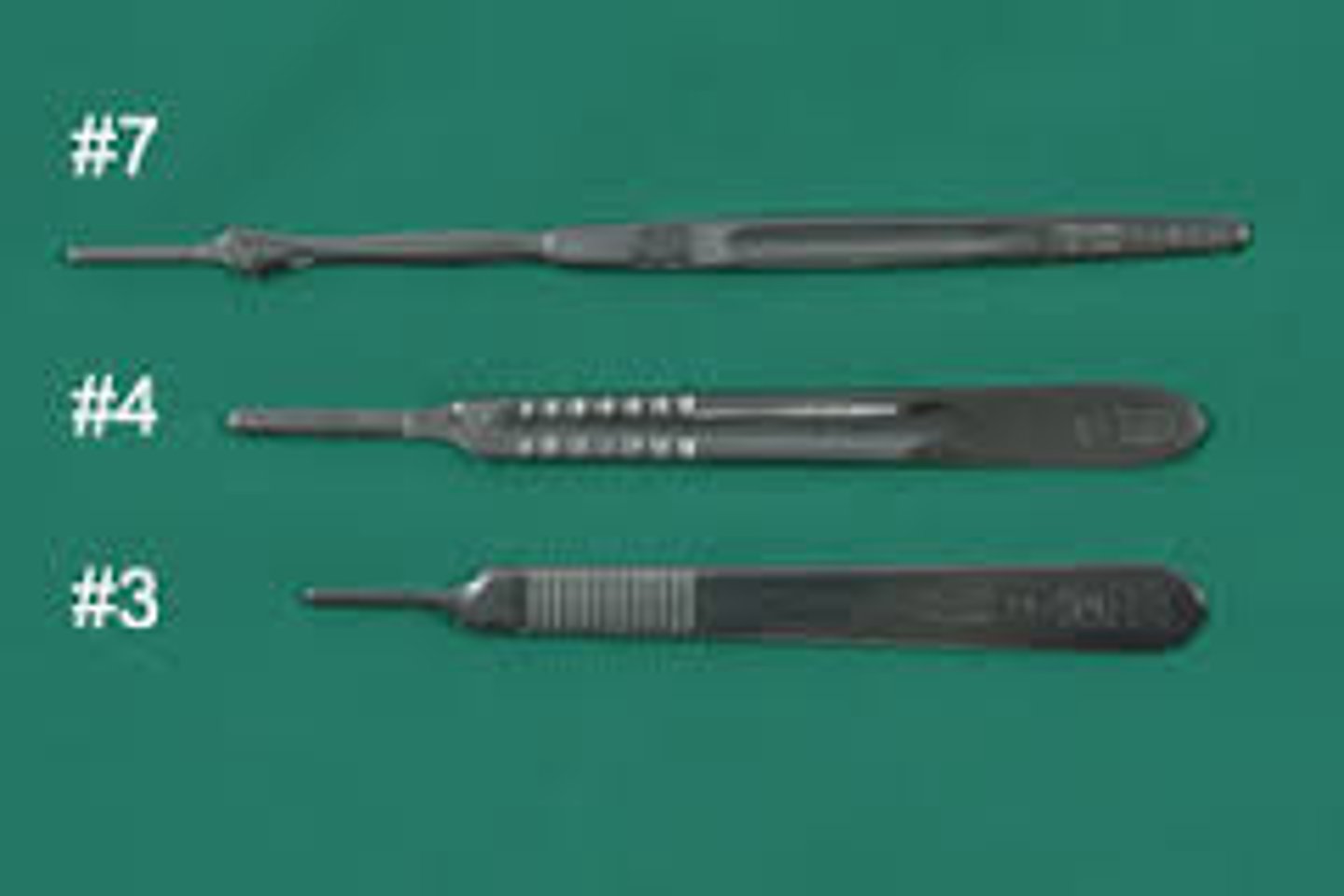
Scalpel #3
Smaller handle used with blades 10, 11, 12, 15
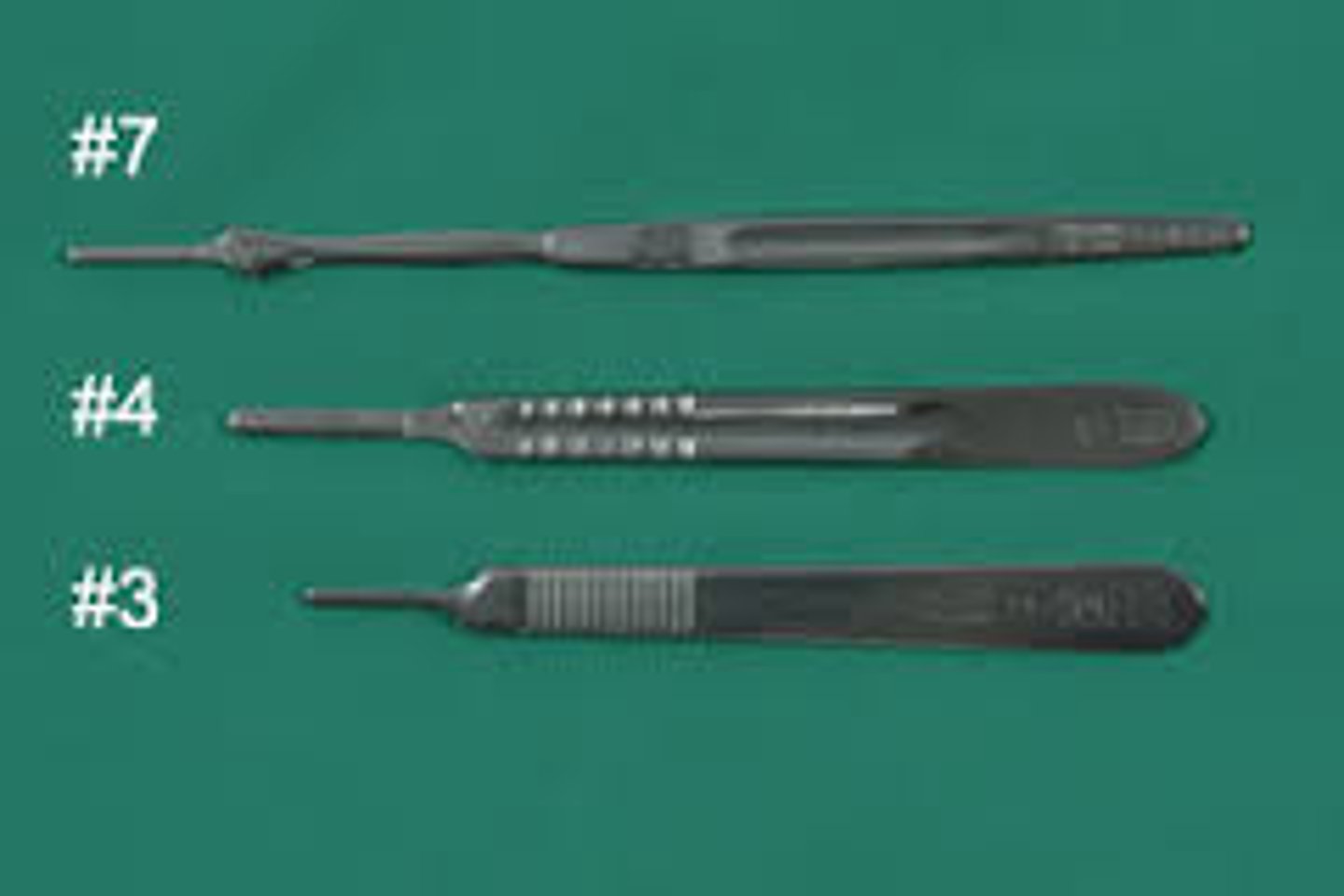

Scalpel #4
Bigger handle used with blades 20-25

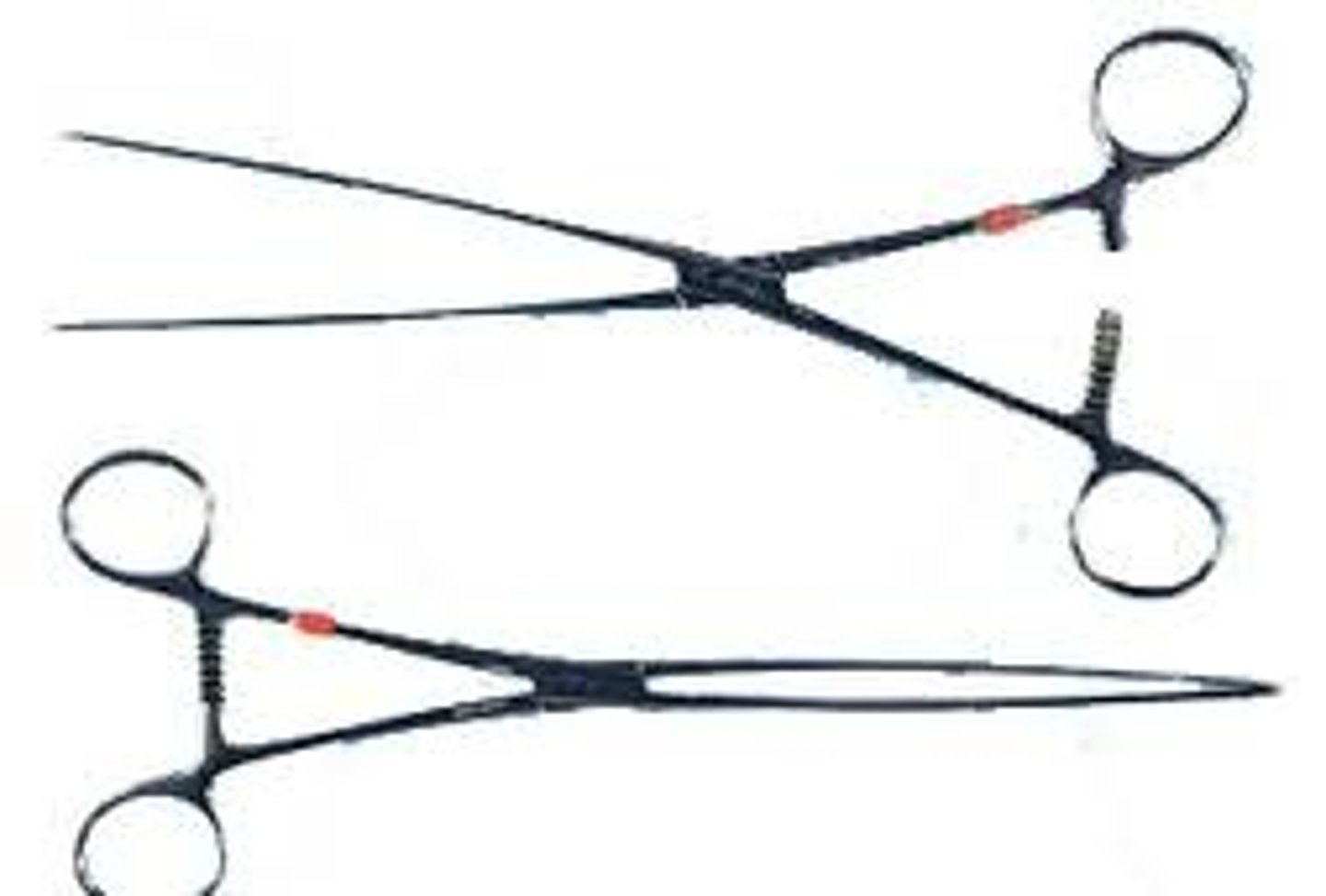
Surgical Clamps
Used for hemostasis; clamping of blood vessels, dissecting, retracting, or holding tissue that is going to be excised

Halstead Mosquito Forceps
Transverse serrations designed to grab tissue with the tip pointed toward the vessel
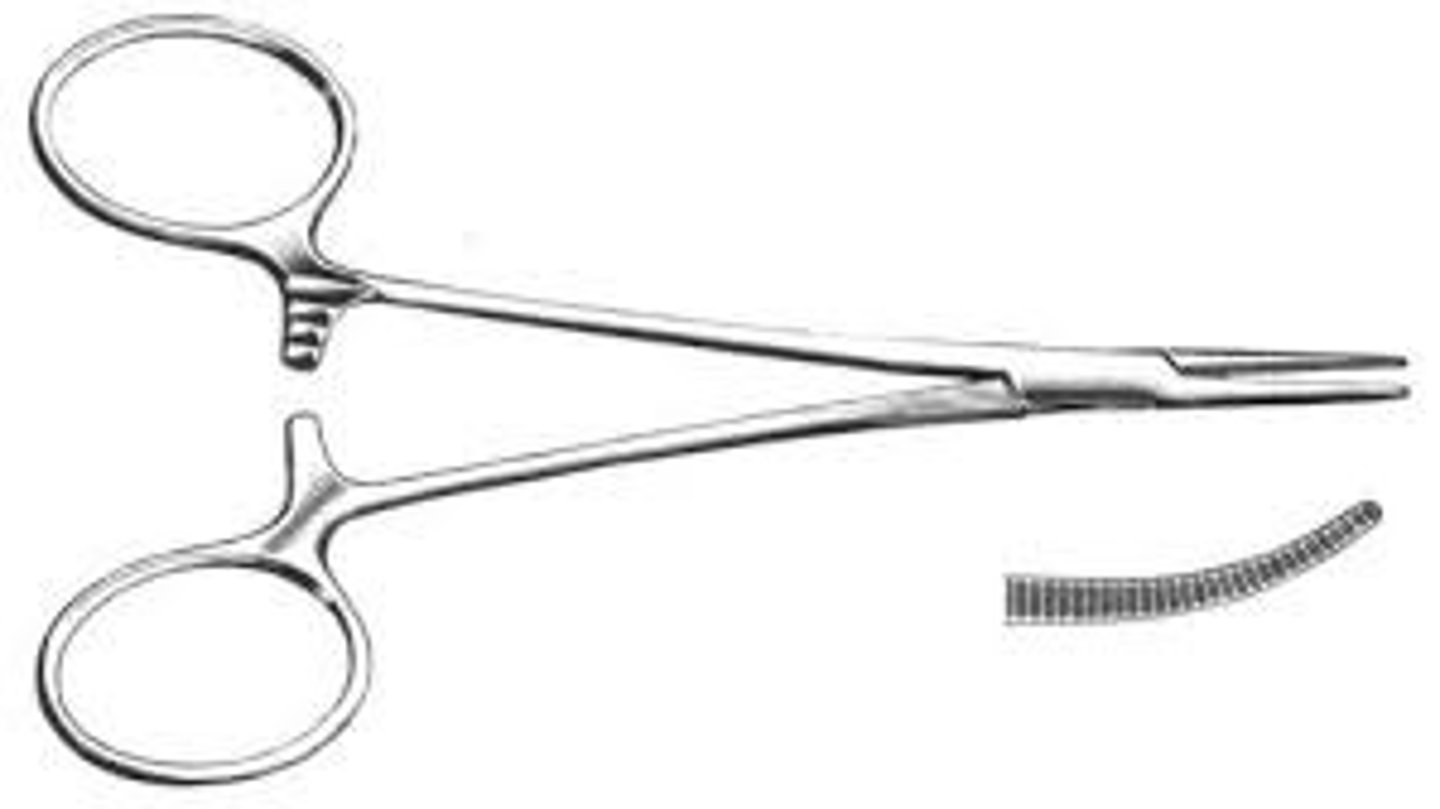
Kelly Forceps
Transverse serrations with one point straight and one point curved
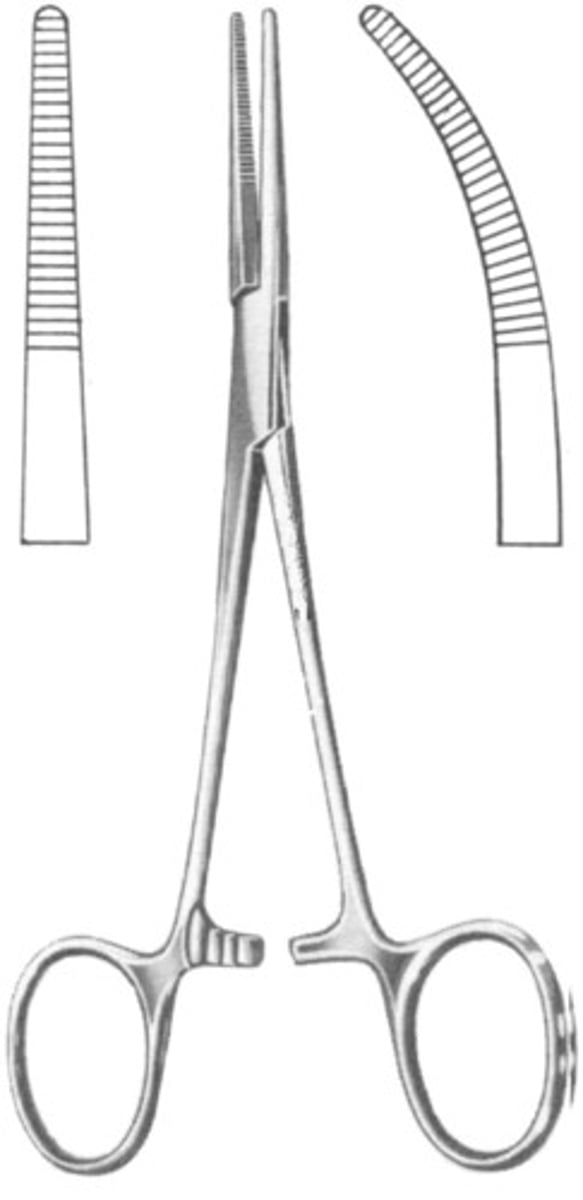
Rochester-Carmalt Forceps
Longitudinally oriented serrations designed to grab tissue with the clamp pointing away
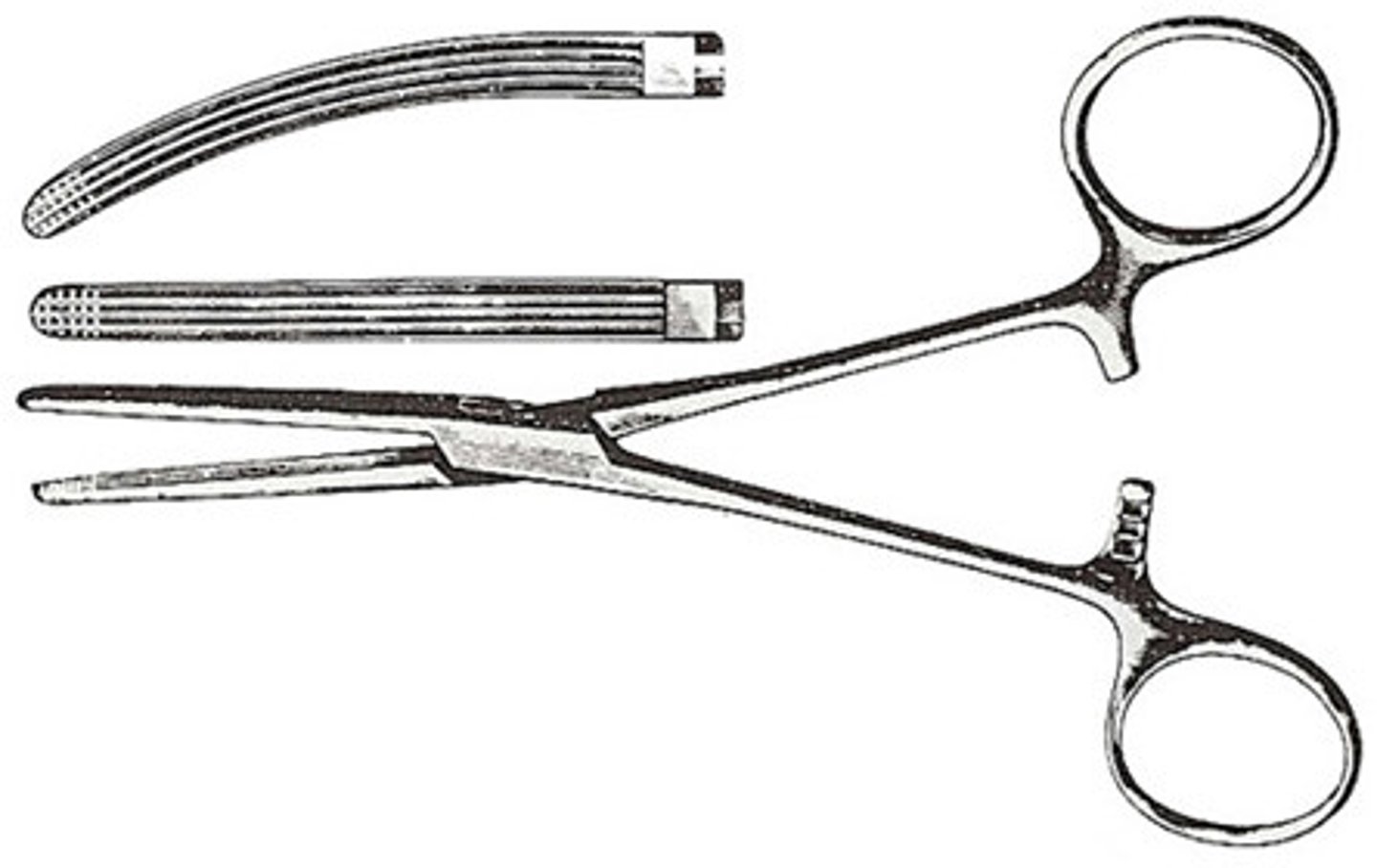
Doyen Intestinal Forceps
Non-crushing and used on tissue that is to remain within the patient

Absorbable Suture
Loses tensile strength within 60 days (Vicryl - braided, Monocryl, Maxon, PDS)
Non-Absorbable Suture
Maintains tensile strength longer than 60 days (Prolene, Vetafil, Silk, Nylon, Stainless steel)
Suture size
2, 1, 0, 2-0, 3-0, 4-0; 0.5, 0.4, 0.35, 0.3, 0.2, 0.15 (mm)
Swage-Eye-End Needle
Non-traumatic, minimizes handling and prep, and don't need to thread
Close-Eye-End Needle
More traumatic, unthreads prematurely
Interrupted Suture Patterns
Every suture has a knot, very safe, but time consuming
Continuous Suture Patterns
Only initial and final stitches are tied but if one knot fails the entire line fails
Simple interrupted
Appositional; "1 circle 1 knot" with good cosmetic result
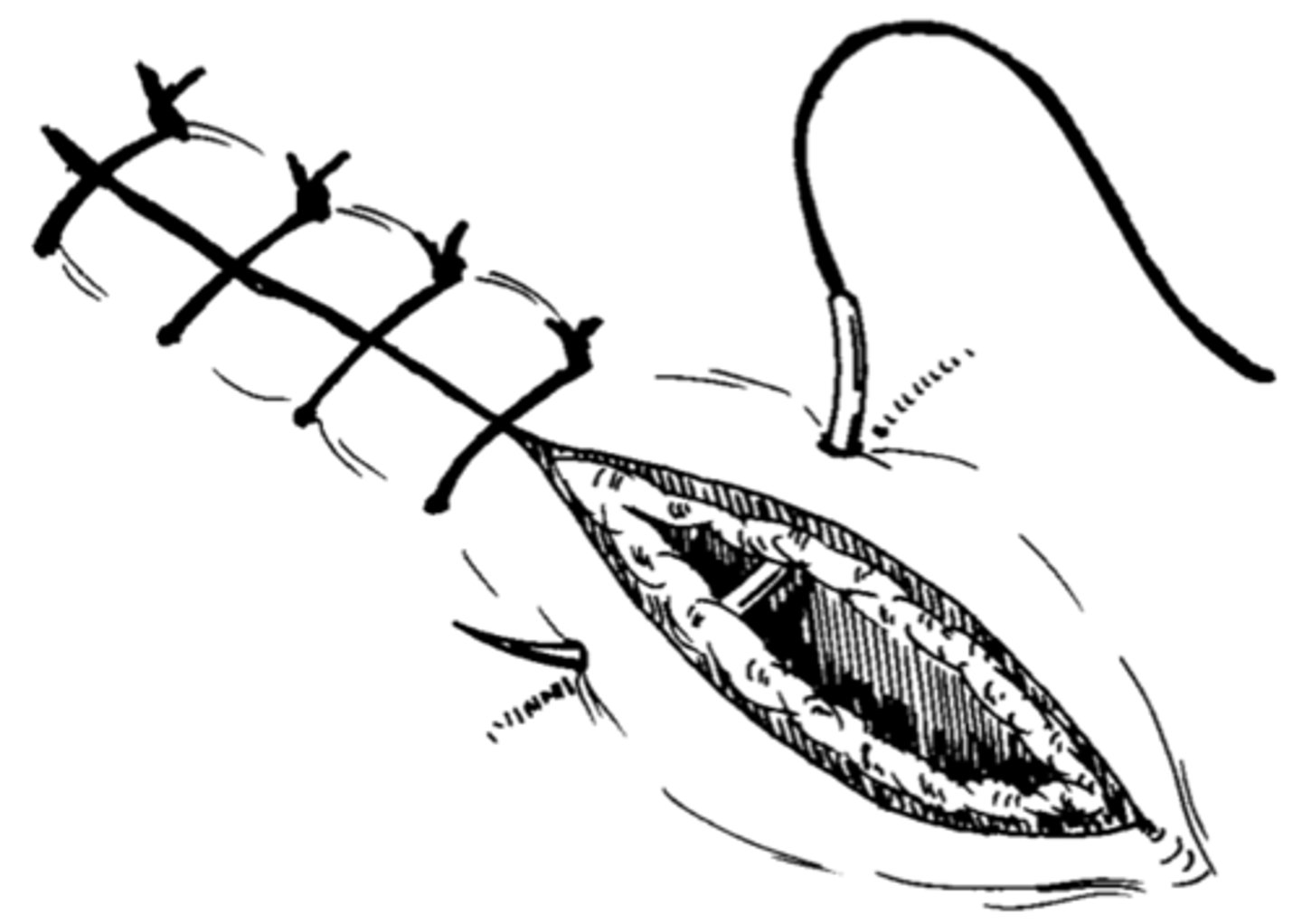
Horizontal mattress
Everting; forms a square and cannot be used for a tension suture
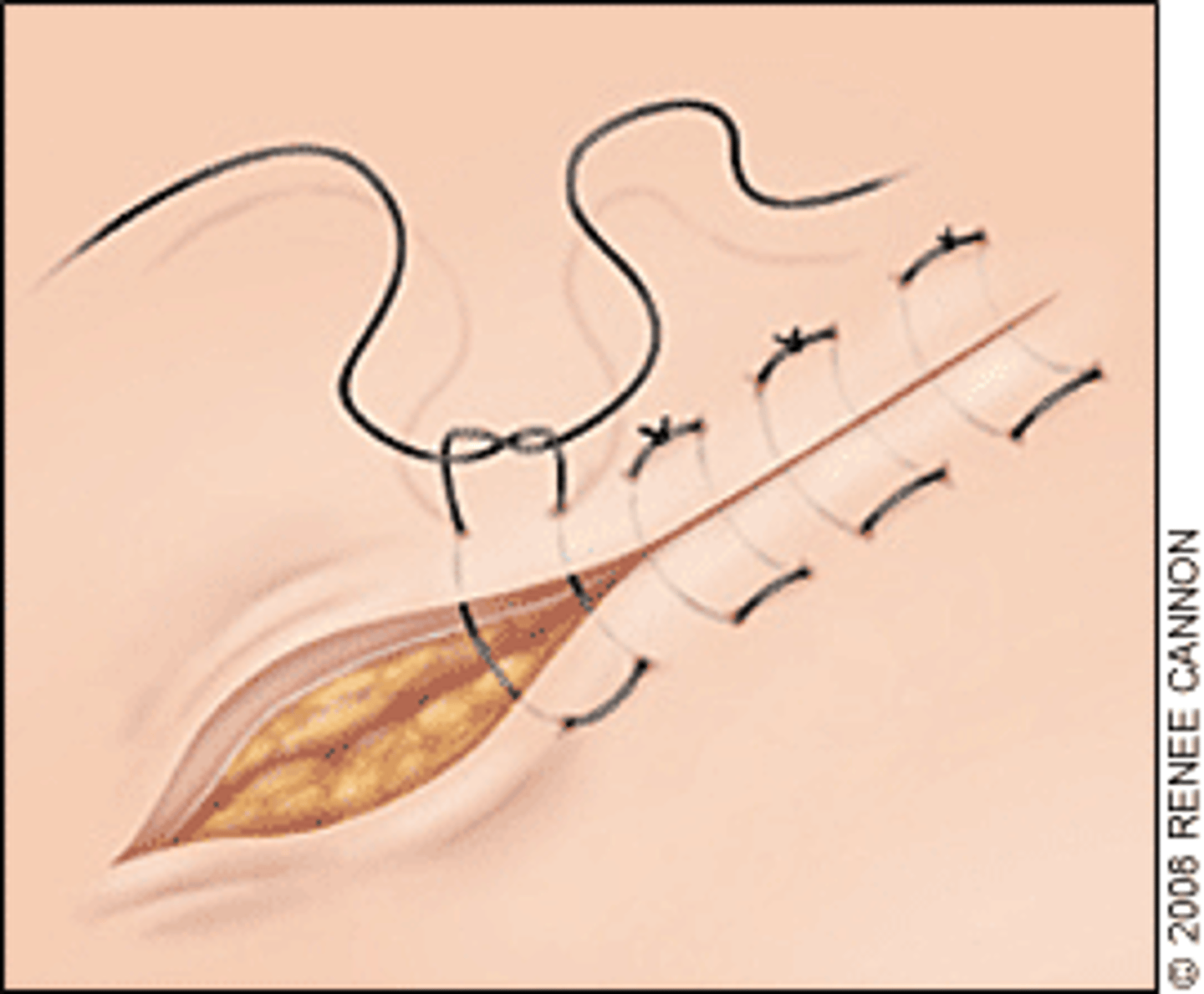
Vertical mattress
Appositional; "far-far-near-near" good cosmetically
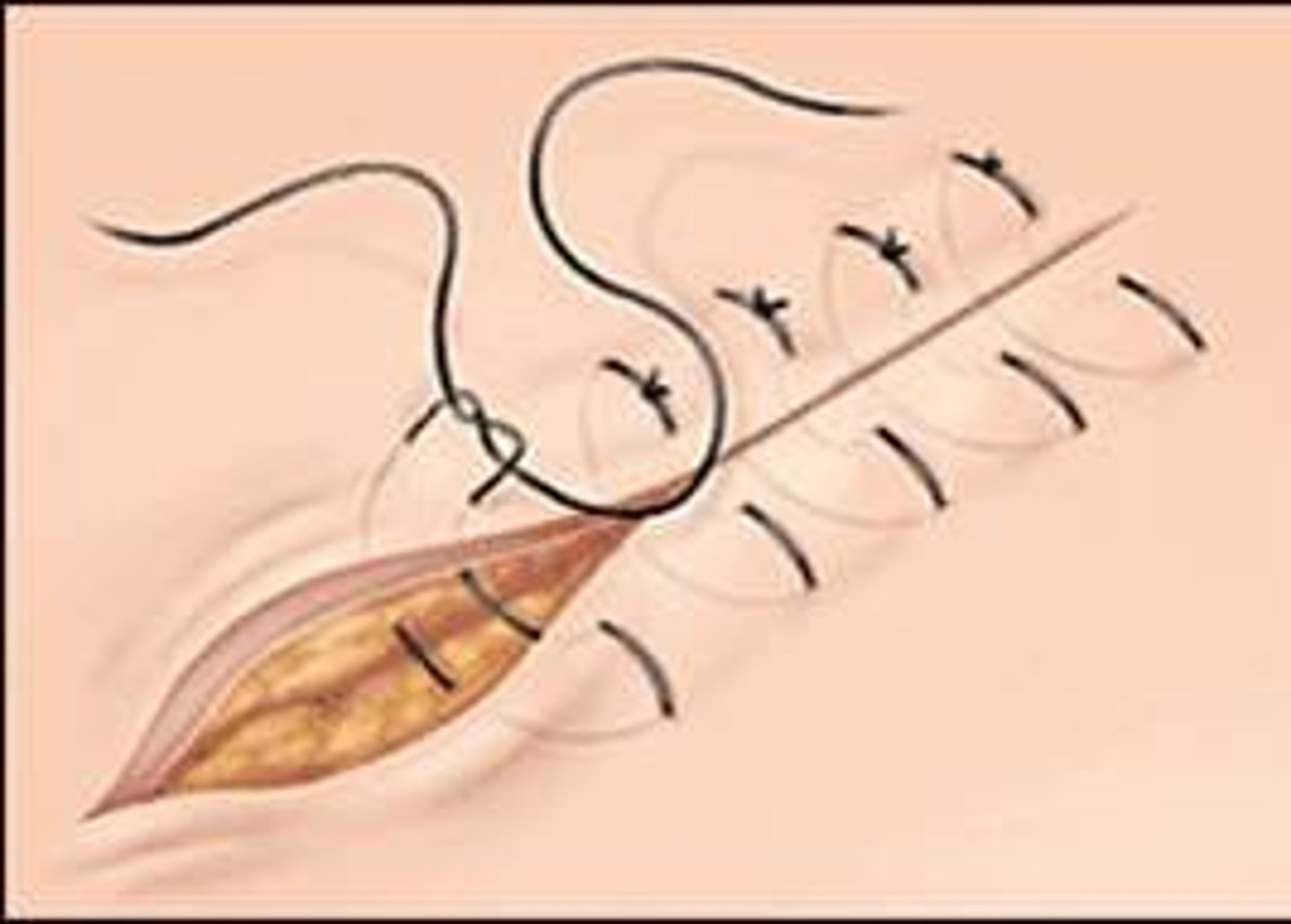
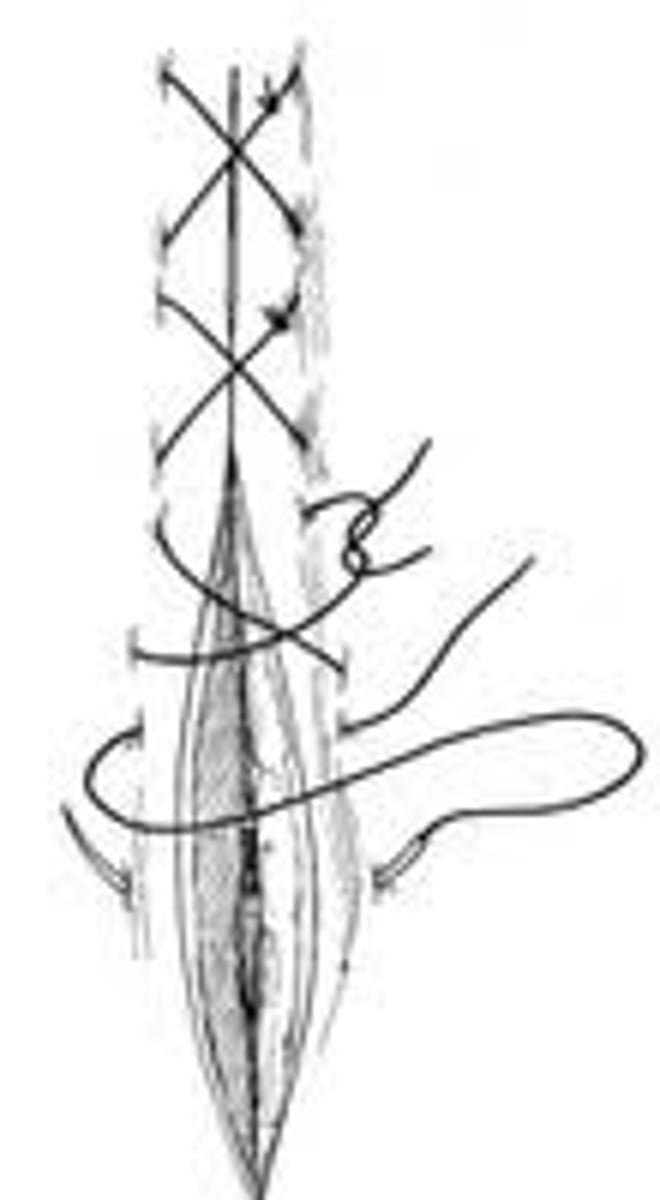
Cruciate
Appositional; forms an X and prevents eversion
