L8_Basic Helicopter Design
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
physical size
safety standards
preliminary design
In designing the modern helicopters, there are many issues concerning with performance, noise level, _____, _____ and so on.
These issues conflict each other and therefore, it will be difficult to satisfy all of them.
The primary objective of the _____ would be to design the smallest, lightest and least expensive.
Operational factors
Economic factors
The goal of the design process is to optimize the mission effectiveness of the design item.
There are two groups of factors which determine an item's mission effectiveness.
Mission readiness
Survivability
Overall Performance
3 Operational Factors
Mission readiness
which is a measure of the degree to which an item is operable at the start of a randomly selected mission.
Mission readiness
is measured by an item's availability, reliability, and maintainability.
Availability
is a function of the mean time between maintenance actions and the maintenance down time.
Reliability
is a function of an item's failure rate.
Maintainability
is measured by the item's mean time to repair.
Survivability
which is a measure of the item’s ability to withstand a hostile man-made environment and still be mission ready.
Overall performance
which is a measure of how well an item performs its designated mission.
principle economic factor I cost,
which is a measure in dollars of the amount required to design, produce, test, and operate a item during its life-cycle.
hover
unprepared sites.
The primary usefulness of light utility type helicopter would be its ability to _____ and to operate from the _____.
Beside this primary ability, there are other civil roles and missions that the light utility type helicopters should carry out.
inaccessible
surveillance, medical support
The typical civil roles that light utility type helicopter should carry out include the followings.
To transport passengers or cargo in the _____ areas
To carry out law activities such as _____, _____, media role and etc.
historical data and the trends
The first phase is a study of the _____ and the _____ in the helicopter design.
rules of thumb
Second, a conceptual study is conducted using "_____" and experience to develop simple layouts.
volumetric sizing
structural concepts
Third, preliminary designs are drawn which include _____, airframe lines, mechanisms, and _____.
proposal status
Fourth, the design enters a "_____" in which detailed subsystems are developed, structural sizing is refined, and mockups are constructed.
final
Fifth, the _____ details are completed.
Trend Study
Conceptual Study
Preliminary Design
“Proposal Status” Design
Details
5 Phases of the Design Process
Trend study
Provide direction for further study
Obtain quick look answers
Conceptual study
Compare configuration
Estimate size and cost
Establish feasibility
Recommend follow-on
Preliminary design
Insure design practicality
Develop structural concepts
Develop concepts for mechanisms
Expand data base
"Proposal status" design
Increase detail of structure, weight, etc.
Increased confidence by risk reduction
Support proposal commitment
Make a rough estimate of the manufacturer's empty weight
Make a rough estimate of gross weight
Calculate the maximum tip velocity
Determine the rotor radius
Determine the maximum rotational velocity
Determination of thrust coefficient
Determine the blade solidity
Determine the number of main rotor blades to be used
Determine the chord and the aspect ratio
Determine the average lift coefficient
Choose an airfoil section for the main rotor blades
Determine average lift curve slope and average profile drag coefficient
Main Rotor Design
Manufacturer's empty weight
weight of the aircraft "as built" and includes the weight of the structure, power plant, furnishings, installations, systems, and other equipment that are considered an integral part of an aircraft before additional operator items are added for operation.
Aircraft gross weight
total aircraft weight at any moment during the flight or ground operation.
Tip velocity
velocity of the outer edge of a wheel or the tip of a propeller.
Rotor Radius
radius of the rotation measured in centimeters or inches.
disk loading
The selection of a main rotor radius will affect the _____ of the blade.
disk loading
function of gross weight and main rotor radius.
Disk Loading of a hovering helicopter
ratio of its weight to the total main rotor disk area.
maximum rotational velocity
can be determined since the maximum tip velocity and the design rotor radius are known.
Maximum Rotational velocity
_____ = Maximum tip velocity / Rotor radius
thrust coefficient
The value of _____ should be determined at the specification density altitude.
Thrust Coefficient
_____ = Thrust of Main Rotor / [ Disk Area of main rotor Density (Tip velocity)2]
Tip velocity
_____ = Rotational velocity * Rotor radius
Solidity
is the function of the blade's ability to absorb power from the engine and the potential to provide rotor thrust.
rotor radius
The number of rotor blades to be used is a function of _____ (as it affects solidity), vibration, and weight.
solidity
For a given _____, more blades would be required if the radius and chord are to be kept small.
vibration
The _____ of the main rotor is a factor in the determination of the number of blades to be used.
aspect ratio
For a helicopter rotor, the _____ is defined as the radius divided by the chord.
15 to 20
Historically, the main rotor aspect ratio has been between _____ to _____.
aerodynamic lift coefficient CL
is a measure of the difference in pressure created above and below a vehicle's body as it moves through the surrounding viscous air.
stall angle of attack
lift curve slope
drag divergence Mach number
pitching moments
The selection criteria for an airfoil are as follows:
High _____ to avoid stall on the retreating side,
High _____ to avoid operation at high angles of attack,
High maximum lift coefficient to provide the necessary lift,
High _____ to avoid compressibility effects on the advancing side,
Low drag at combinations of angles of attack and Mach numbers representing conditions at hover and cruise, and
Low _____ to avoid high control loads and excessive twisting of the blades.
lift curve slope
is a measure of how rapidly the wing generates lift with change in AOA.
drag coefficient
is a dimensionless quantity that is used to quantify the drag or resistance of an object in a fluid environment.
Make preliminary determinations of tail rotor geometry
Determine tail rotor power required at hover OGE, SSL
Tail Rotor Design
Make preliminary determinations of tail rotor geometry
Determine the radius, rotational velocity, drag coefficient, and the number of blades of the tail rotor.
Determine the length of the fuselage from the center of gravity to the tail rotor hub.
Determine the Chord of the tail rotor blades.
out-of-ground effect
The total power of the tail rotor required to hover out of ground effect at standard sea level is the induced power, _____with tip loss, added to the profile power.
Determine tail rotor power required and tip Mach effects for forward flight
These calculations should be made at both standard sea level and at specification density altitude.
The cruise velocity should also be included.

stretch forming
deburred
Airframe: Preparing the tubing
Each individual tubular part is cut by a tube cutting machine that can be quickly set to produce different, precise lengths and specified batch quantities.
Tubing that must be curved to match fuselage contours is fitted over a _____ machine, which stretches the metal to a precisely contoured shape.
The tubes are then _____ (a process in which any ridges or fins that remain after preliminary machining are ground off) and inspected for cracks.
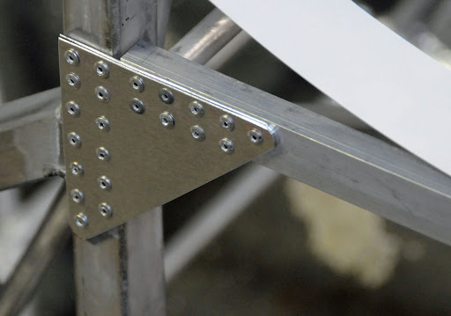
Gussets
forged or investment cast
Airframe: Preparing the tubing
_____(reinforcing plates or brackets) and other reinforcing details of metal are machined from plate, angle, or extruded profile stock by routing, shearing, blanking, or sawing.
Some critical or complex details may be _____ or _____.

MIG (metal-arc inert gas) welded
electrode wire
stress relieved
Airframe: Preparing the tubing
The tubes are chemically cleaned, fitted into a subassembly fixture, and _____.
In this process, a small _____ is fed through a welding torch, and an inert, shielding gas (usually argon or helium) is passed through a nozzle around it; the tubes are joined by the melting of the wire.
After welding, the subassembly is _____—heated to a low temperature so that the metal can recover any elasticity it has lost during the shaping process.
Finally, the welds are inspected for flaws.

blanks
heat-treated
refrigerated
routing
Forming sheet metal details
Sheet metal, which makes up other parts of the airframe, is first cut into _____
Aluminum blanks are _____ to anneal them (give them a uniform, strain-free structure that will increase their malleability).
The blanks are then _____ until they are placed in dies where they will be pressed into the proper shape.
After forming, the sheet metal details are aged to full strength and trimmed by _____ to final shape and size.

riveting or adhesive bonding
anodized
epoxy or other durable coating
Forming sheet metal details
Sheet metal parts are cleaned before being assembled by _____ or _____.
Aluminum parts and welded subassemblies may be _____ which increases corrosion resistance.
All metal parts are chemically cleaned and primer-painted, and most receive finish paint by spraying with _____ or _____.

Nomex
aluminum "honeycomb"
pre-preg ply
epoxy or polyimide
Making the cores of composite components
Cores, the central parts of the composite components, are made of _____ (a brand of aramid produced by Du Pont) or _____, which is cut to size by bandsaw or reciprocating knife.
The material with which each component is built up from its cores (each component may use multiple cores) is called _____.
The plies are layers of oriented fibers, usually _____ or _____, that have been impregnated with resin.

autoclave
autoclave
Making the cores of composite components
Completed layups, as the layers of pre-preg affixed to the mold are called, are then transported to an _____ for curing.
An _____ is a machine that laminates plastics by exposing them to pressurized steam, and "curing" is the hardening that occurs as the resin layers "cook" in the autoclave.
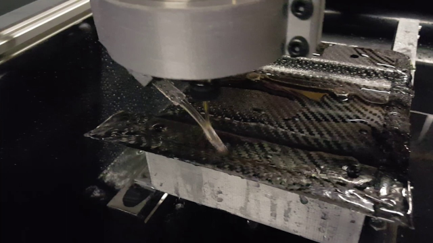
Visible trim lines
band sawing
normal spray methods
metal corrosion or water absorption
Making the cores of composite components
_____ are molded into the panels by scribe lines present in the bond mold tools.
Excess material around the edges is then removed by _____. Large panels may be trimmed by an abrasive water-jet manipulated by a robot.
After inspection, trimmed panels and other composite details are cleaned and painted by _____.
Surfaces must be well sealed by paint to prevent _____ or _____.

polycarbonate sheet
laminated
free blowing
Making the fuselage
Canopies or windscreens and passenger compartment windows are generally made of _____.
Front panels subject to bird strike or other impact may be _____ of two sheets for greater thickness.
All such parts are made by placing an oversized blank on a fixture, heating it, and then forming it to the required curvature by use of air pressure in a _____ process. In this method, no tool surface touches the optical surfaces to cause defects.

turbine
transmission assembly
aluminum or magnesium alloy
Installing the engine, transmission, and rotors
Modern helicopter engines are _____ rather than piston type and are purchased from an engine supplier.
The helicopter manufacturer may purchase or produce the _____, which transfers power to the rotor assembly. Transmission cases are made of _____ or _____.
composite layup shapes
sheet metal layer
Installing the engine, transmission, and rotors
The main and tail rotor assemblies are machined from specially selected high-strength metals.
The rotor blades themselves are machined from _____. Main rotor blades may have a _____adhesively bonded to protect the leading edges.
Wiring harnesses
are produced by laying out the required wires on special boards that serve as templates to define the length and path to connectors.
Tubes
are inspected for dimensional accuracy and to ensure that no cracks are present.
Hydraulic pumps and actuators, instrumentation, and electrical devices
are typically purchased to specification rather than produced by the helicopter manufacturer
subassembly jigs
Finished and inspected detail airframe parts, including sheet metal, tubular, and machined and welded items, are delivered to _____ (fixtures that clamp parts being assembled).
countersunk
Central parts are located in each jig, and associated details are either bolted in place or, where rivets are to be used, match-drilled using pneumatically powered drills to drill and ream each rivet hole.
For aerodynamic smoothness on sheet metal or composite skin panels, holes are _____ so that the heads of flat-headed screws won't protrude. All holes are deburred and rivets applied.
sealant
is often applied in each rivet hole as the rivet is inserted.
semi-automated machines
may be used for moving from one hole location to the next, drilling, reaming, sealing, and installing the rivets under operator control.

brackets
propulsion
Finish-painting and trimming
Final Assembly
After each subassembly is inspected, it typically moves to another jig to be further combined with other small subassemblies and details such as _____. Inspected subassemblies are then delivered to final assembly jigs, where the overall helicopter structure is integrated.
Upon completion of the structure, the _____ components are added, and wiring and hydraulics are installed and tested.
Canopy, windows, doors, instruments, and interior elements are then added to complete the vehicle. _____ and _____ are completed at appropriate points during this process.

propulsion
Final Assembly
After all systems are inspected in final form, along with physical assemblies and appearance aspects, the complete documentation of materials, processes, inspection, and rework effort for each part is checked and filed for reference.
The helicopter _____ system is tested, and the aircraft is flight-tested.
Main Rotor Design
is a complex process and needs to be studied and computed properly to achieve maximum efficiency in a helicopter design.
Tail rotor Design
should also be designed properly to achieve a desirable amount of anti torque thrust that is necessary for all phases of flight.
test flight
is required after assembling the helicopter.